- Challenge Summary
- Details of Implementation
- Download Data
- Description of Data
- Repo directory structure
Picture yourself as a backend engineer for a NASA fan website that generates a large amount of Internet traffic data. Your challenge is to perform basic analytics on the server log file, provide useful metrics, and implement basic security measures.
The desired features are described below:
List the top 10 most active host/IP addresses that have accessed the site.
Identify the 10 resources that consume the most bandwidth on the site
List the top 10 busiest (or most frequently visited) 60-minute periods
-- Note -- Feature 3: implement is done by taking the event as the starting point for the burst window
Detect patterns of three failed login attempts from the same IP address over 20 seconds so that all further attempts to the site can be blocked for 5 minutes. Log those possible security breaches.
Python
sh run.sh
src/process_log.py
-- None --
Feature 1
Feature 2
Feature 3
Feature 4
-- None --
src/logClass.py
# static variables
logCount - Total no of logs
max - maximun no of request count by a host
min - minimum no of request count by the top host
range - number of top host in terms of request count
freqHost - list of top host {list of Log class objects} feature1
# variables
host - name of the host
date - date of the log
request - request string
status - status of the request
size - size of the request
count - request count
rank - rank for feature 1
logInFailTime - List of the recent consicutive logIn fails
isBlocked - flage if the host is blocked or not
# functions
addCount - for updating the feature value if the host obj already exsits
addToFreqHostList - sort the host list on the count value and write to the file
resetRanks - set rank based on the sorting and write the content to file
checkReq - check if the host is blocked or not - if yes write log to file
isLoginFail - Check for the request - if its a fail logIn
isDifLess5 - check the time diffreance less that 5 minutes
isDifLess20 - check the time diffreance less that 20 seconds
resetBlock - reset the block for the host
src/requestClass.py
# static variables
reqCount - Total no of requests
max - maximun request size
min - minimum request size by the top resource
range - number of top resources in terms of request size
freqRes - list of top resources {list of Request class objects}
# variables
res - name of the host
count - count of the resource
size - size of the request
rank - rank for feature 2
# functions
addsize - for updating the feature value of obj
addToFreqResList - sort the resource list on the size value and write to the file
resetRanks - set rank based on the sorting and write the content to file
src/requestClass.py
# static variables
tiemList - top time burst windows
currentTime - start of the current burst window
range - no of burst windows
minWindow - size of the burst window in minutes
# variables
date - date - start of the burst window
count - no of requests in that window
# functions
orderList - update, order and print list to file
timeDifL60 - check for time diffrance between dates
List in descending order the top 10 most active hosts/IP addresses that have accessed the site.
Write to a file, named hosts.txt, the 10 most active hosts/IP addresses in descending order and how many times they have accessed any part of the site. There should be at most 10 lines in the file, and each line should include the host (or IP address) followed by a comma and then the number of times it accessed the site.
e.g., hosts.txt:
example.host.com,1000000
another.example.net,800000
31.41.59.26,600000
…
Identify the top 10 resources on the site that consume the most bandwidth. Bandwidth consumption can be extrapolated from bytes sent over the network and the frequency by which they were accessed.
These most bandwidth-intensive resources, sorted in descending order and separated by a new line, should be written to a file called resources.txt
e.g., resources.txt:
/images/USA-logosmall.gif
/shuttle/resources/orbiters/discovery.html
/shuttle/countdown/count.html
…
List in descending order the site’s 10 busiest (i.e. most frequently visited) 60-minute period.
Write to a file named hours.txt, the start of each 60-minute window followed by the number of times the site was accessed during that time period. The file should contain at most 10 lines with each line containing the start of each 60-minute window, followed by a comma and then the number of times the site was accessed during those 60 minutes. The 10 lines should be listed in descending order with the busiest 60-minute window shown first.
e.g., hours.txt:
01/Jul/1995:00:00:01 -0400,100
02/Jul/1995:13:00:00 -0400,22
05/Jul/1995:09:05:02 -0400,10
01/Jul/1995:12:30:05 -0400,8
…
A 60-minute window can be any 60 minute long time period, windows don't have to start at a time when an event occurs.
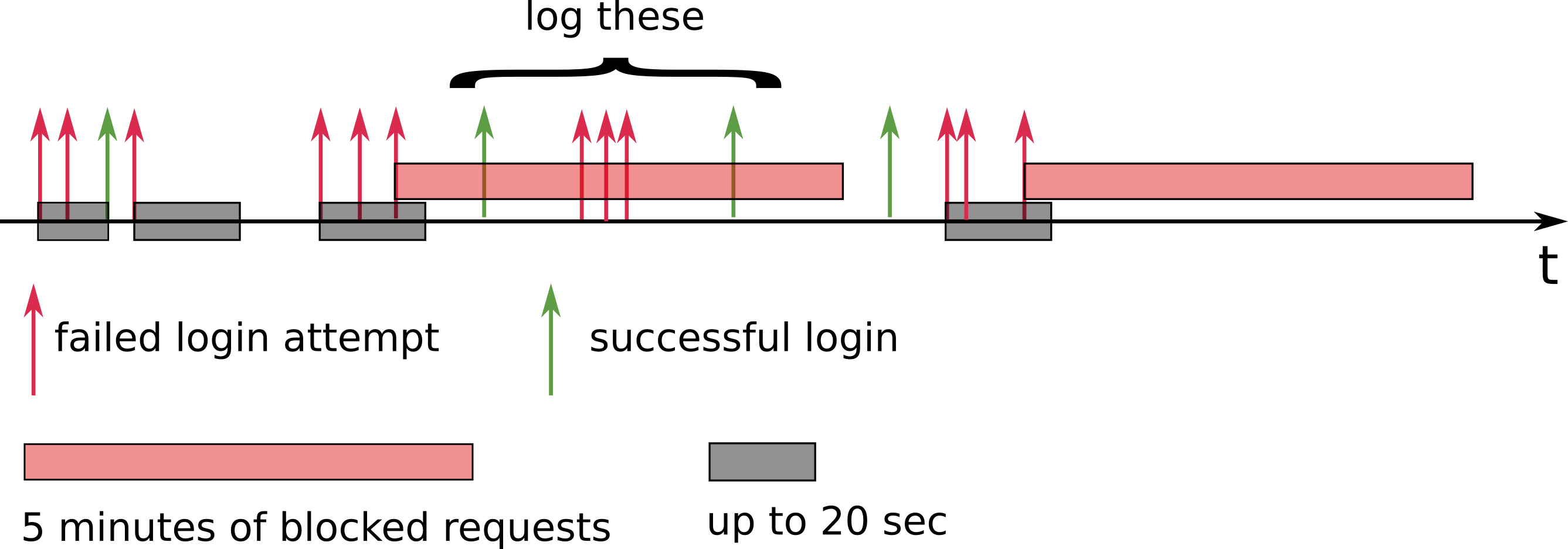
Your final task is to detect patterns of three consecutive failed login attempts over 20 seconds in order to block all further attempts to reach the site from the same IP address for the next 5 minutes. Each attempt that would have been blocked should be written to a log file named blocked.txt.
The site’s fictional owners don’t expect you to write the actual web server code to block the attempt, but rather want to gauge how much of a problem these potential security breaches represent.
Detect three failed login attempts from the same IP address over a consecutive 20 seconds, and then write to the blocked.txt file any subsequent attempts to reach the site from the same IP address over the next 5 minutes.
For example, if the third consecutive failed login attempt within a 20 second window occurred on 01/Aug/1995:00:00:08, all access to the website for that IP address would be blocked for the next 5 minutes. Even if the same IP host attempted a login -- successful or not -- one minute later at 01/Aug/1995:00:01:08, that attempt should be ignored and logged to the blocked.txt file. Access to the site from that IP address would be allowed to resume at 01/Aug/1995:00:05:09.
If an IP address has not reached three failed login attempts during the 20 second window, a login attempt that succeeds during that time period should reset the failed login counter and 20-second clock.
For example, if after two failed login attempts, a third login attempt is successful, full access should be allowed to resume immediately afterward. The next failed login attempt would be counted as 1, and the 20-second timer would begin there. In other words, this feature should only be triggered if an IP has 3 failed logins in a row, within a 20-second window.
e.g., blocked.txt
uplherc.upl.com - - [01/Aug/1995:00:00:07 -0400] "GET / HTTP/1.0" 304 0
uplherc.upl.com - - [01/Aug/1995:00:00:08 -0400] "GET /images/ksclogo-medium.gif HTTP/1.0" 304 0
…
The following illustration may help you understand how this feature might work, and when three failed login attempts would trigger 5 minutes of blocking:
Note that this feature should not impact the other features in this challenge. For instance, any requests that end up in the blocked.txt file should be counted toward the most active IP host calculation, bandwidth consumption and busiest 60-minute period.
You can download the data here: https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B7-XWjN4ezogbUh6bUl1cV82Tnc/view
Assume you receive as input, a file, log.txt, in ASCII format with one line per request, containing the following columns:
-
host making the request. A hostname when possible, otherwise the Internet address if the name could not be looked up.
-
timestamp in the format
[DD/MON/YYYY:HH:MM:SS -0400], where DD is the day of the month, MON is the abbreviated name of the month, YYYY is the year, HH:MM:SS is the time of day using a 24-hour clock. The timezone is -0400. -
request given in quotes.
-
HTTP reply code
-
bytes in the reply. Some lines in the log file will list
-in the bytes field. For the purposes of this challenge, that should be interpreted as 0 bytes.
e.g., log.txt
in24.inetnebr.com - - [01/Aug/1995:00:00:01 -0400] "GET /shuttle/missions/sts-68/news/sts-68-mcc-05.txt HTTP/1.0" 200 1839
208.271.69.50 - - [01/Aug/1995:00:00:02 -400] "POST /login HTTP/1.0" 401 1420
208.271.69.50 - - [01/Aug/1995:00:00:04 -400] "POST /login HTTP/1.0" 200 1420
uplherc.upl.com - - [01/Aug/1995:00:00:07 -0400] "GET / HTTP/1.0" 304 0
uplherc.upl.com - - [01/Aug/1995:00:00:08 -0400] "GET /images/ksclogo-medium.gif HTTP/1.0" 304 0
...
In the above example, the 2nd line shows a failed login (HTTP reply code of 401) followed by a successful login (HTTP reply code of 200) two seconds later from the same IP address.
The directory structure of repo:
├── README.md
├── run.sh
├── src
│ └── process_log.py
│ └── logClass.py
│ └── requestClass.py
│ └── timeClas.py
│ └── utility.py
├── log_input
│ └── log.txt
├── log_output
| └── hosts.txt
| └── hours.txt
| └── resources.txt
| └── blocked.txt
├── insight_testsuite
└── run_tests.sh
└── tests
└── test_features
| ├── log_input
| │ └── log.txt
| |__ log_output
| │ └── hosts.txt
| │ └── hours.txt
| │ └── resources.txt
| │ └── blocked.txt
├── your-own-test
├── log_input
│ └── your-own-log.txt
|__ log_output
└── hosts.txt
└── hours.txt
└── resources.txt
└── blocked.txt