If you are venturing into data science or machine learning, you will most likely encounter the Python library NumPy. NumPy is an open-source library that is widely used in scientific computing and data analysis. It provides robust support for multi-dimensional arrays and matrices, and a wide range of mathematical functions to operate on them. Here are some of the most commonly used functions that can help you get started with NumPy.
Arrays are at the core of NumPy. Creating arrays in NumPy is straightforward, and there are several ways to do it. The most common way of creating arrays is by using the array() function, which takes in a list or tuple and returns an array. For example, to create a 1-dimensional array with three elements, you can use the following code:
import numpy as np
my_array = np.array([1, 2, 3])If you want to create a two-dimensional array with three rows and two columns, you can use a nested list:
my_2d_array = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]])NumPy provides a wide range of mathematical functions to operate on arrays. These functions are optimized for numerical operations and are much faster than their Python counterparts. Some of the most commonly used mathematical functions include:
np.add(): Adds two arrays element-wisenp.subtract(): Subtracts two arrays element-wisenp.multiply(): Multiplies two arrays element-wisenp.divide(): Divides two arrays element-wise
Here is an example of how to use the add() function to add two arrays:
a = np.array([1, 2, 3])
b = np.array([4, 5, 6])
c = np.add(a, b)
print(c)
# output:
[5, 7, 9]NumPy provides several functions for manipulating arrays. Here are some commonly used functions:
np.reshape(): Reshapes an array into a new shapenp.concatenate(): Joins two or more arraysnp.transpose(): Transposes an array
Here is an example of how to use the reshape() function to reshape an array:
a = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
b = np.reshape(a, (2, 3))
print(b)
# output:
[[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]]
Here is an example of how to use the concatenate() function to join two arrays:
a = np.array([1, 2, 3])
b = np.array([4, 5, 6])
c = np.concatenate((a, b))
print(c)
# output:
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]Here is an example of how to use the transpose() function to transpose an array:
a = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]])
b = np.transpose(a)
print(b)
# output:
[[1, 3, 5],
[2, 4, 6]]NumPy provides functions for performing set operations like union and intersect:
np.union1d(): Creates a array of unique elements in two arrays.np.intersect1d(): Finds the intersection between two array.
Here is an example for both
a = np.array([1, 2, 0])
b = np.array([1, 3, 4])
print(np.union1d(a, b))
# output:
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
print(np.intersect1d(a, b))
# output:
[1]NumPy provides functions for finding and manipulating dates:
np.datetime64(): We can get the date in any format.np.is_busday(): To find the business day. By default, it considers saturday and sunday as not business days, however, it is customizable.
Here is an example for both
today = np.datetime64("today")
print(today)
# output:
2023-03-19 print(np.is_busday(np.datetime64('today')))
# output:
False #How to generate a range of dates:
np.arange('2023-01', '2023-02', dtype='datetime64[W]') #W - Week, replace with D
# output:
['2022-12-29' '2023-01-05' '2023-01-12' '2023-01-19']NumPy provides several functions for creating distribution. Here are some commonly used distribution functions:
np.random.normal(): Creates a normal distribution based on mu(mean) and sigma(variance)np.random.uniform(): Creates a uniform distributionnp.random.binomial: Creates a binomial distribution based on n(trials) and p(probability).
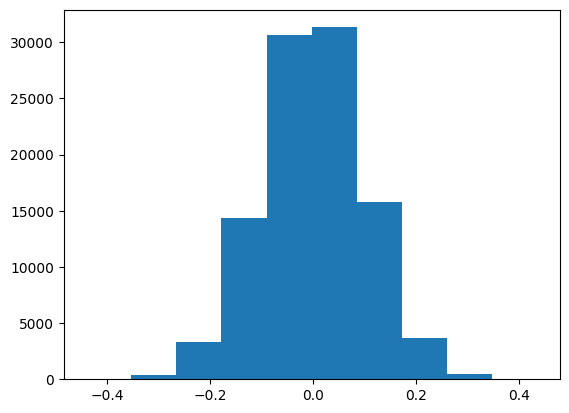
Here is an example of how to use the normal() function to create a normal distribution using an array:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
mu, sigma = 0, 0.1 #mean and variance
z = np.random.normal(mu, sigma, 100000)
plt.hist(z)
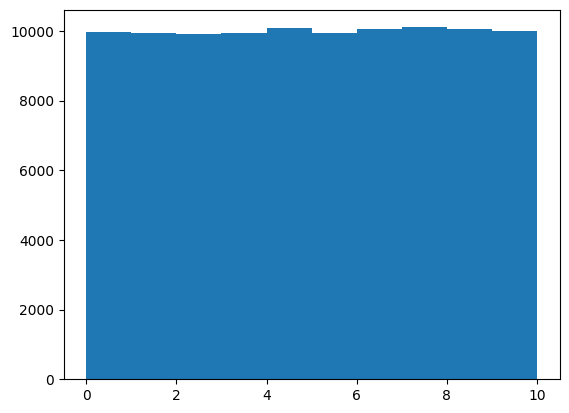
plt.show()Here is an example of how to use the uniform() function to create a uniform distribution using an array:
z = np.random.uniform(0, 10, 100000)
plt.hist(z)
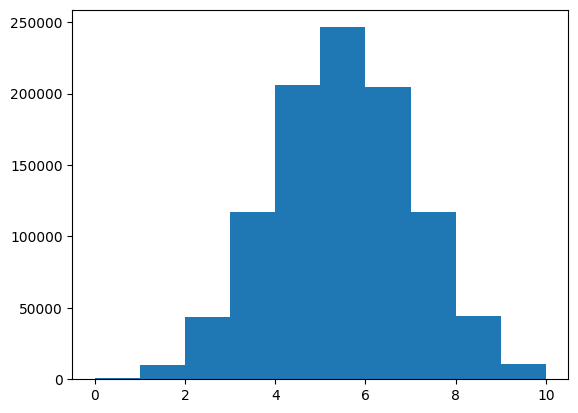
plt.show()Here is an example of how to use the binomial() function to create a binomial distribution using an array:
n, p = 10, 0.5
z = np.random.binomial(n, p, 1000000)
plt.hist(z)
plt.show()These are just a few of the many functions that NumPy provides. With these functions, you can perform a wide range of operations on arrays and matrices. NumPy is a powerful library that can help you streamline your data analysis and machine learning workflows.
Don't forget to subscribe to our newsletter to stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates on data science tools and techniques!