This is an unofficial implementation of VastGaussian: Vast 3D Gaussians for Large Scene Reconstruction. Since this is my first attempt at recreating the entire code from scratch, there might be some errors, and my coding style may seem somewhat naive compared to experts, lacking some engineering techniques. However, I have taken my first step because I couldn't find any implementation of VastGaussian online, so I gave it a try.
If you have any experience or feedback regarding code modifications during usage, please feel free to contact me or simply raise an issue:
Email: 374774222@qq.com
QQ: 374774222
WeChat: k374774222
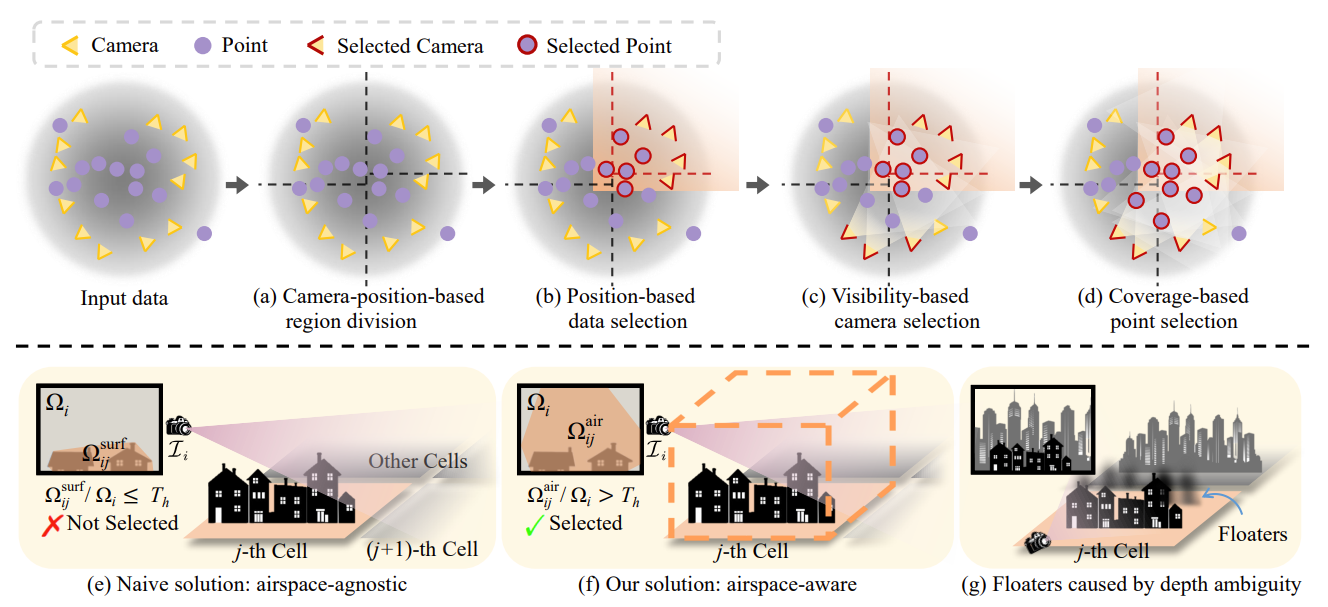
- Implement Camera-position-based region division
- Implement Position-based data selection
- Implement Visibility-based camera selection
- Implement Coverage-based point selection
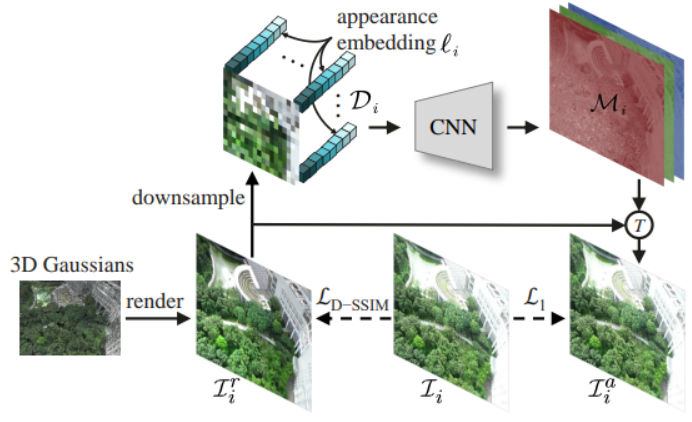
- Implement Decoupled Appearance Modeling
- Implement Seamless Merging
- Implement parallel training of m*n regions on a single GPU after point cloud division
- Conduct experiments on the UrbanScene3D and Mill-19 datasets
-
I made modifications to the original 3DGS by extracting its hyperparameters from
arguments/__init__.pyand placing them in thearguments/parameters.pyfile, making it easier to read and understand the hyperparameters. -
To preserve the original directory structure of 3DGS, I added a new folder
VastGaussian_sceneto store the modules of VastGaussian. Some parts of the code call existing functions from thescenefolder. To resolve import errors, I moved the Scene class to thedatasets.pyfile.
-
The file names match the methods mentioned in the paper for easier reading.
datasets.py: I rewrote the Scene class from 3DGS, splitting it into BigScene and PartitionScene. The former represents the original scene, BigScene, and the latter represents the partitioned smaller scenes, PartitionScene.
data_partition.py: Data partitioning, corresponding toProgressive Data Partitioningin the paper.
decouple_appearance_model.py: Decoupled Appearance Modeling module, corresponding toDecoupled Appearance Modelingin the paper.!
graham_scan.py: Convex hull computation, used in Visibility-based camera selection to project the partitioned cubes onto the camera plane and calculate the intersection of the projection area with the image area.
seamless_merging.py: Seamless merging, corresponding toSeamless Mergingin the paper, merging each PartitionScene into BigScene.
-
I added a new file
train_vast.pyto modify the training process of VastGaussian. To train the original 3DGS, usetrain.py. -
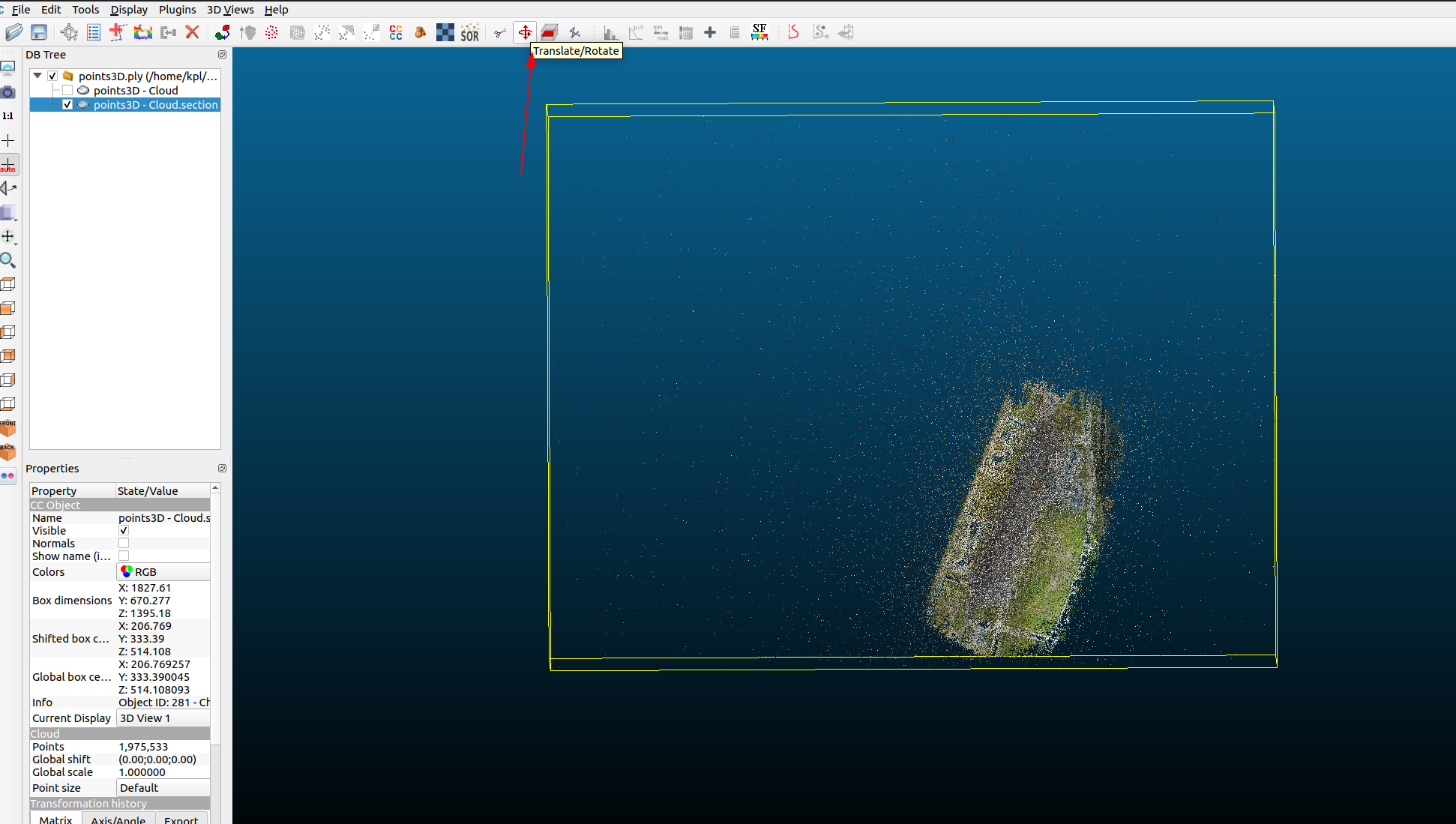
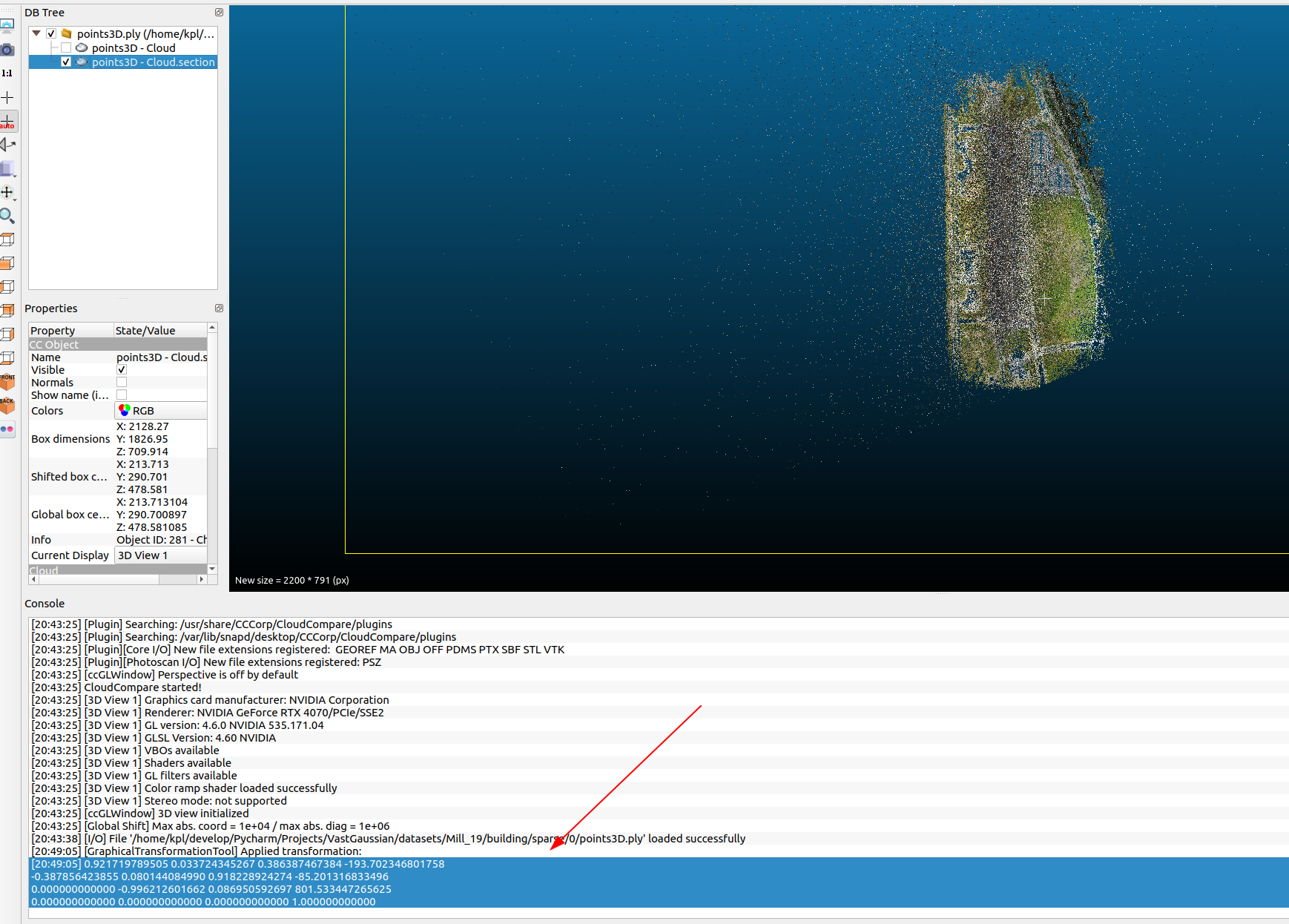
The paper mentions performing
Manhattan-world alignment to make the y-axis of the world coordinate vertical to the ground plane. After consulting an expert, I learned that this can be manually adjusted using CloudCompare software. The general process involves adjusting the bounding box boundaries of the region where the point cloud is located to align with the overall orientation of the point cloud region.
For example, the point cloud in the figure below was originally tilted, but after adjustment, it becomes horizontal and vertical. The expert mentioned that Manhattan-world alignment is a basic operation for large-scale 3D reconstruction (to facilitate partitioning), haha.
-
In my implementation, I used the small-scale data provided by 3DGS for testing. My machine cannot handle larger datasets, which, according to the paper, require at least 32G of VRAM.
-
During the implementation, the authors did not clearly specify some details of the operations in the paper, so some implementations are based on my guesses and understanding. Therefore, my implementation may have some bugs, and some implementations might seem silly to experts. If you encounter any issues during use, please contact me in time so we can improve together.
- The data format and training commands are similar to those of 3DGS. I did not make many personalized modifications. You can refer to the following command (for more parameters, refer to
arguments/parameters.py):
python train_vast.py -s output/dataset --exp_name test-
Urbanscene3D: UrbanScene3D -
Mill-19: Mill-19 -
Test data: Test Data