Multistage building of simple application shows IP addres and current time in Warsaw. The goal is to build lightest weight image.
You can find the image on DockerHub repository
There are three versions of dockerfile:
- default Dockerfile - based on alpine and contains HEALTHCHECK
- Dockerfile_selfTest - based on scratch and contains HEALTHCHECK test wrote in goLang
- Dockerfile_minimal - this is the lightest but don't have any HEALTHCHECK, only the app
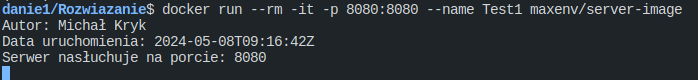
docker run --rm -it -p 8080:8080 --name Test1 maxenv/server-image
Use the following command to create a new builder:
docker buildx create --use --name mybuilder --driver docker-container --bootstrapUse the following command to build the container:
docker buildx build -t local/server-image .I use this command to build the Docker image for multiple platforms and push it to Docker Hub:
docker buildx build --sbom=true --provenance=mode=max --platform linux/amd64,linux/arm64 --cache-from=type=registry,ref=maxenv/server-image:latest --cache-to=type=registry,ref=maxenv/server-image:cache,mode=max --push -t maxenv/server-image:latest .docker run --rm -it -p 8080:8080 --name Test1 local/server-imagedocker run --rm -it -p 8080:8080 --name Test1 maxenv/server-imageAfter running the container, you can retrieve information from the server in your terminal and by visiting http://localhost:8080 in your web browser.
docker history maxenv/server-imageor for localbuild
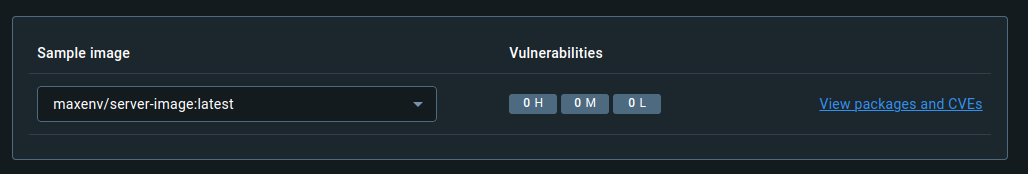
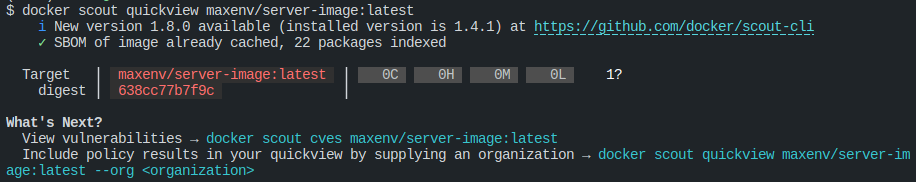
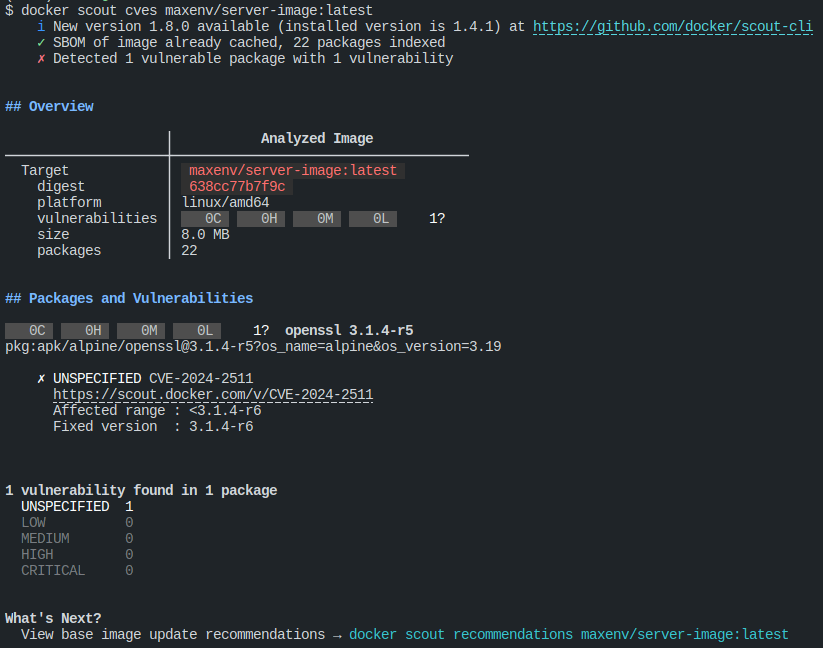
docker history local/server-imagedocker scout quickview maxenv/server-image:latestdocker scout cves maxenv/server-image:latestThe GitHub Actions workflow file, gha_example.yml, automates the process of building, tagging, and pushing a Docker image to DockerHub, as well as scanning the image for vulnerabilities.
Here's a step-by-step breakdown of the workflow:
-
Trigger: The workflow is triggered manually (
workflow_dispatch) or when a new tag is pushed to the repository. -
Checkout: The workflow checks out the source code of the repository.
-
Docker Metadata Definitions: The workflow defines metadata for the Docker image, such as the image name and tags.
-
QEMU and Buildx Setup: The workflow sets up QEMU and Buildx, which are tools used for building Docker images.
-
DockerHub Login: The workflow logs in to DockerHub using the provided username and token.
-
Build and Push Docker Image: The workflow builds the Docker image using the Dockerfile in the repository and pushes the image to DockerHub.
-
Docker Scout Vulnerability Scan: The workflow scans the Docker image for vulnerabilities using Docker Scout. The results are saved in a SARIF file.
-
Install jq: The workflow installs
jq, a command-line JSON processor. -
Show SARIF File: The workflow displays the contents of the SARIF file.
-
Parse SARIF File: The workflow parses the SARIF file and saves the results in a JSON file.
-
Check Vulnerability Scan Results: The workflow checks the vulnerability scan results and counts the number of critical and high vulnerabilities.
-
Show Scanning Results: The workflow displays the number of critical and high vulnerabilities.
-
Docker Push: If there are no critical or high vulnerabilities, the workflow pushes the Docker image to GitHub Container Registry (GHCR). If there are any critical or high vulnerabilities, the workflow skips this step.
This workflow ensures that the Docker image is built and pushed automatically, and that any vulnerabilities in the image are identified and reported. This helps maintain the security and integrity of the Docker image.