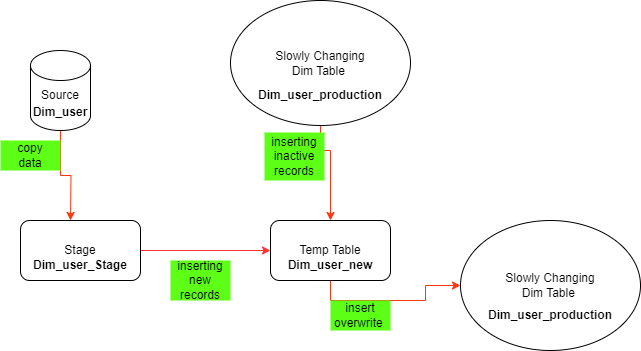
Handling SCD Type 1 and SCD Type 2 may be trivial or at least well-known in other databases, but on HDFS you may face several challenges. The most important are the following ones:
- There is no auto-increment functionality out of the box.
- We Can't use Hive transactional table on an external table.
- Even if we copy data to a transactional table we are facing the probability of corrupting the target data as there is no
ROLLBACKand Only available with specific file formats(ORC). - No direct way to update rows that have been updated from the source on the target table.
but we can work around these limitations by the following steps:
-
Creating a Staging Table: A new table named
dim_user_newis created by copying the schema of the production table (dim_user_production). This table will be used to process new data. -
Copying Records from Production to Staging Table: Records from the production table that do not exist in the staging table are copied over. This ensures that only new data is processed.
-
Handling Inactive (Historical) Records: Inactive records from the production table are copied to the staging table. Any changes classified as SCD Type 1 are applied during this step.
-
Copying Active Records without SCD Type 2 Changes: Active records from the production table that do not have SCD Type 2 changes are copied to the staging table. SCD Type 1 changes are applied if necessary.
-
Inserting New Inactive Versions with SCD Type 2 Changes: New inactive versions of records from the production table with SCD Type 2 changes are inserted into the staging table.
-
Inserting New Active Versions with SCD Type 2 Changes: New active versions of records from the production table with SCD Type 2 changes are inserted into the staging table.
-
Handling Records from Staging Table: Records from the staging table that do not exist in the production table are copied over, ensuring any new data is incorporated.
-
Replacing Content of Production Table: Finally, the content of the production table is replaced with the data from the staging table in a transactional manner, ensuring consistency.
-
Handling NULL Values: Special consideration is given to handling fields with NULL values using the COALESCE function or the <=> operator.
let's go through example to apply these steps:
Let's assume we have the following data in dim_user_production:
-- Create dim_user_production table
CREATE TABLE dim_user_production (
dim_user_id INT,
login VARCHAR(255),
premium_user BOOLEAN,
address VARCHAR(255),
phone VARCHAR(255),
name VARCHAR(255),
surname VARCHAR(255),
year_of_birth INT,
scd_version INT,
scd_start_date TIMESTAMP,
scd_end_date TIMESTAMP,
scd_active BOOLEAN
);
-- Insert sample data into dim_user_production table
INSERT INTO dim_user_production VALUES
(1, 'user1', true, 'address1', '123456789', 'John', 'Doe', 1980, 1, '2024-04-01 00:00:00', '9999-12-31 23:59:59', true),
(2, 'user2', false, 'address2', NULL, 'Alice', 'Smith', 1990, 1, '2024-04-01 00:00:00', '9999-12-31 23:59:59', true);
| dim_user_id | login | premium_user | address | phone | name | surname |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | user1 | true | address1 | 123456789 | John | Doe |
| 2 | user2 | false | address2 | NULL | Alice | Smith |
| year_of_birth | scd_version | scd_start_date | scd_end_date | scd_active |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1980 | 1 | 2024-04-01 00:00:00 | 9999-12-31 23:59:59 | true |
| 1990 | 1 | 2024-04-01 00:00:00 | 9999-12-31 23:59:59 | true |
and we have a staging table with changes in data from source system:
-- Create dim_user_staging table
CREATE TABLE dim_user_staging (
login VARCHAR(255),
name VARCHAR(255),
surname VARCHAR(255),
year_of_birth INT,
premium_user BOOLEAN,
address VARCHAR(255),
phone VARCHAR(255)
);
-- Insert sample data into dim_user_staging table
INSERT INTO dim_user_staging VALUES
('user1', 'John', 'Doe', 1985, true, 'address1', '987654321'),
('user2', 'Alice', 'Smith', 1990, true, 'address2', NULL),
('user3', 'Emma', 'Johnson', 1985, true, 'address3', '987654321');
staging table has :
- changed phone number for user1.
- user2 became a premium_user.
- user3 is added.
| login | name | surname | year_of_birth | premium_user | address | phone |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| user1 | John | Doe | 1985 | true | address1 | 987654321 |
| user2 | Alice | Smith | 1990 | true | address2 | NULL |
| user3 | Emma | Johnson | 1985 | true | address3 | 987654322 |
Step 1: Create a new table by copying the schema of the production table
-- Create dim_user_new table with the same schema as dim_user_production
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS dim_user_new;
CREATE TABLE dim_user_new LIKE dim_user_production;
Step 2: Copy all records from the production table that don't exist in the staging table
-- Insert records from dim_user_production that don't exist in dim_user_staging into dim_user_new
INSERT INTO dim_user_new
SELECT p.*
FROM dim_user_production p
LEFT JOIN dim_user_staging s ON p.login = s.login
WHERE s.login IS NULL;
Step 3: Copy all inactive records from the production table
This step selects inactive records from dim_user_production where scd_active is false and inserts them into dim_user_new. It includes columns from both dim_user_production and dim_user_staging tables.
INSERT INTO TABLE dim_user_new
SELECT
p.dim_user_id,
p.login,
p.premium_user,
p.address,
p.phone,
s.name,
s.surname,
s.year_of_birth,
p.scd_version,
p.scd_start_date,
p.scd_end_date,
p.scd_active
FROM dim_user_production p
JOIN dim_user_staging s ON p.login = s.login
AND p.scd_active = false;
Step 4: Insert active records from dim_user_production without SCD Type 2 changes into dim_user_new
This step inserts active records from dim_user_production into dim_user_new if there are no SCD Type 2 changes detected. It matches records based on login and checks for equality in other columns.
INSERT INTO TABLE dim_user_new
SELECT
p.dim_user_id,
p.login,
p.premium_user,
p.address,
p.phone,
s.name,
s.surname,
s.year_of_birth,
p.scd_version,
p.scd_start_date,
p.scd_end_date,
p.scd_active
FROM dim_user_production p
JOIN dim_user_staging s ON p.login = s.login
AND p.scd_active = true
WHERE p.premium_user = s.premium_user
AND p.address = s.address
AND COALESCE(p.phone, '') = COALESCE(s.phone, '');
Step 5: Insert new inactive versions with SCD Type 2 changes into dim_user_new
This step inserts new inactive versions into dim_user_new for records in dim_user_production where SCD Type 2 changes are detected. It updates the scd_end_date to the current timestamp and sets scd_active to false.
INSERT INTO dim_user_new
SELECT
p.dim_user_id,
p.login,
p.premium_user,
p.address,
p.phone,
s.name,
s.surname,
s.year_of_birth,
p.scd_version,
p.scd_start_date,
current_timestamp(), -- current timestamp for scd_end_date
false -- false for scd_active
FROM dim_user_production p
JOIN dim_user_staging s ON p.login = s.login
WHERE p.scd_active = true
AND (p.premium_user != s.premium_user
OR p.address != s.address
OR COALESCE(p.phone, '') != COALESCE(s.phone, ''));
Adding inactive versions for user1 and user2:
| dim_user_id | login | premium_user | address | phone | name | surname | year_of_birth | scd_version | scd_start_date | scd_end_date | scd_active |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | user1 | true | address1 | 123456789 | John | Doe | 1980 | 1 | 2024-04-01 00:00:00 | 2024-05-25 00:00:00 | false |
| 2 | user2 | false | address2 | NULL | Alice | Smith | 1990 | 1 | 2024-04-01 00:00:00 | 2024-05-25 00:00:00 | false |
Step 6: Insert new active versions for records with SCD Type 2 changes
This step inserts new active versions into dim_user_new for records in dim_user_production where SCD Type 2 changes are detected. It sets dim_user_id to NULL (presumably to be auto-generated), then selects columns from dim_user_staging to be joined with dim_user_production. It sets scd_version to the next value, scd_start_date to the current timestamp, scd_end_date to '9999-12-31 23:59:59', and scd_active to true.
It checks for changes in premium_user, address, and phone columns between dim_user_production and dim_user_staging, and inserts records into dim_user_new accordingly.
INSERT INTO dim_user_new
SELECT NULL, s.login, s.premium_user, s.address, s.phone, s.name, s.surname,
s.year_of_birth, p.scd_version + 1,
current_timestamp(), -- current timestamp for scd_start_date
'9999-12-31 23:59:59', -- default timestamp for scd_end_date
true
FROM dim_user_production p
JOIN (
SELECT
login, premium_user, address, phone, name, surname, year_of_birth
FROM dim_user_staging
) s ON p.login = s.login
WHERE p.scd_active = true
AND (p.premium_user != s.premium_user
OR p.address != s.address
OR COALESCE(p.phone, '') != COALESCE(s.phone, ''));
| dim_user_id | login | premium_user | address | phone | name | surname | year_of_birth | scd_version | scd_start_date | scd_end_date | scd_active |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | user1 | true | address1 | 123456789 | John | Doe | 1980 | 1 | 2024-04-01 00:00:00 | 2024-05-25 00:00:00 | false |
| 2 | user2 | false | address2 | NULL | Alice | Smith | 1990 | 1 | 2024-04-01 00:00:00 | 2024-05-25 00:00:00 | false |
| NULL | user1 | true | address1 | 987654321 | John | Doe | 1980 | 2 | 2024-05-25 12:00:00 | 9999-12-31 23:59:59 | true |
| NULL | user2 | true | address2 | NULL | Alice | Smith | 1990 | 2 | 2024-05-25 12:00:00 | 9999-12-31 23:59:59 | true |
Step 7: Handle records from dim_user_staging that don't exist in the production table
This step inserts records from dim_user_staging into dim_user_new that do not exist in dim_user_production. It sets dim_user_id to NULL (presumably to be auto-generated), sets scd_version to 1, scd_start_date to the current timestamp, and scd_end_date to '9999-12-31 23:59:59'. It also sets scd_active to true.
INSERT INTO dim_user_new
SELECT
NULL,
s.login,
s.premium_user,
s.address,
s.phone,
s.name,
s.surname,
s.year_of_birth,
1,
current_timestamp(),
'9999-12-31 23:59:59',
true
FROM dim_user_staging s
LEFT JOIN dim_user_production p ON s.login = p.login
WHERE p.login IS NULL;
Reaching step7 we will have all data we needed in dim_user_new table as:
| dim_user_id | login | premium_user | address | phone | name | surname |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | user1 | True | address1 | 123456789 | John | Doe |
| 2 | user2 | False | address2 | NULL | Alice | Smith |
| NULL | user1 | True | address1 | 987654321 | John | Doe |
| NULL | user2 | True | address2 | NULL | Alice | Smith |
| NULL | user3 | True | address3 | 987654321 | Emma | Johnson |
| year_of_birth | scd_version | scd_start_date | scd_end_date | scd_active |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1985 | 1 | 2024-04-01 00:00:00.0 | 2024-05-25 00:00:00.0 | False |
| 1990 | 1 | 2024-04-01 00:00:00.0 | 2024-05-25 00:00:00.0 | False |
| 1985 | 2 | 2024-05-25 00:00:00.0 | 9999-12-31 23:59:59.0 | True |
| 1990 | 2 | 2024-05-25 00:00:00.0 | 9999-12-31 23:59:59.0 | True |
| 1985 | 1 | 2024-05-25 00:00:00.0 | 9999-12-31 23:59:59.0 | True |
Step 8: Use ROW_NUMBER() to generate sequential numbers for dim_user_id and overwrite dim_user_production
This step generates sequential numbers for dim_user_id using ROW_NUMBER() over the scd_start_date, then overwrites the dim_user_production table with the modified data from dim_user_new.
INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE dim_user_production
SELECT
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (ORDER BY scd_start_date) AS dim_user_id,
login,
premium_user,
address,
phone,
name,
surname,
year_of_birth,
scd_version,
scd_start_date,
scd_end_date,
scd_active
FROM dim_user_new;
now we have all changed data in our dimension table dim_user_production
| dim_user_id | login | premium_user | address | phone | name | surname |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | user1 | True | address1 | 123456789 | John | Doe |
| 2 | user2 | False | address2 | NULL | Alice | Smith |
| 3 | user2 | True | address2 | NULL | Alice | Smith |
| 4 | user1 | True | address1 | 987654321 | John | Doe |
| 5 | user3 | True | address3 | 987654321 | Emma | Johnson |
| year_of_birth | scd_version | scd_start_date | scd_end_date | scd_active |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1990 | 1 | 2024-04-01 00:00:00.0 | 2024-05-25 19:57:15.654 | False |
| 1985 | 1 | 2024-04-01 00:00:00.0 | 2024-05-25 19:57:15.654 | False |
| 1990 | 2 | 2024-05-25 19:57:43.042 | 9999-12-31 23:59:59.0 | True |
| 1985 | 2 | 2024-05-25 19:57:43.042 | 9999-12-31 23:59:59.0 | True |
| 1985 | 1 | 2024-05-25 19:58:08.305 | 9999-12-31 23:59:59.0 | True |
https://www.softserveinc.com/en-us/blog/process-slowly-changing-dimensions-hive