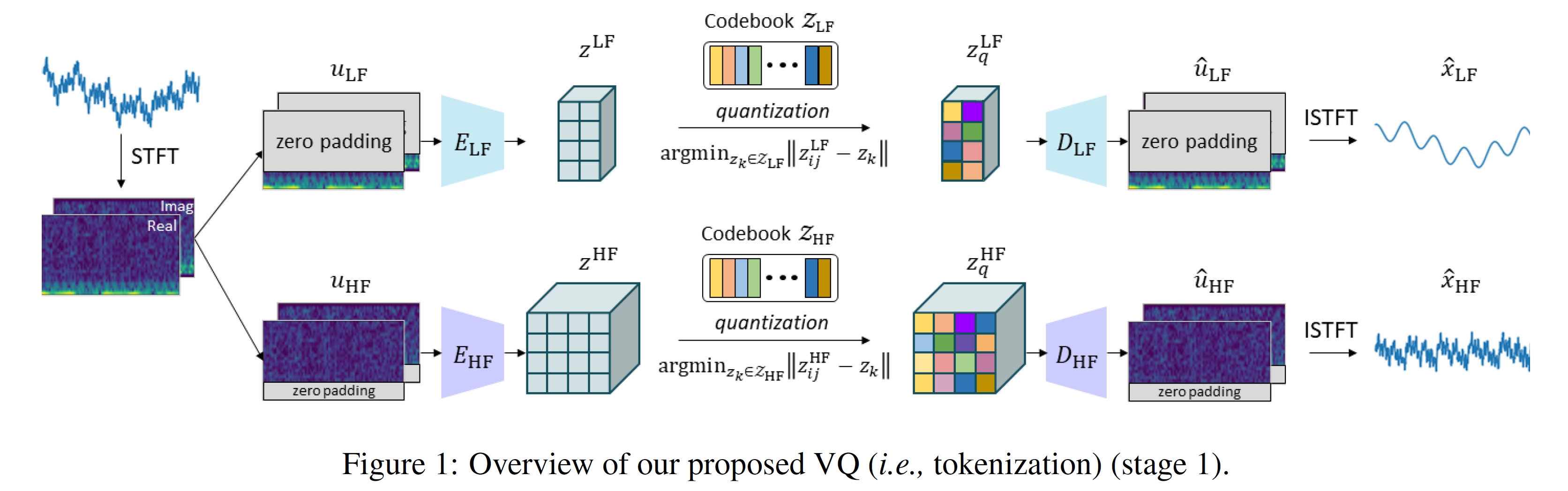
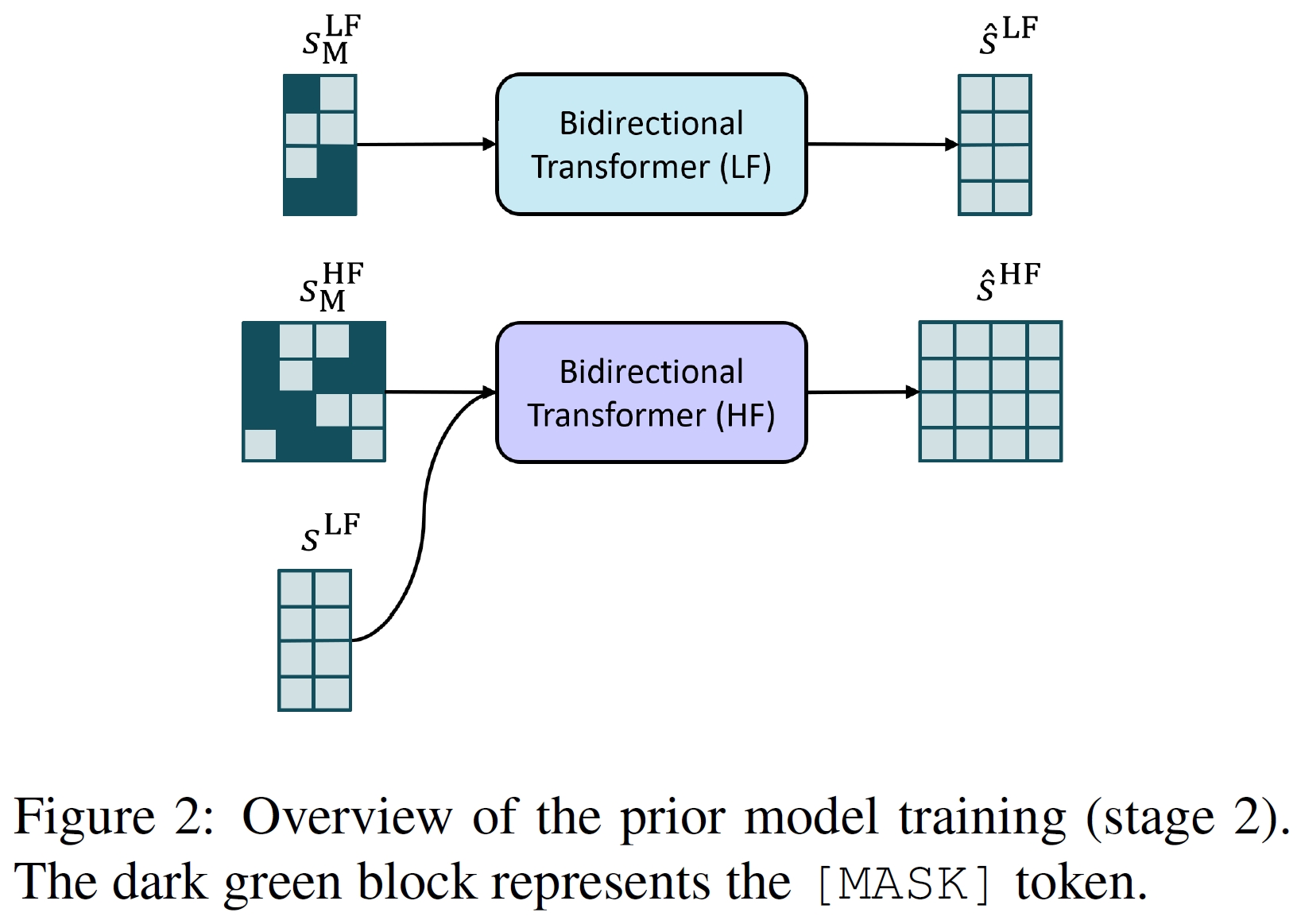
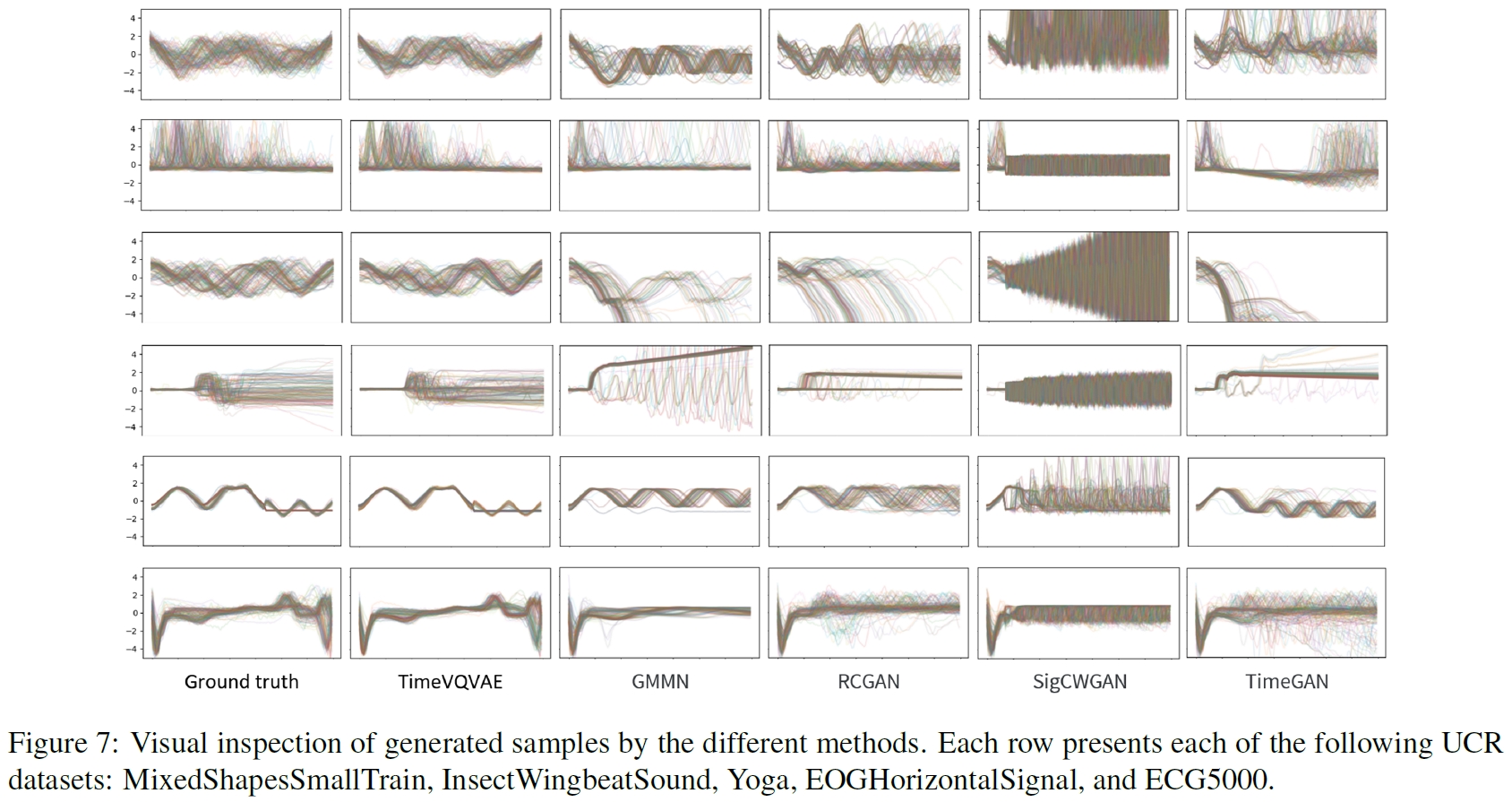
This is an official Github repository for the PyTorch implementation of TimeVQVAE from our paper "Vector Quantized Time Series Generation with a Bidirectional Prior Model", AISTATS 2023.
TimeVQVAE is a robust time series generation model that utilizes vector quantization for data compression into the discrete latent space (stage1) and a bidirectional transformer for the prior learning (stage2).
You should first create a virtual environment, and activate the environment. Then you can install the necessary libraries by running the following command.
pip install -r requirements.txt
The UCR archive datasets are automatically downloaded if you run any of the training command below such as python stage1.py. If you just want to download the datasets only without running the training, run
python preprocessing/preprocess_ucr.py
[update note on July 8, 2024] We now use a larger training set by using the following re-arranged dataset: We reorganized the original datasets from the UCR archive by 1) merging the existing training and test sets, 2) resplitting it using StratifiedShuffleSplit (from sklearn) into 80% and 20% for a training set and test set, respectively. We did so becaused the original datasets have two primary issues to be used to train a time series generative model. Firstly, a majority of the datasets have a larger test set compared to a training set. Secondly, there is clear difference in patterns between training and test sets for some of the datasets. The data format remains the same.
- original datasets: https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/UCR_Archive_2018/21359775
- re-organized datasets: https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/UCR_Archive_2018_resplit_ver_/26206355
- NB! the dataset directory should be located in
TimeVQVAE/datasets. For instance,TimeVQVAE/datasets/UCRArchive_2018orTimeVQVAE/datasets/UCRArchive_2018_resplit.
configs/config.yaml: configuration for dataset, data loading, optimizer, and models (i.e., encoder, decoder, vector-quantizer, and MaskGIT)config/sconfig_cas.yaml: configuration for running CAS, Classification Accuracy Score (= TSTR, Training on Synthetic and Test on Real).
🚀 The stage 1 and stage 2 training can be performed with the following command:
python stage1.py --dataset_names FordA --gpu_device_idx 0
python stage2.py --dataset_names FordA --gpu_device_idx 0
💡 The training pipeline is as follows:
- Run
stage1.pyand it saves trained encoders, decoders, and vector-quantizers for LF and HF. - Run
stage2.pyand it saves the prior model (i.e., bidirectional transformer);stage2.pyincludes an evaluation step which is performed right after the stage 2 training. The evaluation includes a visualization plot of samples, FID score, and IS (Inception Score).
🚀 CAS can be performed with the following command:
python run_CAS.py --dataset_names FordA --gpu_device_idx 0
The following code runs the evaluation step (the same evaluation step as the end of stage2.py).
python evaluate.py --dataset_names FordA --gpu_device_idx 0 -feature_extractor_type supervised_fcn
We found that the representations from ROCKET [5] result in more robust distributional plot with PCA and FID score. That is because the ROCKET representations are the most unbiased representations, as it is not trained at all, unlike any supervised methods like supervised FCN. You can use the ROCKET representations for the PCA visualization and FID calculation by running
python evaluate.py --dataset_names FordA --gpu_device_idx 0 --feature_extractor_type rocket
(NB! make sure to change your notebook setting to GPU.)
A Google Colab notebook is available for time series generation with the pretrained VQVAE. The usage is simple:
- User Settings: specify
dataset_nameandn_samples_to_generate. - Sampling: Run the unconditional sampling and class-conditional sampling.
- The full result tables for FID, IS, and CAS are available in
results/.
- [2024.07.01] compute the prior loss only on the masked locations, instead of the entire tokens.
- [2024.07.02] use a convolutional-based upsampling layer, (nearest neighbor interpolation - convs), to lengthen the LF token embeddings to match with the length of HF embeddings. Linear used to be used; Strong dropouts are used to the LF and HF embeddings within
forward_hfinbidirectional_transformer.pyto make the sampling process robust; Smaller HF transformer is used due to an overfitting problem; n_fft of 4 is used instead of 8. - [2024.07.04] FID score can be computed with ROCKET representations in
evaluate.pyby setting--feature_extractor_type rocket. - [2024.07.08] using the re-organized datasets instead of the original datasets, as decrived above in the Data Download section.
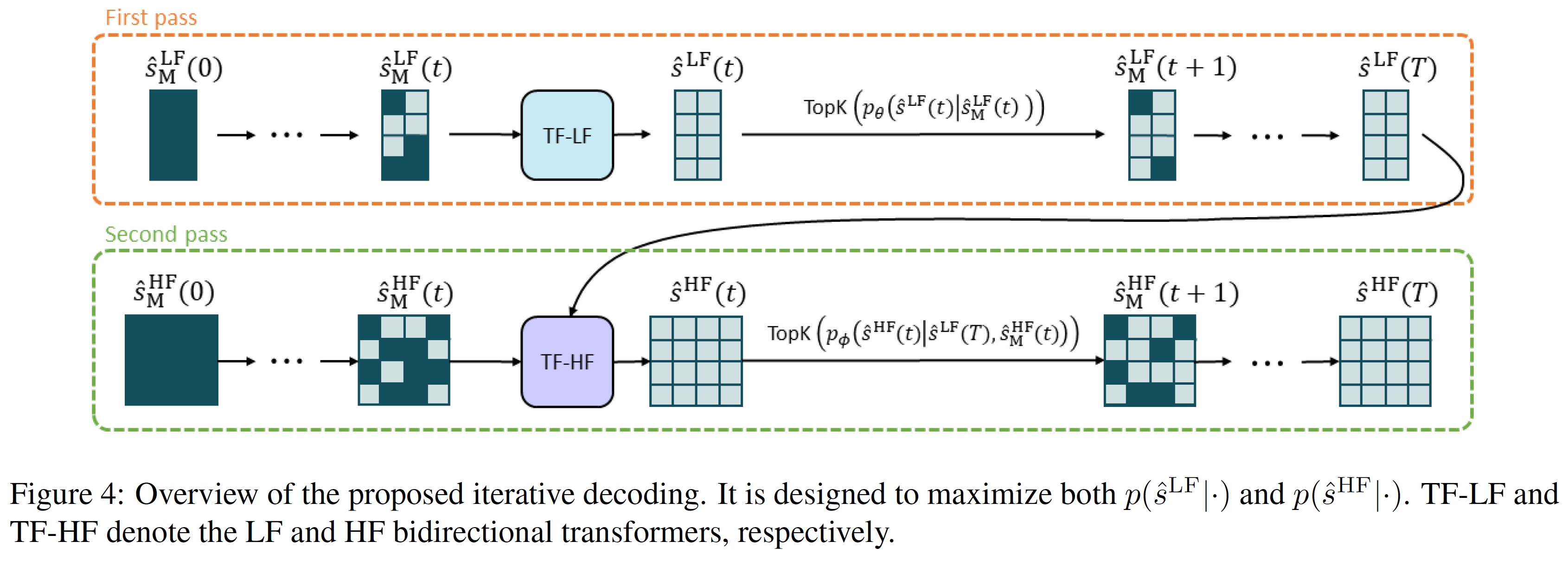
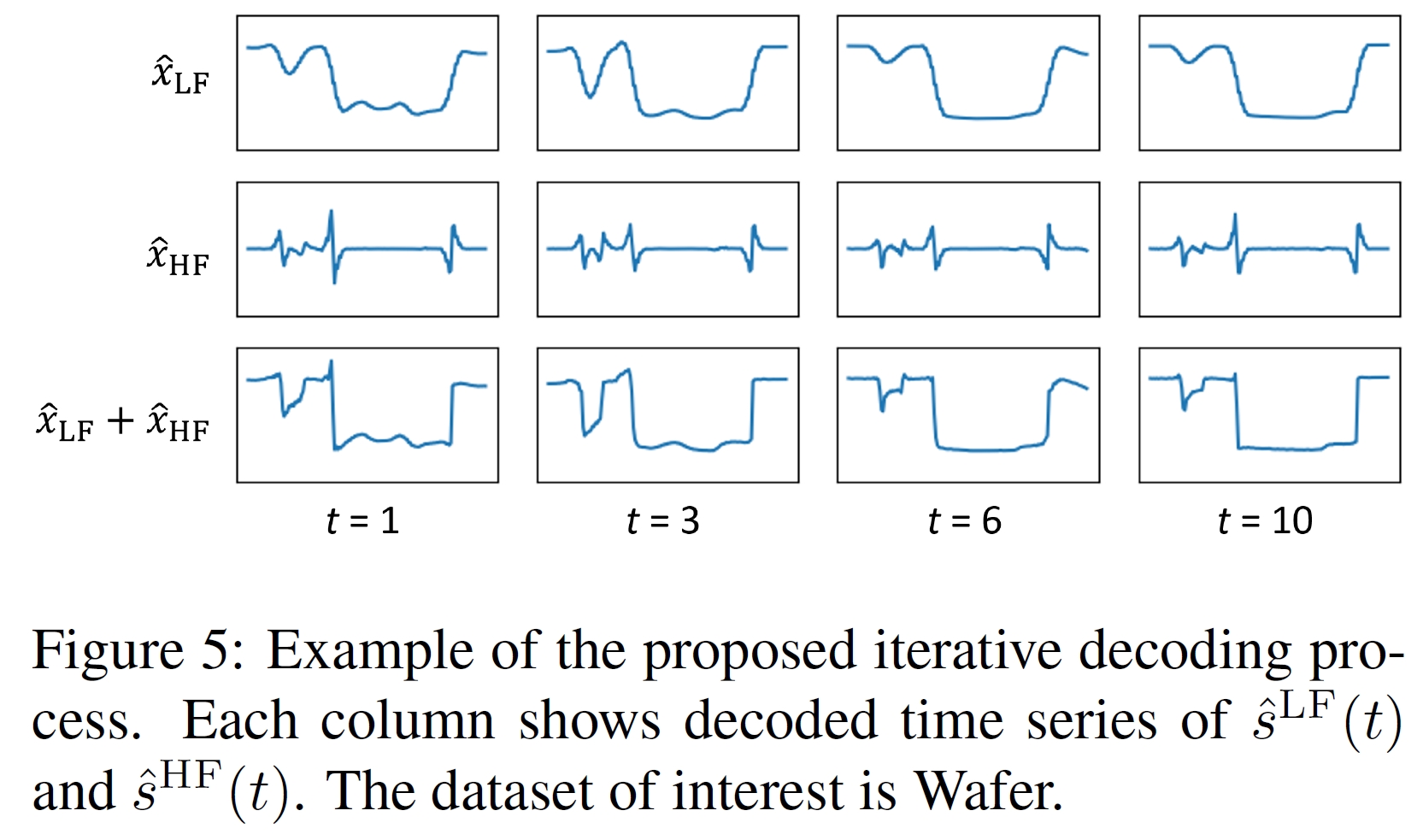
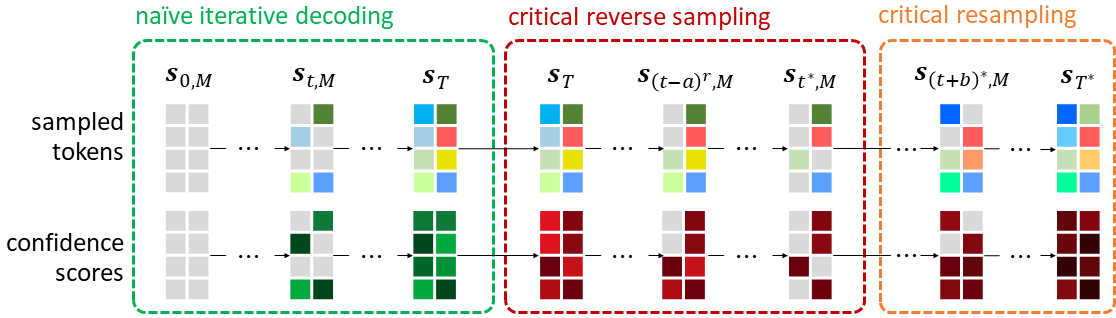
We have published a follow-up paper [2] that enhances the sampling process by resolving its existing limitations, which in turn results in considerably higher fidelity. To be more precise, we first sample a token set with a naive iterative decoding (existing sampling process) and remove the less-likely tokens, and resample the tokens with a better realism approach for tokens. The figure below illustrates the overview of [2].
You can use it by setting MaskGIT.ESS.use = True in configs/config.yaml.
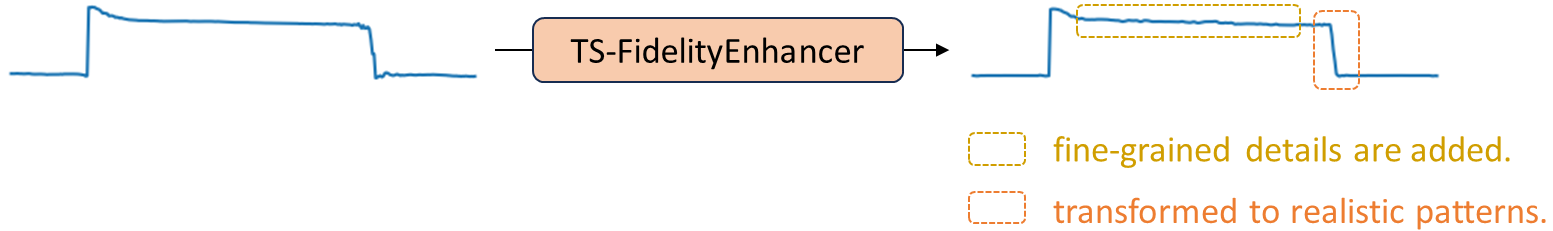
We have published a follow-up paper that proposes, TS-FidelityEnhancer. It acts like a mapping function such that it transforms a generated time series to be more realistic while retaining the original context.
To employ this, the stage1 training must've been finished. Then, you can train the fidelity enhancer by running
python stage_fid_enhancer.py --dataset_names FordA --gpu_device_idx 0 --use_fidelity_enhancer True
TimeVQVAE learns a prior, and we can utilize the learned prior to measure the likelihood of a segment of time series, in which a high likelihood indicates a normal state while a low likelihood indicates an abnormal state (i.e., anomaly). With that principal, we have developed TimeVQVAE-AD. It not only achieves a state-of-the-art anomaly detection accuracy on the UCR Anomaly archive, but also provides a high level of explainability, covering counterfactual sampling (i.e., to answer the following question, "how is the time series supposed look if there was no anomaly?"). If AD is your interest, please check out the paper. Its open-source code is available here.
[1]
@inproceedings{lee2023vector,
title={Vector Quantized Time Series Generation with a Bidirectional Prior Model},
author={Lee, Daesoo and Malacarne, Sara and Aune, Erlend},
booktitle={International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics},
pages={7665--7693},
year={2023},
organization={PMLR}
}
[2]
@article{lee2023masked,
title={Masked Generative Modeling with Enhanced Sampling Scheme},
author={Lee, Daesoo and Aune, Erlend and Malacarne, Sara},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.07945},
year={2023}
}
[3]
[4]
@article{lee2023explainable,
title={Explainable Time Series Anomaly Detection using Masked Latent Generative Modeling},
author={Lee, Daesoo and Malacarne, Sara and Aune, Erlend},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.12550},
year={2023}
}
[5]
@article{dempster2020rocket,
title={ROCKET: exceptionally fast and accurate time series classification using random convolutional kernels},
author={Dempster, Angus and Petitjean, Fran{\c{c}}ois and Webb, Geoffrey I},
journal={Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery},
volume={34},
number={5},
pages={1454--1495},
year={2020},
publisher={Springer}
}