Microsoft Open Source Code of Conduct
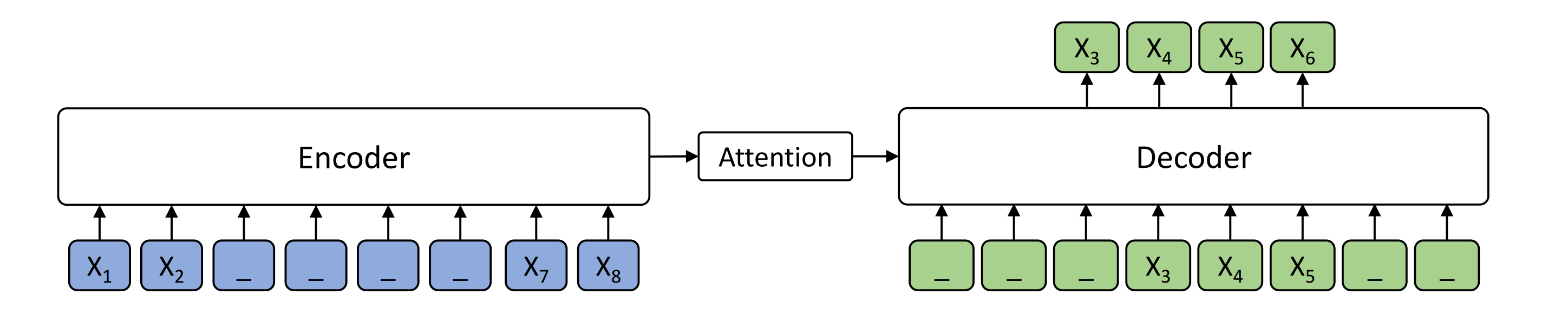
MASS is a novel pre-training method for sequence to sequence based language generation tasks. It randomly masks a sentence fragment in the encoder, and then predicts it in the decoder.
The current codebase is for unsupersied neural machine translation. We will release our implementation for supervised machine translation, and other language generation tasks in the future.
Unsupervised Neural Machine Translation just uses monolingual data to train the models. For this task, we implement MASS on XLM.
We also provide pre-trained and fine-tuned models:
| Languages | Pre-trained Model | Fine-tuned Model | BPE codes | Vocabulary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EN - FR | MODEL | MODEL | BPE codes | Vocabulary |
| EN - DE | MODEL | MODEL | BPE codes | Vocabulary |
| En - RO | MODEL | MODEL | BPE_codes | Vocabulary |
We are also preparing larger models on more language pairs, and will release them in the future.
We use the same BPE codes and vocabulary with XLM. Here we take English-French as an example.
cd MASS
wget https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/XLM/codes_enfr
wget https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/XLM/vocab_enfr
./get-data-nmt.sh --src en --tgt fr --reload_codes codes_enfr --reload_vocab vocab_enfr
python train.py \
--exp_name unsupMT_enfr \
--data_path ./data/processed/en-fr/ \
--lgs 'en-fr' \
--mass_steps 'en,fr' \
--encoder_only false \
--emb_dim 1024 \
--n_layers 6 \
--n_heads 8 \
--dropout 0.1 \
--attention_dropout 0.1 \
--gelu_activation true \
--tokens_per_batch 3000 \
--optimizer adam_inverse_sqrt,beta1=0.9,beta2=0.98,lr=0.0001 \
--epoch_size 200000 \
--max_epoch 100 \
--eval_bleu true \
--word_mass 0.5 \
--min_len 5 \
During the pre-training prcess, even without any back-translation, you can observe the model can achieve some intial BLEU scores:
epoch -> 4
valid_fr-en_mt_bleu -> 10.55
valid_en-fr_mt_bleu -> 7.81
test_fr-en_mt_bleu -> 11.72
test_en-fr_mt_bleu -> 8.80
After pre-training, we use back-translation to fine-tune the pre-trained model on unsupervised machine translation:
MODEL=mass_enfr_1024.pth
python train.py \
--exp_name unsupMT_enfr \
--data_path ./data/processed/en-fr/ \
--lgs 'en-fr' \
--bt_steps 'en-fr-en,fr-en-fr' \
--encoder_only false \
--emb_dim 1024 \
--n_layers 6 \
--n_heads 8 \
--dropout 0.1 \
--attention_dropout 0.1 \
--gelu_activation true \
--tokens_per_batch 2000 \
--batch_size 32 \
--bptt 256 \
--optimizer adam_inverse_sqrt,beta1=0.9,beta2=0.98,lr=0.0001 \
--epoch_size 200000 \
--max_epoch 30 \
--eval_bleu true \
--reload_model "$MODEL,$MODEL" \
To apply MASS on text summarization, we provide an example of how to run MASS pre-training and fine-tuning on the Gigaword dataset.
| Pre-trained Model | BPE codes | Vocabulary |
|---|---|---|
| Coming soon | BPE codes | Vocabulary |
For pre-training, we use the following command:
python train.py \
--exp_name mass_english \
--data_path ./data/processed/en/ \
--lgs 'en' \
--mass_steps 'en' \
--encoder_only false \
--emb_dim 1024 \
--n_layers 6 \
--n_heads 8 \
--dropout 0.1 \
--attention_dropout 0.1 \
--gelu_activation true \
--tokens_per_batch 3000 \
--optimizer adam_inverse_sqrt,beta1=0.9,beta2=0.98,lr=0.0001 \
--epoch_size 200000 \
--max_epoch 100 \
--eval_bleu true \
--word_mass 0.5 \
--min_len 5 \
--english_only true
Different from unsupervised NMT tasks, we directly use paired data (article-title) to fine-tune the pre-trained model. The fine-tuning command is:
MODEL=mass_en_1024.pth
python train.py \
--exp_name mass_summarization \
--data_path ./data/processed/summarization/ \
--lgs 'ar-ti' \
--mt_steps 'ar-ti' \
--encoder_only false \
--emb_dim 1024 \
--n_layers 6 \
--n_heads 8 \
--dropout 0.2 \
--attention_dropout 0.2 \
--gelu_activation true \
--tokens_per_batch 3000 \
--optimizer adam_inverse_sqrt,beta1=0.9,beta2=0.98,lr=0.0001 \
--epoch_size 200000 \
--max_epoch 20 \
--eval_bleu true \
--english_only true \
--reload_model "$MODEL,$MODEL"
If you find MASS useful in your work, you can cite the paper as below:
@inproceedings{song2019mass,
title={MASS: Masked Sequence to Sequence Pre-training for Language Generation},
author={Song, Kaitao and Tan, Xu and Qin, Tao and Lu, Jianfeng and Liu, Tie-Yan},
booktitle={International Conference on Machine Learning},
pages={5926--5936},
year={2019}
}