ONN4ARG is an Ontology-aware Neural Network model for Antibiotic Resistance Gene (ARG) annotation predictions. It employs a novel ontology-aware layer to encourage annotation predictions satisfying the ontology rules (i.e., the ontology tree structure). It requires the Diamond and the HHblits alignment tools to run. Our source codes are available on GitHub, and our pre-built ARG database and our pre-trained model can be downloaded from Zenodo or release. ONN4ARG provides web service for fast ARG prediction.
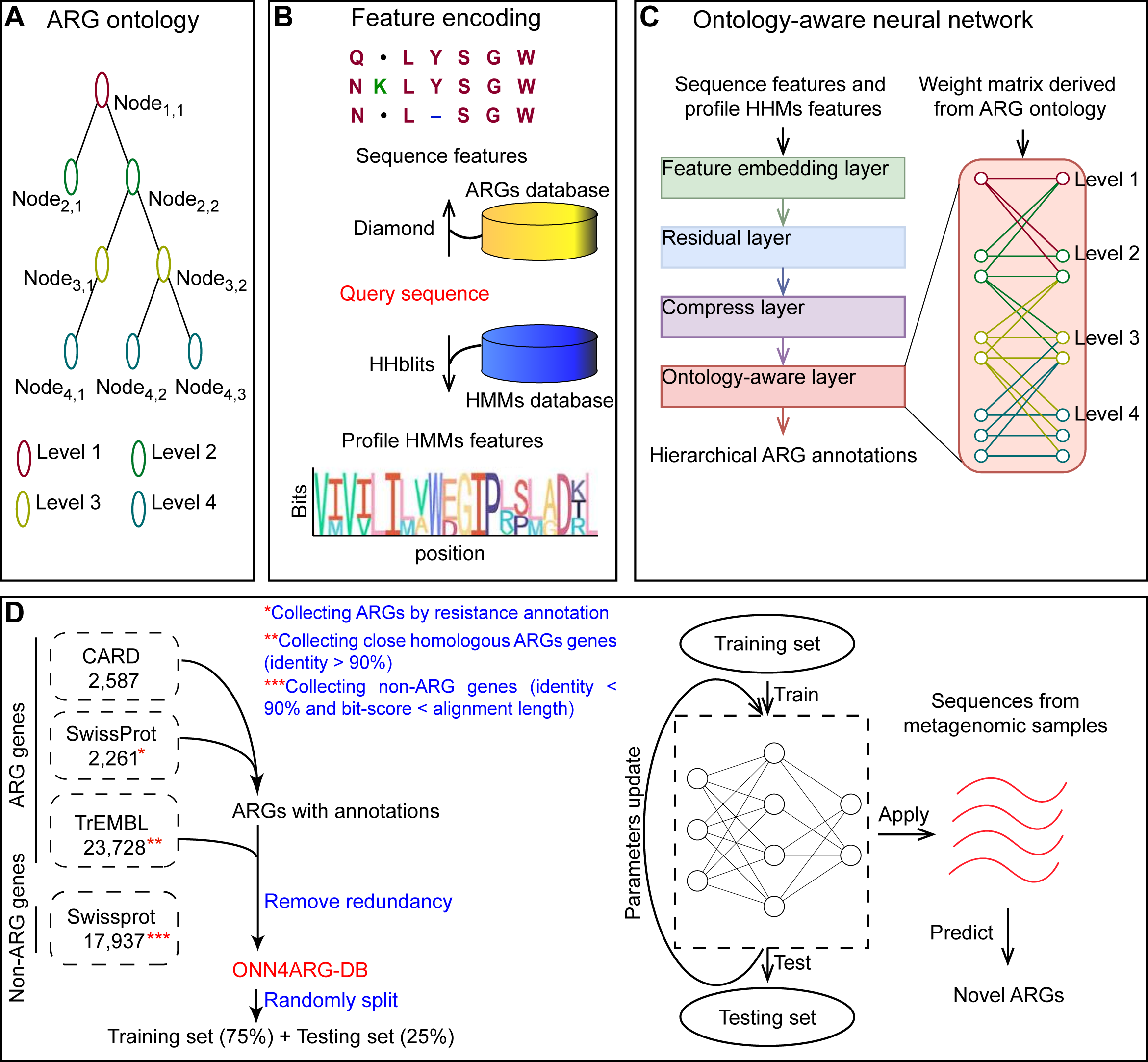
Overview of the ONN4ARG model and its use for novel ARG discovery. (A) The antibiotic resistance gene ontology contains four levels. The root (first level) is a single node, namely, “arg”. There are 1, 2, 34, and 277 nodes from the first level to the fourth level, respectively. (B) The feature encoding procedure of ONN4ARG model. The sequence alignment features and profile HMMs features are encoded by calling Diamond and HHblits. (C) The architecture of the ontology-aware neural network could be described in four functional layers, including feature embedding layer, residual layer, compress layer and ontology-aware layer. The ontology-aware layer is a partially connected layer which encourage annotation predictions satisfying the ontology rules (i.e., the ontology tree structure). Specially, weight between nodes with relationship (e.g., parent and child) satisfying the ontology rules would be saved in the partially connected layer, and weights between irrelevant nodes would be masked. (D) Building the dataset for training and testing, and applying ONN4ARG model on metagenomic samples to discover candidate novel ARGs.The ARGs we used in this study for model training and testing were from the Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database (CARD, v3.0.3). We also used protein sequences from the UniProt (SwissProt and TrEMBL) database to expand our training dataset. First, genes with ARG annotations were collected from CARD (2,587 ARGs) and SwissProt (2,261 ARGs). Then, their close homologs (with sequence identities greater than 90%) were collected from TrEMBL (23,728 homologous genes). These annotated and homologous ARGs made up our positive dataset. The negative dataset was made from non-ARG genes that had relatively weak sequence similarities to ARG genes (with sequence identities smaller than 90% and bit-scores smaller than alignment lengths) but not annotated as ARG genes in SwissProt (17,937 genes). Finally, redundant genes with identical sequences were filtered out. As a result, our ARG gene dataset, namely, ONN4ARG-DB, contained 28,396 positive and 17,937 negative genes. For evaluation and comparison of ONN4ARG, 75% of the dataset was randomly selected for training, and the remaining 25% of the dataset was selected for testing.
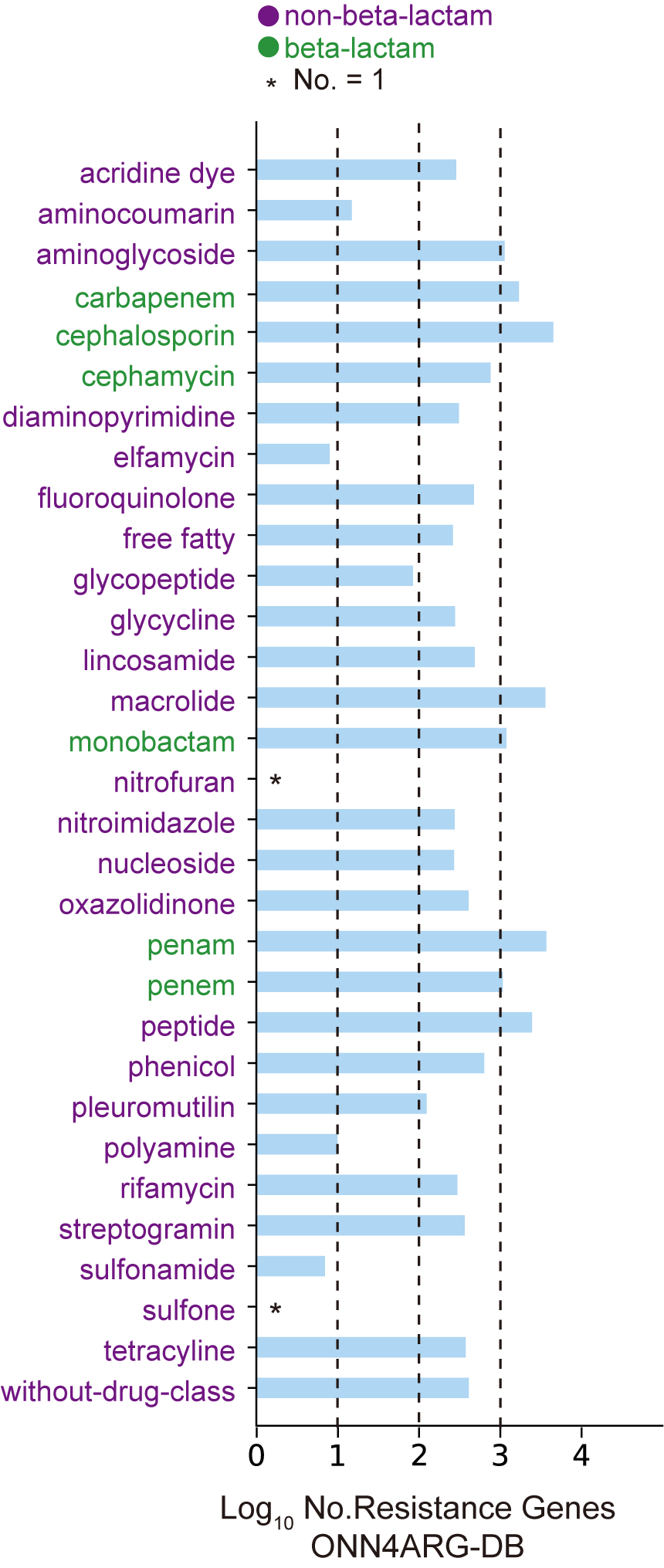
The number of genes in ONN4ARG-DB. The horizontal axis indicates the logarithmic number of genes, and the vertical axis indicates different antibiotic resistance types.The ARGs we used in this study for model training and testing were from the Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database, CARD v3.0.3. We also used protein sequences from the UniProt (SwissProt and TrEMBL) database to expand our training dataset. First, genes with ARG annotations were collected from CARD (2,587 ARGs) and SwissProt (2,261 ARGs). Then, their close homologs (sequence identity > 90% and coverage > 98%) were collected from TrEMBL (23,728 homologous genes). These annotated and homologous ARGs made up our ARG dataset. The non-ARG dataset was made from non-ARG genes that had relatively weak sequence similarities to ARG genes (sequence identity < 90% and bit-scores < alignment lengths) but not annotated as ARG genes in SwissProt (17,937 non-ARG genes). Finally, redundant genes with identical sequences were filtered out. As a result, our ARG gene dataset, namely, ONN4ARG-DB, contained 28,396 ARG genes and 17,937 non-ARG genes.
-
Unix/Linux operating system
-
At least 128 GB free disk space
-
At least 16 GB RAM
We recommend deploying ONN4ARG using git and conda.
# clone this repository
git clone https://github.com/HUST-NingKang-Lab/ONN4ARG.git
# download model
wget https://github.com/HUST-NingKang-Lab/ONN4ARG/releases/download/v1.0/onn4arg.zip
./predict.sh FASTA_fileprefix
The program will take "FASTA_fileprefix.fasta" as input and store the predicted annotations in "FASTA_fileprefix.out". Note that only one sequence is supported in the input FASTA file.
| Name | Affiliation | |
|---|---|---|
| Yuguo Zha | hugozha@hust.edu.cn | School of Life Science and Technology, Huazhong University of Science & Technology |
| Cheng Chen | chencheng3123@163.com | School of Computer Science, Shandong University |
| Qihong Jiao | qhjiao@mail.sdu.edu.cn | School of Computer Science, Shandong University |
| Xiaomei Zeng | xmzeng@hust.edu.cn | School of Life Science and Technology, Huazhong University of Science & Technology |
| Xuefeng Cui | xfcui@email.sdu.edu.cn | School of Computer Science, Shandong University |
| Kang Ning | ningkang@hust.edu.cn | School of Life Science and Technology, Huazhong University of Science & Technology |
Yuguo Zha, Cheng Chen, Qihong Jiao, Xiaomei Zeng, Xuefeng Cui, Kang Ning, Ontology-Aware Deep Learning Enables Novel Antibiotic Resistance Gene Discovery Towards Comprehensive Profiling of ARGs, bioRxiv 2021.07.30.454403 (2021) (download the PDF file)