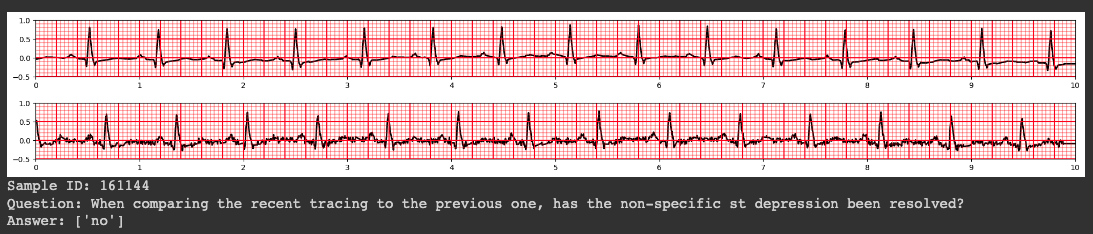
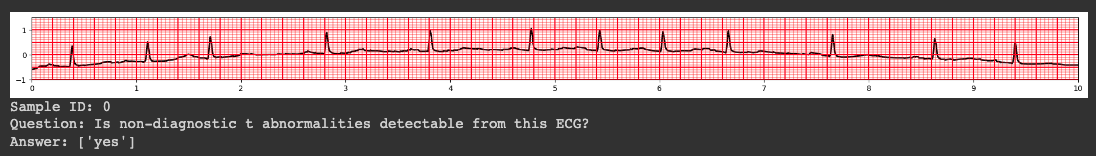
ECG-QA: A Comprehensive Question Answering Dataset Combined With Electrocardiogram
[News] ECG-QA is accepted at NeurIPS 2023 Datasets and Benchmarks Track!
This is the official repository for distributing ECG-QA dataset.
For more detailed information about the dataset, please refer to ECG-QA: A Comprehensive Question Answering Dataset Combined With Electrocardiogram.
Abstract
Question answering (QA) in the field of healthcare has received much attention due to significant advancements in natural language processing. However, existing healthcare QA datasets primarily focus on medical images, clinical notes, or structured electronic health record tables. This leaves the vast potential of combining electrocardiogram (ECG) data with these systems largely untapped. To address this gap, we present ECG-QA, the first QA dataset specifically designed for ECG analysis. The dataset comprises a total of 70 question templates that cover a wide range of clinically relevant ECG topics, each validated by an ECG expert to ensure their clinical utility. As a result, our dataset includes diverse ECG interpretation questions, including those that require a comparative analysis of two different ECGs. In addition, we have conducted numerous experiments to provide valuable insights for future research directions. We believe that ECG-QA will serve as a valuable resource for the development of intelligent QA systems capable of assisting clinicians in ECG interpretations.
Demonstrations
We provide Google Colab Notebook to facilitate the users to skim over the dataset.
Dataset Description
The dataset is organized as follows:
ecgqa
├── answers_for_each_template.csv
├── answers.csv
├── test_ecgs.tsv
├── train_ecgs.tsv
├── valid_ecgs.tsv
├── paraphrased
│ ├─ test
│ │ ├─ 00000.json
│ │ │ ...
│ │ └─ 80000.json
│ ├─ train
│ │ ├─ 00000.json
│ │ │ ...
│ │ └─ 260000.json
│ └─ valid
│ ├─ 00000.json
│ │ ...
│ └─ 60000.json
└── template
├─ test
│ ├─ 00000.json
│ │ ...
│ └─ 80000.json
├─ train
│ ├─ 00000.json
│ │ ...
│ └─ 260000.json
└─ valid
├─ 00000.json
│ ...
└─ 60000.json
- All the QA samples are stored in each .json file, where paraphrased directory indicates its questions are paraphrased and template directory indicates its questions are not paraphrased.
- Each json file contains a list of python dictionary where each key indicates:
- template_id: a number indicating its template ID.
- question_id: a number indicating its question ID. Different paraphrases from the same template question share the same question ID.
- sample_id: a number indicating each QA sample for each split.
- question_type: a string indicating its question type, which can be one of this list:
single-verifysingle-choosesingle-querycomparison_consecutive-verifycomparison_consecutive-querycomparison_irrelevant-verifycomparison_irrelevant-query
- attribute_type: a string indicating its attribute type, which can be one of this list:
scp_codenoisestage_of_infarctionextra_systoleheart_axisnumeric_feature
- question: a question string
- answer: a list of answer strings
- ecg_id: a list of ecg IDs of PTB-XL dataset. For comparison questions, it contains two corresponding ecg IDs. Otherwise, it has only one element.
- attribute: a list of strings indicating the relevant attributes with the question. For comparison questions, it is set to
Nonebecause the primary purpose of this information is aimed to the upperbound experiments where we need to convert each Single QA sample into appropriate ECG classification format.
answers_for_each_template.csvprovides the possible answer options for each template ID.answers.csvprovides the whole answer options over all the QA samples.*_ecgs.tsvindicate which ecg IDs of PTB-XL are included in each split. (index, ecg_id) pair is written in each row, split by\t.
Usage Notes
You can easily open and read data by the following codelines.
>>> import glob
>>> import json
>>> data = []
>>> for fname in sorted(glob.glob("ecgqa/paraphrased/train/*.json")):
... with open(fname, "r") as f:
... data.extend(json.load(f))
>>> len(data)
267539
>>> data[0]
{
"template_id": 1,
"question_id": 0,
"sample_id": 0,
"question_type": "single-verify",
"attribute_type": "scp_code",
"question": "Is there evidence of non-diagnostic t abnormalities on this ECG?",
"answer": ["yes"],
"ecg_id": [12662],
"attribute": ["non-diagnostic t abnormalities"]
}For efficient data processing, we don't provide the raw ECG values paired with each question. Instead, we paired the ECG IDs corresponded with the PTB-XL dataset. So, you may need to manually map each QA sample to its corresponding ECG sample using the paired ECG IDs, by mapping either of the actual ECG values or the ECG file path to the QA samples. Because there are approximately 400k QA samples over 16k PTB-XL ECGs totally, we recommend you to choose the latter approach which is mapping only the file path for each QA sample to save your disk space. We prepared a useful example python code to perform this, so please refer to the following commands when you try to process the ECG-QA dataset.
$ python mapping_samples.py ecgqa/paraphrased \
--ptbxl-data-dir $ptbxl_dir \
--dest $dest_dirYou can also process the template version of ECG-QA by passing ecgqa/template.
$ptbxl_dir should be set to the root directory of the PTB-XL dataset which contains records500/ directory. If you do not specify this argument, the script will automatically download the required PTB-XL data to the cache directory ($HOME/.cache/ecgqa/ptbxl).
Note that $dest_dir is set to output/ by default.
>>> import glob
>>> import json
>>>
>>> data = []
>>> for fname in sorted(glob.glob("output/train/*.json")):
... with open(fname, "r") as f:
... data.extend(json.load(f))
>>> data[0]
{
...,
"ecg_id": [12662],
"ecg_path": [
"$ptbxl_dir/records500/12000/12662_hr"
]
}Quick Start
We implemented all the experiment codes in the fairseq-signals repostiory.
For detailed implementations, please refer to here (See ECG-QA section).
Run QA Experiments
- Install fairseq-signals following the guidelines.
$ git clone https://github.com/Jwoo5/fairseq-signals
$ cd fairseq-signals
$ pip install --editable ./
$ python setup.py build_ext --inplace
$ pip install scipy wfdb pyarrow transformers- Pre-process ECG-QA dataset.
$ python fairseq_signals/data/ecg_text/preprocess/preprocess_ecgqa.py \
/path/to/ecgqa \
--ptbxl-data-dir /path/to/ptbxl \
--dest /path/to/output \
--apply_paraphraseNote that --ptbxl-data-dir should be set to the directory containing ptbxl ECG samples (i.e., records500/...).
- Run experiments.
$ fairseq-hydra-train task.data=/path/to/output/paraphrased \
model.num_labels=103 \
--config-dir examples/scratch/ecg_question_answering/$model_name \
--config-name $model_config_name$model_name: the name of the ECG-QA model (e.g., ecg_transformer)
$model_config_name: the name of the configuration file (e.g., base)
Run Upperbound Experiments
- Install fairseq-signals as the same with the above.
- Pre-process ECG-QA dataset to be compatible with upperbound experiments.
$ python fairseq_signals/data/ecg_text/preprocess/preprocess_ecgqa_for_classification.py \
/path/to/ecgqa \
--ptbxl-data-dir /path/to/ptbxl \
--dest /path/to/output- For W2V+CMSC+RLM:
$ fairseq-hydra-train task.data=/path/to/output \
model.num_labels=83 \
model.model_path=/path/to/checkpoint.pt \
--config-dir examples/w2v_cmsc/config/finetuning/ecg_transformer/grounding_classification \
--config-name base_totalNote that you need to pass the path to the pretrained model checkpoint through model.model_path.
To pre-train the model, refer to here.
- For Resnet + Attention model:
$ fairseq-hydra-train task.data=/path/to/output \
model.num_labels=83 \
--config-dir examples/scratch/ecg_classification/resnet \
--config-name nejedly2021_total- For SE-WRN model:
$ fairseq-hydra-train task.data=/path/to/output \
model.num_labels=83 \
--config-dir examples/scratch/ecg_classification/resnet \
--config-name se_wrn_totalRun LLM Modeling Experiments
- Install fairseq-signals.
- Pre-process ECG-QA dataset.
$ python fairseq_signals/data/ecg_text/preprocess/preprocess_ecgqa.py \
/path/to/ecgqa \
--ptbxl-data-dir /path/to/ptbxl \
--dest /path/to/output \
--apply_paraphraseNote that --ptbxl-data-dir should be set to the directory containing ptbxl ECG samples (i.e., records500/...).
- Sample 10% from the test set.
$ python llm_modeling/random_sample.py /path/to/output \
--subset test \It will output the sampled manifest file test_sampled.tsv in the /path/to/output/ directory.
- Run the experiments:
$ python llm_modeling/llm_modeling.py \
+openai_model=$model_name \
+openai_api_key=$api_key \
common_eval.path=/path/to/checkpoint.pt \
task.data=/path/to/output \
dataset.valid_subset=test_sampled \
--config-dir llm_modeling/config \
--config-name infer_llmNote that you need to pass the path to the upper bound model checkpoint through common_eval.path.
You also need to pass OpenAI's API key ($api_key) to load the OpenAI's GPT model.
$model_name should be set to one of [gpt-4, gpt-3.5-turbo, text-davinci-003].
Contact
If you have any questions or suggestions, feel free to contact me!
Citation
We wil update this section as soon as the paper is published.