This repository containts ongoing work on a low-level systems programming language. One piece of the puzzle is a verified compiler targeting RISC-V. The source language itself is also equipped with a simple program logic for proving correctness of the source programs. It is not ready yet, at least for most uses.
This project has similar goals as bedrock, but uses a different design. No code is shared between bedrock and bedrock2.
The source language is a "C-like" language called ExprImp. It is an imperative language with expressions. Currently, the only data type is word (32-bit or 64-bit), and the memory is a partial map from words to bytes. "Records" are supported as a notation for memory access with an offset.
The following features will be added soon:
- Register allocation (spilling if more local variables are needed than registers are available)
It is a design decision to not support the following features:
- Function pointers
- Recursive functions (we might add them later, but we always want to prove that we don't run out of stack space)
- Non-terminating programs (except for the top-level event loop)
You'll need Coq, version 8.11 or master.
In case you didn't clone with --recursive, use make clone_all to clone the git submodules.
Then simply run make or make -j or make -jN where N is the number of cores to use. This will invoke the Makefiles of each subproject in the correct order, and also pass the -j switch to the recursive make.
This repository is an umbrella repository integrating several sub-projects, allowing us to prove end-to-end theorems describing the I/O behavior of a pipelined processor executing a program written in the bedrock2 language, verified with our program logic, and compiled with our compiler.
There are the following sub-projects:
- coqutil: Coq library for tactics, basic definitions, sets, maps
- riscv-coq: RISC-V specification in Coq
- bedrock2/bedrock2: The bedrock2 language, a simple C-like programming language with a program logic and a few verified sample programs
- bedrock2/compiler: A very simple compiler from the bedrock2 language to bare metal, position independent RISC-V machine code
- kami: Provides a 4-stage pipelined RISC-V processor
- bedrock2/processor: Proves that the hardware-centric RISC-V specification of Kami matches the software-centric specification of riscv-coq
- bedrock2/end2end: Combines all the projects into an end-to-end theorem about a concrete program, the IoT lightbulb demo.
The Kami processor can be extracted to bluespec, which can be compiled to Verilog, and run on an FPGA.
The project dependency structure looks as follows (right depends on left):
bedrock2
/ \
coqutil compiler
\ / \
riscv-coq end2end
\ /
processor
/
kami
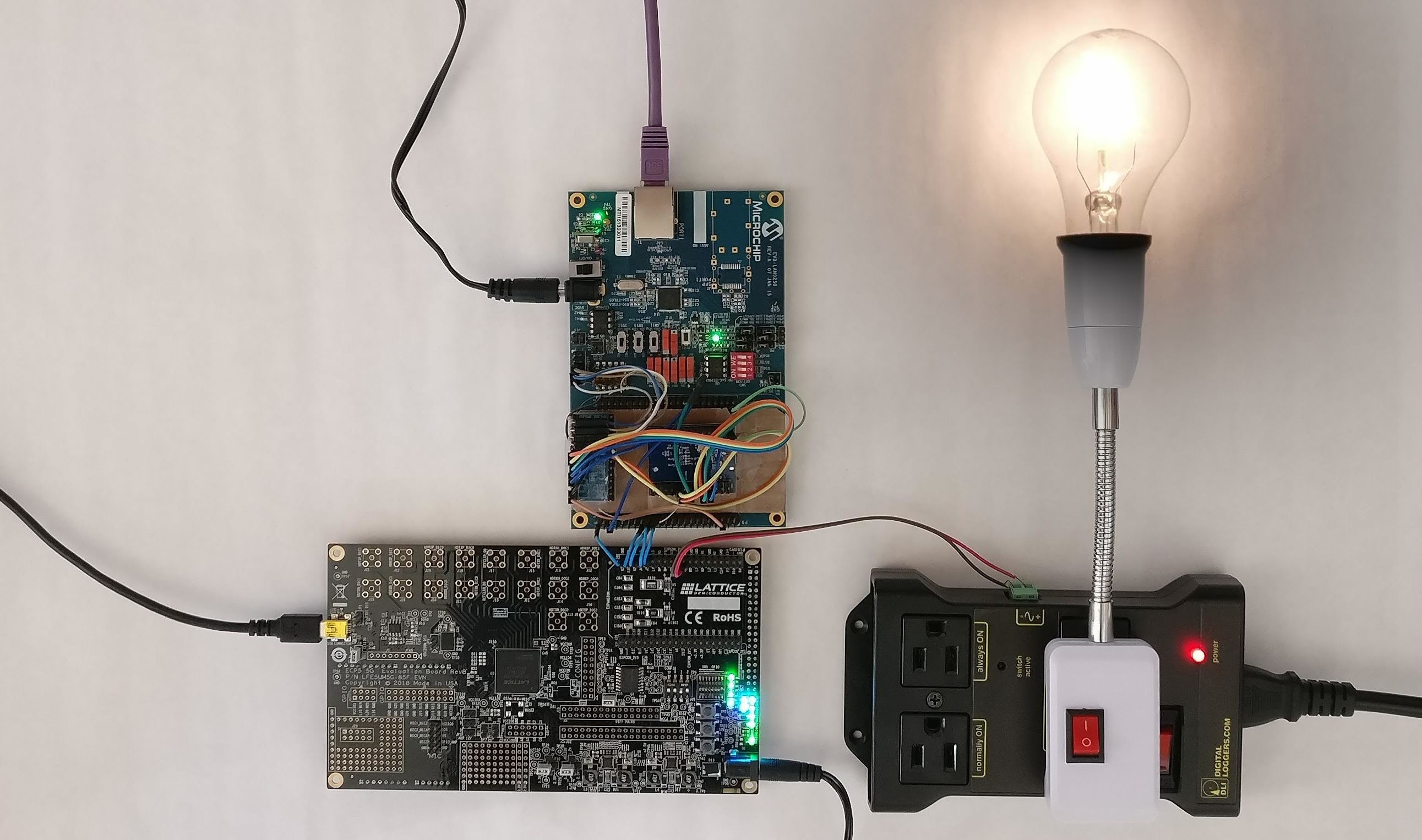
In the above picture, the FPGA at the bottom left is running the Kami processor, which executes a program proven correct using the bedrock2 program logic and compiled to bytes using the bedrock2 compiler. Through a set of blue wires (using SPI), the FPGA is connected to an ethernet card (which we do not verify), and through a red & black wire, it is connected to a power relay which can turn on and off a lightbulb.
Here are the names of the languages and the compiler phases between them:
Syntax.cmd
↓ FlattenExpr
FlatImp.stmt string
↓ RegRename
FlatImp.stmt Z
↓ FlatToRiscv
list Instruction
↓ instrencode
list byte
The compiler provides two interfaces:
Input:
- list of bedrock2 functions
- name of "main"
Output:
- Compiled functions as list of instructions
- Relative position of main function
Correctness theorem: compiler.PipelineWithRename.compiler_correct:
- If all high-level executions satisfy
post, running the compiled program from a "good" initial RISC-V machine leads only to machines whose memory and I/O trace satisfypost.
Input:
- list of bedrock2 functions, name of "init" and "loop". This will result in the following program being compiled:
init();
while (true) {
loop();
}
Output:
- list of instructions to initialize the stack pointer, call
init(), callloop(), jump back to callingloop()followed by the compiled functions - Meant to start execution at beginning of this list
Correctness theorem: compiler.CompilerInvariant.compiler_invariant_proofs:
- There is an invariant
invon RISC-V machines, and- Here's how to establish
inv - Running the machine for one step preserves
inv invimplies that the I/O trace of the machine is good
- Here's how to establish
- We call this the "establish/preserve/use pattern"