This repository containts the code associated with the paper "D-VDAMP: Denoising-based Approximate Message Passing for Compressive MRI," ICASSP, 2021 by Christopher A. Metzler and Gordon Wetzstein and the paper "Suremap: Predicting Uncertainty in Cnn-Based Image Reconstructions Using Stein’s Unbiased Risk Estimate," ICASSP, 2021 by Ruangrawee Kitichotkul, Christopher A. Metzler, Frank Ong, and Gordon Wetzstein.
Note that this code is slightly different from the implementation used to generate results in the papers.
The code has been tested for Python version 3.8.5 with the following packages installed: numpy, matplotlib, Pillow, PyWavelets, torch, torchvision, tensorboard, h5py, statsmodel, bm3d, and torch_dct.
To make sure that the versions of the packages match those we tested the code with, we recommend creating a new virtual environment and installing packages using conda with the following command.
conda env create -f environment.ymlPlug and play (P&P) algorithms iteratively apply highly optimized image denoisers to impose priors and solve computational image reconstruction problems, to great effect. However, in general the "effective noise", that is the difference between the true signal and the intermediate solution, within the iterations of P&P algorithms is neither Gaussian nor white. This fact makes existing denoising algorithms suboptimal. In this work, we propose a CNN architecture for removing colored Gaussian noise and combine it with the recently proposed VDAMP algorithm, whose effective noise follows a predictable colored Gaussian distribution. We apply the resulting denoising-based VDAMP (D-VDAMP) algorithm to variable density sampled compressive MRI where it substantially outperforms existing techniques.
The magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) measurement with variable-density sampling pattern can be modeled as
y = MΩ (F x0 + ε),
where x0 ∈ Cn is the vectorized ground truth image, y ∈ Cn is the measurement, F ∈ Cn×n is a 2-D discrete Fourier transform matrix, MΩ ∈ Rn×n is a variable-density sampling mask, and ε is a complex circular Gaussian noise. Given y, the D-VDAMP algorithm reconstructs the image x̂ estimating x0.
D-VDAMP requires the following ingredients.
- Measurement y
- Sampling mask matrix MΩ
- The probability map matrix P from which we generated MΩ
- A wavelet transform Ψ
- Image domain denoiser D(x; γ τ)
- Regularization parameter γ
- Number of iterations Kit
The paper also proposed a neural network architecture of the image domain denoiser designed for D-VDAMP which is adapted from DnCNN [ZZCMZ17]. The model is implemented in algorithm/denoiser.py.
The code associated to D-VDAMP is in the following files.
algorithmdenoiser.pycontains the model definition of the denoiserColoredDnCNNproposed in the paper. This is the same model as intrain/model.py, but with a slight modification to simplify usage. The weights trained fromtraincan be loaded onto this model definition directly since the underlying architecture is the same.dvdamp.pycontains the implementation of D-VDAMP, a function for generating variable-density sampling mask, and wrappers of denoisers for using with D-VDAMP.simulation.pycontainsdvdamp_simfunction which simulates a MRI measurement with variable-density sampling and then apply D-VDAMP.
experimentdvdamp_exp.pycontains a demo of D-VDAMP. The code simulates MRI measurement, apply D-VDAMP, and then generate plots for the results, including PSNR at each iteration, predicted and real error at each iteration, effective noise in the wavelet bands, and QQ plot of the effective noise.- Note that if the
savemodeargument is notraw-only, the demo will also generate SURE maps of the D-VDAMP reconstruction.
trainmain.pyis the main code for training the denoiser. Run this file to preprocess the data and train the model.model.pycontains the model definition of the denoiser proposed in the paper.preprocess.pycontains functions for preprocessing raw images into the dataset for training.solve.pycontains functions for training and evaluating the model.train_util.pycontains utility functions related to training.
utilgeneral.pycontains general utility functions.plot.pycontains plotting utility functions.transform.pycontains functions related to wavelet transform and Fourier transform.
modelcontains pre-trained model weights ofColoredDnCNNtrained for different noise levels. All models were trained with Haar wavelet and wavelet decomposition level of 4.cdncnn_00_20_real.pthwas trained with noise standard deviation in each band uniformly sampled from [0, 20 / 255] .cdncnn_20_50_real.pthwas trained with noise standard deviation in each band uniformly sampled from [20 / 255, 50 / 255].cdncnn_50_120_real.pthwas trained with noise standard deviation in each band uniformly sampled from [50 / 255, 120 / 255].cdncnn_120_500_real.pthwas trained with noise standard deviation in each band uniformly sampled from [120 / 255, 500 / 255].
Run D-VDAMP demo with the following commands which calls experiment/dvdamp_exp.py.
bash bash/dvdamp_exp.shWe provide bash/preprocess.sh and bash/train.sh as sample bash scripts to train the ColoredDnCNN denoiser. These scripts call train/main.py to perform preprocessing and training respectively. Note that the datadir argument expects the path to a directory organized as follow.
- YOUR_DATA_DIRECTORY
- train
- image 1
- image 2
- ...
- val
- image 1
- image 2
- ...
- test
- image 1
- image 2
- ...
Note that the train set, validation set, and test set directories must be named as train, val, and test respectively. However, the images can have any names. The code expects .jpg images. Please modify the generate_datasets function in train/preprocess to read files of other extensions. Preprocessing will generate .h5 files in the data directory. When training, the train/main.py code expects datadir as path to the directory containing these .h5 files, i.e. the same path you use for preprocessing.
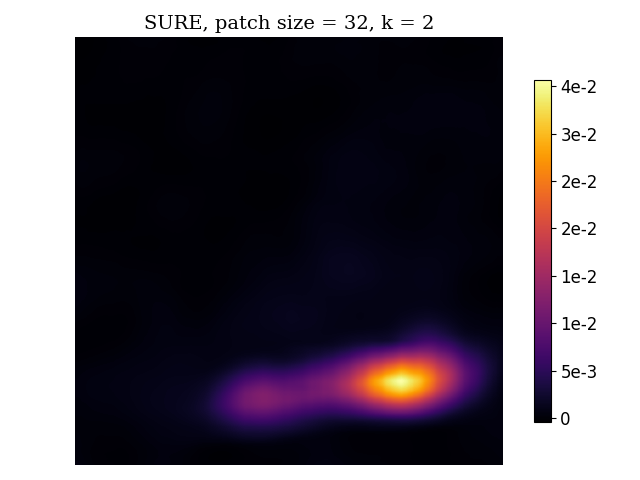
Convolutional neural networks (CNN) have emerged as a powerful tool for solving computational imaging reconstruction problems. However, CNNs are generally difficult-to-understand black-boxes. Accordingly, it is challenging to know when they will work and, more importantly, when they will fail. This limitation is a major barrier to their use in safety-critical applications like medical imaging: Is that blob in the reconstruction an artifact or a tumor? In this work we use Stein’s unbiased risk estimate (SURE) to develop per-pixel confidence intervals, in the form of heatmaps, for compressive sensing reconstruction using the approximate message passing (AMP) framework with CNN-based denoisers. These heatmaps tell end-users how much to trust an image formed by a CNN, which could greatly improve the utility of CNNs in various computational imaging applications.
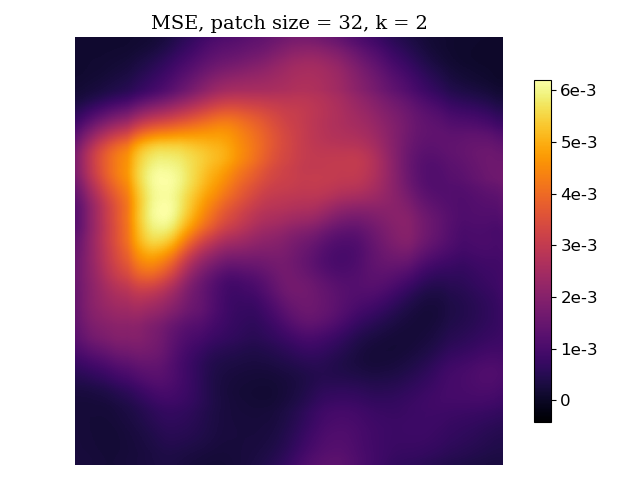
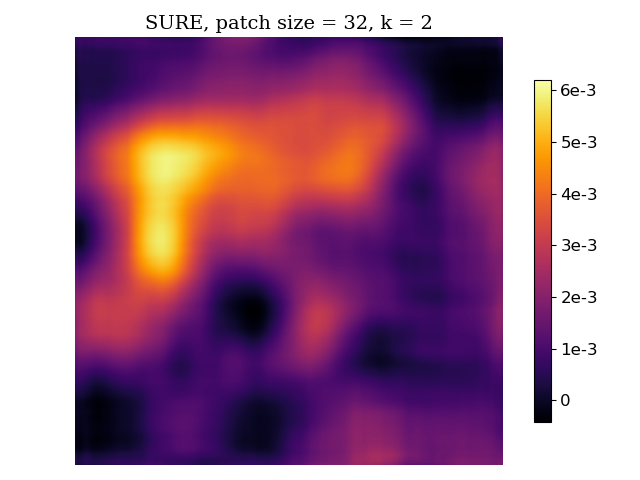
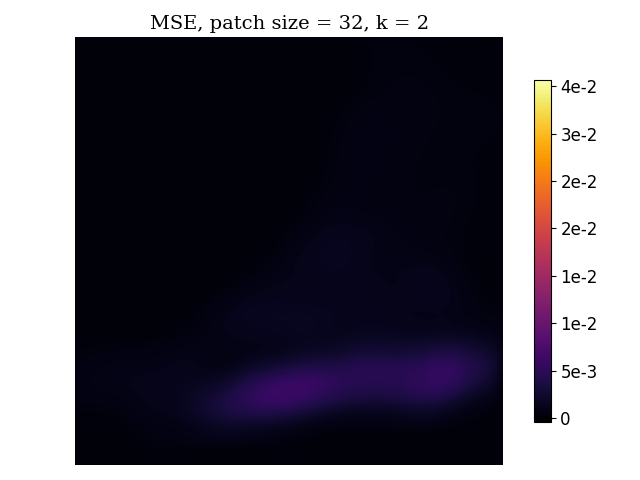
SUREMap calculates an unbiased risk estimate of the mean squared error (MSE) and then patch together square patches of estimates to form a heatmap. There are two variants of SURE heatmaps -- for D-AMP state evolution (additive white Gaussian noise) and D-VDAMP state evolution (colored noise where each wavelet subband has AWGN).
Each iteration of AMP and D-AMP [MMB16] is an AWGN denoising problem.
y = x + η; η ~ N(0, σ2 I)
Let f(y) = x̂ be the denoising result. Then, the MSE is
MSE = 1⁄n ||f(y) - x||2.
The Stein's unbiased risk estimate (SURE) is
S(y, f(y)) = 1⁄n ||f(y) - y||2 + 2 σ2⁄n divy (f(y)) - σ2,
which estimates MSE because E[MSE] = E[S(y, f(y))].
Each iteration of VDAMP [MHMT20] and D-VDAMP is the following denoising problem.
r = x + η; η ~ CN(0, ΨTdiag(τ)Ψ)
Let f(r) = x̂ be the denoising result. Then, the MSE is
MSE = 1⁄n ||f(r) - x||2.
In this case, a SURE-like unbiased risk estimate is
S(r, f(r)) = 1⁄n ||f(r) - r||2 + 2⁄n divu(f(r)) - ∑i τi,
which estimates MSE because E[MSE] = E[S(r, f(r))].
The code associated to D-VDAMP is in the following files.
algorithmcsalgo.pycontains D-AMP algorithm.denoiser.pycontains many denoiser wrappers for using with D-AMP.dvdamp.pycontains D-VDAMP algorithm.heatmap.pycontains SUREMap generation code.simulation.py: contains functions to simulate AWGN denoising, D-AMP reconstruction, VDAMP state evolution, and D-VDAMP reconstruction.
experimentdvdamp_exp.pycontains a demo of D-VDAMP and SUREMap for D-VDAMP.sure_exp.pycontains a demo of AWGN denoising and D-AMP reconstruction and SUREMap.vdamp_se_exp.pycontains a simulation of VDAMP state evolution by adding AWGN to each wavelet subband in the image, perform denoising, and then generate SURE map.
utilcs.pycontains functions for compressive sensing simulation.general.pycontains general utility functions.patch.pycontains functions to perform patching for SURE map generation.plot.pycontains plotting utility functions.transform.pycontains functions related to wavelet transform and Fourier transform.
modelcontains pre-train weights of 20-layer DnCNN models trained for specific noise level and pre-train weights ofColoredDnCNN. A DnCNN weight file namedb-x-y.pthmeans that it was trained with Gaussian noise standard deviation sampled from [x / 255, y / 255].
Run AWGN denoising simulation and then perform SUREMap:
bash bash/den_exp.shRun compressive sensing simulation and reconstruction with D-AMP and then perform SUREMap:
bash bash/cs_exp.shRun a VDAMP state evolution denoising simulation and then perform SUREMap:
bash bash/vdamp_se_exp.shRun a MRI measurement simulation with variable-density sampling and reconstruction with D-VDAMP and then perform SUREMap:
bash bash/dvdamp_exp.shHere is an example of results from compressive sensing simulation and reconstruction with D-AMP. From left to right, the images are the original image, the reconstructed image, the per-pixel squared error, the patch-averaged MSE, and the SURE map.
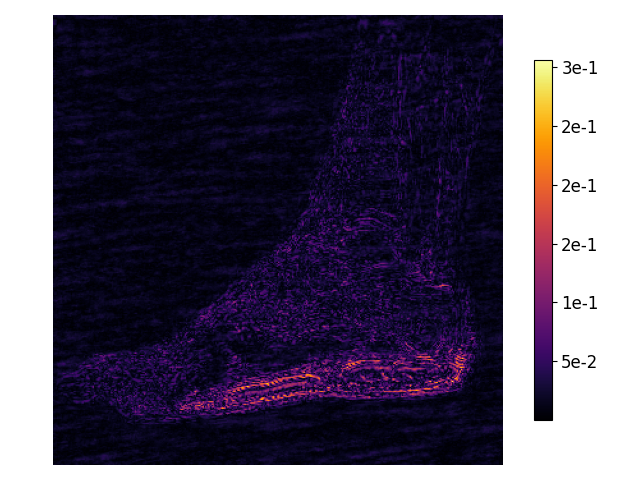
Here is an example of results from MRI measurement simulation with variable-density sampling and reconstruction with D-VDAMP. From left to right, the images are the original image, the reconstructed image, the per-pixel squared error, the patch-averaged MSE, and the SURE map.
We include some images in the data directory.
naturalcontains some natural images.mricontains some MR images. Other than Shepp-Logan, the MR images are thumbnails from mridata.org.
@INPROCEEDINGS{9414306,
author={Kitichotkul, Ruangrawee and Metzler, Christopher A. and Ong, Frank and Wetzstein, Gordon},
booktitle={ICASSP 2021 - 2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP)},
title={Suremap: Predicting Uncertainty in Cnn-Based Image Reconstructions Using Stein’s Unbiased Risk Estimate},
year={2021},
volume={},
number={},
pages={1385-1389},
doi={10.1109/ICASSP39728.2021.9414306}}
@INPROCEEDINGS{9414708,
author={Metzler, Christopher A. and Wetzstein, Gordon},
booktitle={ICASSP 2021 - 2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP)},
title={D-VDAMP: Denoising-Based Approximate Message Passing for Compressive MRI},
year={2021},
volume={},
number={},
pages={1410-1414},
doi={10.1109/ICASSP39728.2021.9414708}}
Parts of the code are based on code in the works listed below.
- D-VDAMP algorithm code and the soft-thresholding denoiser are based on the MATLAB code of VDAMP [MHMT20].
- The variable-density mask generation code is based on
genPDFfunction from VDAMP's MATLAB code [MHMT20], which is in turn based on [LDP07].
[MHMT20] Charles Millard, Aaron T Hess, Boris Mailhe, and Jared Tanner, “Approximate message passing with a colored aliasing model for variable density fourier sampled images,” arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.02701, 2020.
[MMB16] Christopher A Metzler, Arian Maleki, and Richard G Baraniuk, “From denoising to compressed sensing,” IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, vol. 62, no. 9, pp. 5117–5144, 2016.
[DMM09] D. L. Donoho, A. Maleki, and A. Montanari, “Message passing algorithms for compressed sensing,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., vol. 106, no. 45, pp. 18914–18919, 2009.
[ZZCMZ17] Kai Zhang, Wangmeng Zuo, Yunjin Chen, Deyu Meng, and Lei Zhang, “Beyond a gaussian denoiser: Residual learning of deep cnn for image denoising,” IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, vol. 26, no. 7, pp. 3142–3155, 2017.
[LDP07] Michael Lustig, David Donoho, and John M Pauly, “Sparse mri: The application of compressed sensing for rapid mr imaging,” Magnetic Resonance in Medicine: An Official Journal of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, vol. 58, no. 6, pp. 1182–1195, 2007.
If you have questions, please contact Chris Metzler (metzler@umd.edu) or Kao Kitichotkul (rk22@stanford.edu).