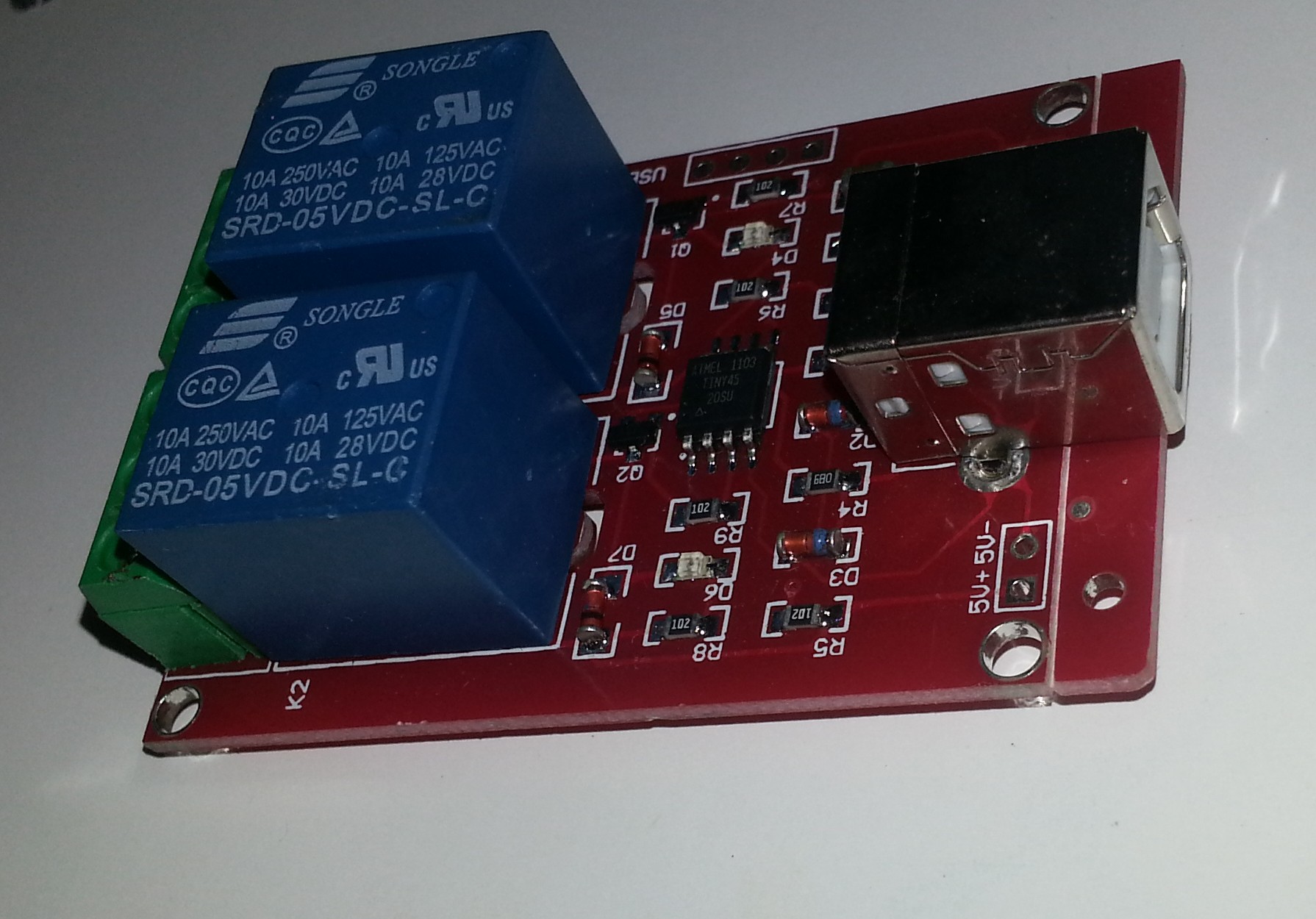
USB Relay driver for linux
A cheap USB relay available from Ebay with 1,2,4 or 8 relay output. The double throw relay ratings are 10A 250VAC each.
The USB device is HID compatible and comes with Windows control software. This code can control the relay vi HIDAPI which is a cross platform library. This code was tested under linux both on x86 and Raspberry Pi ARM. The program is command line only as it is likely to be used by shell scripts.
The output of lsusb for the device is:
Bus 001 Device 003: ID 16c0:05df Van Ooijen Technische Informatica HID device except mice, keyboards, and joysticks
# lsusb -v -d 16c0:05df
Bus 001 Device 003: ID 16c0:05df Van Ooijen Technische Informatica HID device except mice, keyboards, and joysticks
Device Descriptor:
bLength 18
bDescriptorType 1
bcdUSB 1.10
bDeviceClass 0 (Defined at Interface level)
bDeviceSubClass 0
bDeviceProtocol 0
bMaxPacketSize0 8
idVendor 0x16c0 Van Ooijen Technische Informatica
idProduct 0x05df HID device except mice, keyboards, and joysticks
bcdDevice 1.00
iManufacturer 1 www.dcttech.com
iProduct 2 USBRelay2
iSerial 0
bNumConfigurations 1
Configuration Descriptor:
bLength 9
bDescriptorType 2
wTotalLength 34
bNumInterfaces 1
bConfigurationValue 1
iConfiguration 0
bmAttributes 0x80
(Bus Powered)
MaxPower 20mA
Interface Descriptor:
bLength 9
bDescriptorType 4
bInterfaceNumber 0
bAlternateSetting 0
bNumEndpoints 1
bInterfaceClass 3 Human Interface Device
bInterfaceSubClass 0 No Subclass
bInterfaceProtocol 0 None
iInterface 0
HID Device Descriptor:
bLength 9
bDescriptorType 33
bcdHID 1.01
bCountryCode 0 Not supported
bNumDescriptors 1
bDescriptorType 34 Report
wDescriptorLength 22
Report Descriptors:
** UNAVAILABLE **
Endpoint Descriptor:
bLength 7
bDescriptorType 5
bEndpointAddress 0x81 EP 1 IN
bmAttributes 3
Transfer Type Interrupt
Synch Type None
Usage Type Data
wMaxPacketSize 0x0008 1x 8 bytes
bInterval 20
Device Status: 0x0000
(Bus Powered)
HIDAPI
http://www.signal11.us/oss/hidapi
HIDAPI is a fairly recent addition to linux and is available as a package for Fedora 20 but not for Pidora (F18). The package was built for Pidora (Fedora 18) using the F20 hidapi source package.
Installing Debian Packages: This code is a maintained package in Debian (and Raspian). Use normal apt-get commands:
$ sudo apt-get install usbrelay
Other Linux platforms will need to build the source, see below
Protocol: The relay modules does not set the USB serial number but has a unique serial when the HID device is queried, the current state of the relays is also sent with the serial. The HID serial is matched and the ON/OFF command is sent to the chosen relay.
Building the code: Assuming the hidapi and hidapi-devel packages have been installed. Note that there are two options for the hidapi library: hidapi-hidraw or hidapi-libusb. Different distributions have better results with one or the other. YMMV.
### hidapi-hidraw - This is the default if no option is given
# make HIDAPI=hidraw
### hidapi-libusb
# make HIDAPI=libusb
You can also build using Docker. Assuming you have Docker installed, execute the build script:
$ ./build.sh
The usbrelay binary and libusbrelay.so library will be built in the root directory of the repo.
Usage: The code needs to access the device. This can be achieved either by running the program with root privileges (so sudo is your friend) or by putting
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTR{idVendor}=="16c0",ATTR{idProduct}=="05df", MODE="0666"
KERNEL=="hidraw*", ATTRS{busnum}=="1", ATTRS{idVendor}=="16c0", ATTRS{idProduct}=="05df", MODE="0666"
to /etc/udev/rules.d/50-dct-tech-usb-relay-2.rules.
Running the program will display each module that matches device 16c0:05df the debug information is sent to stderr while the state is sent to stdout for use in scripts. The only limit to the number of these relays that can be plugged in and operated at once is the number of USB ports.
$ sudo ./usbrelay
Device Found
type: 16c0 05df
path: /dev/hidraw1
serial_number:
Manufacturer: www.dcttech.com
Product: USBRelay2
Release: 100
Interface: 0
PSUIS_1=1
PSUIS_2=0
To get the relay state
$ sudo ./usbrelay 2>/dev/null
PSUIS_1=1
PSUIS_2=0
To use the state in a script:
$ eval $(sudo ./usbrelay 2>/dev/null)
$ echo $PSUIS_2
0
To set the relay state of 1 or more modules at once:
$ sudo ./usbrelay PSUIS_2=0
$ sudo ./usbrelay PSUIS_2=1 PSUIS_1=0
$ sudo ./usbrelay PSUIS_2=0 PSUIS_1=1 0U70M_1=0 0U70M_2=1
If for some reason the USB id changes, (ie other than 16c0:05df) set the USBID environment variable to the correct ID
$sudo USBID=16c0:05df ./usbrelay
Change the serial permanently
Use the fictitious relay 0 to set the serial permanently. If you have duplicate serials, make sure only one is plugged in when you change it. Maximum of 5 character serial. It is probably sensible to change one module at a time to avoid serial collisions.
$ sudo ./usbrelay
Device Found
type: 16c0 05df
path: /dev/hidraw4
serial_number:
Manufacturer: www.dcttech.com
Product: USBRelay2
Release: 100
Interface: 0
Number of Relays = 2
ZXCV_1=0
ZXCV_2=0
$ sudo ./usbrelay ZXCV_0=ZAQ12
Orig: ZXCV, Serial: ZXCV, Relay: 0 State: 0
Device Found
type: 16c0 05df
path: /dev/hidraw4
serial_number:
Manufacturer: www.dcttech.com
Product: USBRelay2
Release: 100
Interface: 0
Number of Relays = 2
Serial: ZXCV, Relay: 0 State: 0
1 HID Serial: ZXCV
Serial: ZXCV, Relay: 0 State: 0 --- Not Found
$ sudo ./usbrelay
Device Found
type: 16c0 05df
path: /dev/hidraw4
serial_number:
Manufacturer: www.dcttech.com
Product: USBRelay2
Release: 100
Interface: 0
Number of Relays = 2
ZAQ12_1=0
ZAQ12_2=0
This also optionally includes a python extension. In order to build the python extension, you must have the Python 3 development libraries installed.
Debian:
##Install Python3 dev pacakage
# sudo apt install libpython3.5-dev
Fedora:
##Install Python3 dev pacakage
# yum install python3-devel
With the dependency installed, the library can be built and installed with:
##Build libusbrelay_py.so
$ make python
##Install to global python
$ sudo make install_py
Once installed, the library can be used by any python script, assuming it is running as a user with suitable permissions per the changes to udev above.
The following is a test script included as test.py, showing how to use the library:
import usbrelay_py
import time
count = usbrelay_py.board_count()
print("Count: ",count)
boards = usbrelay_py.board_details()
print("Boards: ",boards)
if(len(boards)>0):
board = boards[0]
print("Board: ",board)
relay = 1
while(relay < board[1]+1):
result = usbrelay_py.board_control(board[0],relay,1)
print("Result: ",result)
relay += 1
relay = 1
while(relay < board[1]+1):
result = usbrelay_py.board_control(board[0],relay,0)
print("Result: ",result)
relay += 1
Once the library is installed, you can run the test script in python as follows:
$ python3 test.py
It will turn on and then off every relay attached to every board on your system.
Enjoy