FriendlyPatterns is a repo that uses common design patterns in a simple way to explain how each one works.
The app will take you on a tour where design patterns reside.
Each activity will have its own design pattern, except MainActivity which works as the main gate.
I read a few articles that really helped me understand the patterns better, so I will include everything that has been useful as well.
First, let’s talk about what the MVVM pattern is. The MVVM pattern is a pattern derived from the MVP pattern defined by Martin Fowler in the 1990s. The MVVM (Model-View-ViewModel) pattern helps to completely separate the business and presentation logic from the UI, and the business logic and UI can be clearly separated for easier testing and easier maintenance. Let’s take a look at View, ViewModel and Model
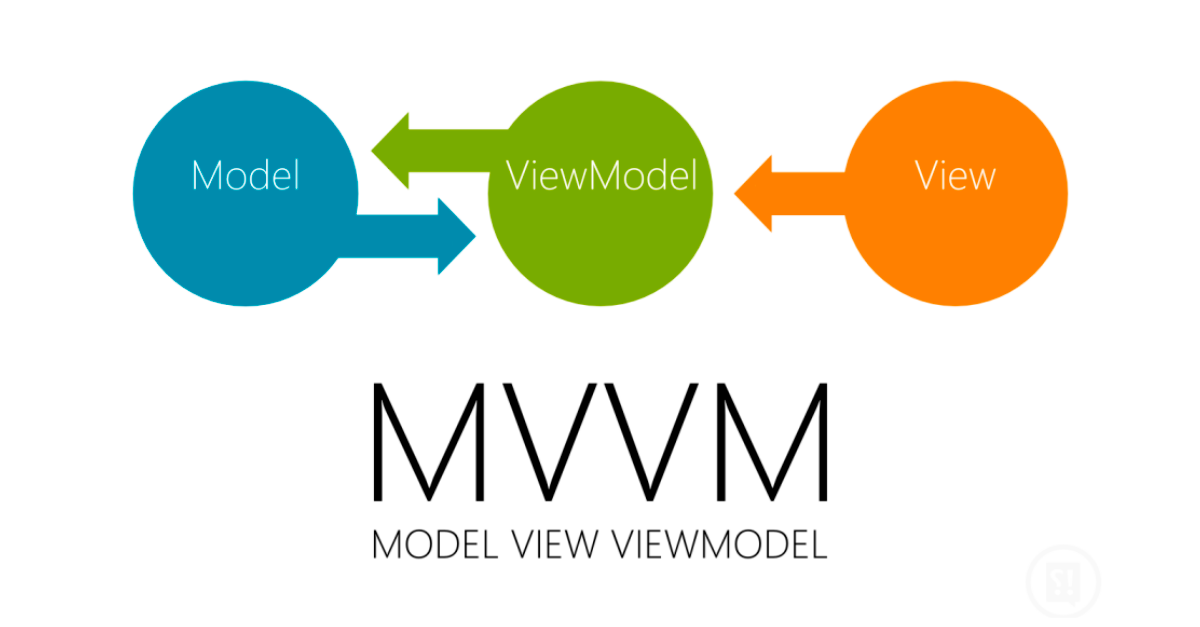
View is responsible for the layout structure displayed on the screen. You can also execute UI logic.
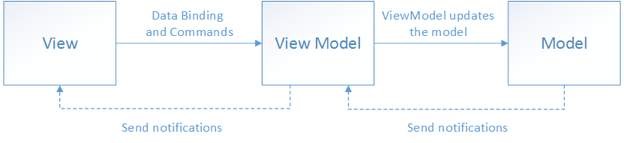
The ViewModel implements the data and commands connected to the View to notify the View of state changes via change notification events. Then, the View that receives the state change notification determines whether to apply the change.
Model is a non-visual class that has the data to use. Examples include DTO (Data Transfer Objects), POJO (Plain Old Java Objects) and entity objects. It is commonly used service or repository that need to access or cache data.
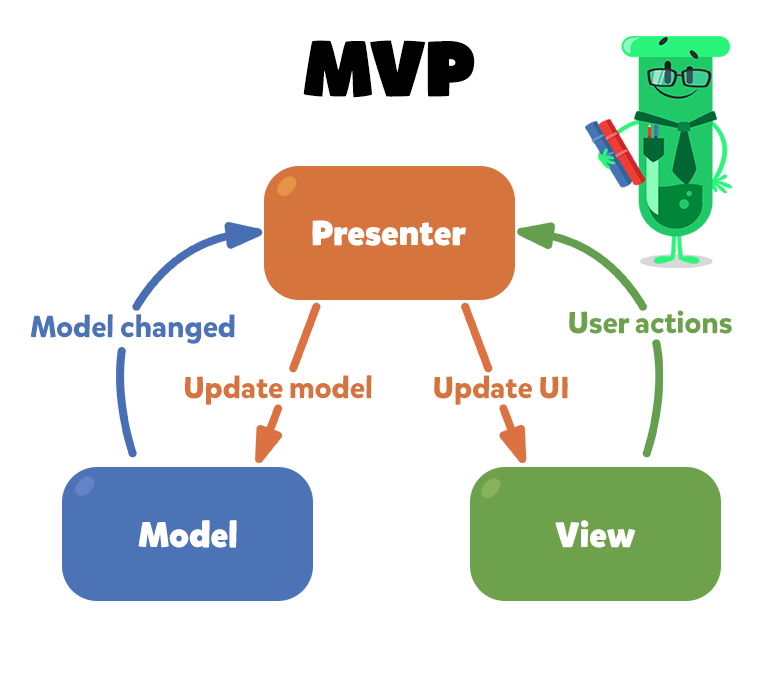
MVP (Model View Presenter) pattern is a derivative from the well known MVC (Model View Controller), and one of the most popular patterns to organize the presentation layer in Android Applications.
The MVP pattern allows separating the presentation layer from the logic so that everything about how the UI works is agnostic from how we represent it on screen. Ideally, the MVP pattern would achieve that the same logic might have completely different and interchangeable views.
In an application with a good layered architecture, this model would only be the gateway to the domain layer or business logic. See it as the provider of the data we want to display in the view. Model’s responsibilities include using APIs, caching data, managing databases and so on.
The View, usually implemented by an Activity, will contain a reference to the presenter. The only thing that the view will do is to call a method from the Presenter every time there is an interface action.
The Presenter is responsible to act as the middle man between View and Model. It retrieves data from the Model and returns it formatted to the View. But unlike the typical MVC, it also decides what happens when you interact with the View.
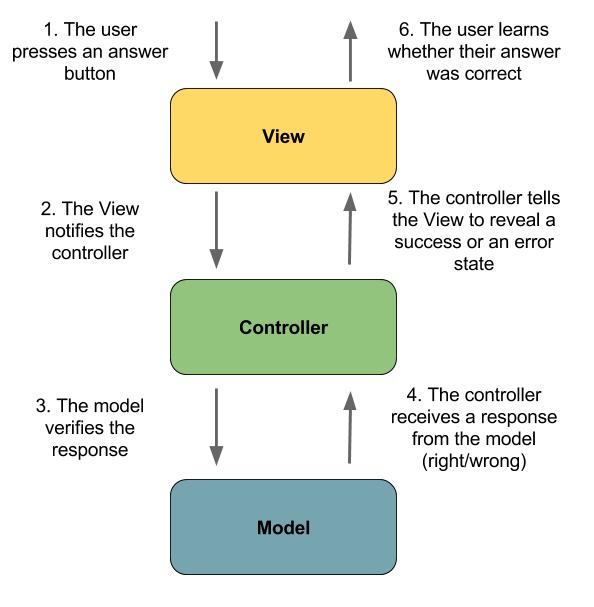
MVC is known as an architectural pattern, which embodies three parts Model, View and Controller, or to be more exact it divides the application into three logical parts: the model part, the view and the controller. It was used for desktop graphical user interfaces but nowadays is used in designing mobile apps and web apps.
MVC is an architectural pattern which means it rules the whole architecture of the applications. Even though often it is known as design pattern but we may be wrong if we refer it only as a design pattern because design patterns are used to solve a specific technical problem, whereas architecture pattern is used for solving architectural problems, so it affects the entire architecture of our application. It has three main components:
-Model
-View
-Controller
and each of them has specific responsibilities
It is known as the lowest level which means it is responsible for maintaining data. Handle data logically so it basically deals with data. The model is actually connected to the database so anything you do with data. Adding or retrieving data is done in the model component. It responds to the controller requests because the controller never talks to the database by itself. The model talks to the database back and forth and then it gives the needed data to the controller. Note: the model never communicated with the view directly.
Data representation is done by the view component. It actually generates UI or user interface for the user.
Views are created by the data which is collected by the model component but these data aren’t taken directly but through the controller, so the view only speaks to the controller.
It’s known as the main man because the controller is the component that enables the interconnection between the views and the model so it acts as an intermediary. The controller doesn’t have to worry about handling data logic, it just tells the model what to do.
After receiving data from the model it processes it and then it takes all that information it sends it to the view and explains how to represent to the user. Note: Views and models can not talk directly.
I hope you enjoyed reading and hopefully the code wasn't hard to read. For sure everything can be improved and refactored to a better shape of it.
Everything you need to know about MVC architecture
MVC (Model View Controller) Architecture Pattern in Android (GeeksForGeeks)
Model View Presenter(MVP) in Android
Create Android app with MVVM pattern
Databinding in Android using Kotlin
Difference Between MVP vs MVVM
MVP (Model View Presenter) Architecture Pattern (GeeksForGeeks)
Difference Between MVC, MVP and MVVM Architecture Pattern in Android
Implementing MVVM architecture in Android using Kotlin
How to Use Data Binding Library with Kotlin
LiveData Clean Code using MVVM and Android Architecture Components