This repository contains a modified version of Elephant python package where 9 new kernel functions are developed onto, and 2 tutorials to explain the properties of latent trajectories extracted by Gaussian Process Factor Analysis(GPFA) with new kernels. Original version of Elephant at link.
To install package, go to elephant_gpfa_extker directory and execute pip install -e. in command line.
Added Exponential, Triangular, Rational Quadratic, Matern, Spectral Mixture kernels and 3 Production of kernels: Triangular times Rational Quadratic, Exponential times Rational Quadratic, Exponential times Triangular kernels.
Parameters of new kernels are currently optimized by 2 gradient-free method: Scipy.optimize.minimize Powell mehthod and a built-in Bayeisian Optimization script.
Kernel names are in short, choose kernel in '{'rbf', 'tri', 'exp', 'rq', 'matern', 'sm','tri_times_rq', 'exp_times_rq', 'exp_times_tri'}' at parameter field covTpe.
Specify optimization method at parameter bo. Default is False to use Powell method. Input a positive numbers will use Bayesian Optimization instead, the number will be iterations of Bayesian Optimisation.
The following example initialize GPFA with Spectral Mixture kernel, and optimize its kernel parameter by Bayesian Optimization in 50 iterations. Time binned in 20ms, extract trajectory to 3 dimensional space.
gpfa_3dim_sm = Elephant.gpfa.GPFA(bin_size=20*pq.ms, x_dim=3,covType='sm',bo=50)
gpfa_3dim_sm.fit(spiketrains)In order to unify the expressions of kernels, equations of each kernel used in the Elephant GPFA python package are listed here:
The 9 kernels are benchmarked in neuroscience dataset collected from Salamander Retina Ganglion cells in Spikes directory
data available at link. The benchmark results are at cloud storage link,
please refer to README.md file in directory Experiments Data for detail information of this benchmark result.
In terms of data log-likelihood returned by GPFA model,
Spectral Mixture kernel with 2 spectral mixtures has a significant improvement over than originally adopted rbf kernel.
GPFA_visualisation_addons contains plot_trajectories_vs_time, which is developed in addition to viziphant.gpfa.plot_trajectoires.
This function emphasize temporal order between neural states by adopting gradient color in plotting single trail latent trajectories.
The function invokes GPFA internally, parameter fields are nearly the same with viziphant.gpfa.plot_trajectoires. Example to use this function to extract latent trajectories to 3D.
plot_trajectories_vs_time(spikeTrains,GPFA_kargs = {'x_dim':3, 'bin_size': 20 *pq.ms, 'covType' : 'sm', 'bo': False}, dimensions=[0, 1, 2])Example of plotted latent trajectory of the first experiment of NaturalImages1.mat dataset.
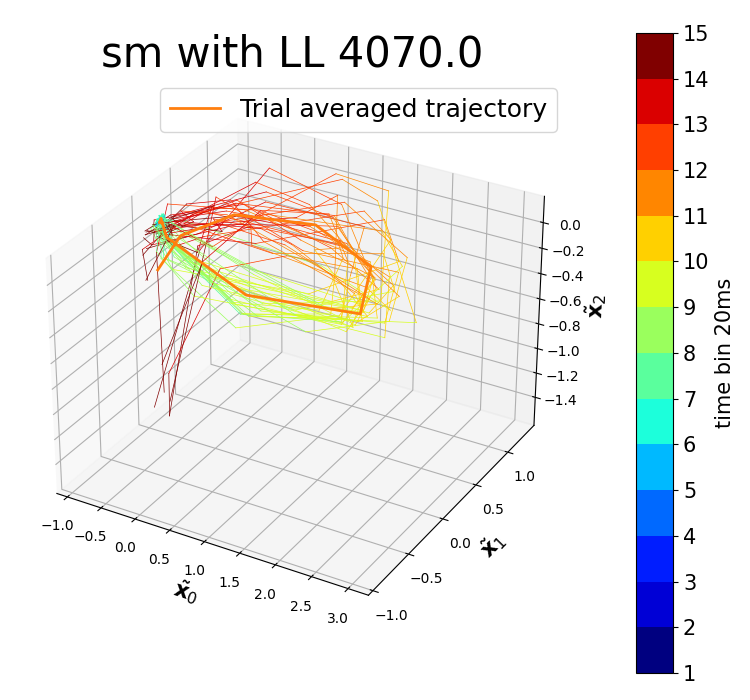
kernels_inGPFA_tutorial.ipynb has a detailed practice to perform this modified GPFA on the first
experiment of NaturalImages1.mat dataset. It compares the difference of extracted trajectories between rbf and spectral
mixture kernel in part 1. Then it demonstrates the new plotting function in part 2, and shows the way to achieve multi-threading
when running on a large dataset in part 3.
analyze_kernels_in_synthetic_data.ipynb compares the smoothness property of the 9 kernels on synthetic data with
pre-defined harmonic oscillator latent dynamics.