Content
javascript - beginner - Arrays - Functions - objects - DOM & BOM - Elements & Element.Attributes
- JavaScript is the world's most popular programming language.
- JavaScript is the programming language of the Web.
- JavaScript is easy to learn.
I will be showing you the journey, How I learned JAVASCRIPT 🧨
The Day I started this journey is 09/24/2020.
In Javascript variables are declared with var, let, and const. With so many options which one should you choose? Let's break it down:
var: Main variable instantiator pre-ES6, no longer in common usage- Can be scoped globally or to a function, but can be re-declared elsewhere in the code making it less trustworthy than its newer counterparts
letandconst
- Can be scoped globally or to a function, but can be re-declared elsewhere in the code making it less trustworthy than its newer counterparts
let: The updateable variable brought to you by ES6- A block ->
{}scoped variable for when you need something updateable that cannot be redeclared in the same block
- A block ->
const: The non-updateable variable brought to you by ES6- A recommended default for declaring variables unless you have a case for
letas it is block scoped likelet, but cannot be updated or redeclared once declared
- A recommended default for declaring variables unless you have a case for
In Javscript some Naming convention has been set aside For Variables we use camelCase of naming convention Something like this
let firstname = 'Robin';
// bad
let first_name = 'Robin';
// bad
let FIRSTNAME = 'Robin';
// bad
let FIRST_NAME = 'Robin';
// good
let firstName = 'Robin';
For boolean we use 'is' or 'has' keyword before the variable like
let isVisible = true;
let hasEncryption = true;
JavaScript functions are written in camel case too. In addition, it's a best practice to actually tell what the function is doing by giving the function name a verb as prefix. Like so
// bad
function name(firstName, lastName) {
return `${firstName} ${lastName}`;
}
// good
function getName(firstName, lastName) {
return `${firstName} ${lastName}`;
}
There is more so please do check this
| Method | Discription |
|---|---|
| concat() | Joins two or more arrays, and returns a copy of the joined arrays |
| copyWithin() | Copies array elements within the array, to and from specified positions |
| entries() | Returns a key/value pair Array Iteration Object |
| every() | Checks if every element in an array pass a test |
| fill() | Fill the elements in an array with a static value |
| filter() | Creates a new array with every element in an array that pass a test |
| find() | Returns the value of the first element in an array that pass a test |
| findIndex() | Returns the index of the first element in an array that pass a test |
| forEach() | Calls a function for each array element |
| from() | Creates an array from an object |
| includes() | Check if an array contains the specified element |
| indexOf() | Search the array for an element and returns its position |
| isArray() | Checks whether an object is an array |
| join() | Joins all elements of an array into a string |
| keys() | Returns a Array Iteration Object, containing the keys of the original array |
| lastIndexOf() | Search the array for an element, starting at the end, and returns its position |
| map() | Creates a new array with the result of calling a function for each array element |
| pop() | Removes the last element of an array, and returns that element |
| push() | Adds new elements to the end of an array, and returns the new length |
| reduce() | Reduce the values of an array to a single value (going left-to-right) |
| reduceRight() | Reduce the values of an array to a single value (going right-to-left) |
| reverse() | Reverses the order of the elements in an array |
| shift() | Removes the first element of an array, and returns that element |
| slice() | Selects a part of an array, and returns the new array |
| some() | Checks if any of the elements in an array pass a test |
| sort() | Sorts the elements of an array |
| splice() | Adds/Removes elements from an array |
| toString() | Converts an array to a string, and returns the result |
| unshift() | Adds new elements to the beginning of an array, and returns the new length |
| valueOf() | Returns the primitive value of an array |
There are two ways to access properties on an object:
- Dot Notation
- Bracket Notation
let obj = {
cat: 'meow',
dog: 'woof'
};
let sound = obj.cat;
console.log(sound);
// meowlet obj = {
cat: 'meow',
dog: 'woof'
};
let sound = obj['cat'];
console.log(sound);
// meowUse the Dot Notation. But if you’re dealing with invalid identifier or variables, use the Bracket notation.
Read this Article for more info Dot VS Bracket
A closure is the combination of a function bundled together (enclosed) with references to its surrounding state (the lexical environment). In other words, a closure gives you access to an outer function’s scope from an inner function. In JavaScript, closures are created every time a function is created, at function creation time.
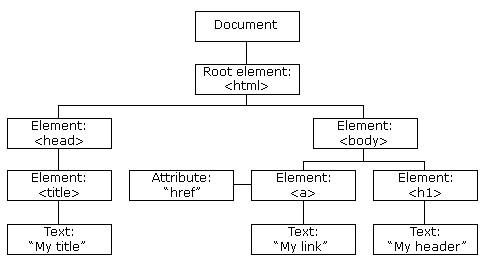
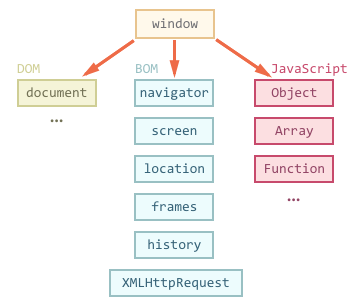
The Document Object Model (DOM) connects web pages to scripts or programming languages by representing the structure of a document—such as the HTML representing a web page—in memory. Usually, that means JavaScript, although modeling HTML, SVG, or XML documents as objects are not part of the core JavaScript language, as such.
The Browser Object Model (BOM) allows JavaScript to talk to the browser about matters other than the content of the page. There are no official standards for the BOM, albeit browser vendors have implemented almost the same features for interoperability.
One Cannot learn and memorise all of these elements and their respective attributes, so what you can do is save or bookmark these links.
Element.Attributes Read these MDN Docs. They will help in the best ways.