University of Pennsylvania, CIS 565: GPU Programming and Architecture, Project 2
- Hanlin Sun
- Tested on: Windows 10, i7-8750H @ 3.2GHz 32GB, NVIDIA Quadro P3200
This Project involves:
- CPU version of scan
- CPU version of scan without using scan
- CPU version of compact with scan
- GPU version of naive scan
- GPU version of work-efficient scan
- GPU version of String Compact scan
These three CPU implements was used to test whether GPU implements was right. I have collected the data across 8 executions with different array sizes to collect the data. This program generates a new array of random values with each execution, where the size of array is customisable. I have varied the size of the arrays by powers of two, starting from 2^8^ all the wai to 2^20^. The program also executes each algorithm for arrays of size "non- power of two" which are generated truncating the "power of two" arrays.
****************
** SCAN TESTS **
****************
[ 21 28 22 23 38 18 20 9 44 26 14 10 3 ... 25 0 ]
==== cpu scan, power-of-two ====
elapsed time: 0.0015ms (std::chrono Measured)
[ 0 21 49 71 94 132 150 170 179 223 249 263 273 ... 6273 6298 ]
==== cpu scan, non-power-of-two ====
elapsed time: 0.0014ms (std::chrono Measured)
[ 0 21 49 71 94 132 150 170 179 223 249 263 273 ... 6223 6226 ]
passed
==== naive scan, power-of-two ====
elapsed time: 0.25088ms (CUDA Measured)
[ 0 21 49 71 94 132 150 170 179 223 249 263 273 276 ... 6298 ]
passed
==== naive scan, non-power-of-two ====
elapsed time: 0.23552ms (CUDA Measured)
[ 0 21 49 71 94 132 150 170 179 223 249 263 273 276 ... 0 ]
passed
==== work-efficient scan, power-of-two ====
elapsed time: 0.185344ms (CUDA Measured)
[ 0 21 49 71 94 132 150 170 179 223 249 263 273 ... 6273 6298 ]
passed
==== work-efficient scan, non-power-of-two ====
elapsed time: 0.185344ms (CUDA Measured)
[ 0 21 49 71 94 132 150 170 179 223 249 263 273 ... 6223 6226 ]
passed
==== thrust scan, power-of-two ====
elapsed time: 13.1092ms (CUDA Measured)
[ 0 21 49 71 94 132 150 170 179 223 249 263 273 ... 6273 6298 ]
passed
==== thrust scan, non-power-of-two ====
elapsed time: 2.18214ms (CUDA Measured)
[ 0 21 49 71 94 132 150 170 179 223 249 263 273 ... 6223 6226 ]
passed
*****************************
** STREAM COMPACTION TESTS **
*****************************
[ 1 2 2 3 2 2 0 3 0 0 0 0 1 ... 3 0 ]
==== cpu compact without scan, power-of-two ====
elapsed time: 0.0014ms (std::chrono Measured)
[ 1 2 2 3 2 2 3 1 1 3 2 1 1 ... 3 3 ]
passed
==== cpu compact without scan, non-power-of-two ====
elapsed time: 0.0013ms (std::chrono Measured)
[ 1 2 2 3 2 2 3 1 1 3 2 1 1 ... 3 1 ]
passed
==== cpu compact with scan ====
elapsed time: 0.0038ms (std::chrono Measured)
[ 1 2 2 3 2 2 3 1 1 3 2 1 1 ... 3 3 ]
passed
==== work-efficient compact, power-of-two ====
elapsed time: 0.309248ms (CUDA Measured)
[ 1 2 2 3 2 2 3 1 1 3 2 1 1 ... 3 3 ]
passed
==== work-efficient compact, non-power-of-two ====
elapsed time: 0.274432ms (CUDA Measured)
[ 1 2 2 3 2 2 3 1 1 3 2 1 1 ... 3 1 ]
passed
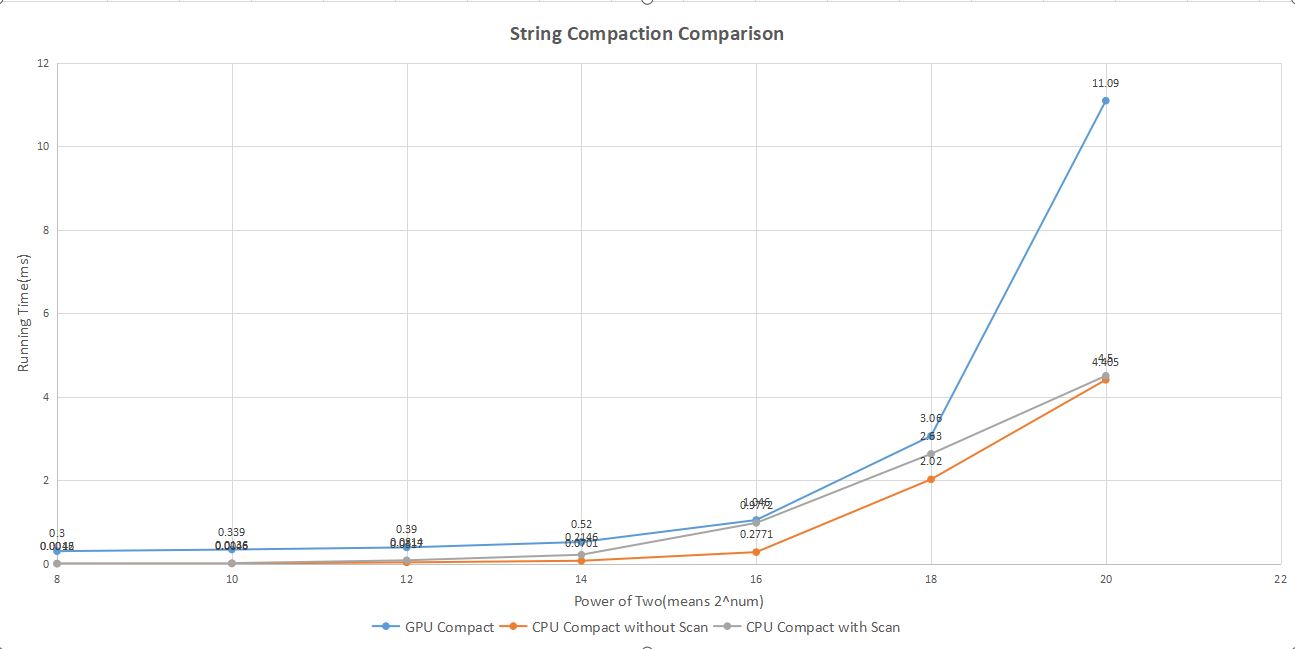
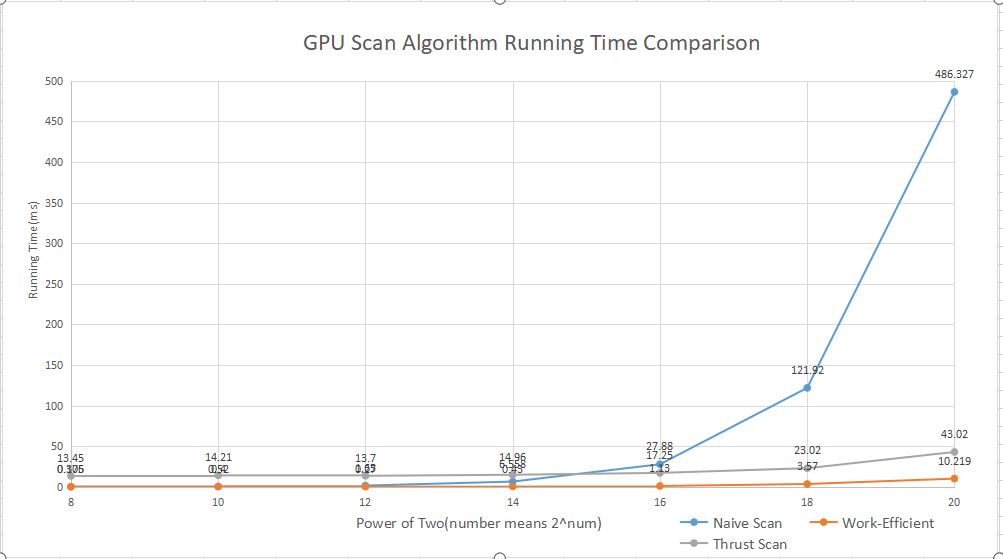
In this chart, the lower the attribute is, the better its performance. We can see that when the array number is generally small, the performance gap between naive method and work-efficient method is generally small, but with the array length increased, this gap become larger and larger. The reason why the second method is more efficient is that even though we have limited the number of active threads, when we are doing naive scan, threads which are not doing anything have to wait for the other active threads in the warp to finish to become available again. But in upsweep and downsweep method, upsweep only use half number of threads to finish the work, and the rest of threads can be utilized by the GPU to do other tasks(like downsweep). So through that method we launch the same number of threads, but use less depth than the naive method. That's why it is way more faster.