Code Release for HACMan: Learning Hybrid Actor-Critic Maps for 6D Non-Prehensile Manipulation.
Please feel free to open an issue or email us at {wenxuanz, bowenj}@andrew.cmu.edu if you have any questions.
First, install the conda environment:
conda create --name hacman python=3.8
conda activate hacman
Install the requirements.txt
pip install setuptools==65.5.0 "wheel<0.40.0" # because of gym 0.21 issue https://github.com/openai/gym/issues/3176.
pip install -r requirements.txt
Install Pytorch 1.11.0 + cu113. Note: the compatibility with other Pytorch version has not been tested.
pip install torch==1.11.0+cu113 torchvision==0.12.0+cu113 torchaudio==0.11.0 --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu113
Install the following packages with THE SPECIFIED VERSIONS:
# Torch Geometric
pip install torch-scatter==2.0.9 -f https://data.pyg.org/whl/torch-1.11.0+cu113.html
pip install torch-sparse==0.6.15 -f https://data.pyg.org/whl/torch-1.11.0+cu113.html
pip install torch-geometric==2.0.4
pip install torch-cluster==1.6.0 -f https://data.pyg.org/whl/torch-1.11.0+cu113.html
Install this package:
pip install -e .
Our training script is based on stablebaselines3, which supports logging with Weight & Bias.
If you do not wish to use WandB, you can turn off streaming by running wandb off from your training directory or setting the environment variable WANDB_MODE=offline.
To configure the WandB logging function, set the following environment variables.
export WANDB_ENTITY=[your Wandb ID]
export WANDB_PROJECT=[your project name]
HACManBinEnv is the object pose alignment task shown in our paper. Running this simulation environment requires Mujoco and Robosuite. Please skip this section if you do not intend to run this task.
Install mujoco-py using the instructions here.
Install our modified verion of robosuite.
cd robosuite && pip install -e .
-
To verify your installation, try training HACMan on SimpleEnv.
SimpleEnvis a simple 2D tabletop cube pushing environment. -
To reproduce the training curves in the paper, see train HACMan on HACManBinEnv.
Note: if you have correctly configured your WandB logging, you should be able to see the training curve for any of the following training tasks on your W&B project page (note: change the x-axis to global step).
The following command launches HACMan trining on the task SimpleEnv. You should expect a success rate of ~50% at 50k training steps.
python scripts/run.py \
--env simple_env \
--algo HybridTD3
Important: make sure you have installed the HACManBinEnv dependencies.
The following command launches HACMan training on the task HACManBinEnv. If everything is configured correctly, this should reproduce the performance of our experiment All Objects 6D Goals (Fig. 4) in our paper. You should expect a success rate of ~85% at 200k training steps.
LD_PRELOAD="" MUJOCO_PY_FORCE_CPU=1 python scripts/run.py \
--env hacman_bin_env \
--clamp_critic_max 0 \
--clamp_critic_min -20 \
--ExpID 1000
To experiment with other goal configurations, set goal_mode.
--goal_mode {GOAL_MODE}
The available goal modes are:
- 6d goals:
any_var_size - planar goals:
translation - upright goals:
upright
To experiment with a specific object, set object_name as follows:
--object_name {MESH_NAME}
You can find the full list of mesh names in bin_env/assets/housekeep_all/models_processed/meshes/. For example, rubiks_cube_077_rubiks_cube_M is the name of the cube object used in our experiments.
Important: make sure you have installed the HACManBinEnv dependencies.
The following command evaluates a trained HACMan policy for 100 episodes. We have provided some checkpoints here. Download the checkpoint and save it to a directory of your choice (e.g. scripts/ckpts/). Then, run the following command to evaluate the policy.
LD_PRELOAD="" MUJOCO_PY_FORCE_CPU=1 python scripts/run.py \
--env hacman_bin_env \
--ExpID 1001 \
--gradient_steps 0 \
--initial_timesteps 0 \
--load_ckpt scripts/ckpts/rl_model_200000_steps.zip --eval 100
To render the videos, add the following arguments
--record_video --record_from_cam agentview
docs: Documentation fileshacmanalgosfeature_extractorsfeature_extractors.py: Networks for extracting features from point clouds
hacman_td3.py: HACMan hybrid TD3 implementationlocation_policy.py: Location policy implementation. Location policies score per-point actions and select the best point to execute the action.mix_td3.py: An ablation implementation of HACMan TD3.setup_model.py: Model setup functions.
envssim_envsbase_env.py: Base class for simulation environments used by HACMan.simple_env.py: Simple 2D tabletop cube pushing environment.hacman_bin_env.py: HACMan Bin environment.
location_policy_wrappers.py: Wrappers for location policy used in env. Location policy is included in the env wrapper since we add contact point index part to be part of the environment observation.wandb_wrappers.py: WandB logging wrappers.setup_envs.py: Environment setup functions.setup_location_policy.py: Location policy setup functions.
networkscommon.py: Common network modules.point_transformer.py: Point Transformer implementation.pointnet2.py: PointNet++ implementation.
sb3_utils: Stable Baselines 3 utilities.- ...
utilslaunch_utils.py: Utility functions for launching training.plotly_utils.py: Utility functions for plotting 3D PCD visualizations.robosuite_transform_utils.py: Utility functions used bytransformations.py. Copied fromrobosuite.transformations.py: Utility functions for transforming 3D PCDs.
scriptstest_simple_env.py: Test script forSimpleEnv.run.py: Training script.
bin_envassets: Assets used byHACManBinEnv.housekeep: Cylindrical housekeep objects.housekeep_all: All housekeep objects.- ...
controller_configs: Controller configuration files.datahousekeep: Goal pose data for cylindrical housekeep objects.housekeep_all: Goal pose data for all housekeep objects.
base_env.py: Base environment. It contains initialization functions for the environment and object loading functions.bin_arena.py: Bin workspace.osc.py: Controller for controlling robot arm via operational space control.poke_env.py: Top-level sim environment directly used byHACManBinEnv. It contains functions for interacting with the environment, resetting the environment, and setting goals.- ...
To create a new environment that inherits from BaseEnv, you will need to define a new class that inherits from hacman/envs/sim_envs/base_env.py. Here is an example of what your new class could look like (see hacman/envs/sim_envs/simple_env.py for a more complete example):
import gym
from hacman.envs.sim_envs.base_env import BaseEnv
class MyCustomEnv(BaseEnv):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.my_custom_sim = MyCustomSim()
def step(self, action):
# Define your custom step function here
return observation, reward, done, info
def reset(self):
# Define your custom reset function here
return observation
For reference, the custom environment will also inherit the following functions from BaseEnv:
set_prev_obs: (Required) After an environment step, a location policy computes the location index and stores it back to the environment through this function. The environment uses the computed location index to retrieve contact location in the next step._evaluate_goal: By default, HACMan computes the norm of the flow as reward and evaluates the success of task completion.
Afterwards, add the new environment to hacman/envs/setup_envs.py.
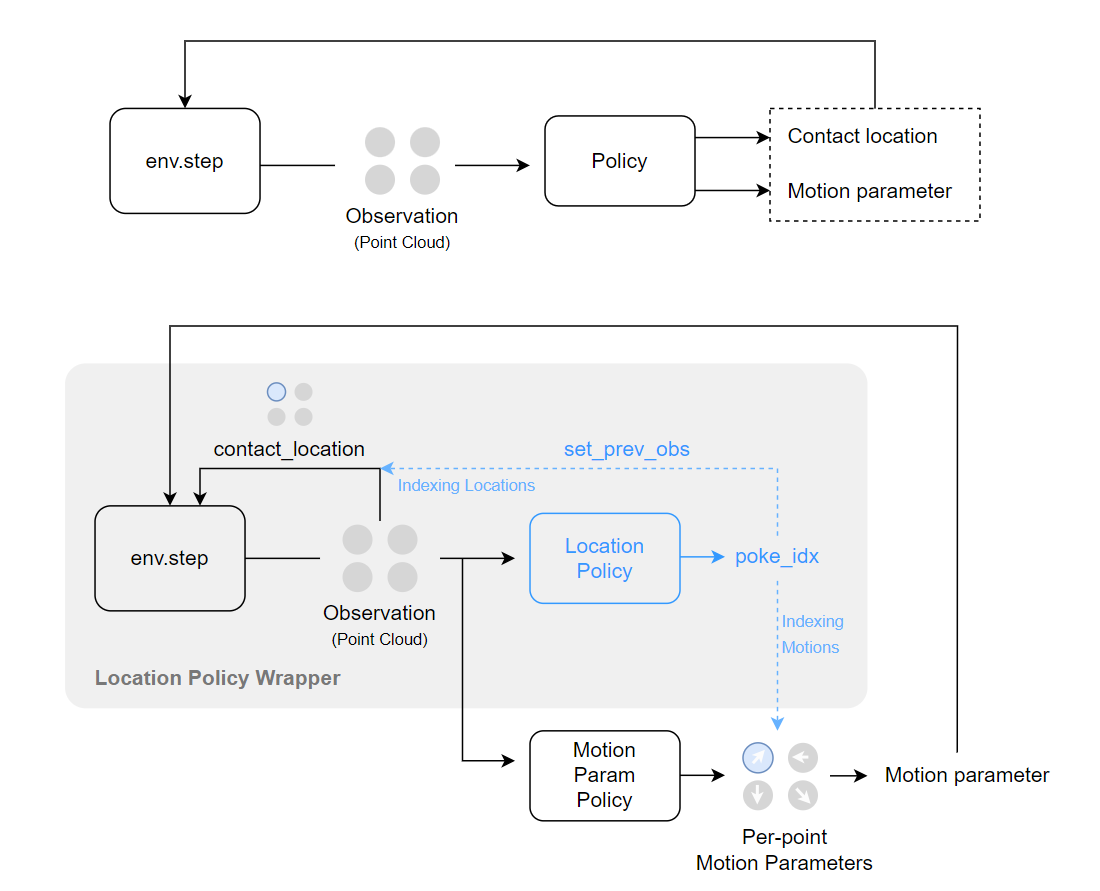
In the paper, we propose a hybrid action space with a discrete component (action location) and a continuous component (motion parameters). Unfortunately, Stable baselines3 does not support hybrid action space. We design a workaround to incorporate the hybrid action space into Stable baselines3 that can be combined with existing continuous action space algorithms with minimal modifications.
The main idea is to include the discrete part of the policy (location policy) into the environment as an environment wrapper. As illustrated in the figure below, the raw output of env.step will be passed into a location policy wrapper (implemented as SubprocVecEnvwithLocationPolicy or DummyVecEnvwithLocationPolicy in hacman/envs/location_policy_wrappers.py). The location policy then selects the discrete action based on the current model and appends the action as poke_idx into the observation. Then, the full observation, including the original observation and poke_idx, will be passed into the RL algorithm of Stable baseline3. In addition, we pass the poke_idx back to the simulation environment by set_prev_obs to be used for the next env.step. In this way, the discrete component of the policy is off-loaded into the environment and we can use any algorithm with continuous action space seamlessly.
Note that the wrappers in hacman/envs/location_policy_wrappers.py serve as a connection between the environment and the wrapper. The actual "policy" (how we select the discrete action) is defined as LocationPolicyWithArgmaxQ in hacman/algos/location_policy.py.
This section presents the complete list of environment wrappers employed in this project.
Environment wrappers' order:
VecEnvwithLocationPolicy<[NUM_ENVS * <Monitor<TimeLimit<Env>>]>
For evaluation, we add one more wrapper WandbPointCloudRecorder on top to record the point cloud visualizations or video footages.
-
SubprocVecEnvwithLocationPolicy/DummyVecEnvwithLocationPolicy.This wrapper embeds the location policy into the environment. It is utilized for both parallel and non-parallel training, where SubprocVecEnvwithLocationPolicy is used for parallel training, and DummyVecEnvwithLocationPolicy is employed for non-parallel training (useful for debugging). These wrappers incorporate the policy model to calculate the poke_idx and action_score, which are appended to the observation using set_prev_obs, as described in the previous section. The poke_idx determines the point where the action is executed, while the action_score is used for logging. The implementations of these wrappers can be found in
hacman/envs/location_policy_wrappers.py. -
Monitor.This wrapper logs the agent's performance during training, providing information on episode reward, episode length, and episode time. These values are subsequently uploaded to wandb. The implementation is imported from
stable_baselines3.common.monitor. -
TimeLimit.This wrapper limits the maximum number of steps per episode. When the episode reaches the maximum number of steps, it sets done to True. The implementation is imported from
gym.wrappers.time_limit. -
WandbPointCloudRecorder.This wrapper is used to record and generate point cloud visualizations of episodes and upload them to wandb. Please note that only the first of the parallel environments will have point cloud visualizations. Additionally, it records video footages if enabled. The implementation can be found in
hacman/envs/wandb_wrappers.py.
HACMan is MIT licensed. See the license for details.