UML summary
UML is not tied to a specific development tool, specific programming language, or specific target platform on which the system to be developed must be used. Neither does UML offer a software development process. UML in fact separates the modeling language and modeling method. UML use models, models are a representation of a system that is reduced to the essentials in order to minimize the complexity of the system to manageable aspects. The characteristics of a models are Abstraction, Understandability, Accuracy, Predictiveness, Cost-effectiveness. The objected oriented phylosophy has a definite approach that evolve with the time as best methods. In UML, a model is represented graphically in the form of diagrams.
- Structure Diagrams
- The Class Diagram
- The Object Diagram
- The Package Diagram
- The Component Diagram
- The Composition Structure Diagram
- The Deployment Diagram
- The Profile Diagram
- Behavior Diagrams
- The Use Case Diagram
- The State Machine Diagram
- The Activity Diagram
- The Sequence Diagram
- The Communication Diagram
- The Timing Diagram
- The Interaction Overview Diagram
General terms:
- classes
- In many object-oriented approaches, it is possible to define classes that describe the attributes and the behavior of a set of objects (the instances of a class) abstractly and thus group common features of objects.
- objects
- The instances of a class are referred to as its objects.
- encapsulation
- Encapsulation is the protection against unauthorized access to the inter nal state of an object via a uniquely defined interface. Different levels of visibility of the interfaces help to define different access authorizations.
- messages
- Objects communicate with one another through messages.
- inheritance
- The concept of inheritance is a mechanism for deriving new classes from existing classes.
- polymorphism
- In general terms, polymorphism is the ability to adopt different forms. During the execution of a program, a polymorphic attribute can have references to objects from different classes. Real life example of polymorphism, a person at a same time can have different characteristic. Like a man at a same time is a father, a husband, a employee. So a same person posses have different behavior in different situations.
Class diagram
The purpose of class diagram is to model the static view of an application. Class diagrams are the only diagrams which can be directly mapped with object-oriented languages and thus widely used at the time of construction.
UML diagrams like activity diagram, sequence diagram can only give the sequence flow of the application, however class diagram is a bit different. It is the most popular UML diagram in the coder community.
The purpose of the class diagram can be summarized as:
-
Analysis and design of the static view of an application.
-
Describe responsibilities of a system.
-
Base for component and deployment diagrams.
-
Forward and reverse engineering.
Attribuses
A significant piece of data containing values that describe each instance of a class. Also called fields, variables, propieties.
-name: string
-id:int
Methods
Methods are actions
-setName()
Visibility
- The symbol
-means the field or method is private. - The symbol
+means the field or method is public. - The symbol
~means the field or method is available to every class in the same package. - The symbol
#means the field or method is protected.- it means that can be accessed only from the class or subclass
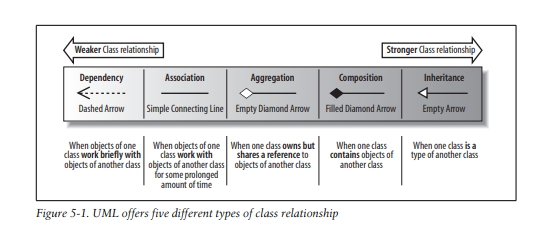
Type of associations:
Dependency
A dependency implies only that objects of a class can work together; therefore, it is considered to be the weakest direct relationship that can exist between two classes. The dependency relationship is often used when you have a class that is providing a set of general-purpose utility functions, such as in Java’s regular expression (java.util.regex) and mathematics (java.math) packages. Classes depend on the java.util.regex and java.math classes to use the utilities that those classes offer.
Association
The associations explains a generic association between these two classes.
- eg: sportman ---- association(play)---- sport
- eg: sportfan ---- association(drink)---- beer
Aggregation
The aggregation explains a group of the same objects into an association.
- eg: sportman ---- aggregate ---- sport team
- eg: sportfan ---- aggregate ---- sport fan club
Composition
The composition explains an association between a child objects and a parent objects in which the child objects exists iff the parent exists. The line is denoted with a line ending with a black rhombus
- eg: hotelBathroom ---- composition ---- hotel
- eg: teamFanClub ---- composition ---- sport team
Inheritance
Subclasses Inherite the attributes from the super class it is denote with an arrow.
- eg: sportman ---- inherite ---- human
- eg: sportfan ---- inherite ---- human
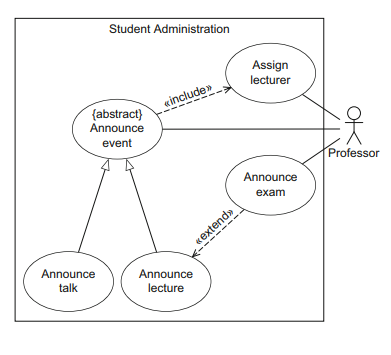
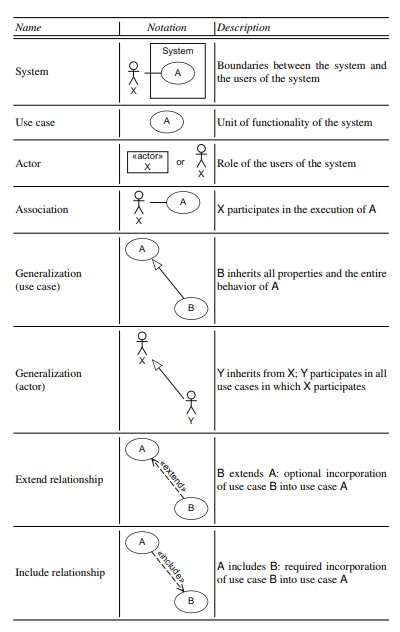
Use case diagram
A use case describes functionality expected from the system to be deA veloped. It encompasses a number of functions that are executed when using this system. Specifically, we can employ a use case diagram to answer the following questions:
-
- What is being described? (The system.)
-
- Who interacts with the system? (The actors.)
-
- What can the actors do? (The use cases.)
Actors
To describe a system completely, it is essential to document not only what the system can do but also who actually works and interacts with the system. In the use case diagram, actors always interact with the sys- tem in the context of their use cases, that is, the use cases with which they are associated. Actors can be human (e.g., student or professor) or non-human (e.g., e-mail server).
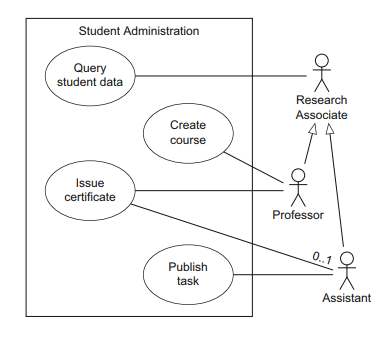
Relationship between use cases
This is a complete version of a use case diagram.