FOOOF is a fast, efficient, physiologically-informed model to parameterize neural power spectra, characterizing both the 1/f background, and overlying peaks (putative oscillations).
The model conceives of the neural power spectrum as consisting of two distinct functional processes:
- A 1/f background, modeled with an exponential fit, with:
- Band-limited peaks rising above this background (modeled as Gaussians).
With regards to examing peaks in the frequency domain, as putative oscillations, the benefit of the FOOOF approach is that these peaks are characterized in terms of their specific center frequency, amplitude and bandwidth without requiring predefining specific bands of interest. In particular, it separates these peaks from a dynamic, and independently interesting 1/f background. This conception of the 1/f as potentially functional (and therefore worth carefully modeling) is based on work from our lab suggesting that the 1/f slope may index excitation/inhibition balance (Gao, Peterson, Voytek, NeuroImage 2017; Voytek & Knight, Biol Psychiatry 2015). At the very least, however, the 1/f appears to change with task (Podvalny et al., J Neurophysiol 2015), with aging (Voytek et al., J Neurosci 2015).
A full description of the method and approach is available in the paper linked below.
If you use this code in your project, please cite:
Haller M, Donoghue T, Peterson E, Varma P, Sebastian P, Gao R, Noto T, Knight RT, Shestyuk A,
Voytek B (2018) Parameterizing Neural Power Spectra. bioRxiv, 299859.
doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/299859
Link: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/early/2018/04/11/299859
FOOOF runs on Python 3.5 and 3.6.
- numpy
- scipy >= 0.19
- matplotlib (optional)
- pytest (optional)
That is, if you are using Anaconda, then you are good to go.
If you aren't using Anaconda, it is one way to get and manage these dependencies.
Matplotlib is not required for running the model fitting, but is used if you want to visualize model fits.
Pytest is only required to run the test suite.
To install the latest stable release of fooof, you can use pip:
$ pip install fooof
Note that this will install only the core (non-optional) fooof requirements.
If you don't have matplotlib installed, and want to include it for plotting functionally, install using:
$ pip install fooof[plot]
To get the lastest, development version, you can get the code using git:
$ git clone https://github.com/voytekresearch/fooof
To then install the development version (without making changes to it), move into the directory you cloned and run:
$ pip install .
Otherwise, if you want to install an editable, development version, move into the directory you cloned and install with:
$ pip install -e .
FOOOF is object oriented, and generally follows a similar approach as used in scikit-learn.
With a power spectrum loaded (with 'freqs' storing frequency values, and 'spectrum' storing the power spectrum, both as 1D arrays in linear space) FOOOF can be used as follows:
from fooof import FOOOF
# Initialize FOOOF object
fm = FOOOF()
# Define frequency range across which to model the spectrum
freq_range = [3, 40]
# Model the power spectrum with FOOOF, and print out a report
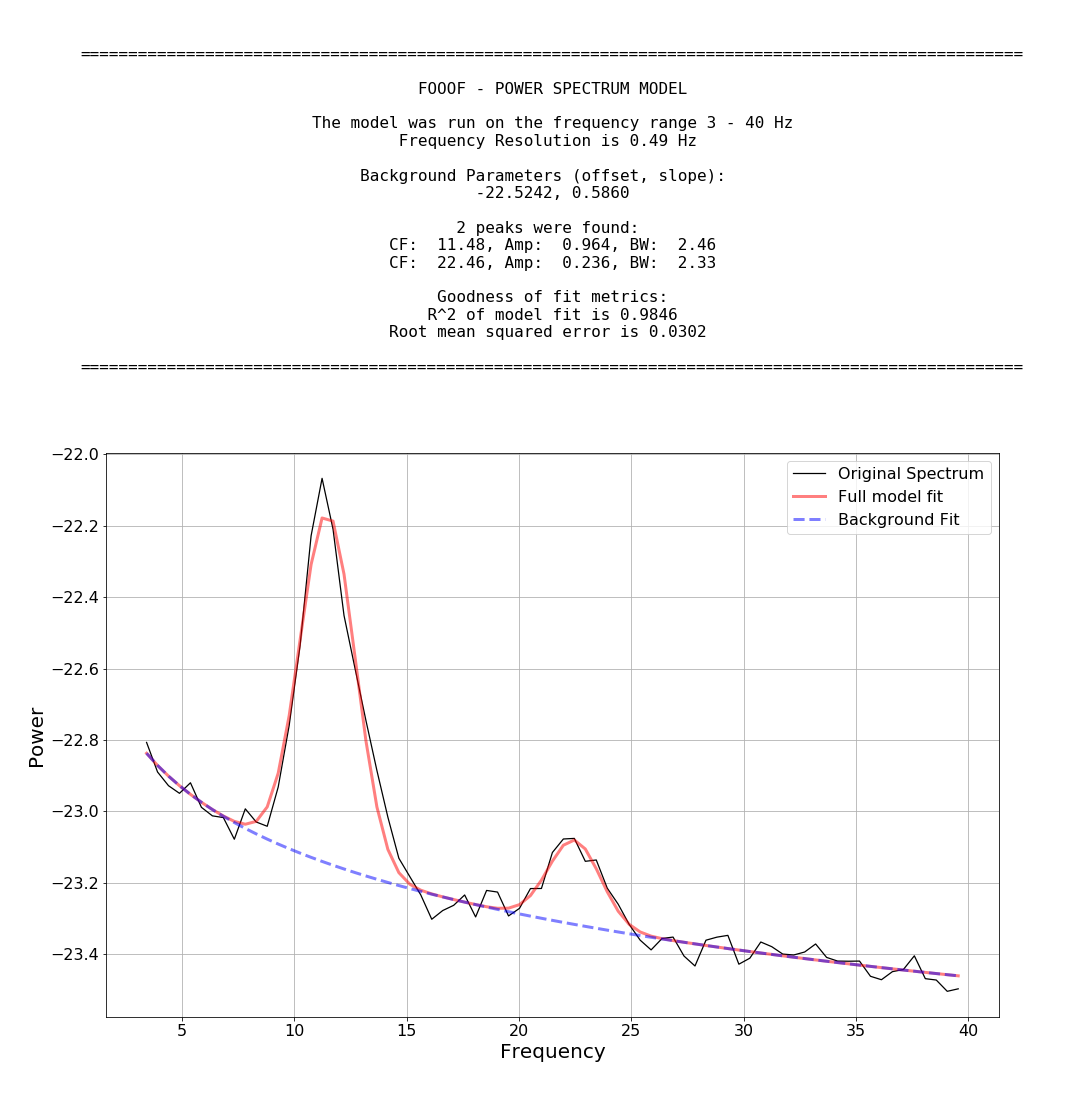
fm.report(freqs, spectrum, freq_range)FOOOF.report() fits the model, plots the original power spectrum with the associated FOOOF model, and prints out the parameters of the model fit for both background 1/f and Gaussian parameters for any identified peaks.
FOOOF also accepts parameters for fine-tuning the fit. For example:
fm = FOOOF(peak_width_limits=[1.0, 8.0], max_n_peaks=6, min_peak_amplitude=0.1, peak_threshold=2.0)- peak_width_limits sets the possible lower- and upper-bounds for the fitted peak widths.
- max_n_peaks sets the maximum number of peaks to fit (in decreasing order of amplitude).
- min_peak_amp sets an absolute limit on the minimum amplitude (above background) for any extracted peak.
- peak_threshold, also sets a threshold above which a peak amplitude must cross to be included in the model. This parameter is in terms of standard deviation above the noise of the flattened spectrum.
FOOOF also has convenience methods for running the FOOOF model across matrices of multiple power spectra, as well as functionality for saving and loading results, creating reports from FOOOF outputs, and utilities to further analize FOOOF results.
An example workflow, with 'freqs' as 1D array of frequency values, and 'spectra' as a 2D array of power spectra.
# Initialize a FOOOFGroup object, specifying some parameters
fg = FOOOFGroup(peak_width_limits=[1.0, 8.0], max_n_peaks=8)
# Fit FOOOF model across the matrix of power spectra
fg.fit(freqs, spectra)
# Create and save out a report summarizing the results across the group of power spectra
fg.save_report()
# Save out FOOOF results for further analysis later
fg.save(file_name='fooof_group_results', save_results=True)Example output for a FOOOF fit of MEG data:
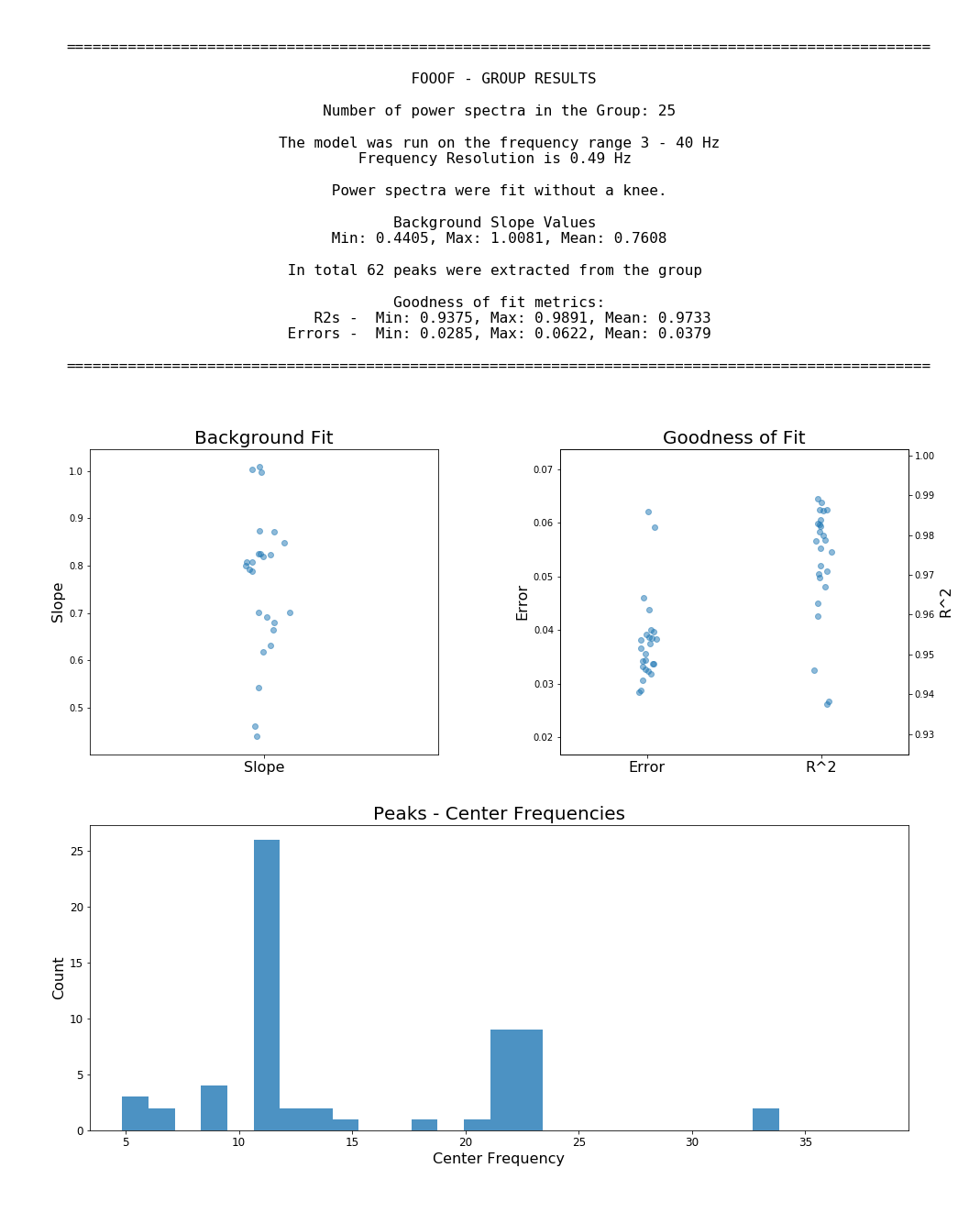
Example output for running FOOOF across a group of power spectra (with FOOOFGroup):