Materials come from AZ-900 Microsoft Azure Fundamentals Bootcamp
Describe cloud concepts (15-20%)
Describe core Azure services (30-35%)
Describe security, privacy, compliance, and trust (25-30%)
Describe Azure pricing Service Level Agreements, and Lifecycles (20-25%)
Module 2: Cloud Computing Models. Regions, Availability Zones (AZ), Availability Sets. Azure Management Interfaces.
- SaaS works on a subscription based model - pay annually or monthly.
- Cloud Advantages against other solutions:
Advantages of Cloud Computing PDF
- Upfront investments - buying taxis. And, after upfront investments, the value reduces over time.
- If you go on your own in your business - then you will pay more. You will pay less with Azure.
Regions and AZ PDF Some additional information via link PDF
-
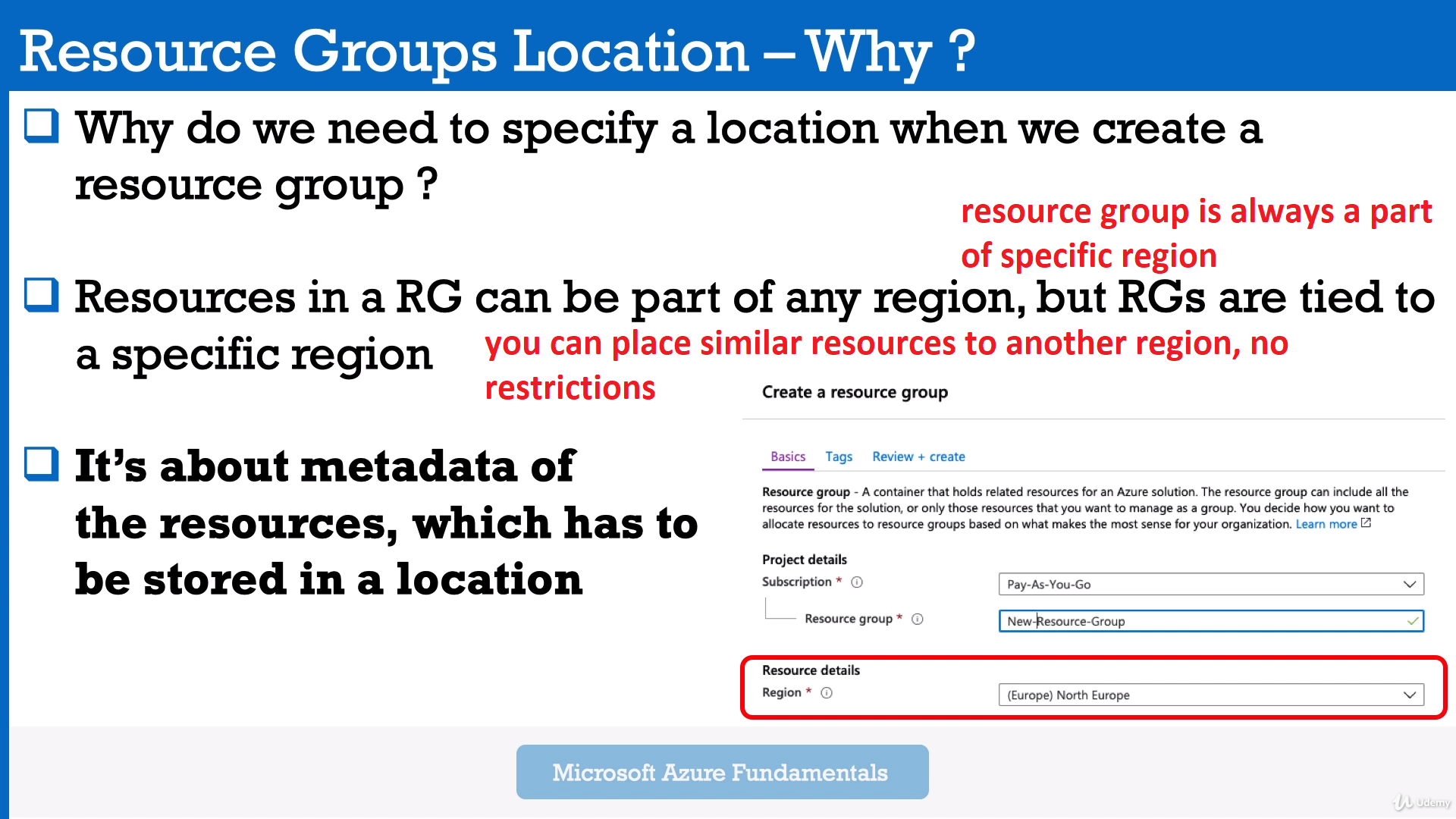
Region us a part of one Geography + Specific service availability.
Example of Geographies: In America there are 4 geographies: United States, Azure Government, Canada, Brazil. -
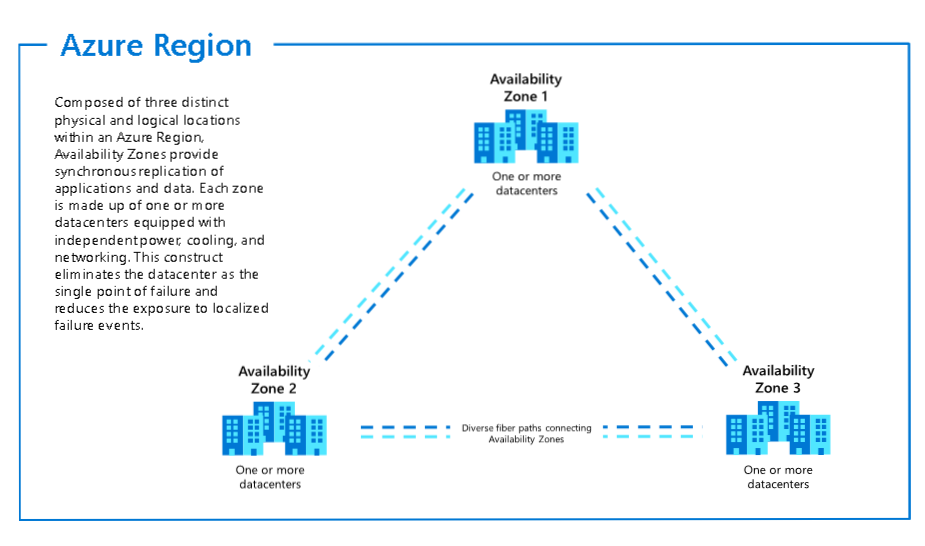
AZ - physically separate datacenters withing Azure Region, with independent power, network and cooling.
Example: In West Europe Region there are 3 different AZ zones - AZ-1, AZ-2, AZ-3. They are interconnected by low-latency links.
Required for mission-critical applications.
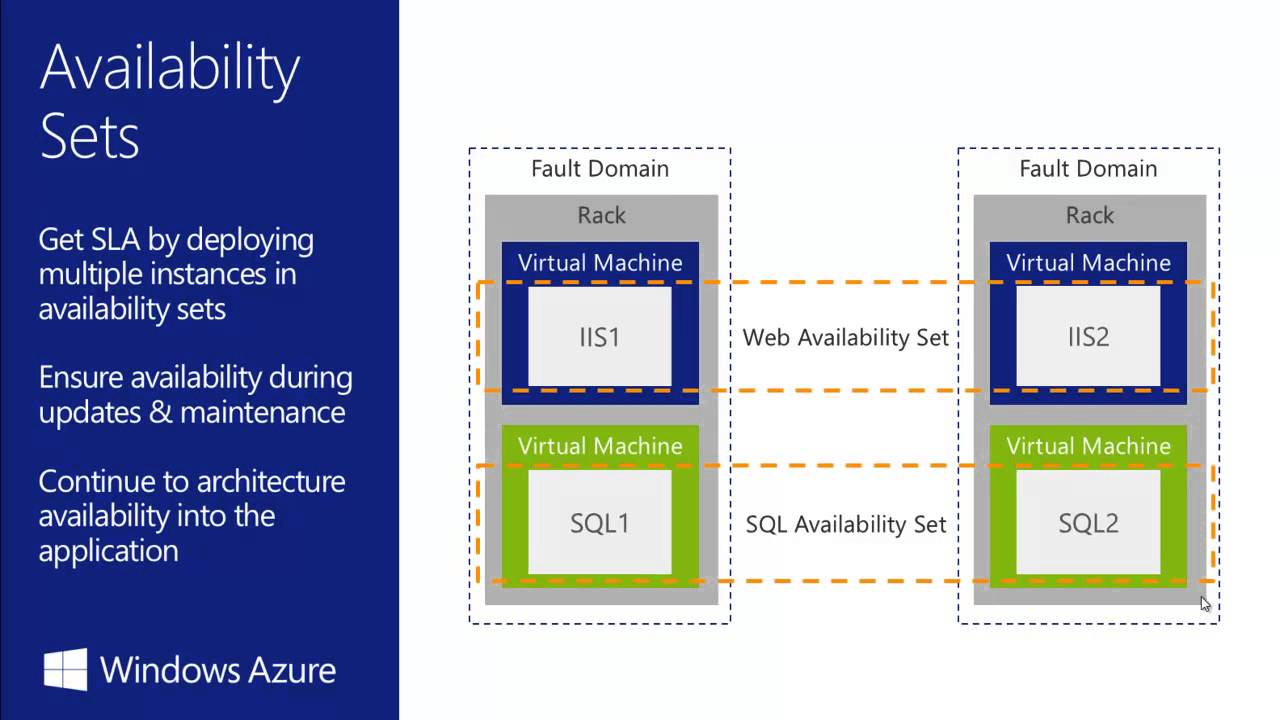
- Availability Sets - is a logical grouping of two or more VMs within a DataCenter that allows Azure to understand how your App is build to provide redundancy and availability.
- With Availability Sets, Azure will split your pool of VMs on different racks of servers which called "Fault Domains" to prevent app outage in case of unplanned maintenance events (power, hw failure, etc). Racks is really different in the datacenter.
- The main idea - if Azure need to update the hardware or software in Fault Domain 1 - your site still be available.
-
Region Pairs - For disaster compliance. When the entire Azure Region goes down - you can recover your app using another Region which is in a pair with yours.
-
Azure Portal
-
Azure CLI (Command Line Interface) - console for Windows\Mac\Linux
-
Azure PowerShell module - mostly the same as a CLI option. Also, it is a console with additional command line abilities.
Allow you to use scripts and make some automations. -
Azure Cloud Shell Browser-accessible pre-configured virtual machine (all required applications is already installed)
- Accessible from Azure Portal, from shell.azure.com and from Azure Mobile App.
-
Azure SDK Collections of libraries for developers.
-
Azure Mobile App Monitoring the health and servers statuses, Run commands, diagnose and fix issues.
Module 2: Azure Subscriptions. Management Groups + Azure Resource Hierarchy.
-
In enterprise world there could be several kinds of subscriptions: Development subscription, testing subscription, production subscription
-
One azure account you can have one or more subscriptions.
- Billing Boundaries: Billing Boundaries will help you to organize and control your costs using billing reports, invoices etc.
- Access Control Boundaries: Apply access policies at the different subscription levels + control different resources.
In details: Azure Subscription is for:
- Environment separation: Dev environment, Testing env, Prod env.
- Create distinct organizational structures: HR, Marketing, Management, IT etc. Subscription per department.
- Billing purposes: aggregate costs per subscription
- Subscription limitation: set some restrictions per subscription, for example 10vCPU per subscription, other hard limits.
Another Azure Subscription Offers like $200 credit in 30 first days.
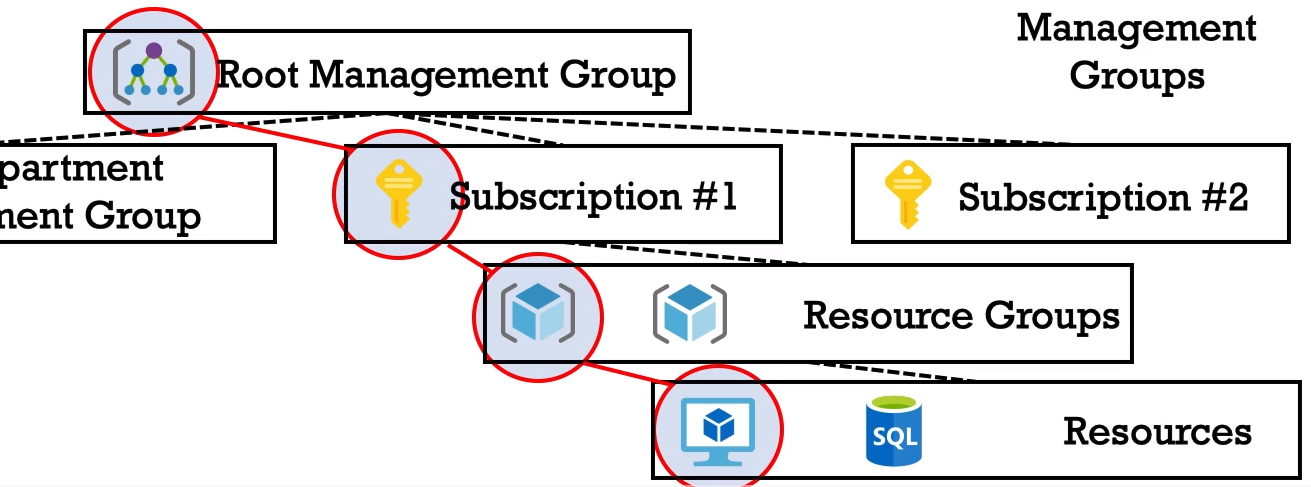
Azure Resource Hierarchy:
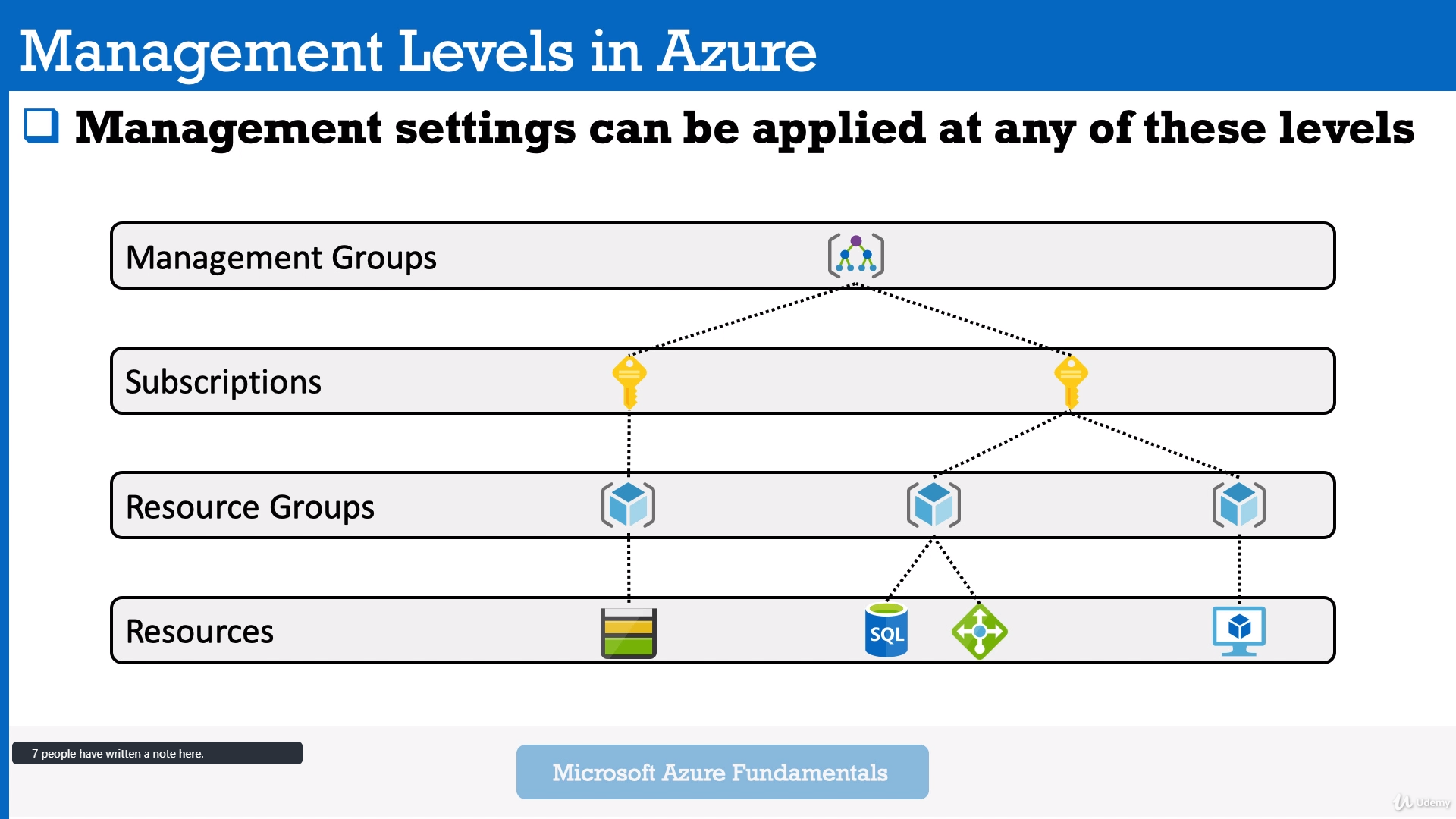
- Management Groups - is a container for multiple subscriptions.
Root Management Group -> Per Department Management Group + Subscriptions - Subscriptions - can have Resource Groups.
- Resource Groups - can have Resources (which you can deploy in Azure: SQL DBs, VMs, etc).
In my next practise it will be named "AZ900 Resource Group". - Resources: SQL DBs, VMs, etc.
Module 3. Azure Core Services. Virtual Machines. Azure Managed Disks. Application Security Group (ASG). Network Security Group (NSG).
Module 3: Practical lessons. Launch VMs, NSG, ASG, Load Balancer
- sudo su - update your privileges
- sudo apt update - update all pre-installed packages to the last versions
- sudo apt apache2 - apache for linux web server.
- sudo systemctl status apache2 - to check is apache running
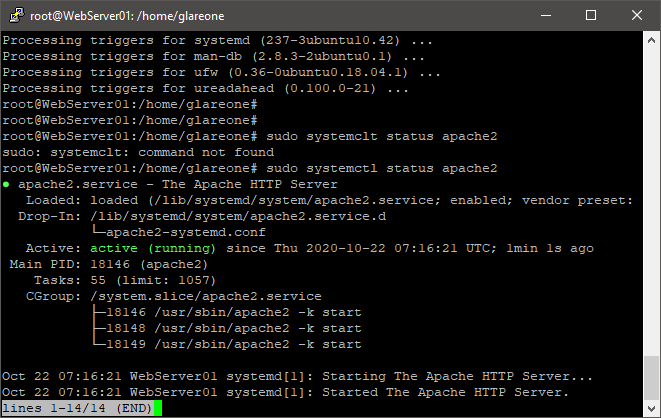 4.1. to test that everything is ok - curl localhost - will check will apache make a response us.
4.2 create(mostly update) index.html page:
4.1. to test that everything is ok - curl localhost - will check will apache make a response us.
4.2 create(mostly update) index.html page:
cd /var/www/html
ls
rm index.html-- remove previous html filenano index.html- create your own html file:<html><body><h1>Webserver 01</h1></body></html> - NSG configuration
- Azure Virtual Machines represent IaaS Computing Model.
The most flexible option. Types:
- General Purpose - (Balanced CPU and Memory)
- Compute Optimized - (High CPU, lower memory)
- Memory Optimized - (High memory, lower CPU)
- Storage Optimized - (High disk throughput and IOPS)
- GPU - (Heave rendering traffic)
- High Performance Compute - (Most Powerful CPUs)
More information about sizes link
Virtual Networking, VM, High Availability. PDF
-
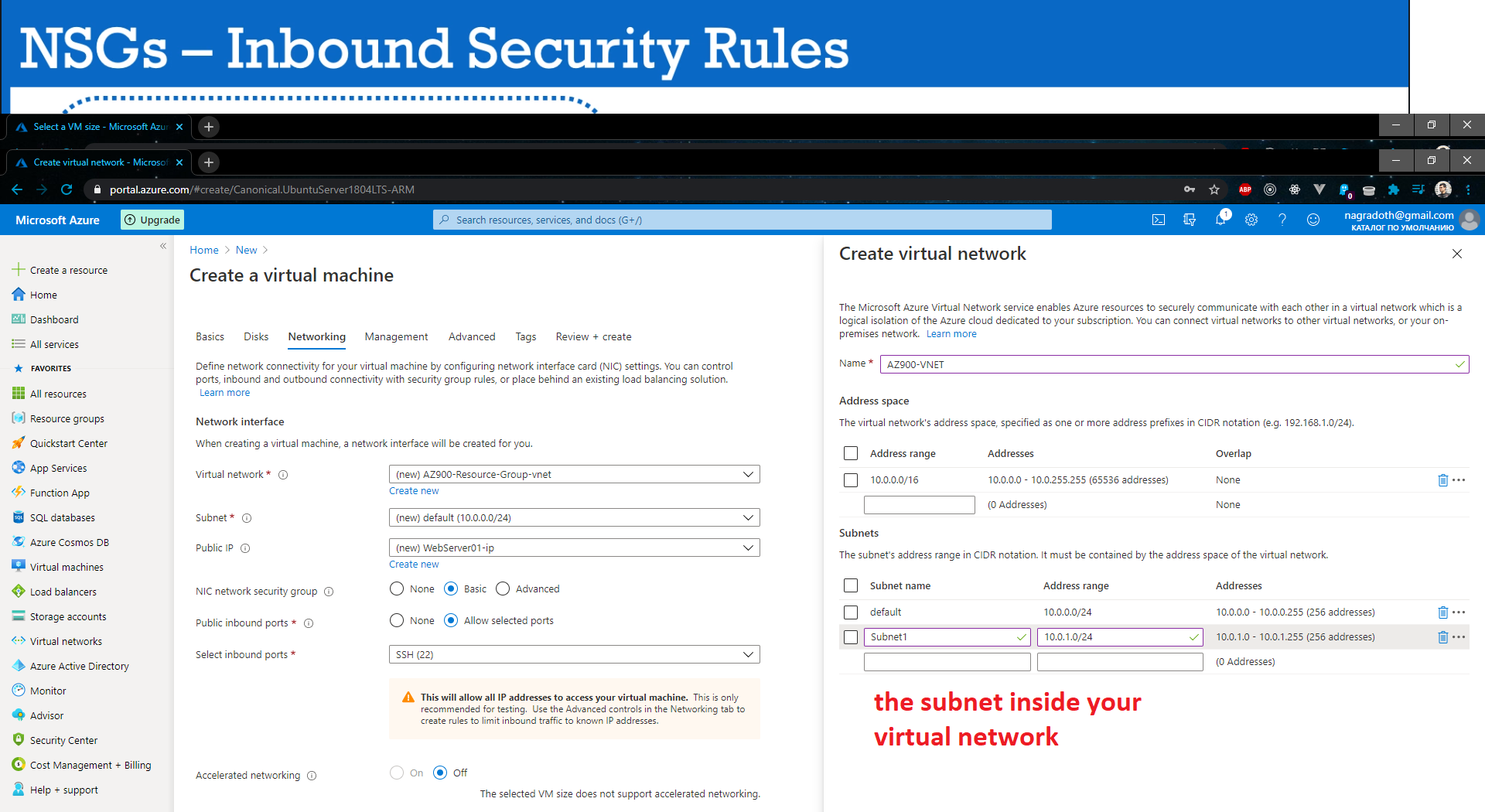
vNET - Azure Virtual Networks. Enable to communicate between VMs and over the internet with you on-prem machines.
-
vNET - is equivalent of VPC in AWS Cloud.
-
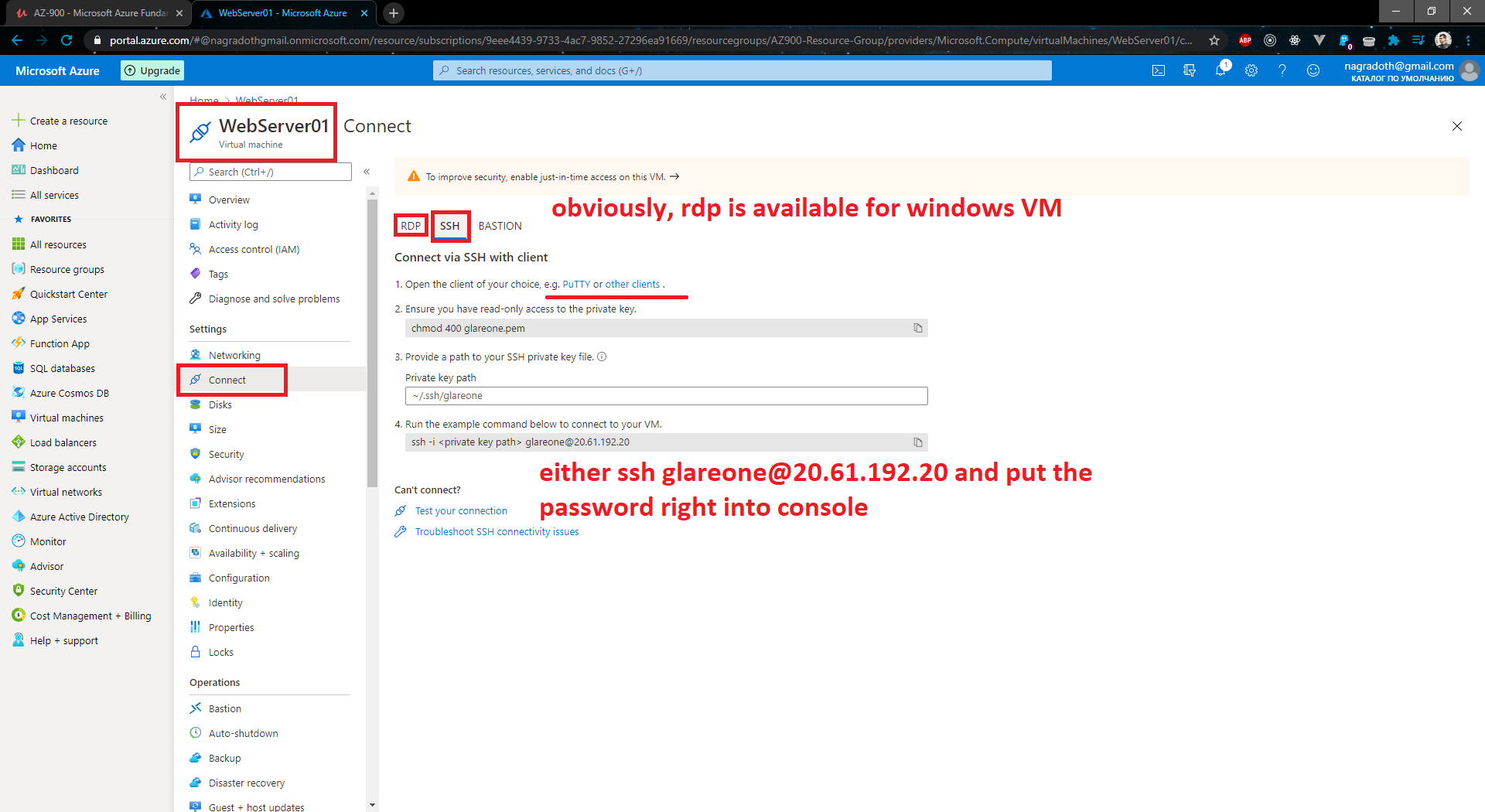
Allow you using SSH to connect to your Virtual Machines throw Public IP address inside your vNET.
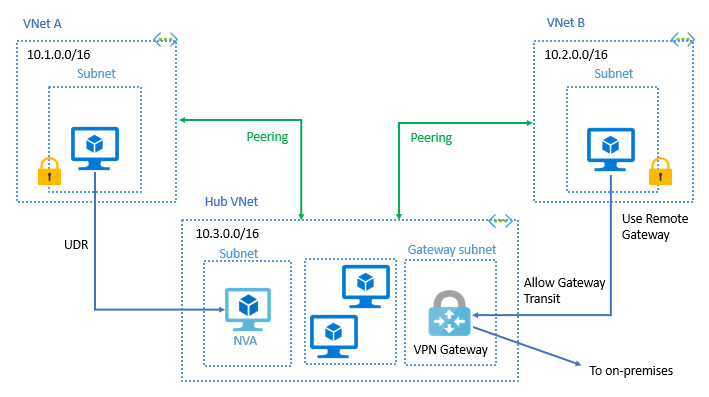
-
Virtual Machine Scale Sets - group of identical VMs under Load Balancer. The number of instances can be automatically increase and decrease according network load.
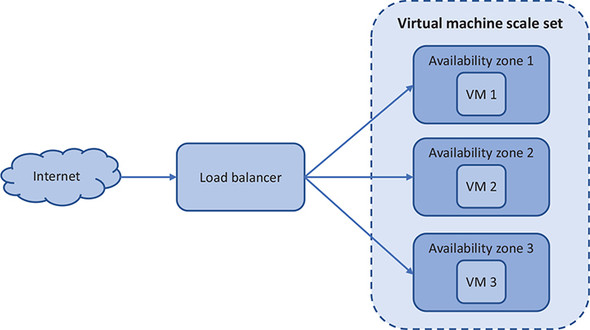 Bear in mind! They can be stored in a same AZ
Bear in mind! They can be stored in a same AZ -
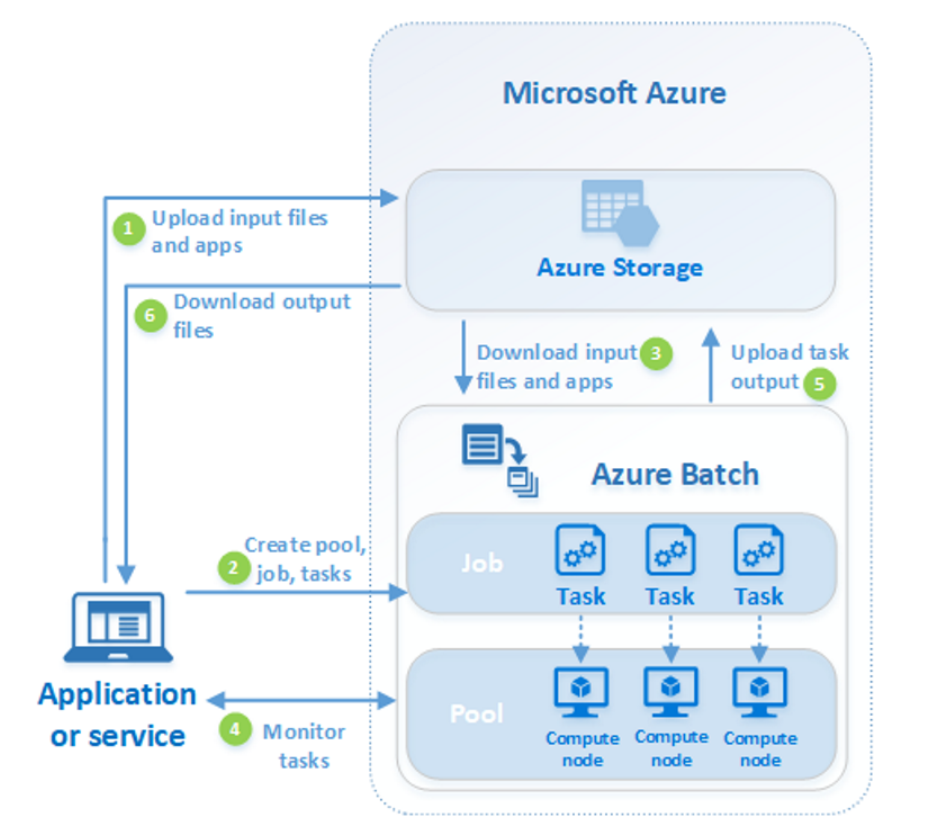
Azure Batch - large-scale job scheduler. Let you make huge jobs, creating and managing tens\hundreds\thousands of VMs (pools of VMs) under the hood.
- Azure managed disks are block-level storage volumes that are managed by Azure and used with Azure Virtual Machines.
Managed disks are like a physical disk in an on-premises server but, virtualized. Azure will provision the disk on their own, you just specify the size of your virtual disk More information about disks link - 4 disk types to aim the specific customer scenarios:
- Ultra disk (IO-intensive: SQL, Oracle and other transaction-heavy workloads)
- Premium SSD (Production)
- Standard SSD (Web services, lightly enterprise apps)
- Standard HDD (Backups, non-critical apps)
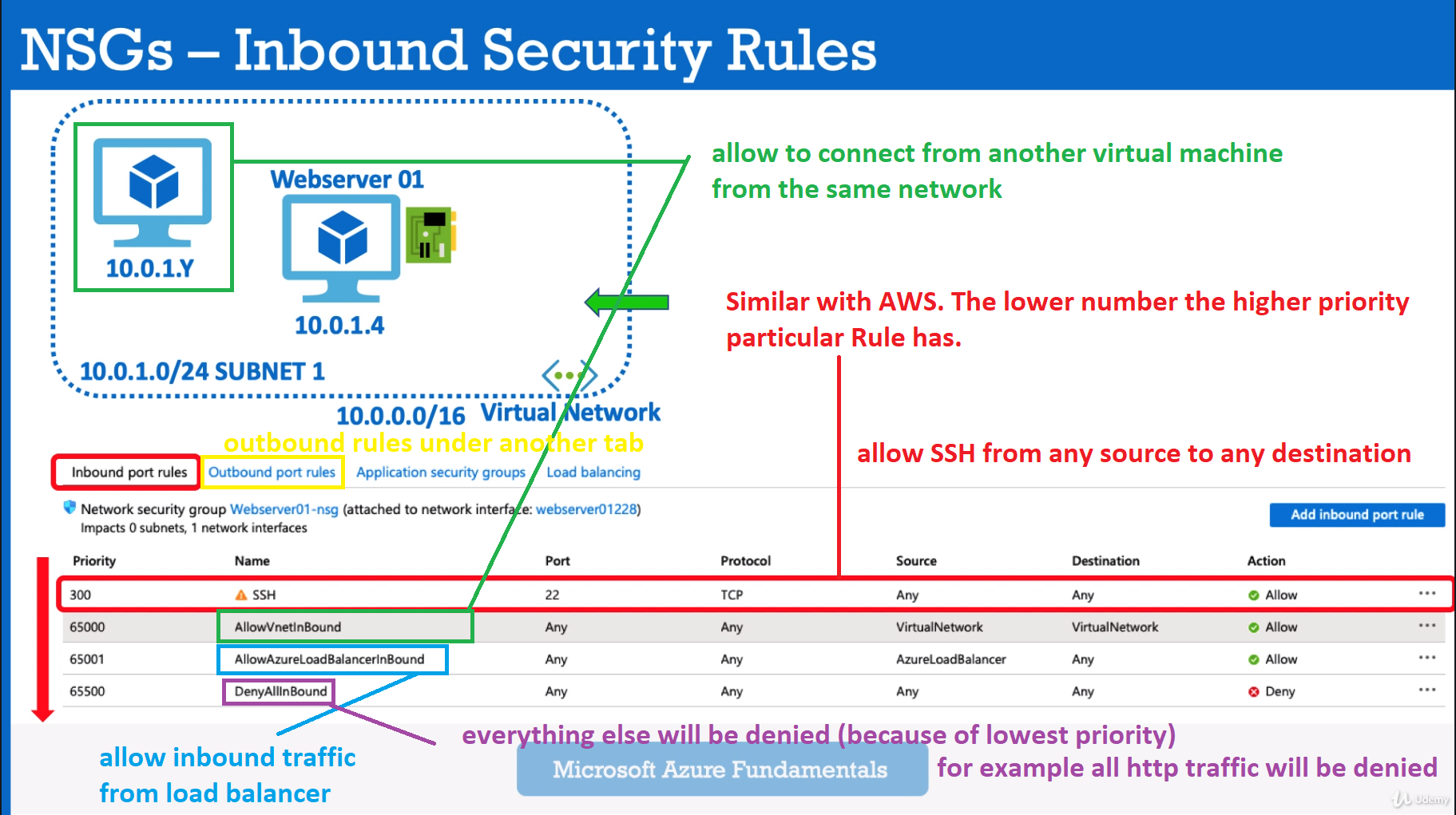
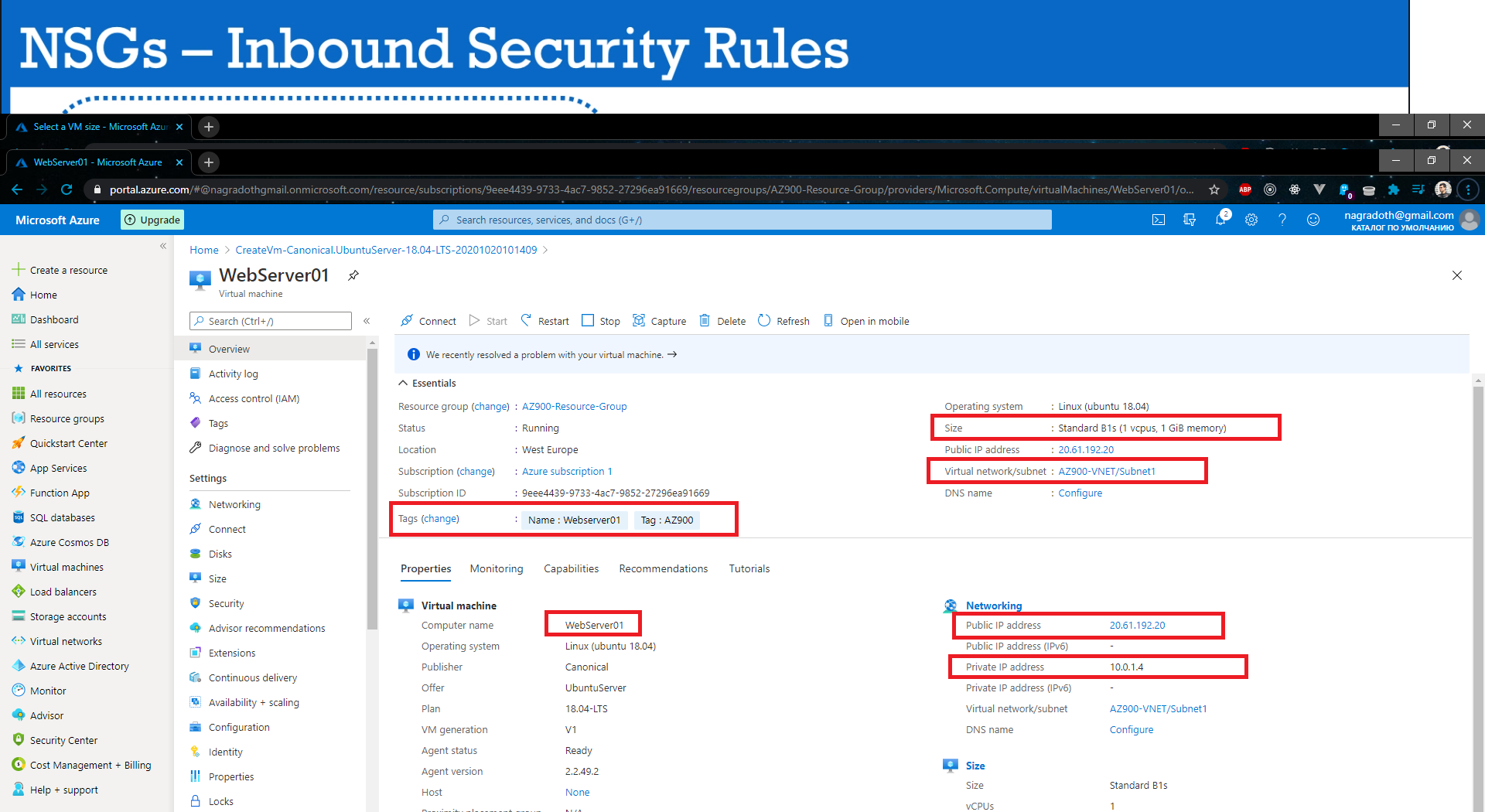
- Network Security Group is the Azure Resource that you will use to enforce and control the network traffic with,
whereas Application Security Group is an object reference within a Network Security Group.
NSG’s control access by permitting or denying network traffic in a number of ways, whether it be Network and Security Groups
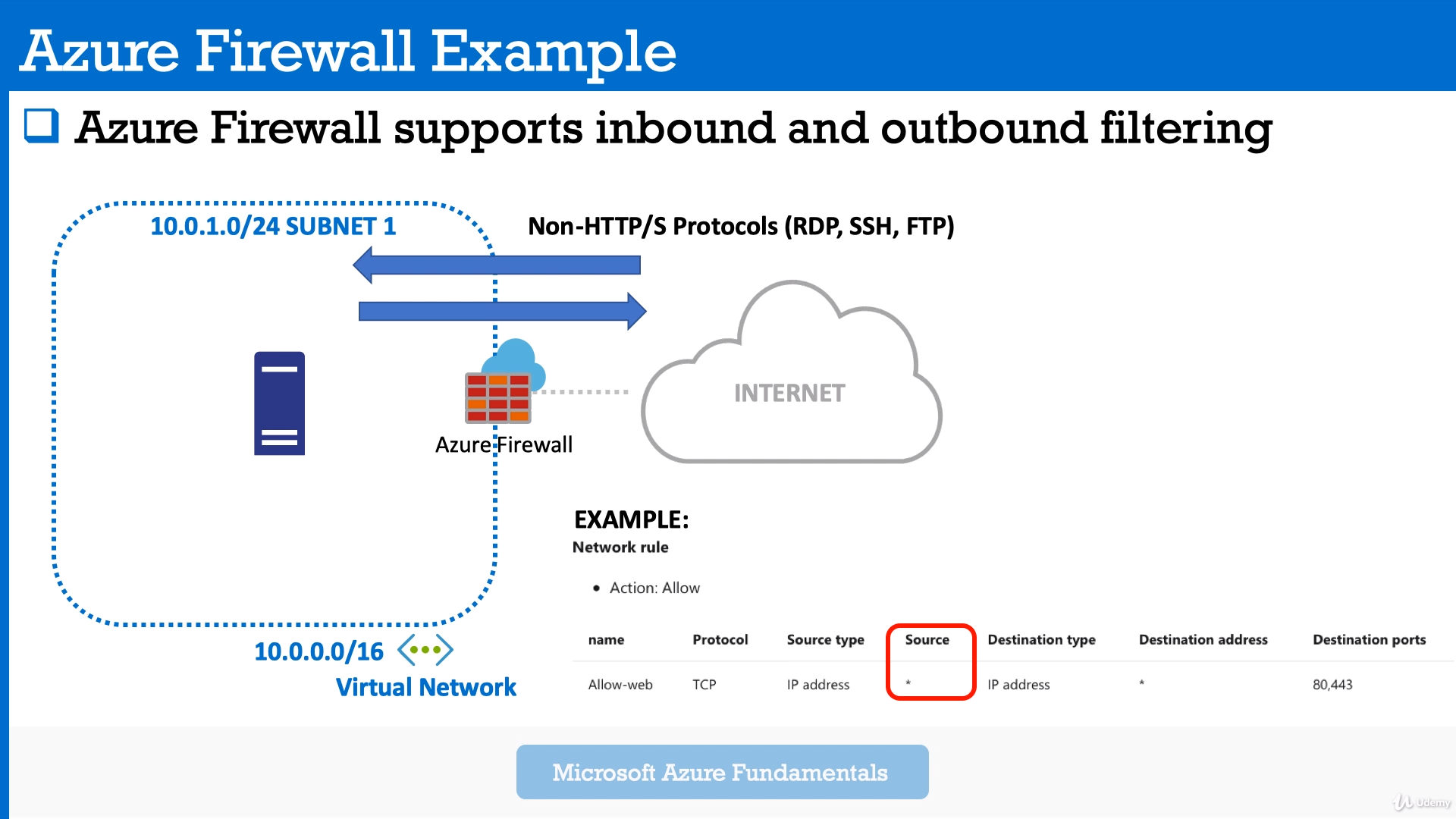
- Azure Network Security Groups act as a firewall for your VMs. Controls inbound and outbound traffic
- Works on subnet level or Network Interface Card (NIC)
- Different VMs can have different NSGs applied
- You can add rules to your NSG.
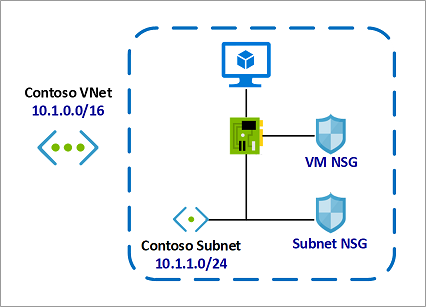
ASGs are used within a NSG to apply a network security rule to a specific workload or group of VMs – defined by ASG worked
as being the “network object” & explicit IP addresses which are added to this object.
This provides the capability to group VMs into associated groups or workloads, simplifying the NSG rule definition process.
Another great use of this is for scalability, creating the virtual machine and assigning the newly created the virtual machine to its ASG will provide it with all the NSG rules in place for that specific ASG – zero distribution to your service!
- Allows you to group your virtual machines and define network security policies for them.
- You add rules that control inbound traffic to instances and separate rules that control outbound traffic
Module 3: Practical lessons. Launch VMs, NSG, ASG, Load Balancer
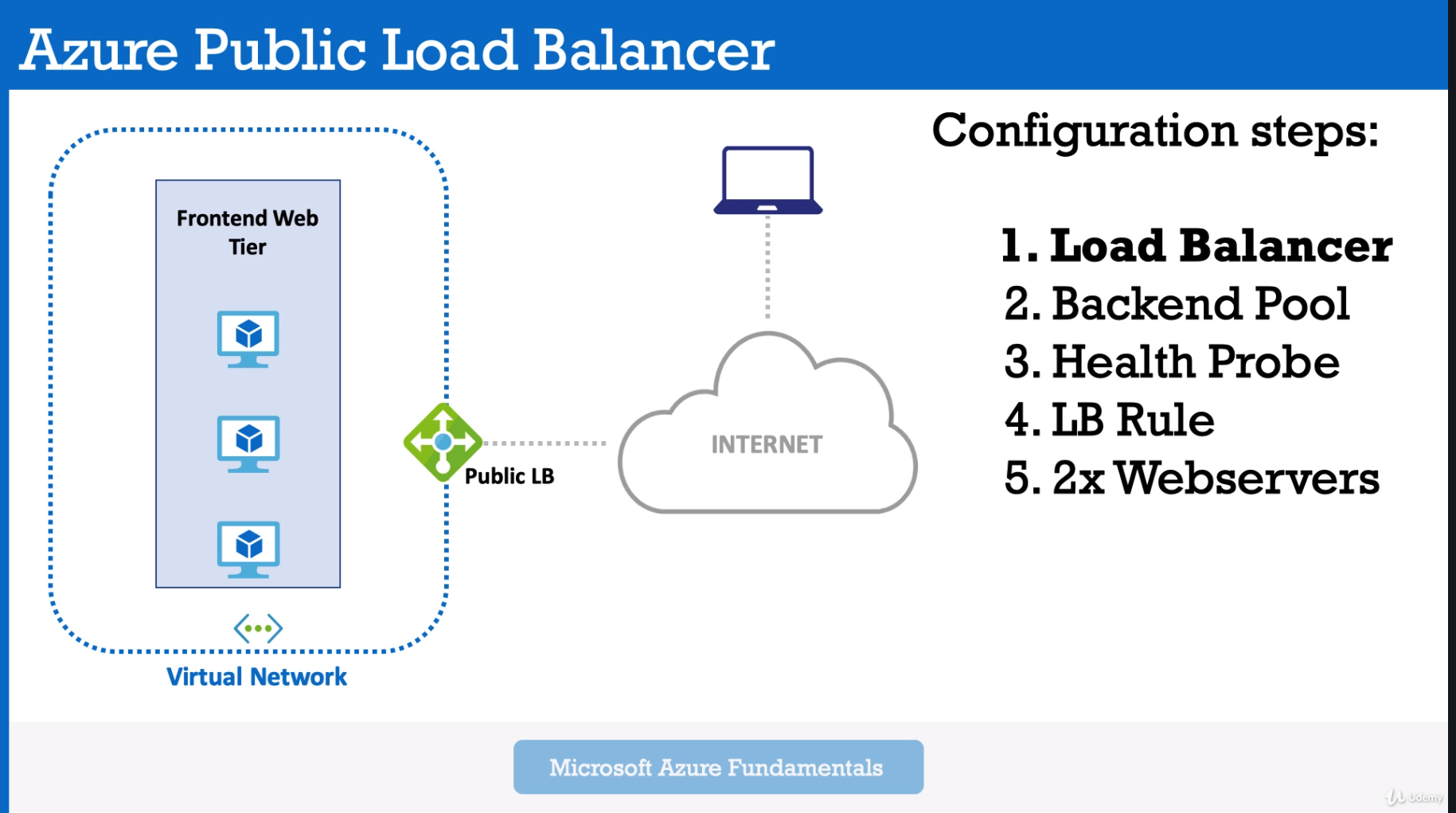
Load Balancer
Let you equally distributing load to a group of servers (backend servers pool)
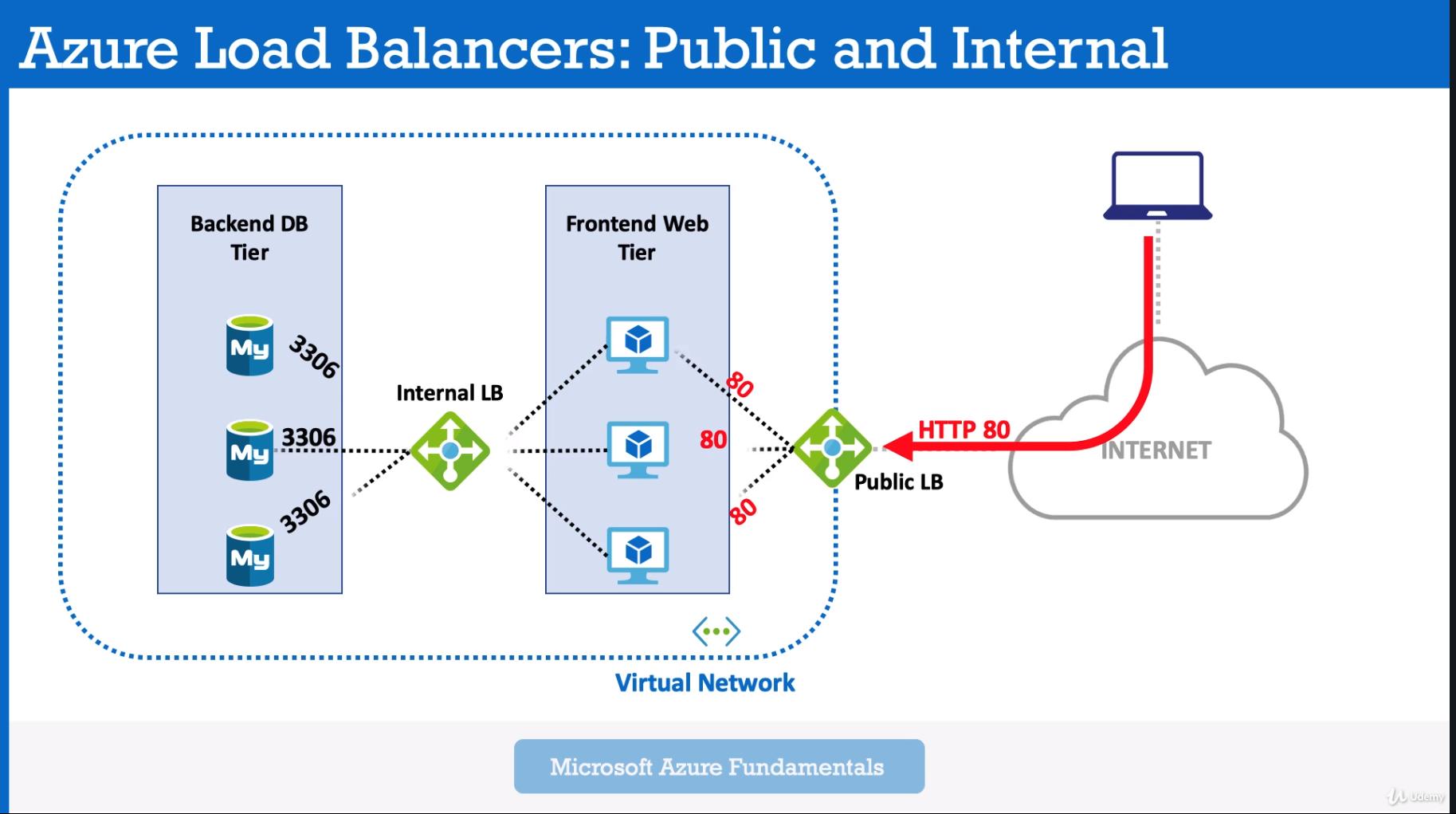
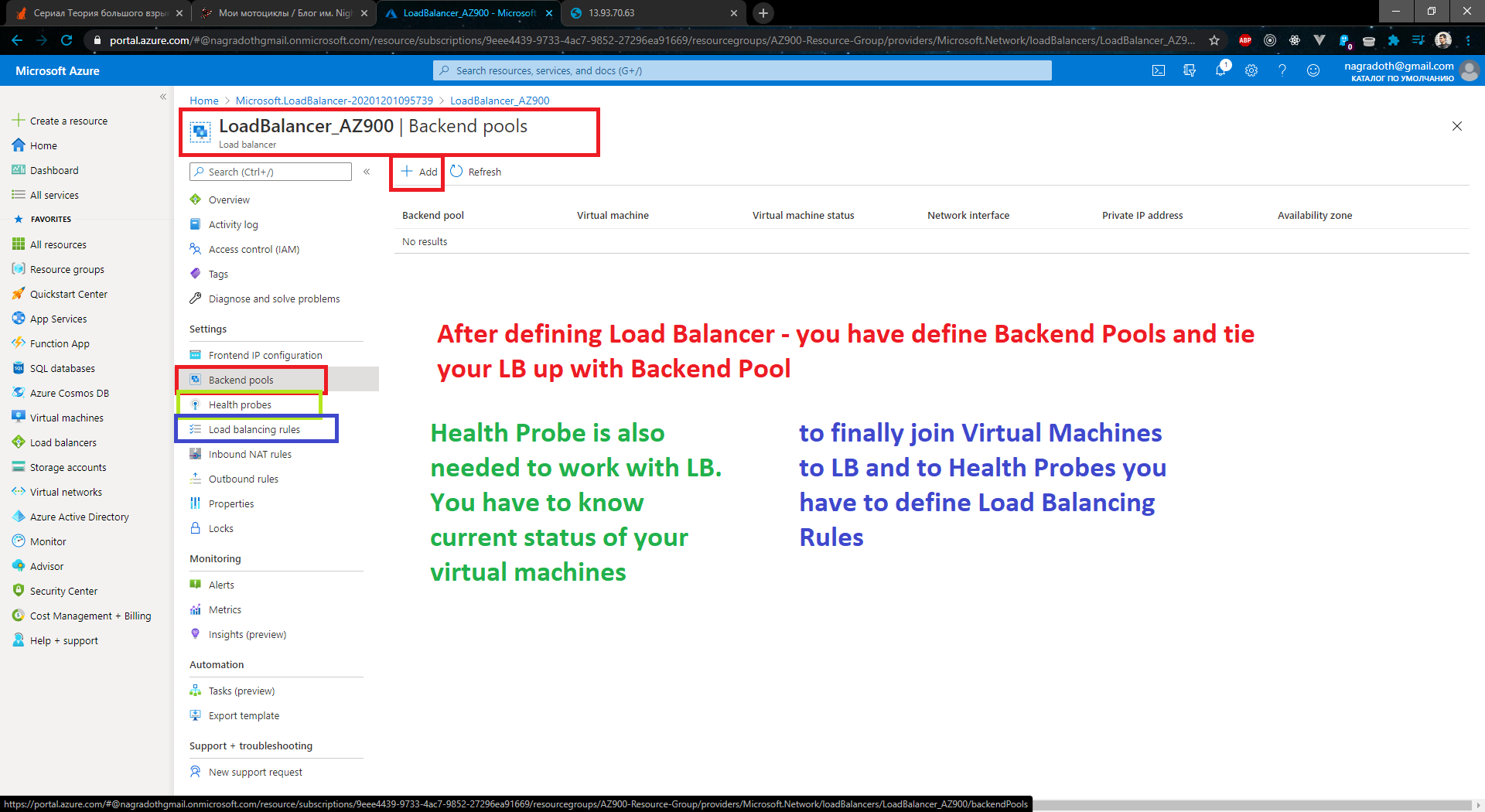
- Create and Configure Load balancer
- Define Frontend pool - pool of your FE servers.
- Health probe - probe which controls your FE servers (is your server in a good condition and ready to work)
- Load Balancer Rules - for example wait request on 80 port (HTTP) from outside (Internet) and send it via 443 port (HTTPS)) to your backend pool (Frontend Web Servers).
- Create Public Load Balancer 1.2) Create Backend Pool 1.3) Create Health Probe for LB
- Create WebServers and Attach it to Load Balancer
2.1) Configure Inbound Port rules for webservers
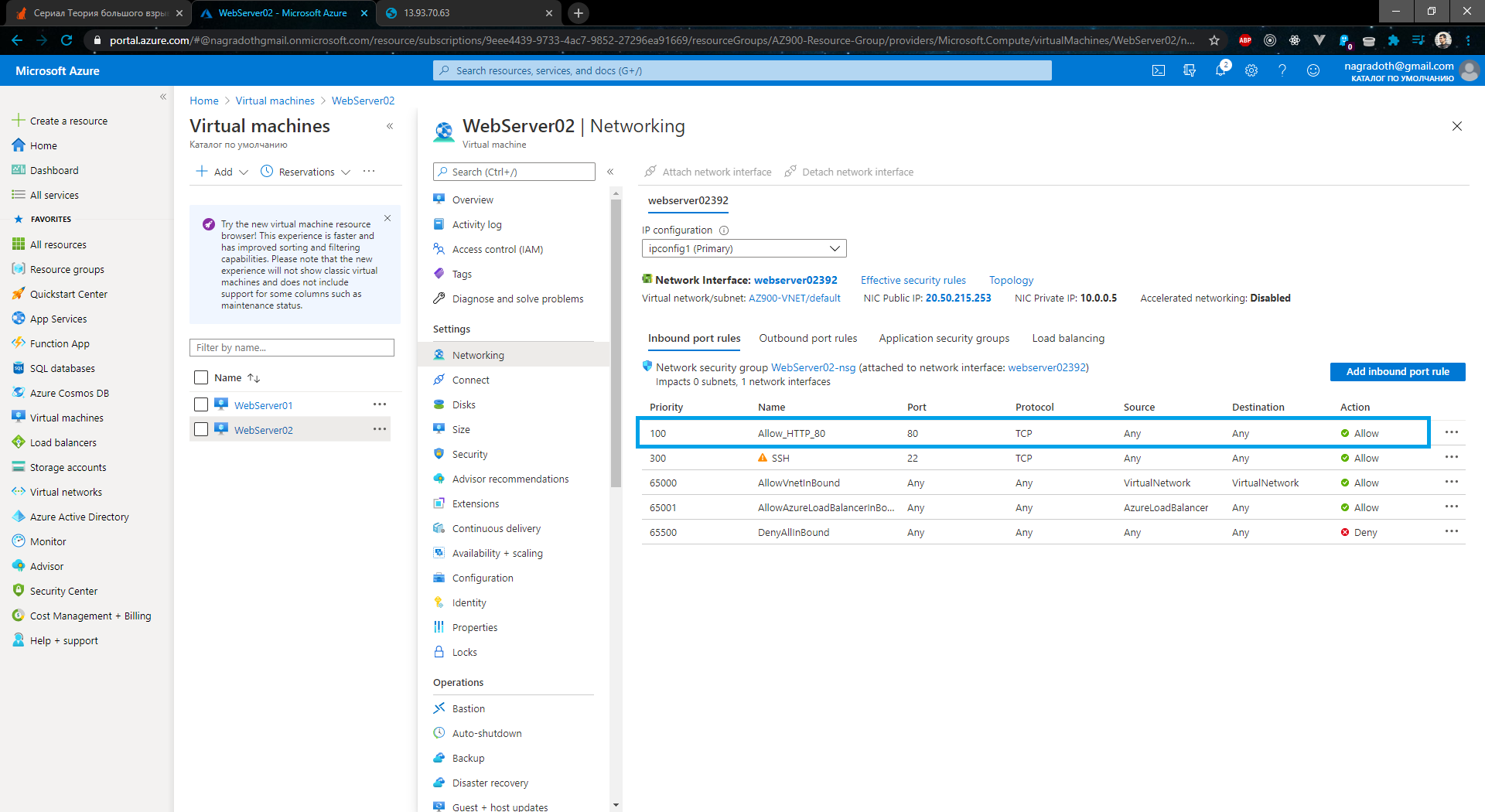
- Connect to your Webservers via SSH, update them, install Apache and so on.
Azure Traffic Manager is DNS-based traffic load balancer Azure Traffic Manager - DNS LOAD BALANCER
- Works with Hybrid cloud deployment - On + Premise + Azure Cloud. It can monitor your resources availability.
- Able to work between different regions.
- If you have 2 different regions - it can decide what the resource is the most suitable for end user (depending on latency)
- If your destination region in not available - can switch end user to another region.
Module 3: Exam Hints
Module 3 Exam Hints:
Exam Hints
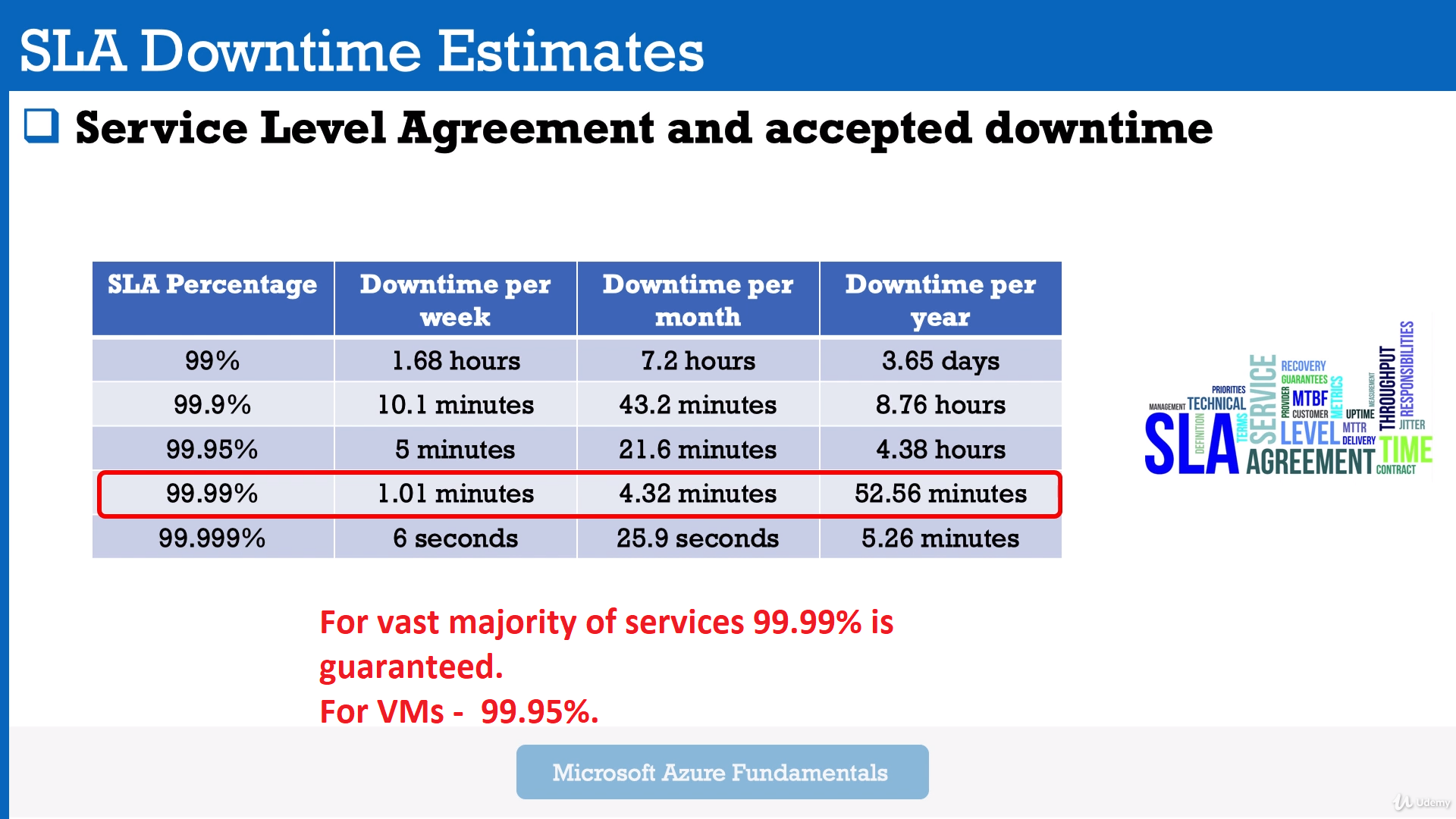
- SLA - Service Level Agreement
- DC - Data Center
- VMSS - Virtual Machine Scale Sets - work only with Load Balancer
- NSG - Network security Group - is a virtual firewall for your VMs. Different VMs can have Different NSGs applied. Tied with port configuration rules (Inbound & outbound traffic).
In other words - your network security rules destination is Virtual Network with your VMs. - ASG - Application Security Group - is a group of VMs with defined security policies for whole group.
In other words - your network security rules destination is a dedicated group of selected VMs.
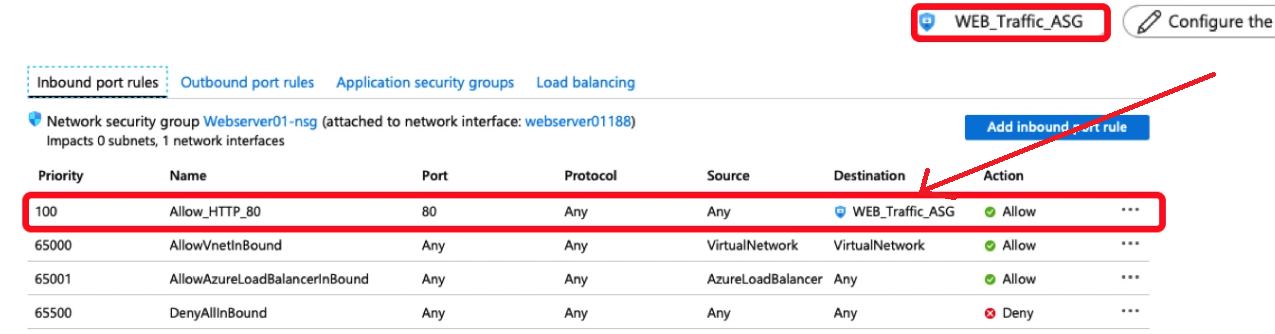
- Load Balancer could be internal Load Balancer - Within Azure Cloud, between your servers and SQL DBs.
Module 4: Azure Compute Options
Azure Compute Options, Introduction:
Azure Compute Options
Azure Containers Materials:
Azure Containers 101
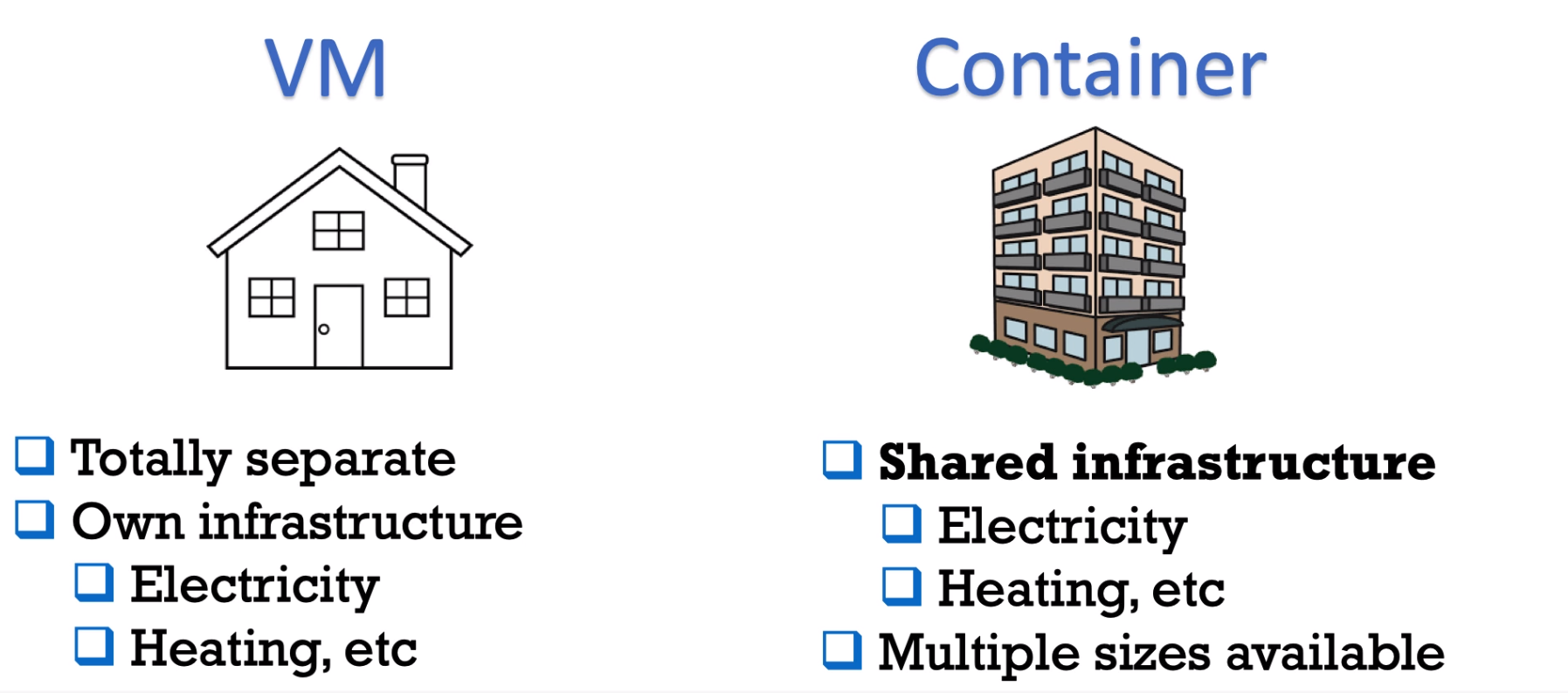
VM:
- VMs need infrastructure (server in Data Center)
- We need Host Operating System, i.e. Windows \ Linux \ Mac.
- We need Hypervisor: VMware, ESXi.
- You may do whatever you want with your VM - install different libraries, apps, update some apps.
Containers:
- Containers also need infrastructure
- Containers need Host Operating System: any kind of Linux OS.
- Instead of Hypervisor we need Docker Container Daemon - It's a process which runs behind the scenes in a Host Operating System. Managed and runs containers.
- Everything packed inside container: dependencies, binaries and so on. These apps packed into images.
Comparing Containers and VMs:
- Containers boot time - much faster than VM boot time
- VMs have Guest OS. Containers have no Guest OS.
- VMs Resource Demanding is high (CPU, RAM, Storage). Containers Resource Demanding is pretty low.
- VMs isolate your systems (environments). Containers isolate your applications.
- To run containers in Azure you might use Azure Container Instances (ACI).
- ACI - is PaaS. Allows you to upload and use your containers. ACI is good for a couple of containers.
- AKS is good for a fleet of them.
Tips:
- when you create a container - you have to text the image name. Name should be - mcr.microsoft.com/YOUR_SELECTED_CATALOG/ACI_OR_CONTAINER_NAME.
YOUR_SELECTED_CATALOG - is not required in simple cases. - DNS Label name - you have to select the container name to reach it after that using http. This name should be unique! 2.1) It's cool when Container name and his DNS name label are similar.
- To reach your container you have to copy FQDN (Fully Qualified Domain Name) and pass it into your browser URL.
Module 4: App Service (PaaS) - host WebApp, RestAPI, Mobile BE.
App service is PaaS.
Pricing is based on a selected Plan. 3 Plan options (1 of them is free and shared).
Usage:
- You can use App service if you don't want to configure VMs and don't care about infrastructure. Just upload your code to Azure and this code will be run.
1.1) You can upload your code from a github. - You can use App Service to Build & Deploy your web apps faster. You can scale your apps easier. With App Service you can use containerized web apps as well.
- You can get access to App Service and use it using Azure Cloud Shell (terminal right on the Azure Portal). Or using App Service menu.
Course Doc: Azure App Service
Module 4: Serverless: Azure Functions. Azure Logic Apps.
- HA - High Availability. Serverless ideas:
- App code runs based on triggers or events (run function when it receives a Http Request)
- Pay only for the duration your code runs.
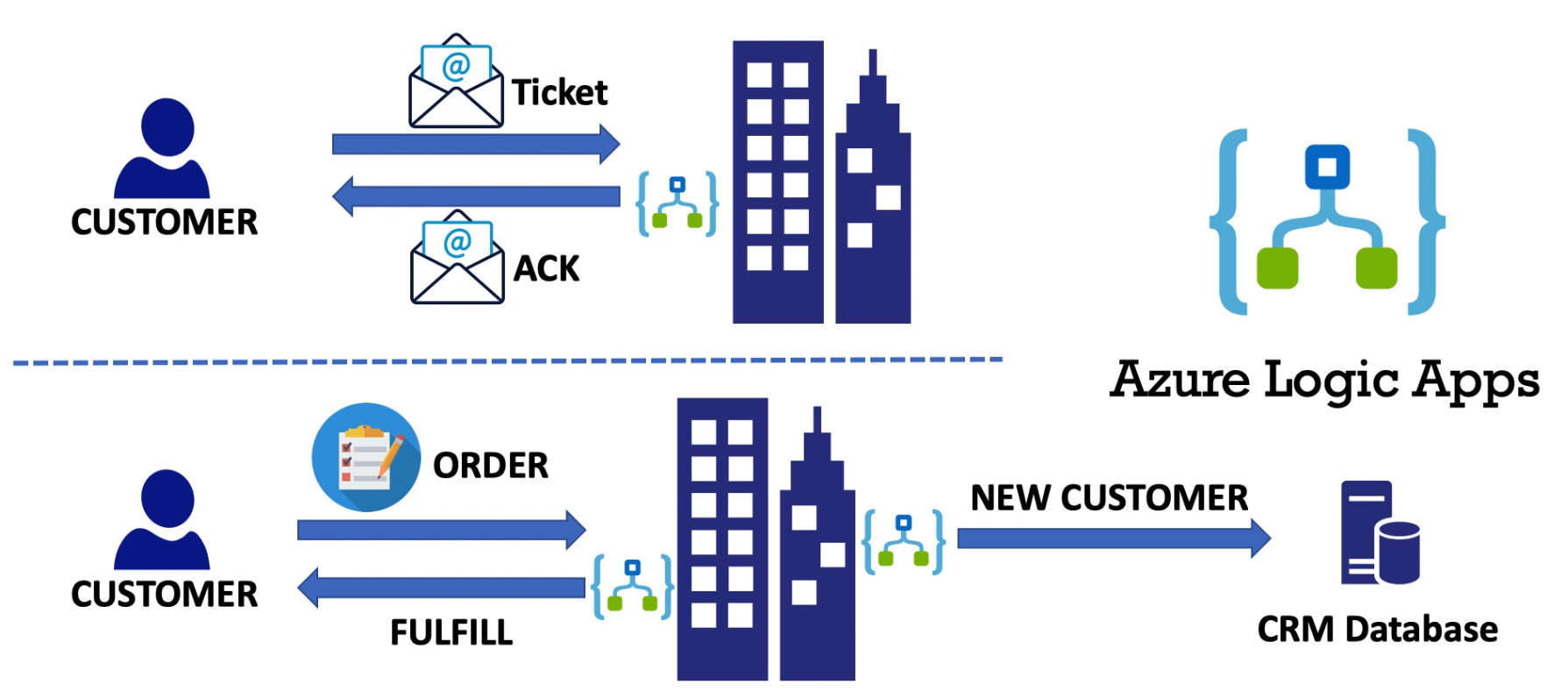
Azure Function vs Azure Logic App.
- Function runs a small piece of code triggered by event. Logic Apps Automate and orchestrate tasks. Function executes code while Logic App executes workflows (using prebuilt logic blocks) Workflow is to visualize, design, build and automate business processes as series of steps.
- Logic Apps is for situations when you need to integrate apps, data, systems and services across enterprises.
- Logic App could be a part of Schedule or Schedule itself.
- Logic App could be created using Azure Portal Visual Designer or Visual Studio.
Real example: Using the Logic App designer on the portal -> select RSS -> RSS Trigger on feeds.reuters.com/reuters/topNews -> then send an email on selected email.
Course Doc: Azure App Service
Module 4: Azure Event Grid.
Allows you to build applications with event-based architectures.
Course Doc: Azure Event Grid
Example: You subscribed to Azure Resource to know its status. For example - status of your VM. In EventGrid world:
- Select VM, Set EventHandler (set Logic App for example), if your VM stopped -> send an email with notification.
- Select VM, Set EventHandler (set Logic App for example), if your VM stopped -> turn your VM on again. It's one of possible ways to prevent your VM from being stopped.
You can work with any Azure Portal events or define your own events.
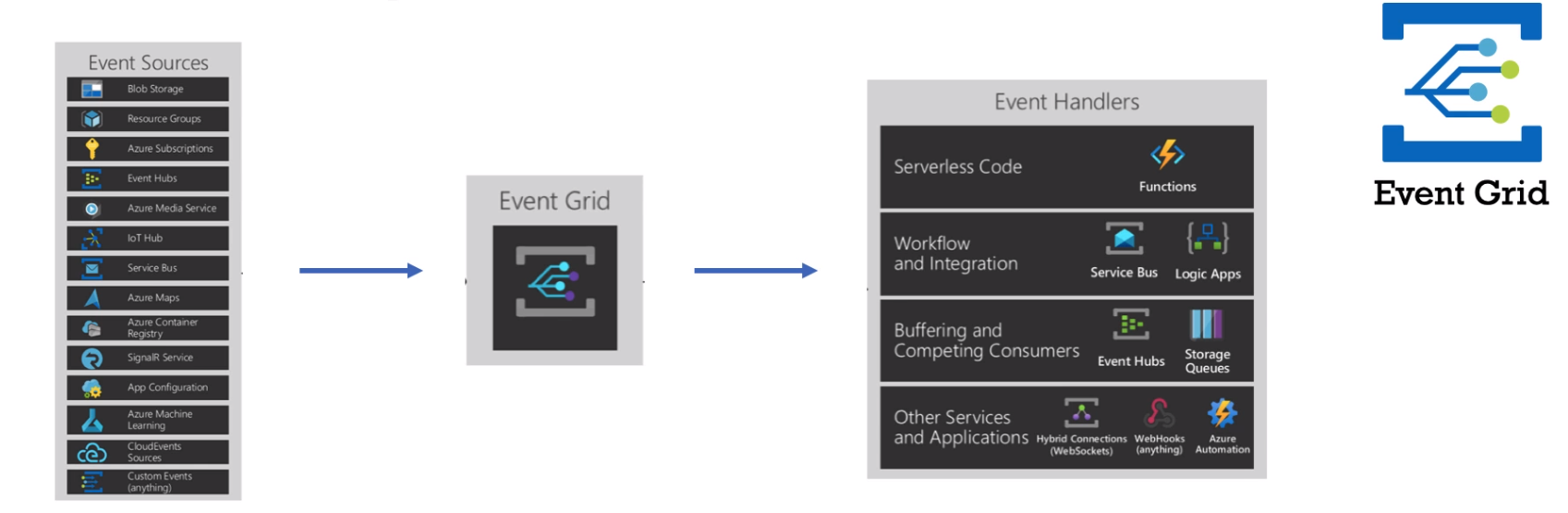
Module 4 Exam Hints:
Link to PDF: Module-4 Exam Hints
- Azure Compute Options is an on-demand computing service.
- 4 Options: VMs, Containers (Run with ACI or AKS), Azure App Service, ServerLess (Functions & Logic Apps)
- ACI - Azure Container Instances. Is PaaS.
- App Service - Http-based service for hosting web applications, REST APIs and mobile BE. Is PaaS. Based on your selected Plan (has free plan).
- Serverless - is abstraction of servers. Is PaaS. You shouldn't worry how it runs in the cloud. High Availability. Event-Driven.
- Logic Apps - your integration between business processes as a series of steps. (Example: Check RSS -> Get update -> Was Updated? Send an email. Everything in several clicks).
Link to PDF: Module-5 Azure Storage Fundamentals
- 4 Types:
- Azure Blob Storage - BLOB is Binary Large Objects. It is a scalable object store.
Good for unstructured data (text or binary data).
Suitable for:
1.1) Store images and files
1.2) Store video and audio
1.3) Log files
1.4) for BackUp and Restore purposes. For disaster recovery use cases. - Azure Files - managed file share
- Azure Queues - messaging store
- Azure Tables - NoSQL structured data
Module 5: Blob Storage (Azure Containers). Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2
Link to PDF: Module-5 Azure Blob Storage
BLOB is Binary Large Objects. It is a scalable object store. Good for unstructured data (text or binary data, but there is no hard restrictions).
1.1) Store images and files
1.2) Store video and audio
1.3) Log files
1.4) for BackUp and Restore purposes. For disaster recovery use cases.
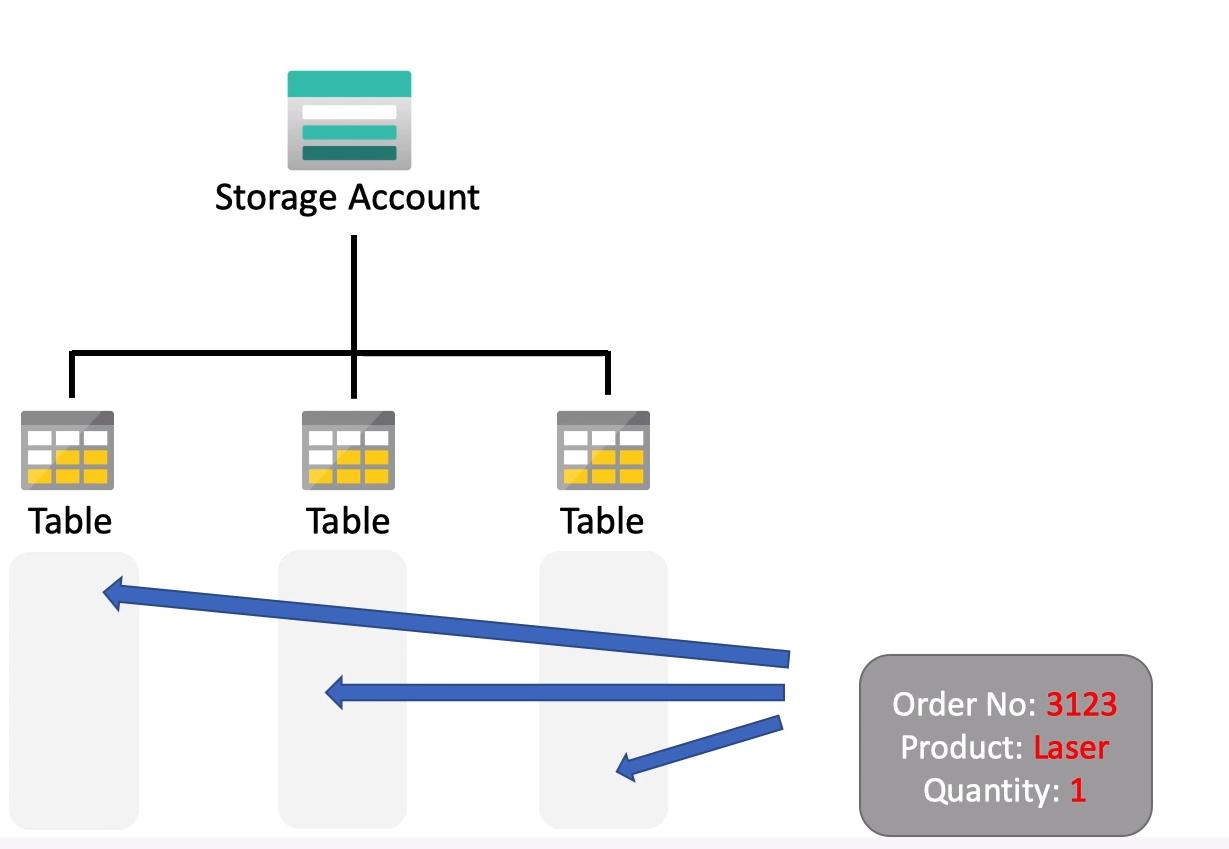
Storage Account (unique namespace in Azure) -> Container (like a folder) -> Blob-files (your actual files)
- Files are accessible via HTTP/HTTPS protocol.
- Support thousands of connections.
Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 is a data analytics solution for the cloud.
- It is built using two services: Azure Storage + Azure Data Lake Storage Gen1.
- Big Data analytics capabilities for structured and unstructured data.
- Scalable up to exabytes, 1M TB.
- Cost Effective
Tiers:
- Hot - frequently accessed data
- Cool - infrequently accessed data (you have to store your data at min 30 days). Cheaper than Hot.
- Archive - rarely accessed data (you have to store your data at stored min 180 days). Cheaper than Cool.
- Thus, we have multiple access tiers available, we can build a storage lifecycle policy (Cost-effective storage). Policy: HOT -> COOL -> Archive.
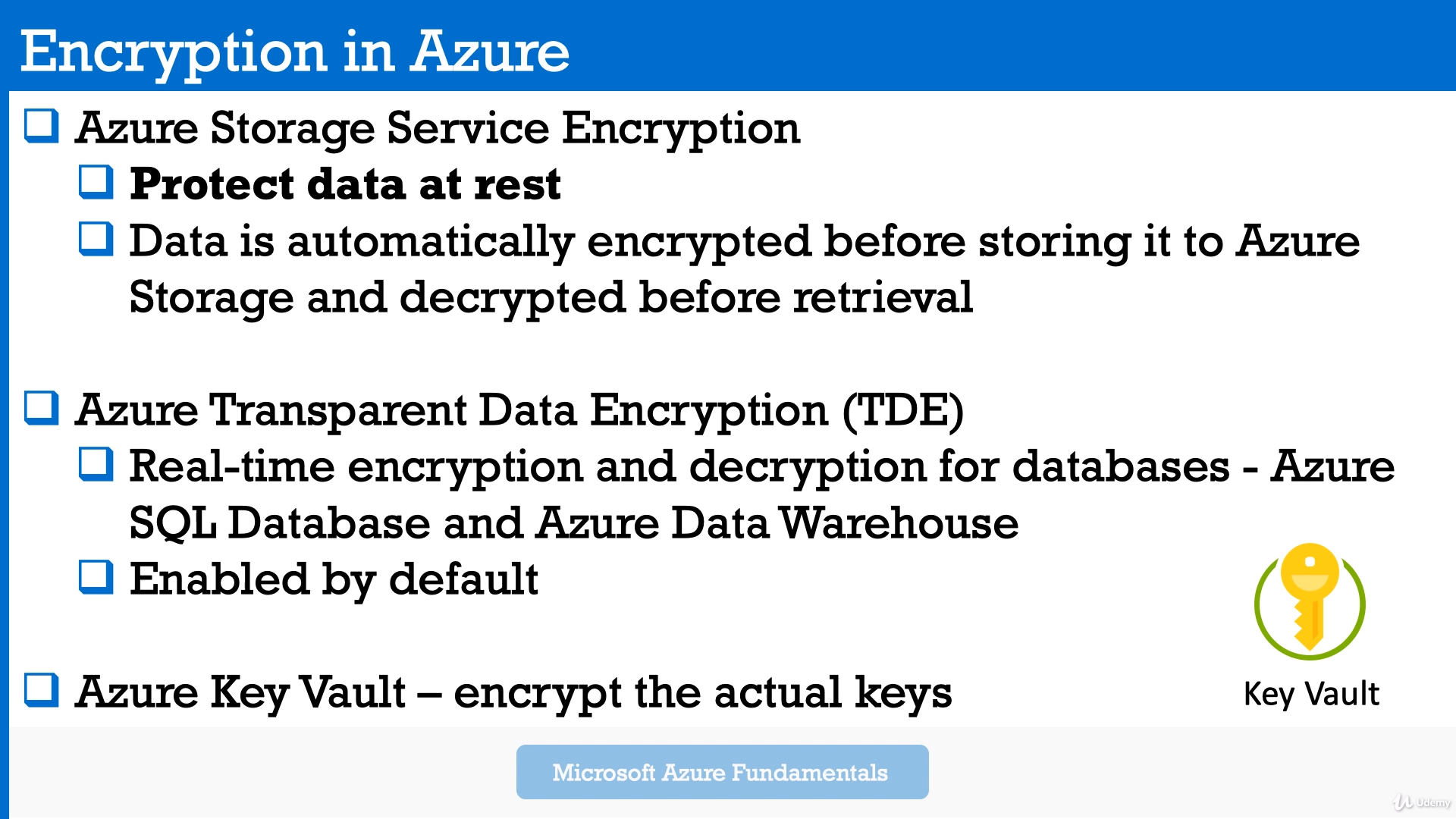
Automatically encrypts your data in Azure. 2 ways:
- Microsoft-managed encryption keys (Azure Storage Service Encryption - SSE)
- Customer encryption keys (client-side encryption)
Azure always replicates data in your storage to ensure durability and high availability.
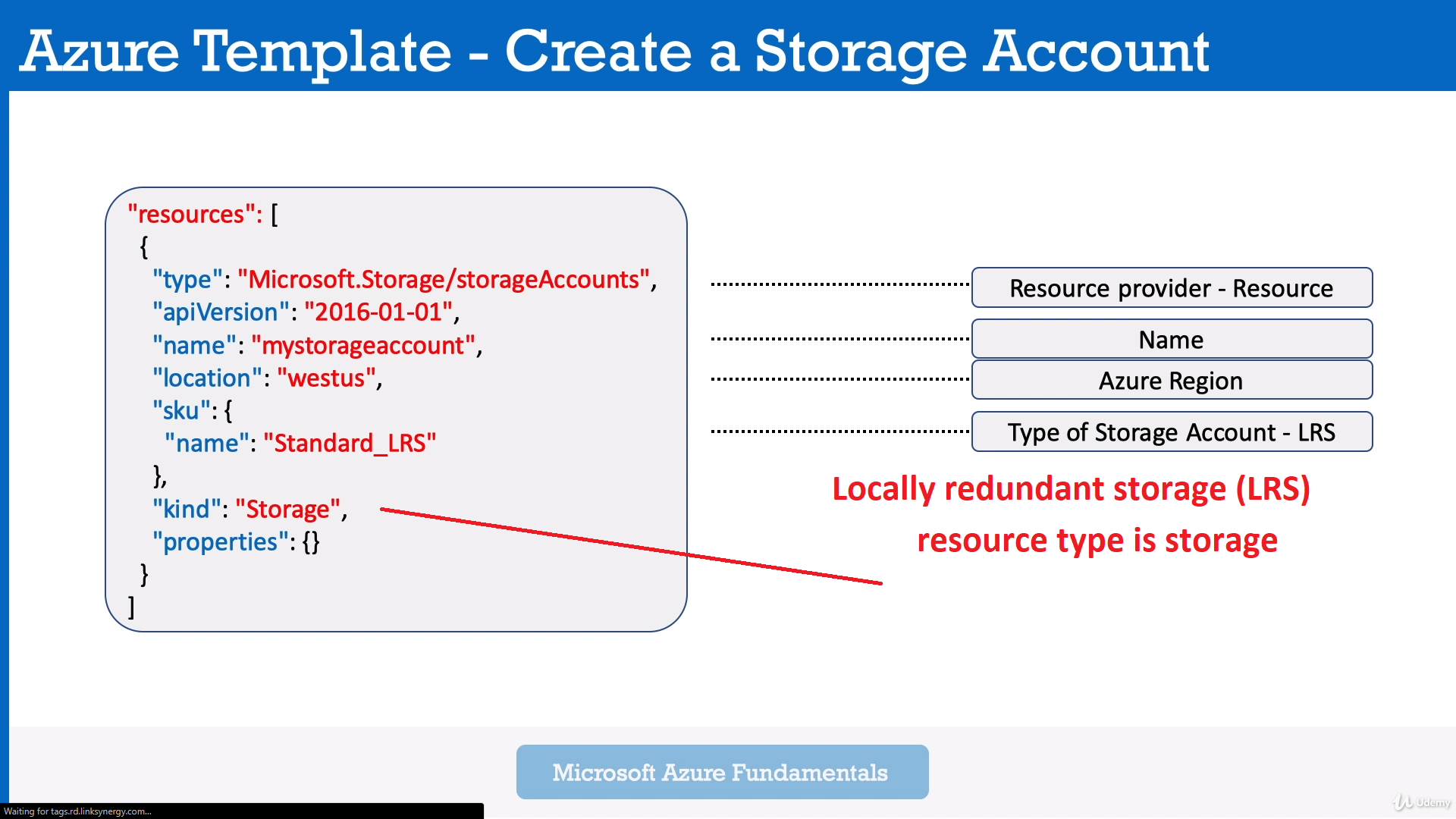
- "Local-redundant storage", "LRS". Can be replicated within Data Center. will be replicated 3 times in your DataCenter.
- "Zone-redundant storage", "ZRS". Across zonal Data Centers within region . Will be replicated on 3 storage clusters in all 3 AZs of the region.
- "Geo-redundant storage" "GRS". Across geographically separated regions. Will be replicated to a secondary region (min 300 miles away.)
- "Read-access geo-redundant storage", "RA-GRS". Provides read-only access in the secondary location. In Addition to "GRS". Preview Replica Types:
- "Geo-Zone-redundant storage", "DZRS" combines "ZRS" and "GRS". Data in 3 AZs in a 1st region and 1AZs in a 2nd region.
- "Read-access geo-zone-redundant storage".
- Redundancy option can be selected when account is created.
Module 5: Azure Managed Disks (Dedicated Virtual Hard Drive Disk For 1 VM)
Link to PDF: Module-5 Azure Managed Disks
Share files between Virtual Machines.
- Azure will manage the storage .VHD files (Virtual Hard Drives). It's just a volume where you can create a disk using "Disk Management" tool.
- Standard HDD
- Standard SSD
- Premium SSD
- Ultradisk
- OS disk - has preinstalled OS
- Temporary disk - short-term storage. Data can persist a VM reboot (in normal condition). Power off = data is lost.
- Data disk
99.999% of availability 11th 9's -> local redundant storage 16th 9's -> Geo-ZRS
-
Disks are isolated from each other to avoid Single Point of Failure (SPOF)
-
Fully integrated with AZ. They are protected from DataCenter failures.
-
Assign specific permissions for a managed disk to one or more users.
-
Every Azure VM machine comes with OS disk + Temp disk. And you are able to attach Data disk.
Section 5: Azure Files Shares (Disks to share info between Virtual Machines). Serverless
Azure file storage is a storage which you may use to share persistent information between different Virtual Machines.
Link to PDF: Module-5 Azure File Storage
Storage Account -> Azure Files -> files for Windows VM01 and Windows VM02.
- Azure File Shares con be mounted by both: On-Premise and Cloud machines.
- Access via SMB Protocol
- Access via NFS Protocol
- Can be mounted (attached) by any machines: on-premise and cloud machines.
- Work on Windows, Mac and Linux.
- Azure takes care of hardware and software updates + system patching
- Work with Azure CLI, Powershell.
- No Windows maintenance.
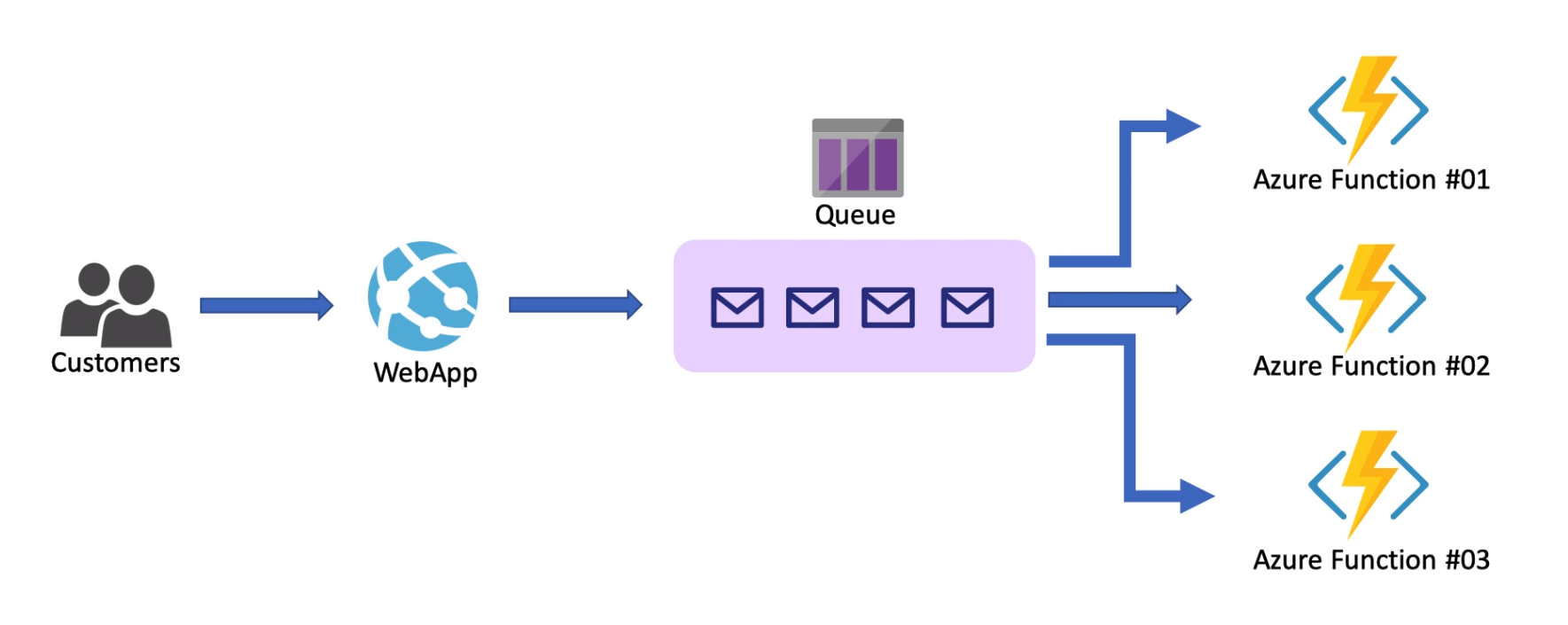
Module 5: Queue Storage
Link to PDF: Module-5 Azure Queue Disks
- For storing large number of messages, accessible from anywhere.
- For reliable messaging between application components.
- Provides asynchronous message queueing for communication between app components.
Storage Account -> Storage Queue -> Queue (Container for your messages.)
Example of queue: incoming queue, outgoing queue, returned messages.
Module 5: Tables Store. for NoSQL data (Excel like structure with 2 Primary columns)
It's a "Key / attribute" storage with a schemaless design. Something like between Redis (key-value) and Mongo (BSON). Or even Excel.Link to PDF: Module-5 Azure Managed Disks
For storing structured NoSQL data, non-relational.
- Table will scale as demand increases.
- Doesn't have fixed data structure.
- Process up to 20.000 rows\s per Storage Account
- Process up to 2000\s per Table
Module 5 Exam Hints:
Link to PDF: Module-5 Exam Hints
Module 6: Cosmos Database. Document Database
Link to PDF: Module-5 Azure CosmosDB
- Multi-model database service.
- It's a document DB. Format is JSON.
- Schema-agnostic, but generally classified as NoSQL database
- horizontally scalable.
- Global Distribution - transparent multi-region distribution. It replicates your data in multi-region environment transparently.
- Regional presence - 56+ regions
- Highly available - 99.999%
- Elastic Scale
- Low latency guarantee (<10ms of 99% of requests)
- No Schema or index management. Can have different properties or formats.
- SQL (core API) - Also has JSON Formatted documents, but works with SQL-query syntax.
- Cassandra
- MongoDB
- Gremlin
- Azure Table Storage
Database Account -> Database -> Container (Table \ Collection) -> Items (rows of data \ elements)
- The cost of usage depends on Request Units - read, insert, delete, query.
- No matter how much CPU or RAM used.
Items in a container are divided into distinct subsets called logical partitions.
Module 6: SQL Database. Managed Service (like PaaS).
Link to PDF: Module-5 Azure Database Fundamentals
- general-purpose relational Database-as-a-service (DBaaS).
- Managed Service (like PaaS)
-
Single - isolated database, fully managed.
-
Elastic Pool - collection of single databases with a shared set of resources.
-
Managed instance - A fully managed instance of SQL Server. Full SQL server capabilities (vs Single) - Allows you to easy accommodate and migrate your database to the cloud.
-
Azure SQL Database Server - is a center administrative point where you are able to configure your databases.
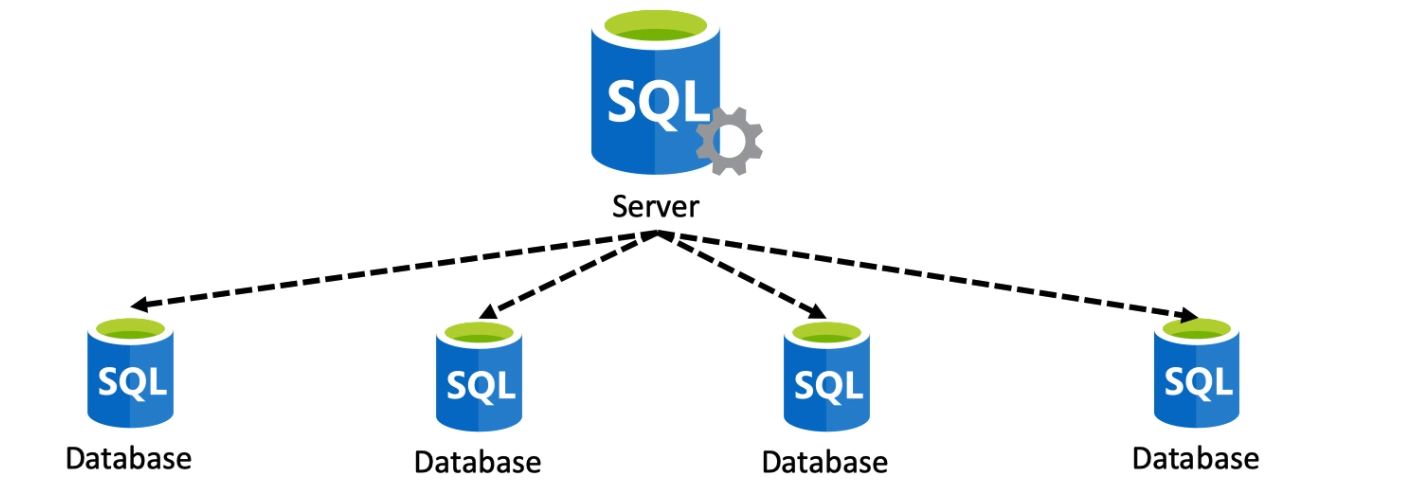
- Database Transaction Unit (DTU) - With DTU you are able to scale storage with compute at the same time
- Virtual Core (vCore) - with vCore you are able to scale storage independently of compute (virtual cores and storage).
- Serverless model - vCore based.
Tip:
- your traditional sql server license on On-premise database - may be used only with vCore model.
- when you create SQL Database you must select Server - this Server is SQL SERVER.
Module 6: MySQL. PostgreSQL
Link to PDF: Module-6 MySQL Link to PDF: Module-6 PostgreSQL
- HA
- Pay-as-you-go pricing
- Single Server - allow only vertical scaling
- Hyperscale - scales db horizontally (multiple machines of the same type), faster responses on large datasets.
It goes as a part of server group with coordinator node and worker node roles.
- support automatic backups
- built-in security: in-motion or at-rest.
Module 6: Azure SQL Managed Instance ("AZURE SQL"). PaaS. Expensive! Fully managed instance-as-a-service with 100% features of SQL Server Database
EXPENSIVE CHOICE: minimum is 640eur per month for 4-vCore and 32GB of Storage Deploying up to 6 hours
Link to PDF: Module-6 Azure SQL Managed Instance
- Fully managed isolated instance-as-a-service with 100% features of SQL Server Database.
- Best option for most migrations to Azure Cloud (let you shift your on-premise customers to the cloud).
You literally can take your application as it is without modifying it and running it afterwards in the cloud. - Reduce management overhead. Patching, versioning and updates.
- High availability. 99,99%
- On-premise applications which you would like to switch on Azure Cloud database (and migrate all data there).
- For modern applications as well created from scratch.
- Network Group
- Route table
- Virtual network
- Everything for databases
- PaaS, quick provisioning and scaling.
- Combines best features of SQL database & Server Engine.
- 99,99% of availability. HA.
- vNet (virtual network) is not connected to your database. It's in isolated environment and isolated from another either.
- Azure Active Directory (AD) authentication. SSO Support.
- You can use Azure resource manager API for automating provisioning and scaling. (you can do provisioning manually or automatically via Azure resource manager API)
- vCore - allows you to change compute, memory and storage independently, based on your workload needs.
- Azure SQL Managed Instance is available in two service tiers (both options has 99,99% of availability):
- General Purpose
- Business critical (low latency)
Module 6: Azure Database Migration Service. Seamless migrations from multiple database sources to Azure Cloud
- Migration Service is a service designed to enable seamless migrations from multiple database sources to Azure Cloud. Link to PDF: Module-5 Azure Database Migration
Lost of scenarios described in the official doc. Different database sources and different available database destinations (in Azure of course). Microsoft Documentation for Azure Database Migration Service
- Support different migration scenarios from on-premise to cloud database: offline (one-time) and online (continuous sync)
Module 6 Exam Hints:
Link to PDF: Module-6 Exam Hints
Module 7. Other Azure Core Services. Networking. IoT. BigData. AI and ML. Bot Service. DevOps in Azure. GithubActions in Azure.
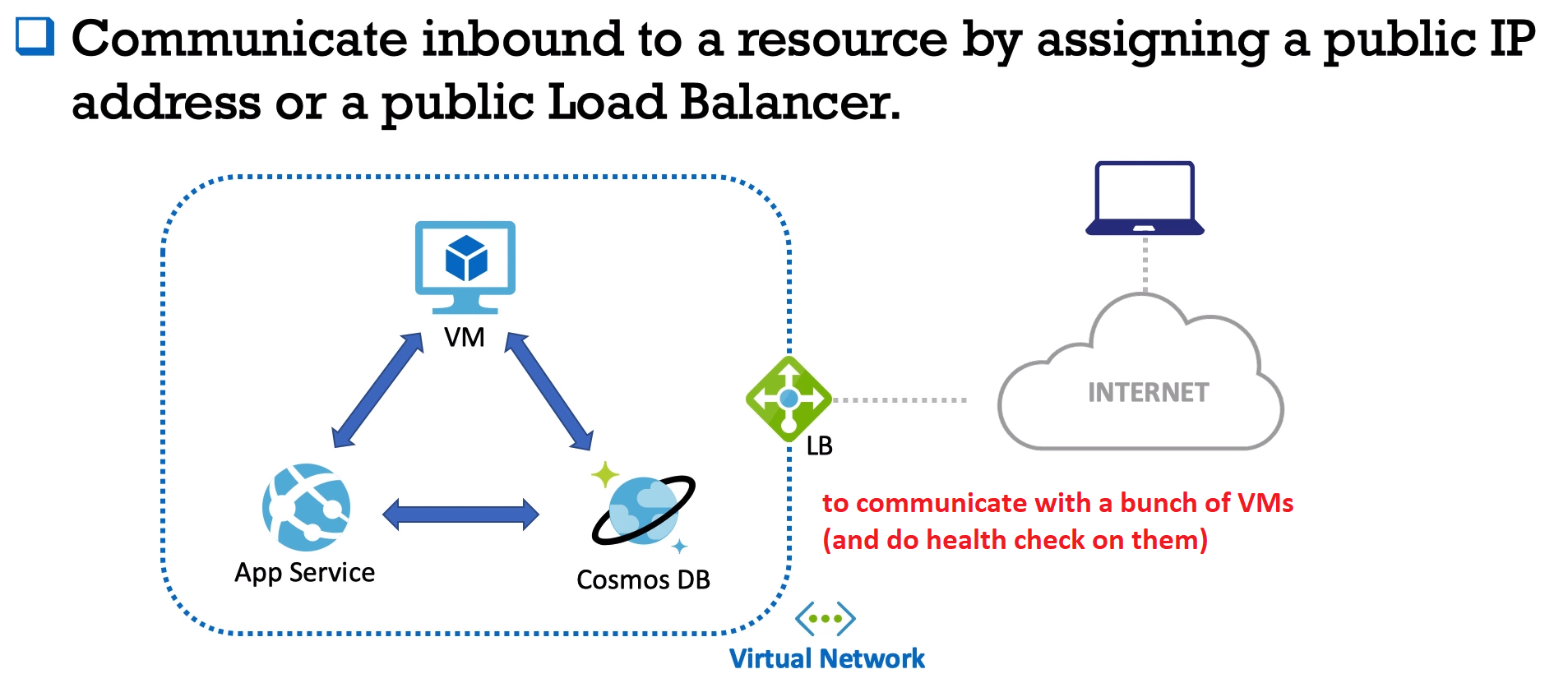
Module 7: Networking in Azure Cloud. Connectivity services (vNet, ExpressRoute, VPN Gateway, LoadBalancer, Application Gateway). Application Delivery Services(CDN).
- Connectivity services: vNet, ExpressRoute, VPN Gateway.
- Application Protection Services - part of Module 10. Security Related Services: DDos protection, Firewall, NSGs (Network Security Groups), WAF (Web Application Firewall).
- Application Delivery Services - CDN, Load Balancer, Application Gateway.
- Network Monitoring Tools - part of Module 9. Azure Monitor, Azure Service Health, Network Watcher.
vNet - fundamental building block for your private network in Azure (private DC).
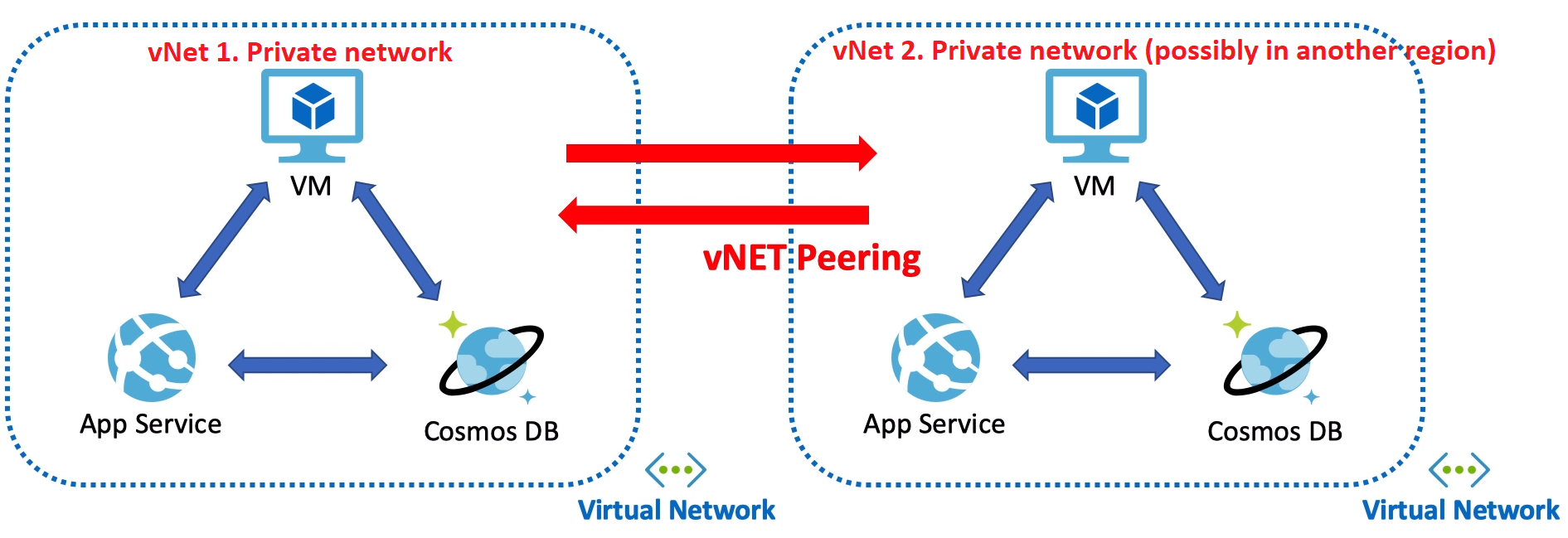
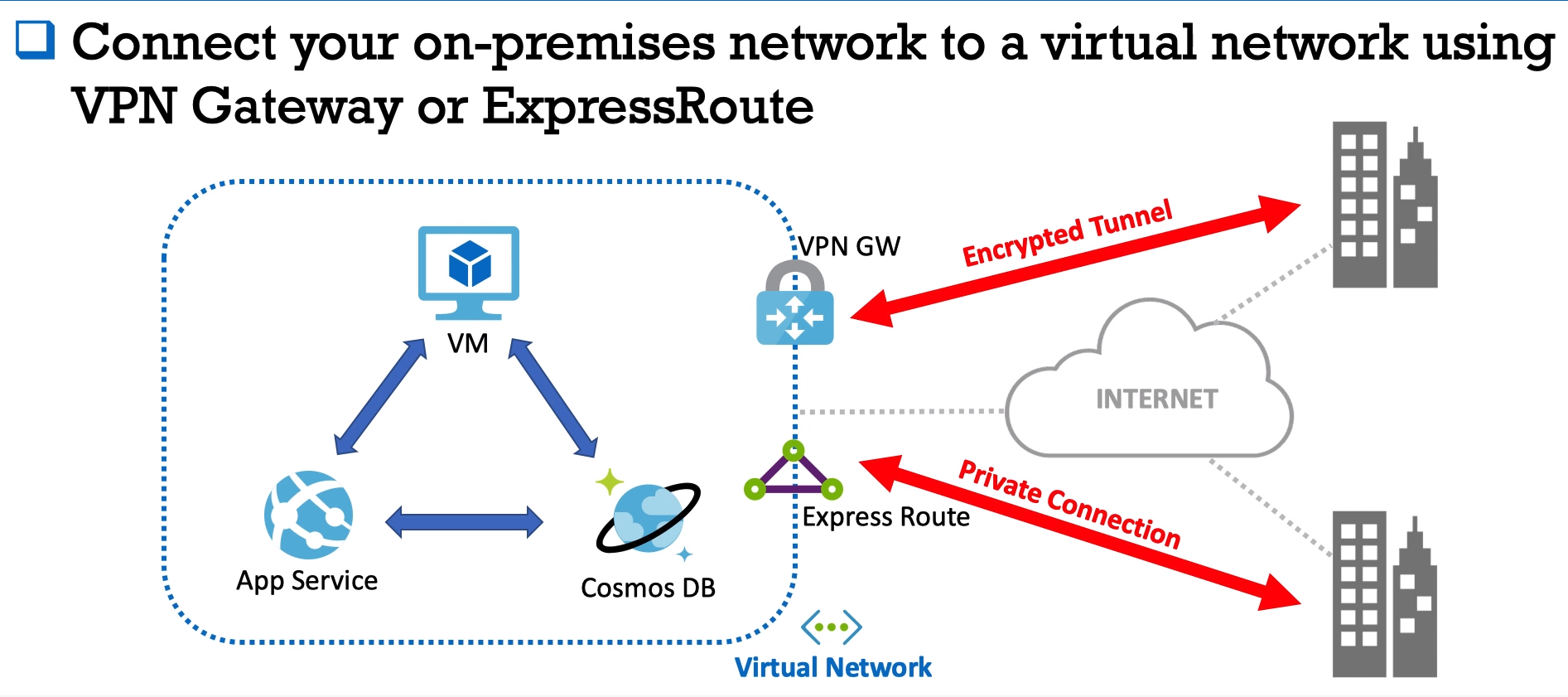
- You may use these two options to connect your on-premise network to a vNet in Azure Cloud.
- Also, VPN Gateway may allow you to connect to your azure services from your laptop if you are in the airport or in any other public zone.
- Express Route only to connect your On-Premise DC to Azure Cloud.
###Difference:
- Express Route - is a private dedicated tunnel. It is an AWS Direct Connect in AWS Cloud world.
- VPN Gateway traffic goes through public networks.
- To build ExpressRoute you have to ask your regional Azure DC to make this link.
Delivers high-bandwidth content to users by caching their content at strategically placed physical nodes across the world.
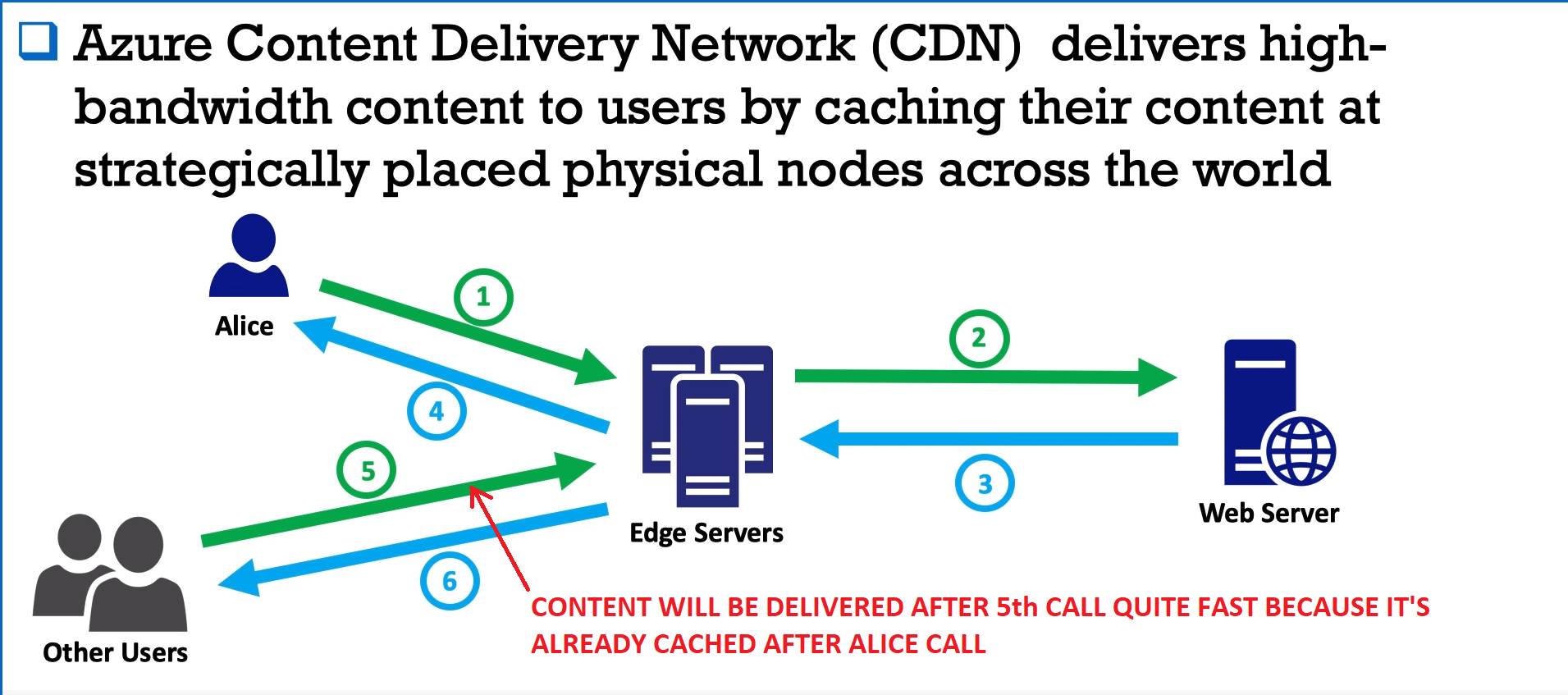
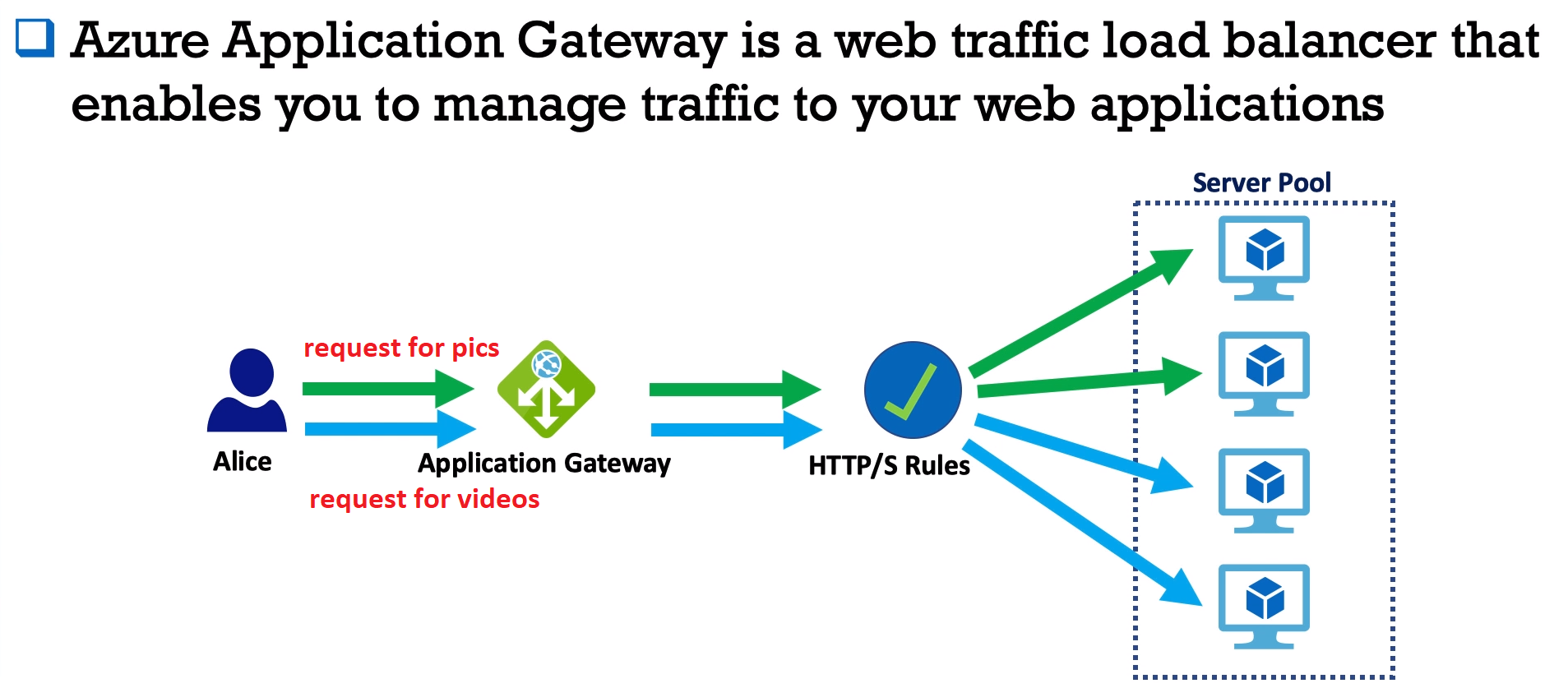
- Web Traffic - is a Load Balancer that allows you to manage traffic to your web application using rules.
- Has Http\Https rules. For Example Content rules - some info will come from one VMs (pictures), another kind of inro will come from another bunch of VMs (videos).
Module 7: Azure ExpressRoute (Some info in prev block). ExpressRoute Premium. Like AWS Direct Connect
- Partner Edge on the pic - is a Microsoft Partner or another company who provides an ability to connect via their dedicated links to Microsoft Edge and Microsoft Resources.
- Layer 3 connectivity (IP-level in OSI network model)
- BGP - Border Gateway (Routeway) Protocol.
- HA support for all peering locations with primary and secondary connections.
- SLA - service level agreements. Microsoft guarantees update connection.
- You are able to get Private Global Connectivity with ALL regions if you choose ExpressRoute Premium
- Unlimited Data: Flat fee per month. Unlimited data.
- Metered Data: Monthly fees. Inbound traffic is out of charge, outbound is charge per Gigabyte. (Cost varies from region to region)
- Premium add-on (Premium Circuit): 1 or 2nd option of prev two + more routes allowed (private peering, from 800 up to 10000 routes) + global connectivity services.
Module 7: Azure IoT. IoT Hub. IoT Central (Paas)
IoT Hub can route messages to Azure Blob Storage and Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2..
- Smart houses, Smart phones, Smart trucks. Connected world I would say.
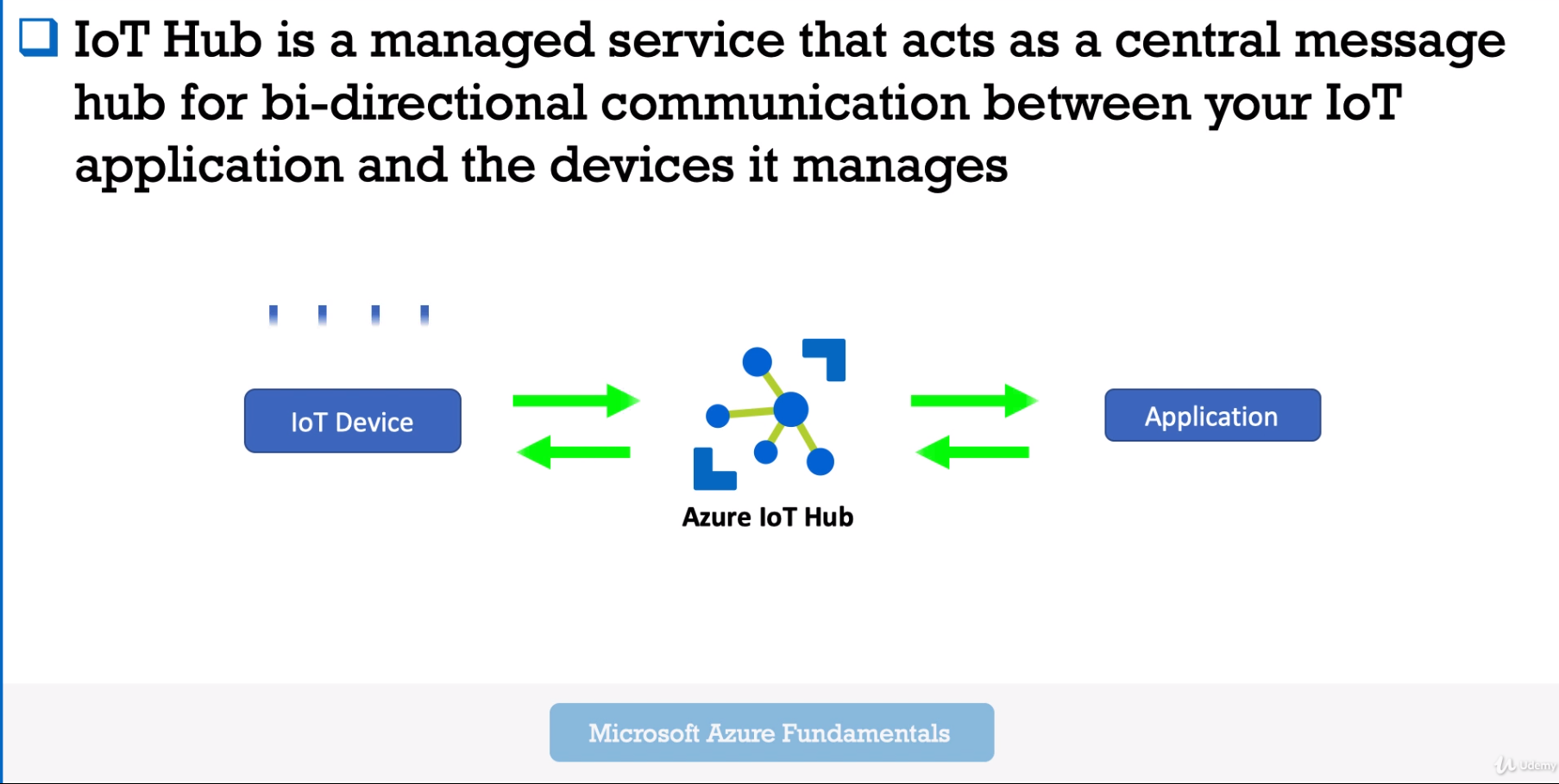
Azure IoT Hub - managed Service, central message hub for bi-directional communication between your IoT apps and devices.
- To reduce the cost of developing, managing and maintaining enterprise-grade IoT solutions.
- Cloud-hosted IoT solutions for your organization: IoT deviced connected to your cloud-based Application(s) and your Cloud-based Application.
Module 7: Azure BigData. Azure SQL Data Warehouse (now known as Azure Synapse Analytics). PaaS.
As with all PaaS services from Microsoft, SQL Data Warehouse offers an availability SLA of 99.9%. Microsoft can offer 99.9% availability because it has high availability features built into the platform
- Works with SQL, with Azure Blob Storage, Azure Cosmos, Azure Data Lake.
EXAM HINT: Think about it like about open-source database: MySQL or PostgresSQL.
- You can work with Apache Hadoop, Apache Spark, Apache Kafka.
- Can be integrated with other services: Data Factory, Data Lake Storage.
Module 7: Azure AI and ML .Machine Learning. Azure Machine Learning and Azure Machine Learning Studio (Classic). NOT AVAILABLE IN PORTAL. NAVIGATE TO ml.azure.com
NOT AVAILABLE IN PORTAL. NAVIGATE TO ml.azure.com
- Can use without writing code (in designer)
- you can use designer or SDKs and CLI to prep data, write code, train and deploy machine learning models.
- Adds scalability and enterprise security.
Module 7: Azure Bot Service
- Azure Bot Service is Microsoft AI chatbot offered as-a-service.
- Monthly subscription.
Module 7: DevOps in Azure. Azure Boards, Azure Pipelines, Azure Test Plans, Azure Repos, Azure Artifacts, DevTest Labs
- Azure provides several services that provide a solution for creating step-by-step production and continuous improvement chain.
- Enables to manage VMs and PaaS resources without waiting for approvals.
- You can test the latest versions of apps and speed up the process of creating and terminating testing environments.
Module 7: GitHub, GitHub Actions for Azure
Link: Module-7 Azure GitHub Actions
- GitHub Actions enables you to create custom software development life cycle (SDLC) workflows directly in your GitHub repo.
- With GitHub Actions you can build CI (Continuous Integration) and CD (Continuous Deployment) in your repository.
Module 7 Exam Hints:
- vNet - fundamental block of your "Private DC" in Azure.
- vNet Peering - communicate between different vNets within same or different regions.
- Azure LoadBalancer - public IP address to your resource. Also possible to make LoadBalancer as a private inbound point (between different Azure resources, VMs and DBs)
- VPN Gateway - Encrypted Tunnel throughout public network (internet)
- Express Route - like Aws Direct Connect. Private dedicated link from your on-premise DC to Azure.
- Application Gateway - LoadBalancer + Https rules. (for example split your content by type between sources)
- IoT Hub - central message hub for bi-directional communication between your IoT application and devices.
- IoT Hub can route messages to Azure Blob Storage and Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2.
- IoT Central - PaaS. IoT Application Platform that reduces burden and cost of developing, managing, maintaining IoT solutions.
- Azure BigData - Azure SQL Data Warehouse. Azure DataBricks. Azure HDInsight.
- Azure SQL Data Warehouse - cloud-based data warehouse. You can run high-performance analytics and massively parallel processing (MPP).
- Azure Databricks - Apache Spark-based analytics platform.
- Azure HDInsight - cost-effective enterprise-grade service, but only for open source analytics.
- Azure ML Machine Learning and AI - Machine Learning Studio (classic) and Machine Learning Studio (also known as Machine learning Studio (preview)).
- Azure Machine Learning Studio (classic) provides designer, SDKs and CLI to quickly prep data, train and deploy machine learning models.
- Azure Machine Learning is not
- Azure Bot - chatbot based on ML.
Module 8: Azure Resource Manager (Like AWS Cloud Formation)
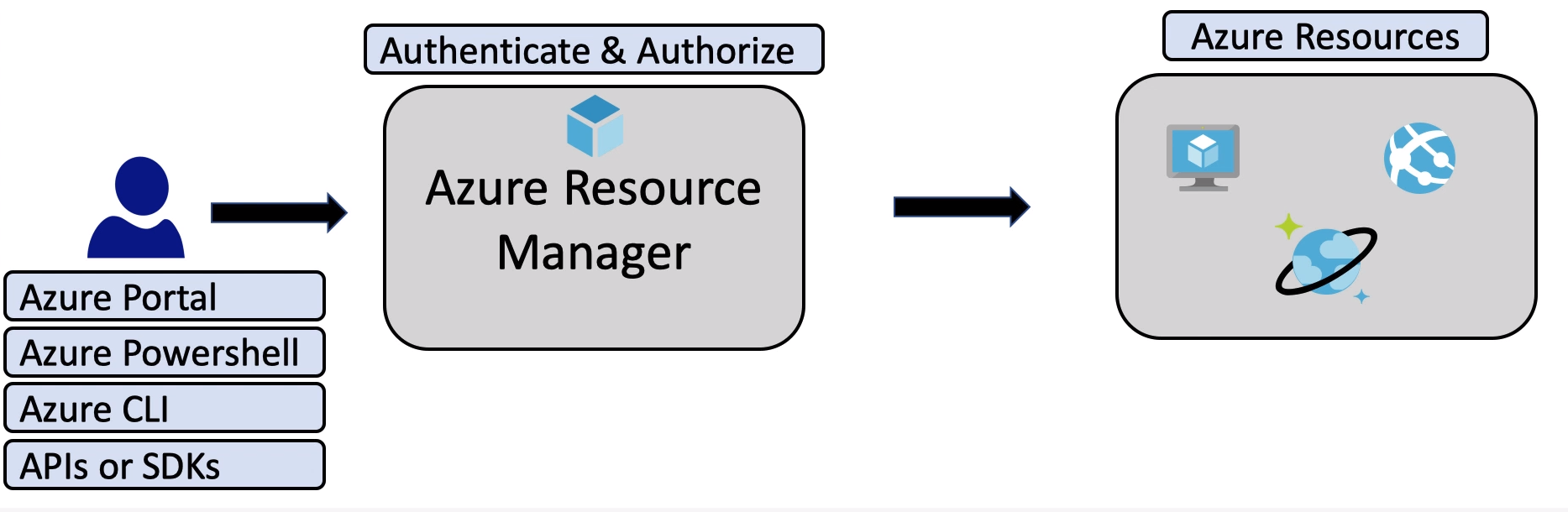
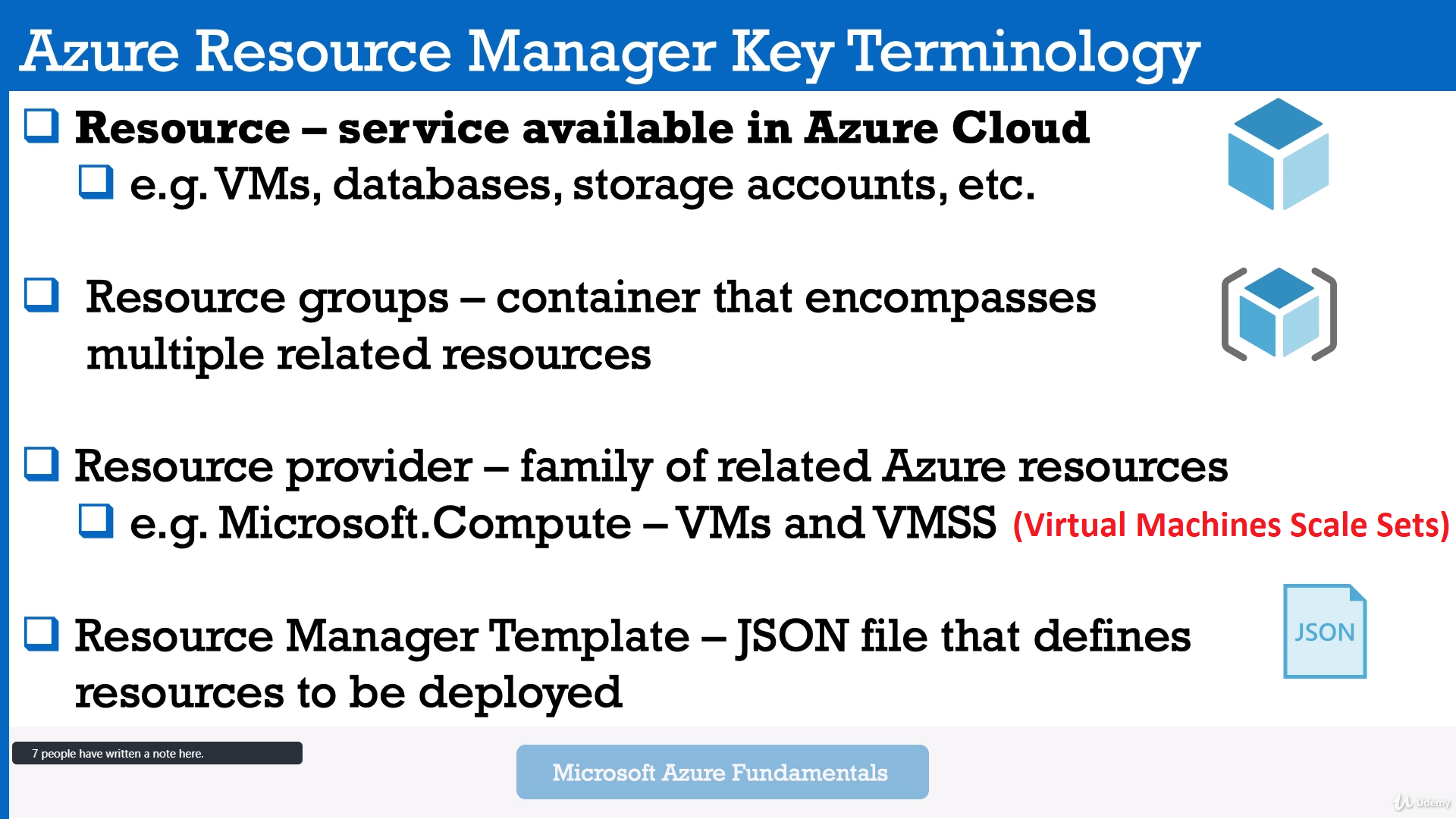
Azure Resource manager - is a deployment and management service in Azure.
After being authorized it allows you to manage any of your resources in Azure (create,delete,update containers, storages, VMs and so on).
Module 8: Azure Policies.
Link: Module-8 Azure Policies
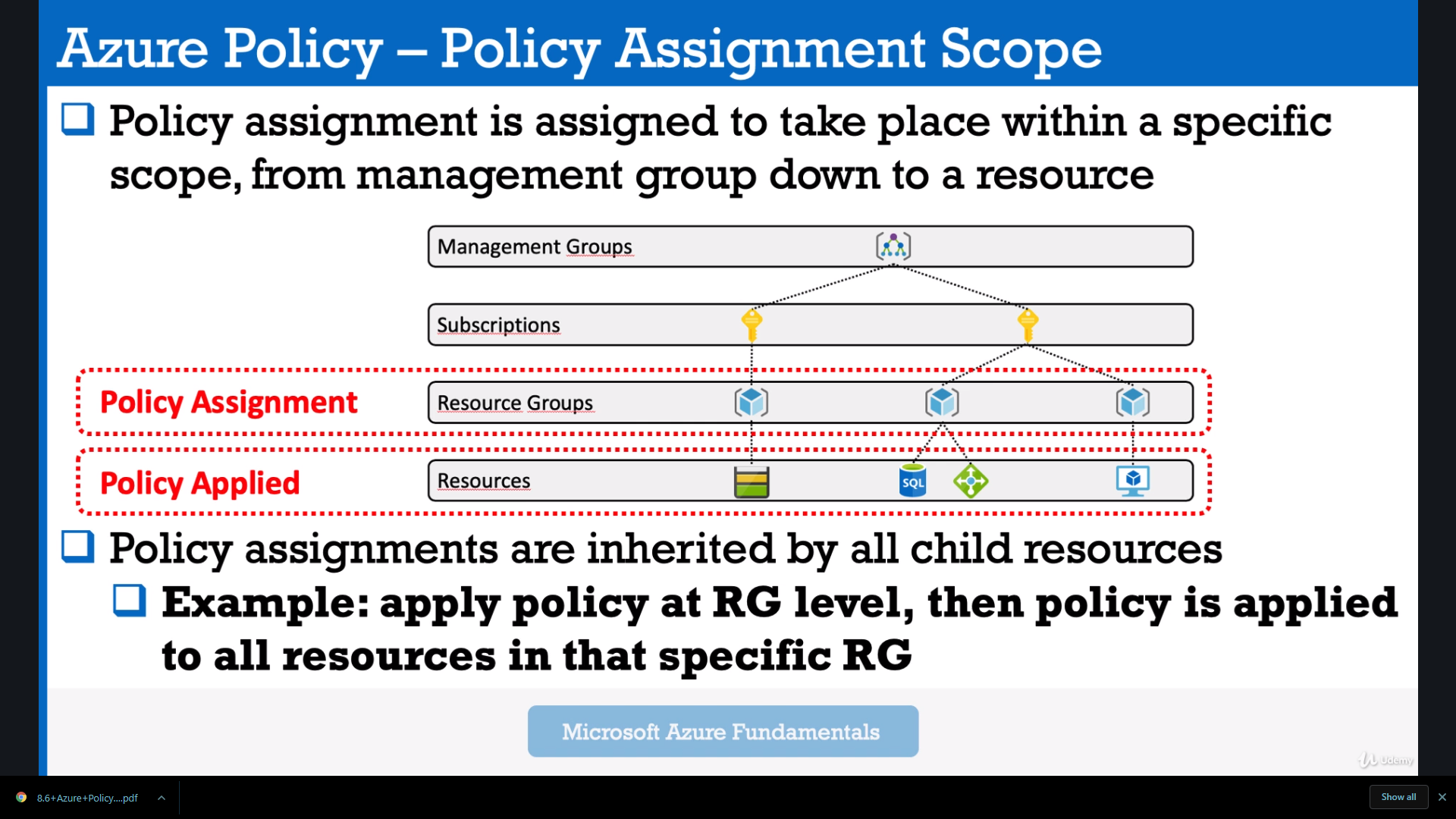
Policies allow you to create rules or restrictions for any actions. For example - to let you create only B1s tier Virtual Machines.
So we create the policy and then you have conditions, like when to enforce the specific policy and the effect, the action, what to enforce.
So if you apply it for example in the middle resource group then the SQL database and also the load balancer will have to comply with the policy definition.
-
There are also some built in Azure policies available, by default covering most common scenarios.
-
So for example, Allowed locations - new resources, as I said, to be deployed only in specific locations, allowed virtual machines SKUs, so only specific VM SKUs to be used, but you can also enforce tag and its value and we have talked about tags in a previous lecture.
-
So enforcing a required tag, but also its value to a specific resource.
-
So what if you need to apply multiple policies at once ? So initiative definitions simplify managing and assigning policy definitions, by grouping a set of policies as one single item.
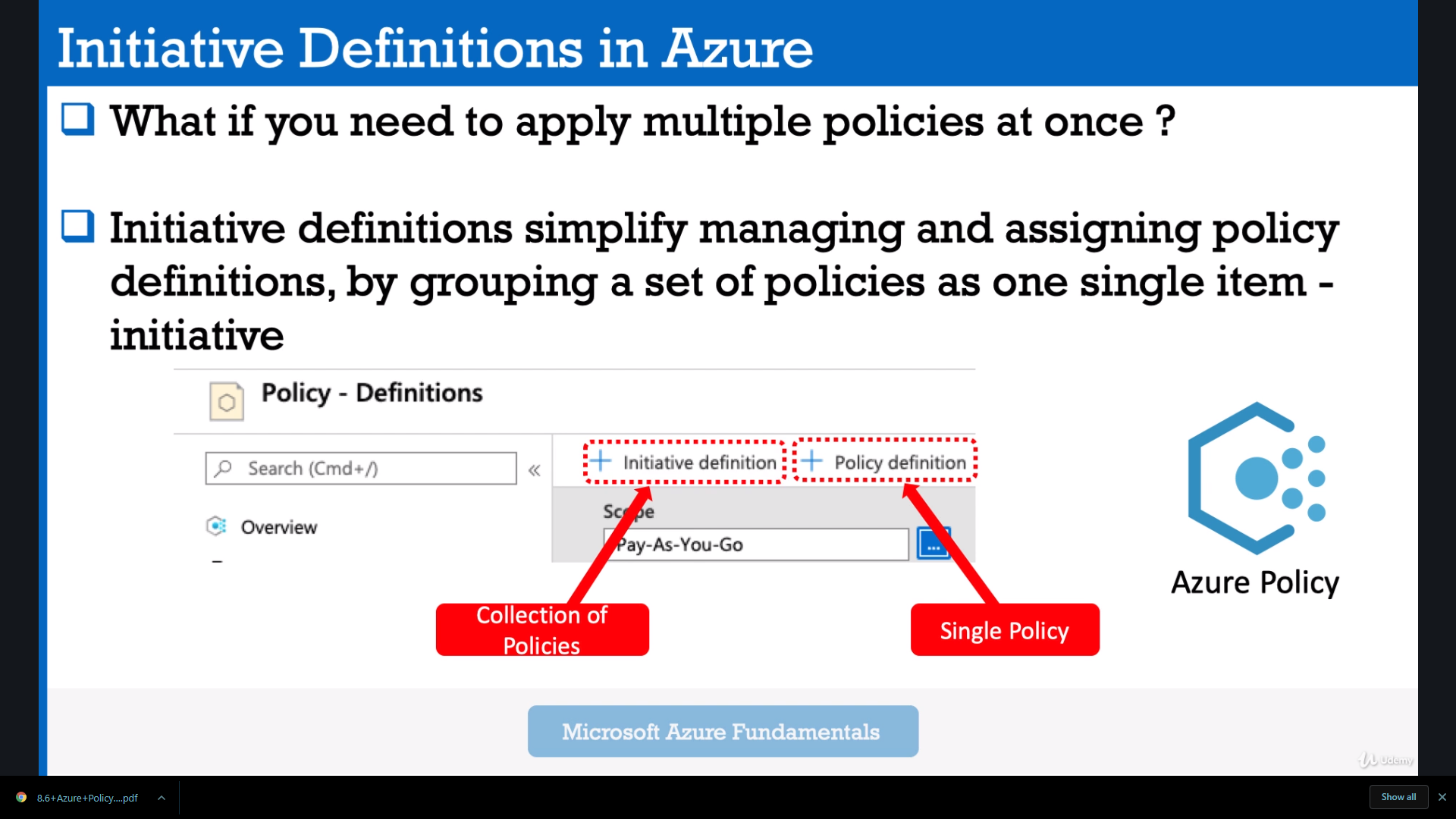
-
So in the Azure portal, you can just create a single policy or use an existing one and edit it in order to create a new one, or you can create an initiative.
So that is grouping a set of policies and using that as a single one item.
It's the bind between resource (or resource group or something else) and initiative or policy.
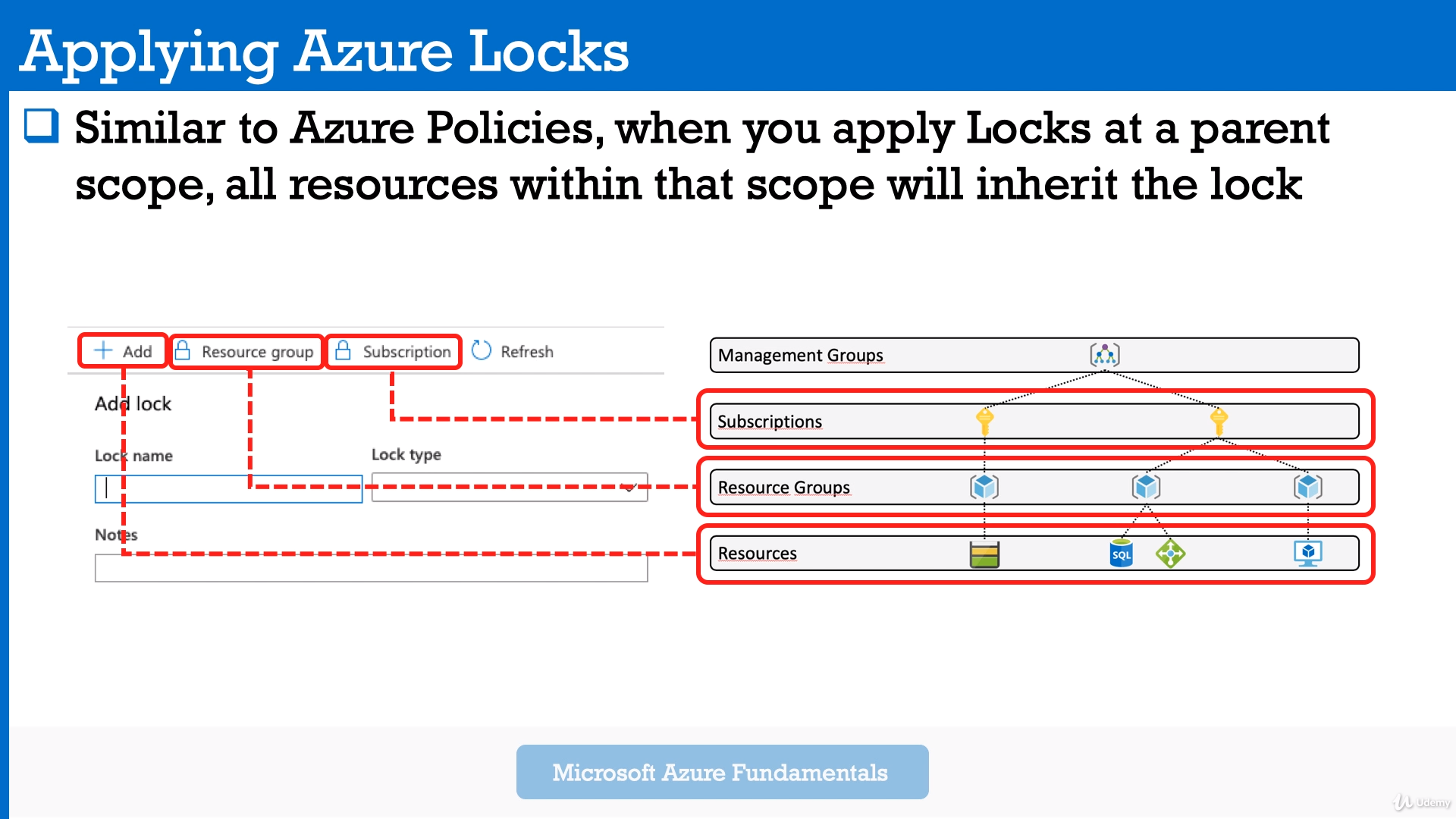
Module 8: Azure Locks.
Similar to the Policies. Applied to the upper scope, all resources within the scope will inherit all attached locks
Azure Locks prevent users in your organization from accidentally deleting or modifying critical resources.
And currently there are two options available.
- So first option is Delete.
And with this option you can read and modify a resource, but you can't delete it, while with the second one, read only, you can read a resource, but you can't modify or delete that specific resource.
** Read-only lock also prevents VM from being started or stopped.**
Can be applied on one of tree levels: Resource, Resource Group, Subscription
- GDPR - General Data Protection Regulation - only for Europe
- HIPAA - Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
- ISO - International Organization for Standartization
- IEC - International Electrotechnical Commission 27018
- NIST CSF - National Institute of Standards and Tech Cybercecurity Framework
- Azure Government - public cloud for state agencies in USA.
Module 9: Azure BluePrints
 With Azure blueprints you deploy and update cloud environments in a repeatable manner.
With Azure blueprints you deploy and update cloud environments in a repeatable manner.
After deployment process finished there is no more connections between ARM and Resources. Blueprint has such connections.
- Now what's the advantage with blueprints?
Well there are a couple of advantages, so not only one.
With blueprints, the relationship between the blueprint definition, so what should be deployed, and the blueprint assignment, what was deployed, is preserved. - So this is great for tracking and auditing the deployment.
You really have the deployment ready, but afterwards you can track and audit your infrastructure because you have this continuous relationship between the blueprint and the resource deployed.
With Azure Blueprints you are able to update several subscriptions at once. With ARM, you are not able to do that.
Azure Blueprint are able to operate "Azure Resource Manager Templates", "Resource Groups", "Policies", "Roles"
For example you may apply policy related to required tag on every resource.
Module 9: Azure Advisor
Azure Advisor helps you follow best practices and optimize your Azure deployments.
- cost effectiveness - optimize and reduce your overall azure spending.
- performance - improve the speed of your application
- high availability - ensure and improve to continuity your critical business apps.
- security of your Azure resources - detect threats.
- operational excelence - archive process and workflow efficiency, resource manageability and deployment best practices.
Module 9: Azure Monitor, Azure Service Health
Azure Monitor collects, analyses and acts on telemetry from your cloud.
Azure Monitor will monitor your cloud environment and then perform different functions such as analysis, alerting and streaming to external systems.
- You can create smart alerts and automated actions,
- You can monitor resources and drill into monitoring data with Azure Log Analytics.
- You can detect and diagnose issues across applications and dependencies with Application Insights.
- Create visualizations with Azure dashboards.
- You can combine these three type of health resources to notify you about any of availability changes in Azure.
- Provides you comprehensive view on the situation in Azure.
- Azure Status informs you of service outages in Azure (WHEN SOMETHING WRONG WITH AZURE SERVICES OR AZURE REGIONS).
- Azure Service Health provides a personalized view of the health of the Azure services and regions you're using.
- Azure Service Health alerts to be notified of any service issues, plan maintenance or even changes in Azure.
- Azure Resource Health, which provides information about the health of your individual, this time, cloud resources.
Module 10: Cloud Shared Responsibility.
Link: Module-10 Azure Cloud Shared Responsibility
When you hear cloud share responsibility model, you really must think security. It's about the responsibilities and how you manage security in your cloud or hybrid environment.
In general,
Well responsibility is shared between the cloud provider and the client or customer.
The responsibility level depends on the type of applications run in the cloud, but also on the cloud deployment model.
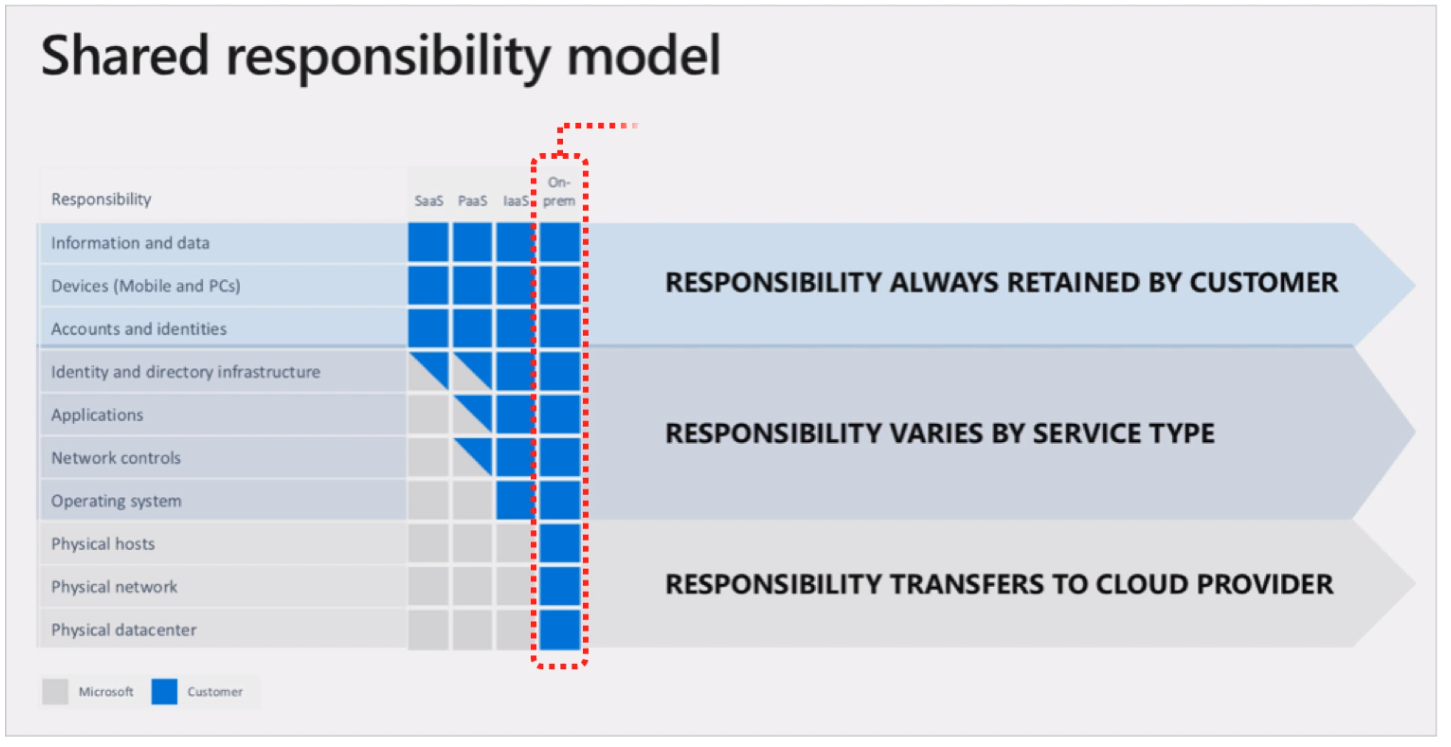
Think of it like about onion, in the middle - sensitive data, layers - security layers.
The first layer of defense is physical security and that is really the cloud provider's responsibility.
Data center security with cameras, restricted access, trained personnel and so on
You can think of this step as implementing SSO, so Single Sign-On and MFA (Multi-factor authentication).
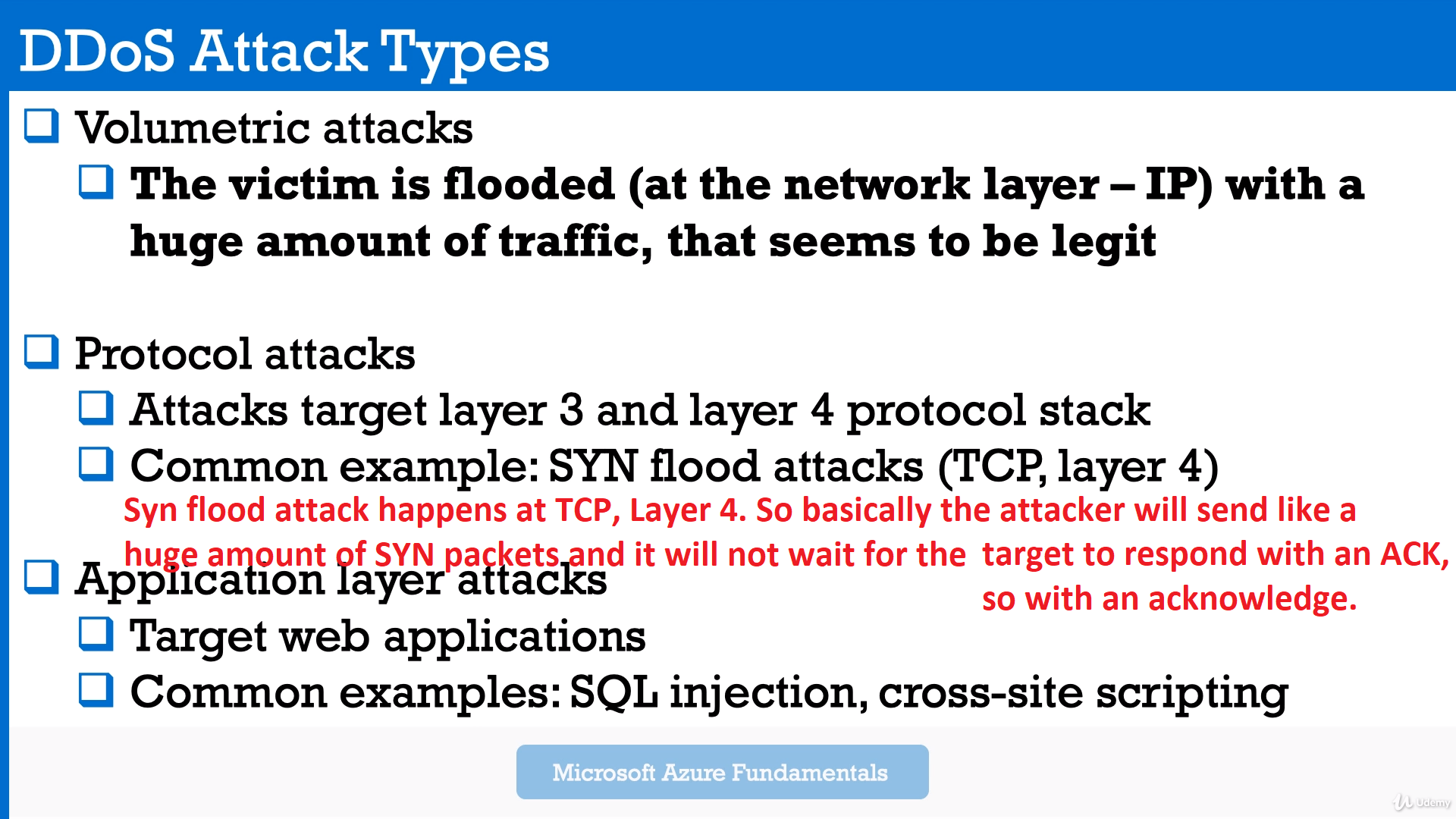
So DDoS protection, Distributed Denial of Service protection and firewall security should be taken into consideration, at this step.
-
You should deny inbound internet access. NSG Configuration.
-
Limit the connectivity between resources. You should limit connectivity between resources in the same vNET, but also between virtual networks. Example if your VM or service is compromised inside Azure cloud, you don't want for the hacker to be able to jump from the compromised resource to another one.
-
Security to your own premises data center should be taken into consideration. So if you're running in a hybrid cloud environment and you also have your traditional data center connected to Azure cloud, well some security should be implemented for the connection between the data center and Azure cloud.
-
Security for compute Consist of patching your VMs, implement endpoint protection. Endpoint Protection is similar to how you install, for example, an antivirus on your laptop or workstation.
Implement secure access to VMs. -
Security for application Implement security in app dev lifecycle. So actually this means that you should integrate security while building the application and not enforcing security after the application has been built and developed.
-
Data Security So security of the data itself.
So this is customer's responsibility.
- Data stored in Databases
- VM disks
- Cloud storages
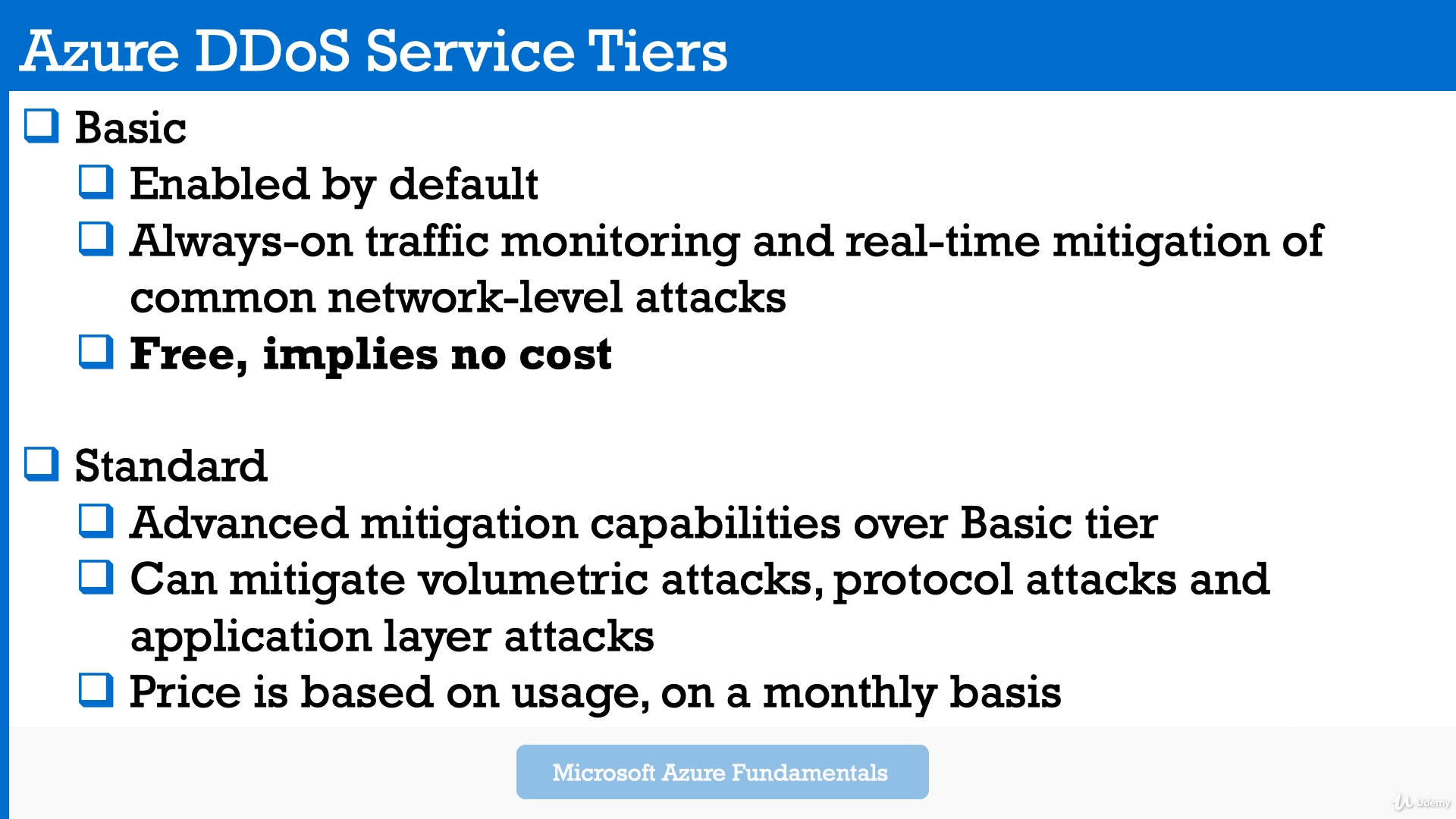
Module 10: Azure Security Center.(In Free tier only recommendations and overall score)
Link: Azure Sec Center Link
- Strengthen security posture means that Azure Security Center identifies security issues and implements best practices across your machines,
- Protect against threats. Azure Security Center evaluates workloads and raises threat prevention recommendations and security alerts.
- While get secure faster means that the security is really implemented at cloud speed.
-
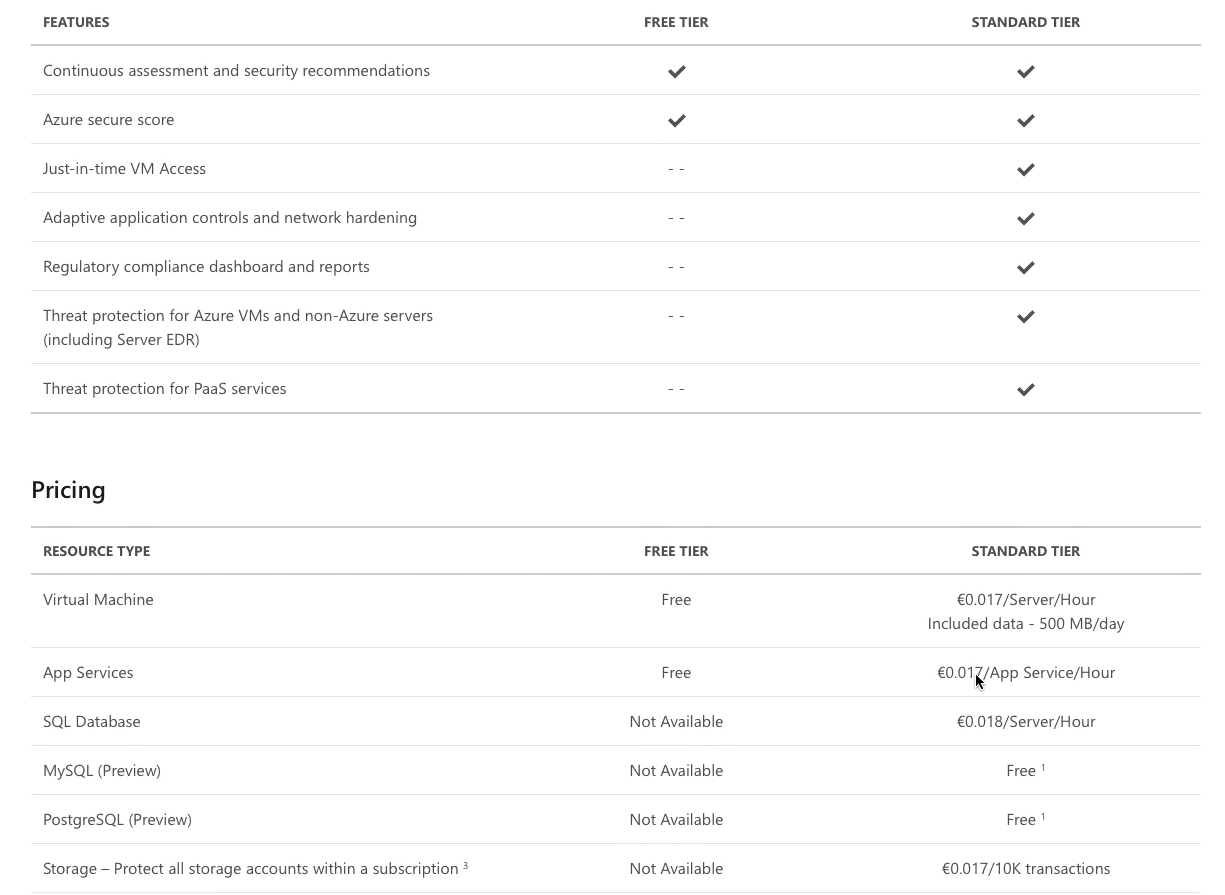
Free tier
1.1) Well this tier is limited to assessments and recommendations
1.2) And you also get an overall Azure secure score. -
Standard tier Standard, you get continuous monitoring, threat detection and all the capabilities Azure Security Center supports.
- Region depended prices.
- Hour and Monthly costs is available.
- Free tier let you overall score and some recommendations. But for example to apply these recommendations for VMs - you need to switch to Standard tier.
Module 10: Azure Identity Services. Azure Active Directory (AAD). Azure Privileged Identity Manager (PIM). MFA (Milti-factor Auth)
Active Directory or Azure AD is:
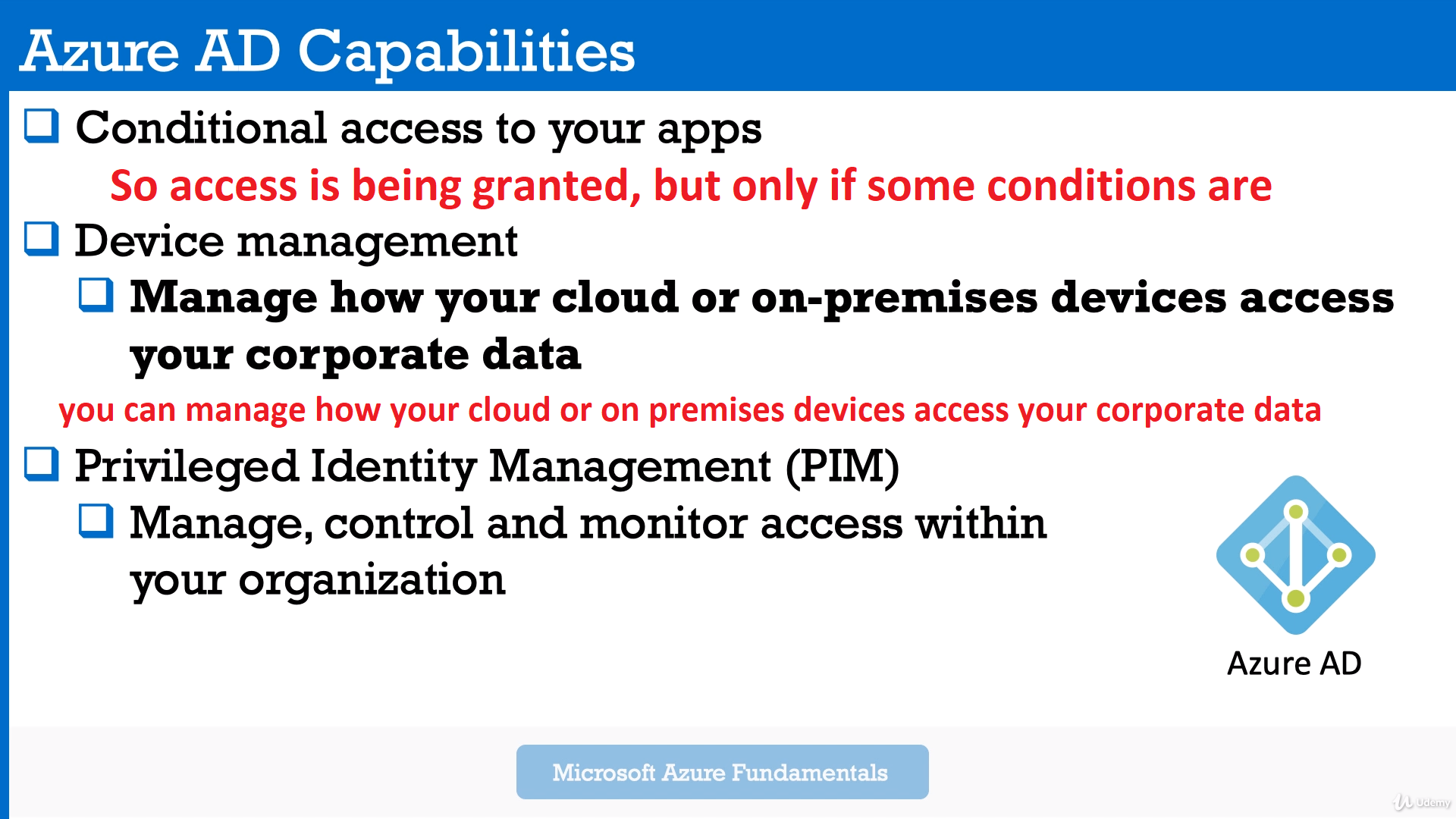
- Microsoft's cloud based identity service, that can also integrate with your traditional on premises infrastructure. All your applications running either in the cloud or on traditional infrastructures can share the same credentials And as a result of this, with Azure AD, you can centralize access control to your applications and data, with a single pane of glass over identity management.
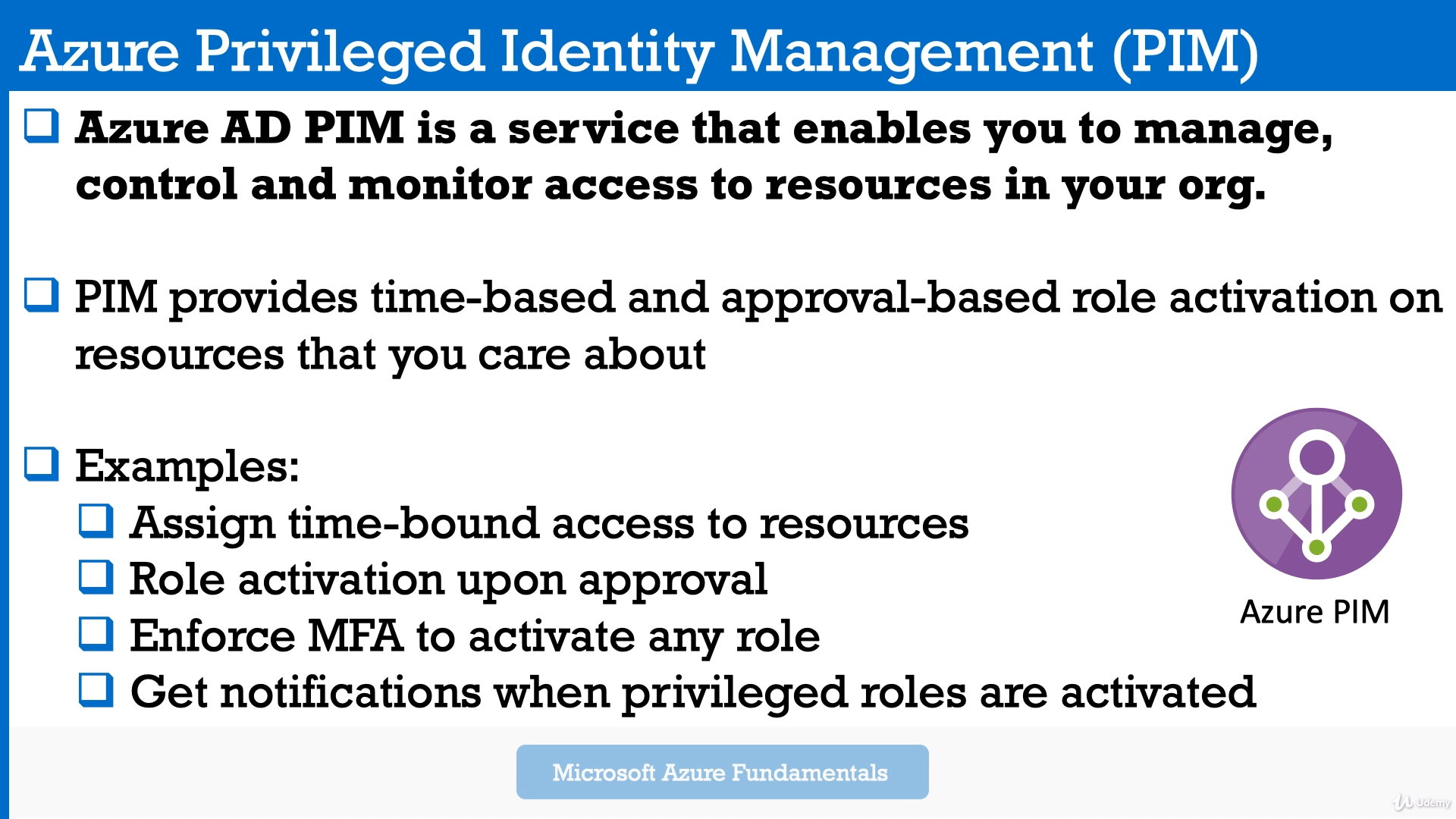
- Privileged Identity Management (PIM) is a service in Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) that enables you to manage, control, and monitor access to important resources in your organization. These resources include resources in Azure AD, Azure, and other Microsoft Online Services such as Microsoft 365 or Microsoft Intune.
Organizations want to minimize the number of people who have access to secure information or resources, because that reduces the chance of a malicious actor getting that access, or an authorized user inadvertently impacting a sensitive resource.
-
Time bound access to resources, which means that you will define a start time and an end time, when access is provided.
-
Role activation upon approval - for now just imagine that a role will give you privileges. So not all your users need the same permissions in order to perform their job. So think that you have multiple roles.
-
Also enforce MFA, so multi factor authentication to activate any role.
-
Get notifications is self-explanatory thing.
Module 10: Conditional Access. Single Sign-On (SSO). Application Proxy
SSO allows users to log in once and have access to various applications without having to go through the same identity verification process each time.
This great capability is free and integrated with any Azure ad subscription.
-
Example: Let's cover one popular example with SSO where applications are really popular these days and these are offered as a service. You can think of Microsoft 365 Salesforce.
So you sign up for the service and you can start using it right away.
You only need to authenticate first.
Once you authenticate, single sign on makes it possible for the users to navigate between the various web applications again without having to sign in multiple times.
One thing to note is that single sign on can be implemented for both cloud and on premises applications.
Module 10: Azure role-based access control (Azure RBAC, Built on Azure Resource Manager). Security Principal, Scope, Role
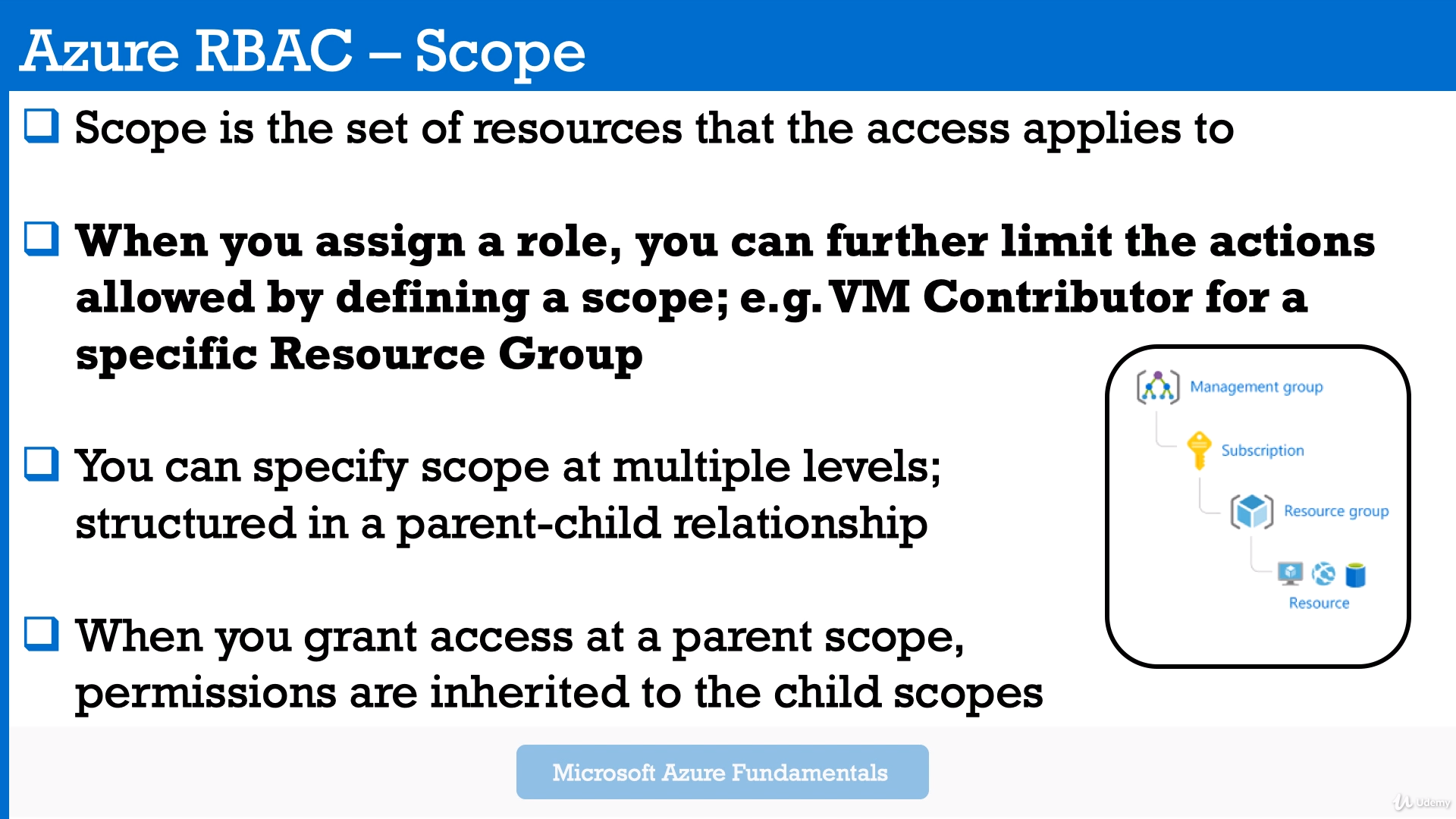
Azure role-based access control (Azure RBAC) helps you manage who has access to Azure resources, what they can do with those resources, and what areas they have access to. Granular access to your resources.Here are some examples of what you can do with Azure RBAC:
- Allow one user to manage virtual machines in a subscription and another user to manage virtual networks
- Allow a DBA group to manage SQL databases in a subscription
- Allow a user to manage all resources in a resource group, such as virtual machines, websites, and subnets
- Allow an application to access all resources in a resource group
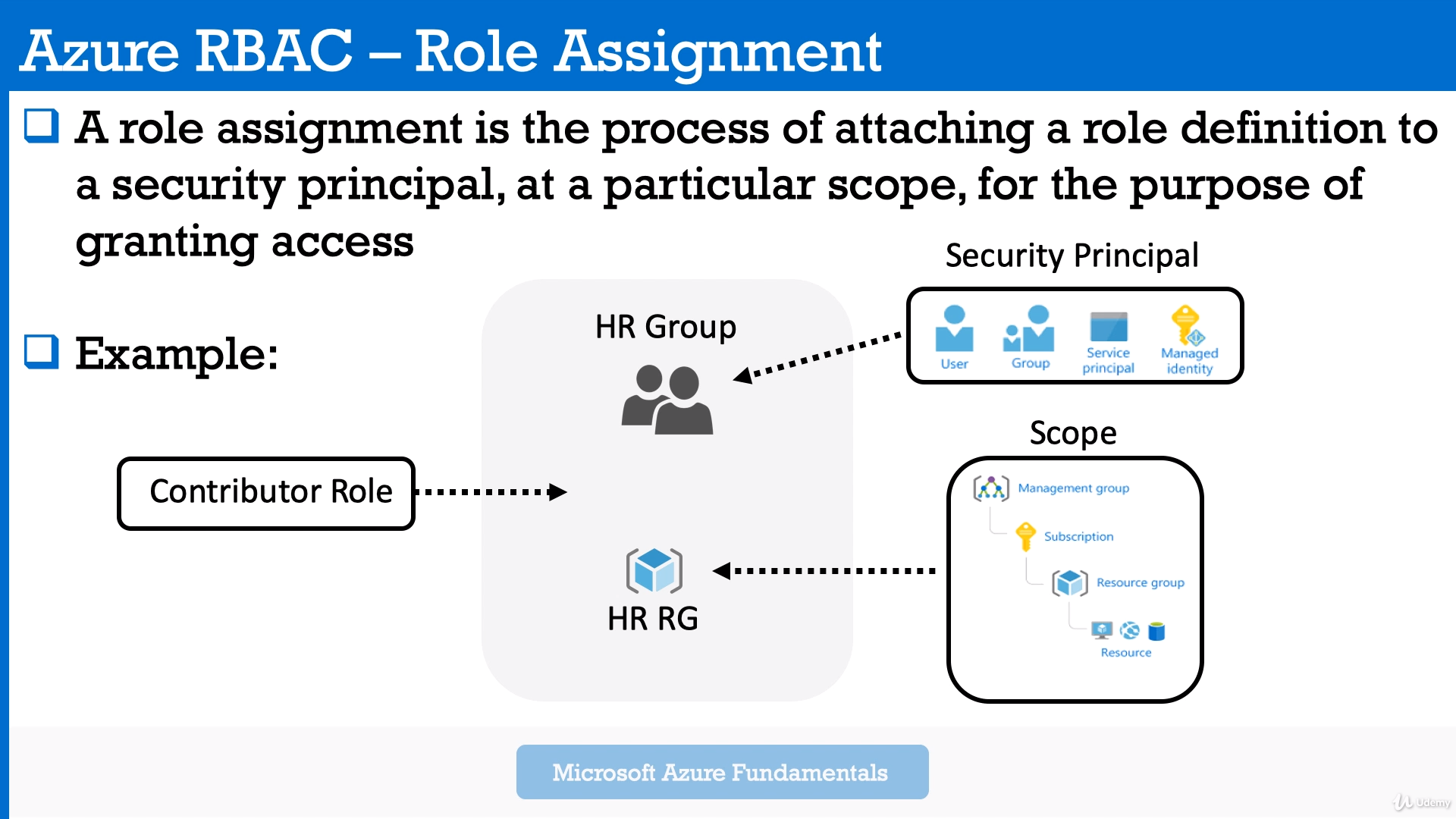
The way you control access to resources using Azure RBAC is to create role assignments. This is a key concept to understand – it's how permissions are enforced. A role assignment consists of three elements: security principal, role definition, and scope.
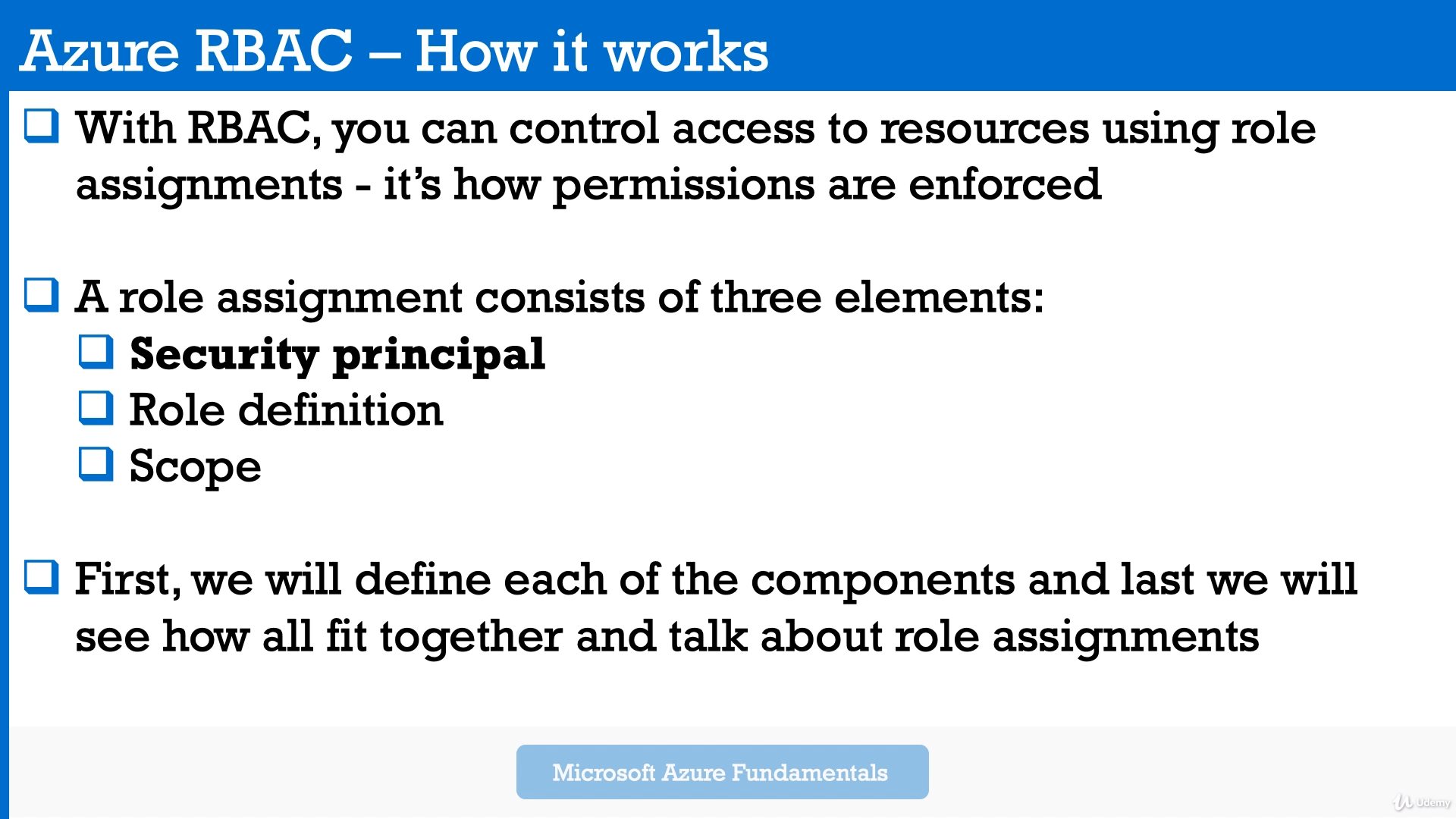
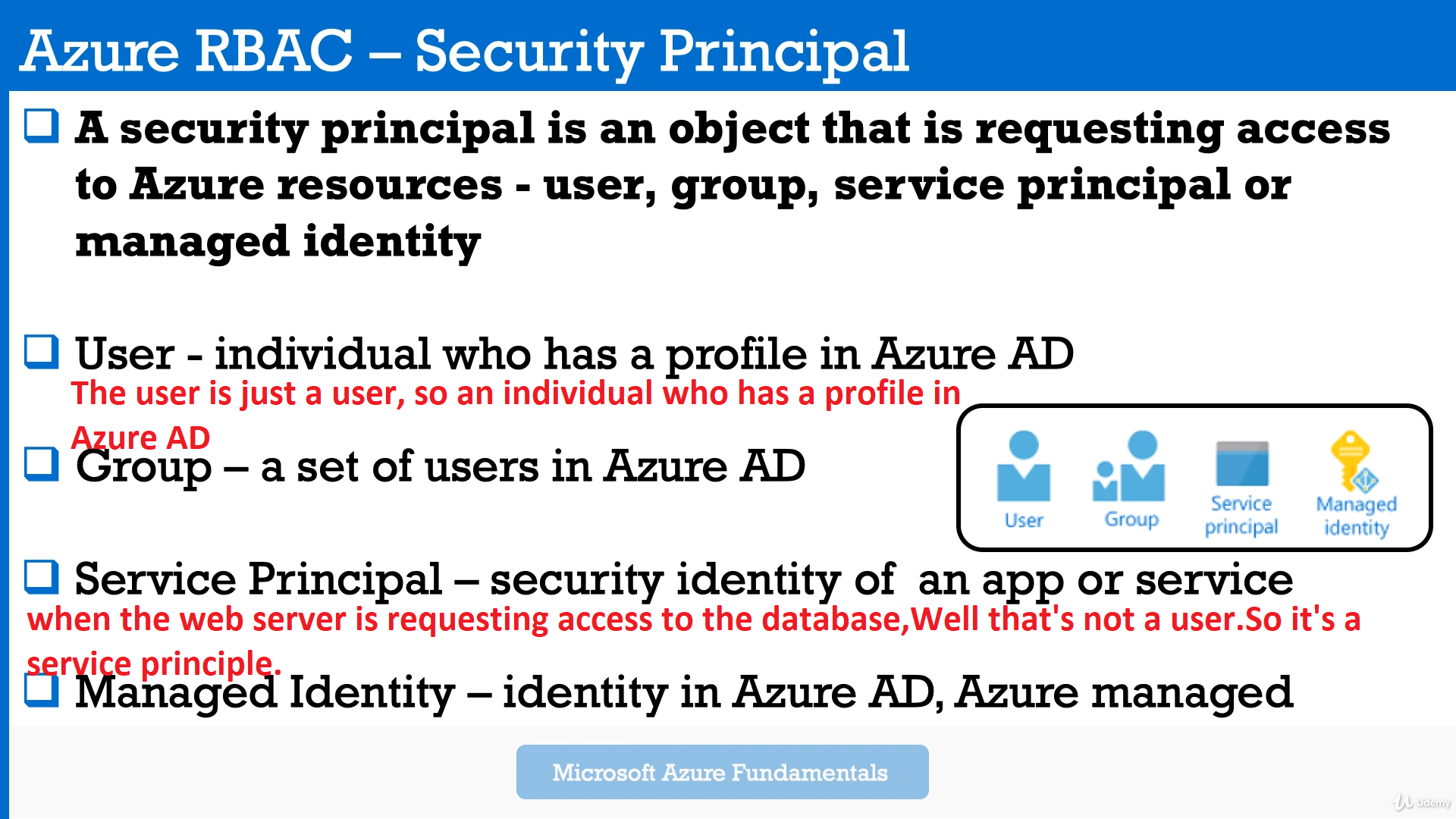
A security principal is an object that represents a user, group, service principal, or managed identity that is requesting access to Azure resources. You can assign a role to any of these security principals.
Security principal for a role assignment.

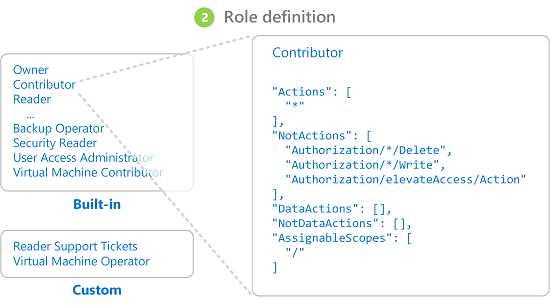
A role definition is a collection of permissions. It's typically just called a role. A role definition lists the operations that can be performed, such as read, write, and delete. Roles can be high-level, like owner, or specific, like virtual machine reader.
Module 10: Azure Firewall. DoS, DDoS Protection
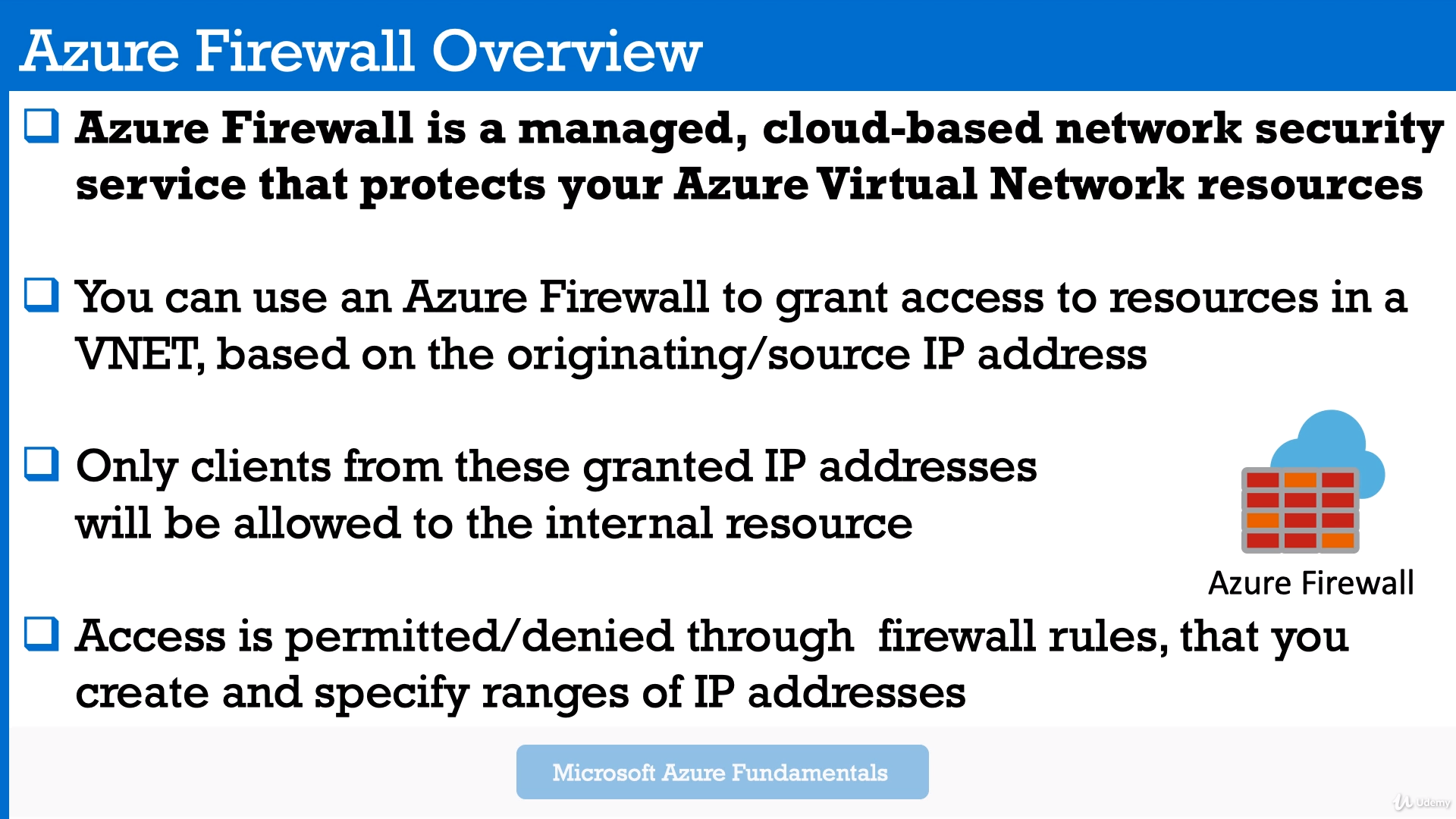
Azure Firewall is a managed cloud based network security service that protects your Azure vNETs.
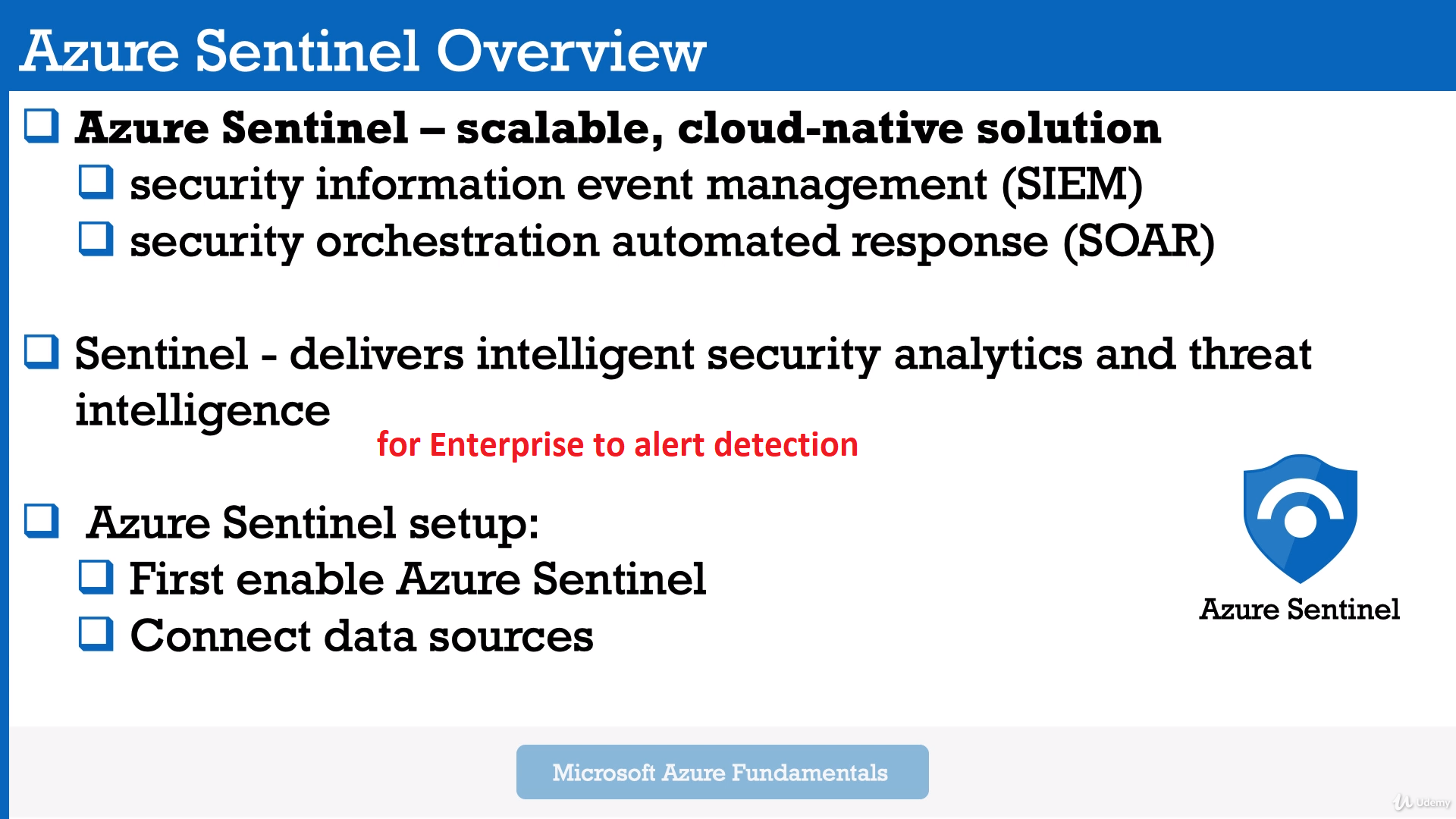
Module 10: Azure Sentinel (consist of SIEM "Security Information Event Manager" and SOAR Security Orchestration Auromated Response)
- For clouds and on-premise as well.
- Well, as a sentinel needs to be connected to the different services that you may be running. For example, Microsoft 365, including here, Office 365, Azure AD, Microsoft 365 or Defender and other more. And by connecting Sentinel with the various Microsoft solutions you may be using, Sentinel will start to receive data and events that appear throughout your organization. Once this happens, Sentinel will start providing recommendations and visibility.
Tips: Can automate common tasks in Azure Security Center
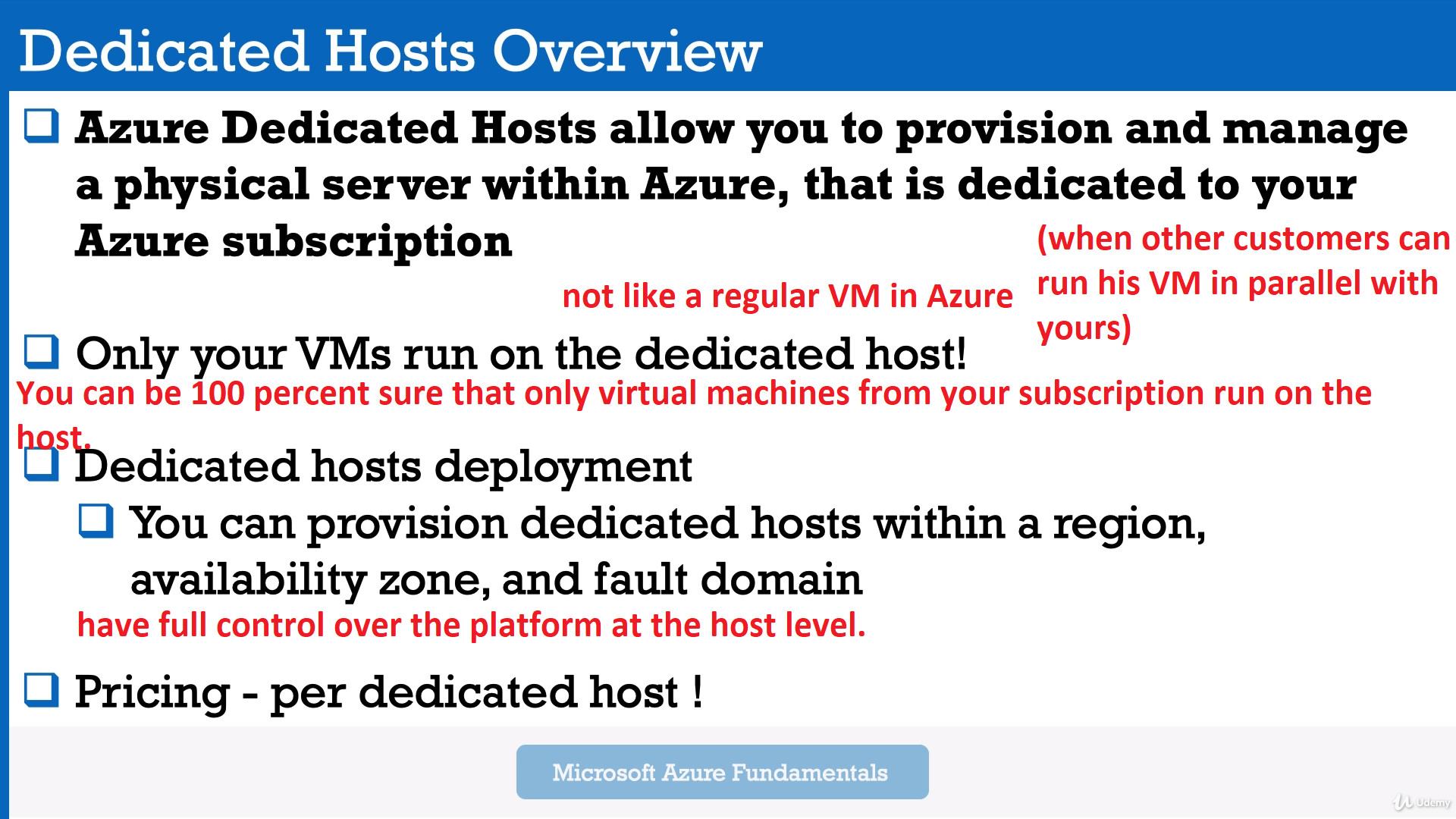
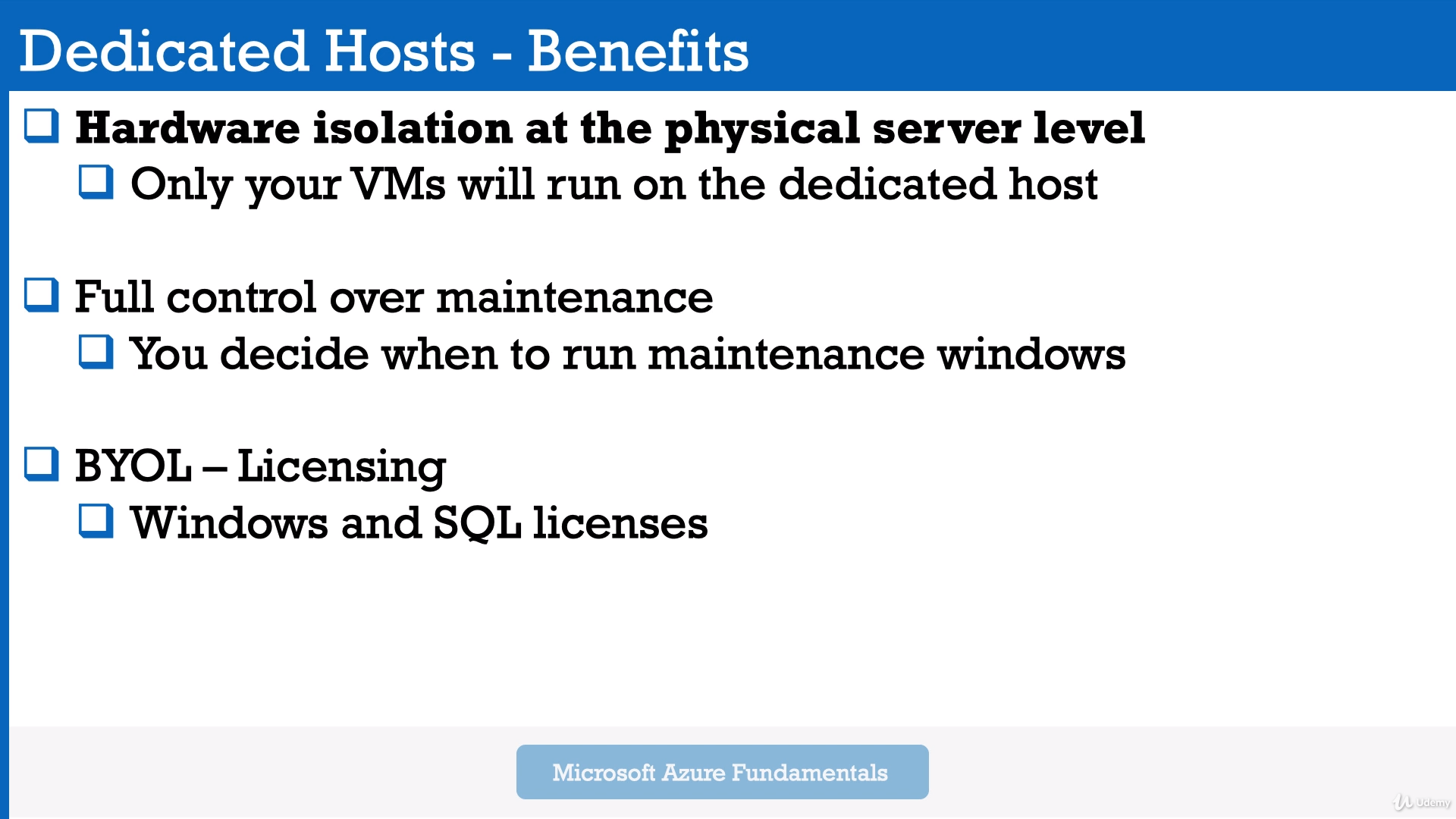
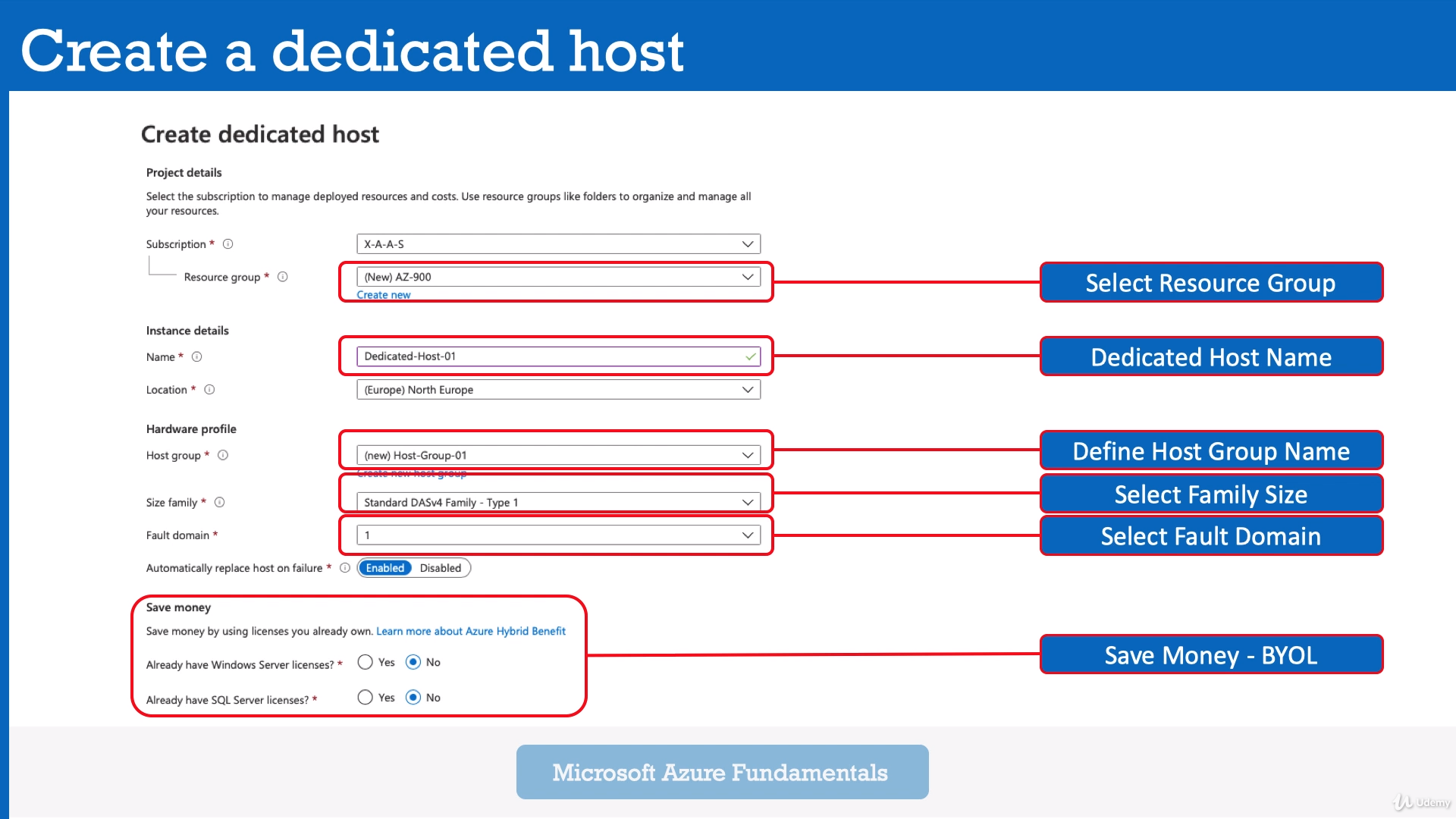
Module 10: Azure Dedicated Hosts
So if you deploy a dedicated host, then you don't run any virtual machines, you will definitely pay the house price, which is based on the virtual machine family type.
So this is the hardware side and the region where it is deployed.
Module 10: Azure Encryption(Azure Storage Service Encryption, Azure Transparent Data Encryption), Key Vault (Name-Pass storage)
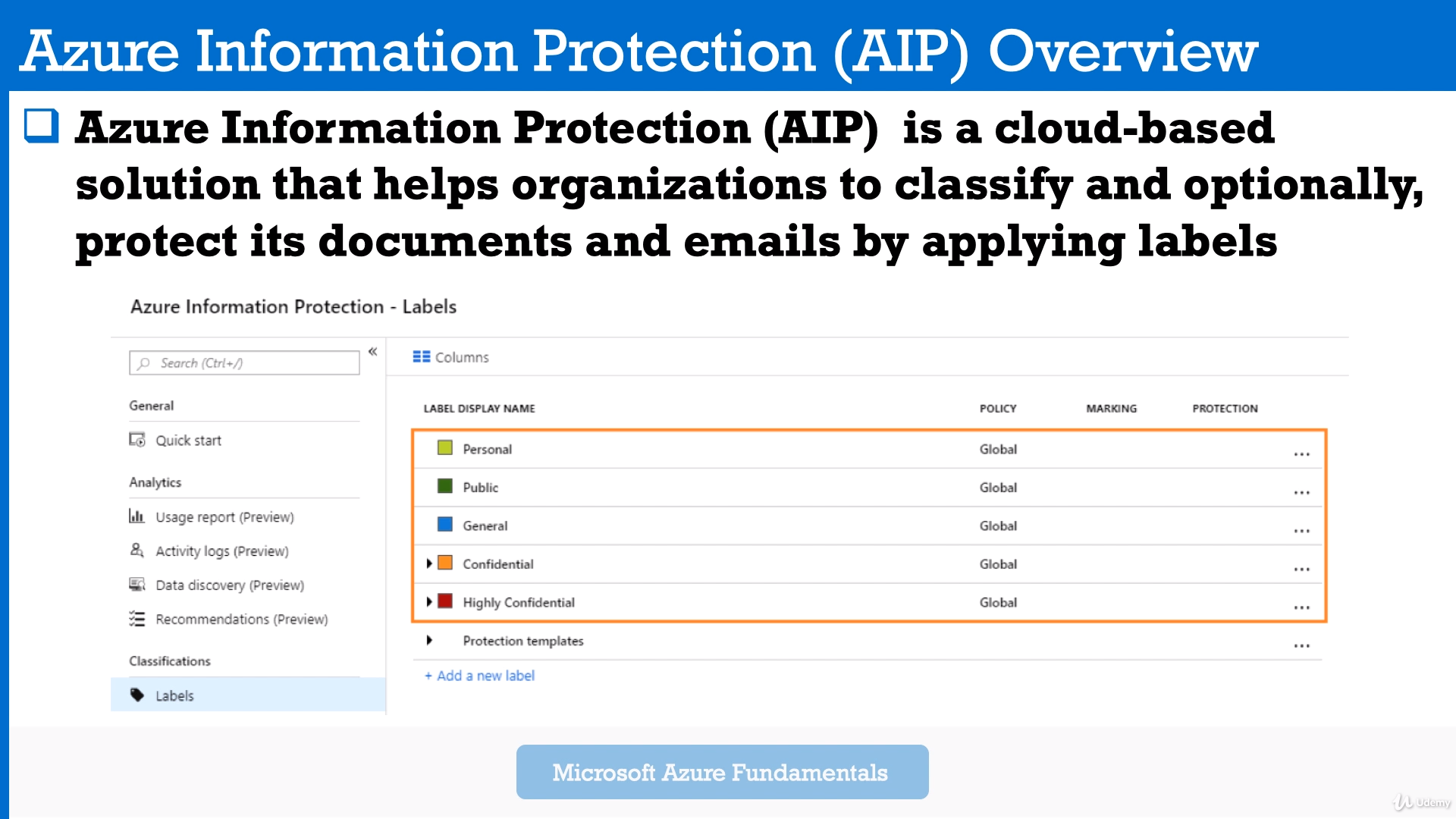
Module 10: AIP, ATP (Advanced Threat Protection)
Module 11: Azure Pricing. Cloud Pricing. Azure VMs Pricing.
-
Azure resources are always charged based on usage.
-
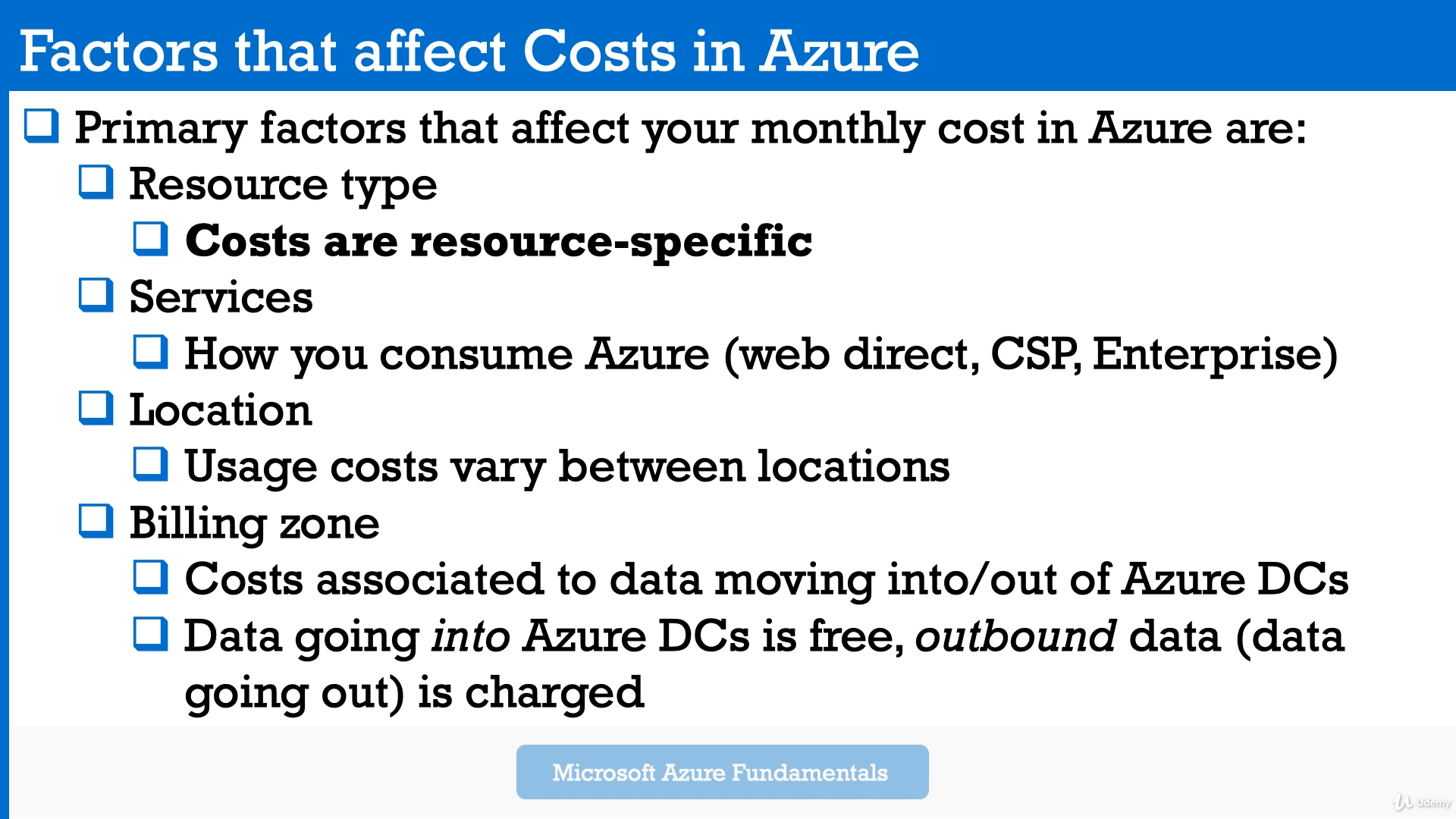
Primary factors that affect the total monthly cost:
- Usage cost can vary between locations.
- Data is going into Azure is free, data is going out of Azure is charged.
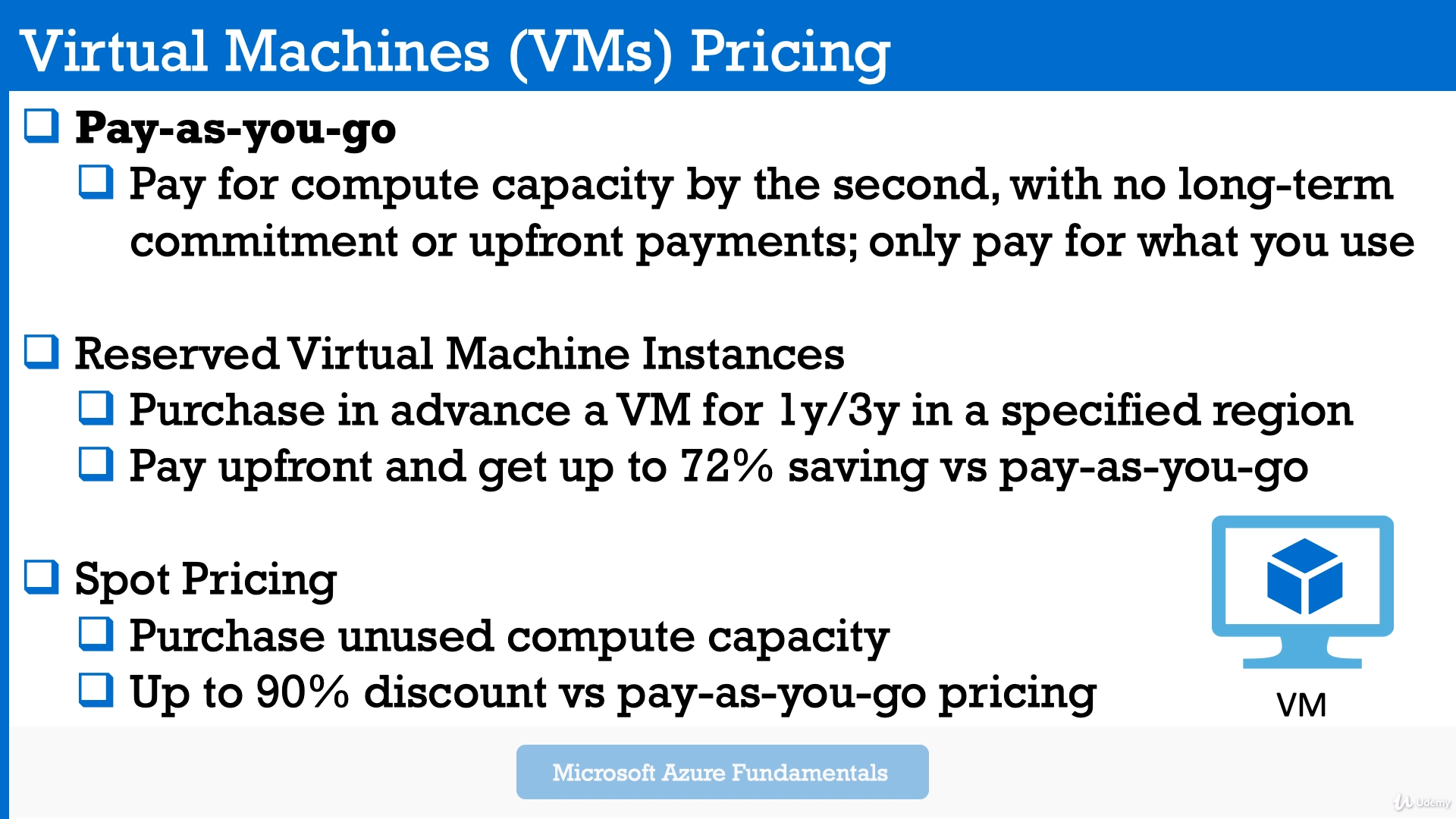
- "pay as you go", so you pay for compute capacity, by the second, with no long term commitment
- "pay upfront for resrved instances".
To reduce price: Reserved VM Instances
You purchase in advance a VM, for a 1 year or 3 year period, in a specified region,
And because of this, well paying upfront will get you up to 72% savings, as opposed to pay as you go pricing. - "spot pricing" - this option is not always available.
Module 11: Azure Total Cost Ownership Calculator (TCO). (Predict your saving if you migrate workloads to Azure)
Calculator: TCO Calculator link
Link: Module-8 Azure Policies
So in order to predict and analyze your spending in Azure for new or existing services, Pricing Calculator and Cost Management Advisor are tools that can help.
But if you are in the process or intend to migrate workloads to Microsoft Azure then you can use the Total Cost of Ownership Calculator in order to predict your cost savings.
Module 11: Azure Cost Management. Azure Advisor (recommendations to reduce cost)
- ExpressRoute is a private link between Azure DCs and your on-premise DC.
- Use Visual studio subscription. You have 50\150$ credit for testing purposes in Azure.
- Use spending limits.
- Use Reserved Instances for VMs with upfront payment on 1 or 3 years.
- Use Low Cost Locations and Regions
- Resize Underutilized VMs. Oversized VMs might ask you to pay much more.
- Run VMs only when it needed. Schedule Automatic Shutdown.
- Delete Unused VMs.
- Change Cloud deployment model. Migrate to PaaS from IaaS (when applicable). It's cheaper.
- Linux vs Windows VMs. Linux is cheaper because of license cost. 9.1) You can reuse Windows Server License. Microsoft provides the right to use this license in Azure as well. 9.2) Reuse SQL Server Licenses.
- Use Dev\Test subscription options. Non-production env use.
- Use SQL Server Developer Edition for non-production needs.
- Use dedicated VM types for Database. (with low vCPU). cost reduction on compute.
Example: DS, ES, GS, MS families of Virtual Machines.
Module 11: Azure Support Plans (Basic -> Developer -> Standard -> Professional Direct)
Link: Azure Support Plans Standard is free, others have charge.
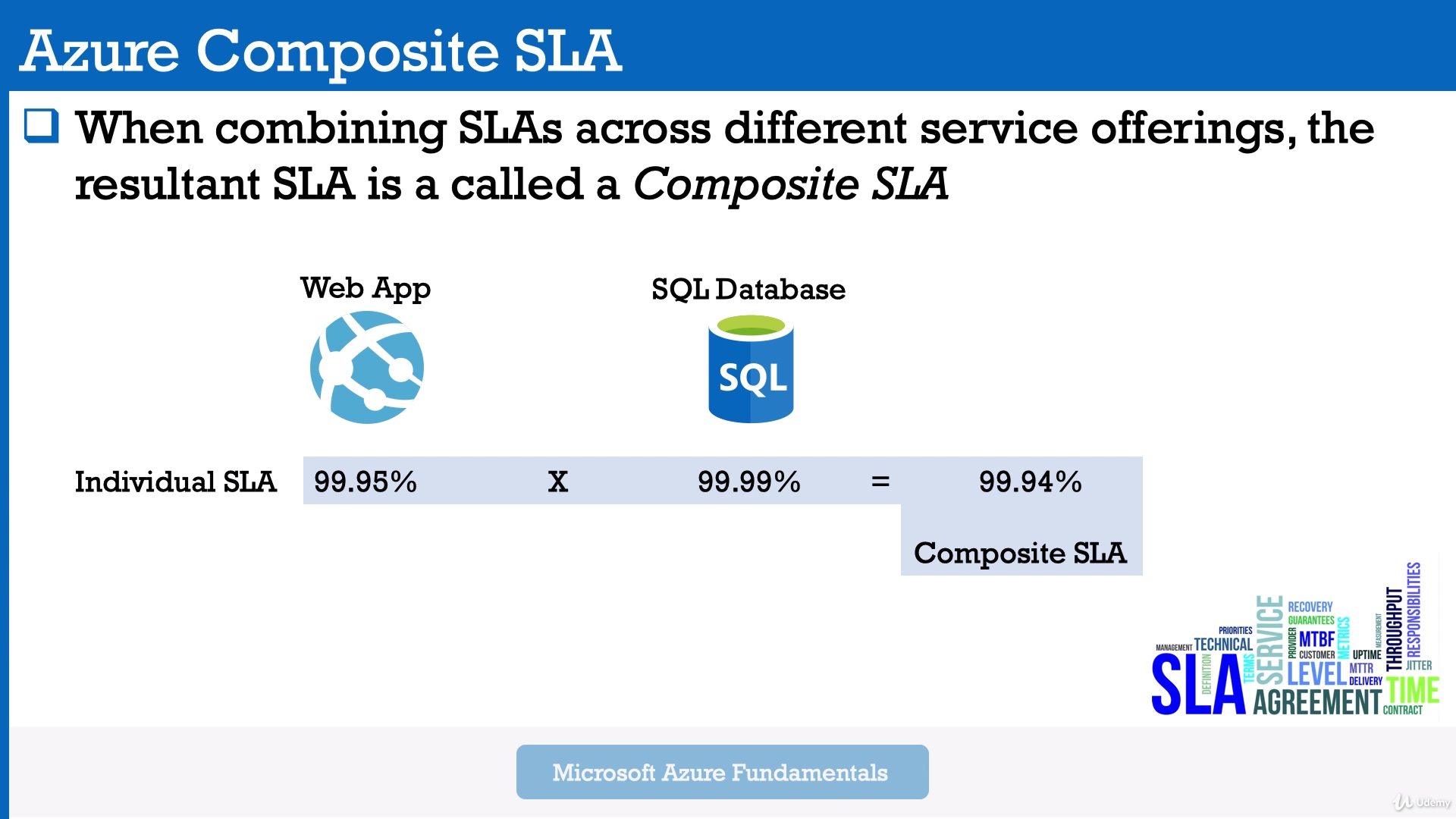
Module 11: SLA (Service Level Agreements, % of availability). Composite SLA
SLA is formal documents that describe performance standards or commitments that apply to Azure.
Link: Azure SLA
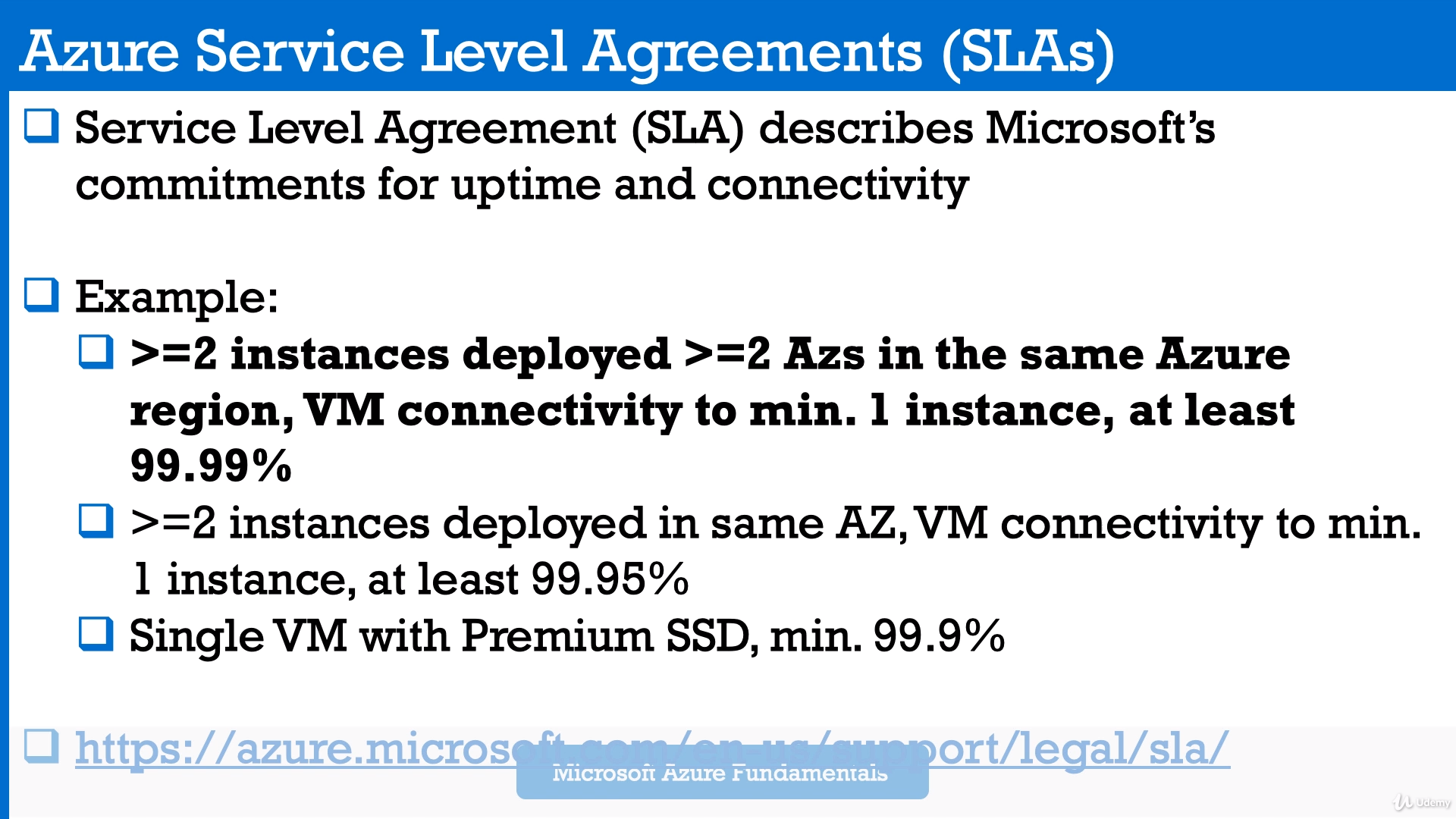
Example: If you run two VMs in different regions and uptime of them is lower than 95% - you have 100% Service Credit, which means that this service is for free for you in this month.
Simply put, the service credit represents the discount applied to the Azure bill.
Module 11: Service Lifecycle (use preview services)
To see preview services:
- Portal -> Marketplace -> preview in a search bar
- Or visit preview.portal.azure.com
Microsoft offers previews of different Azure services, features and functionalities, and this is for evaluation purposes.
Users can test the new products or services before the official release and provide feedback to Microsoft that will help improving the Azure service.
- Private preview mode for new service - available to some or certain Azure customers
- Public preview mode - available for all Azure customers
Some of the previews are not covered by customer support
Bootcamp Q&A. Additional Info. Azure Backup MARS agent(Azure Backup agent).
-
What is the location of the additional learning resources for this course mentioned in the presentation. Our Learning Path is available at: Azure Information Portal
-
Azure Backup MARS agent: Link MARS agent stands for Microsoft Azure Recovery Services Agent. It's an agent that controls the Backup services in your local machine, if you're using Azure Backup
-
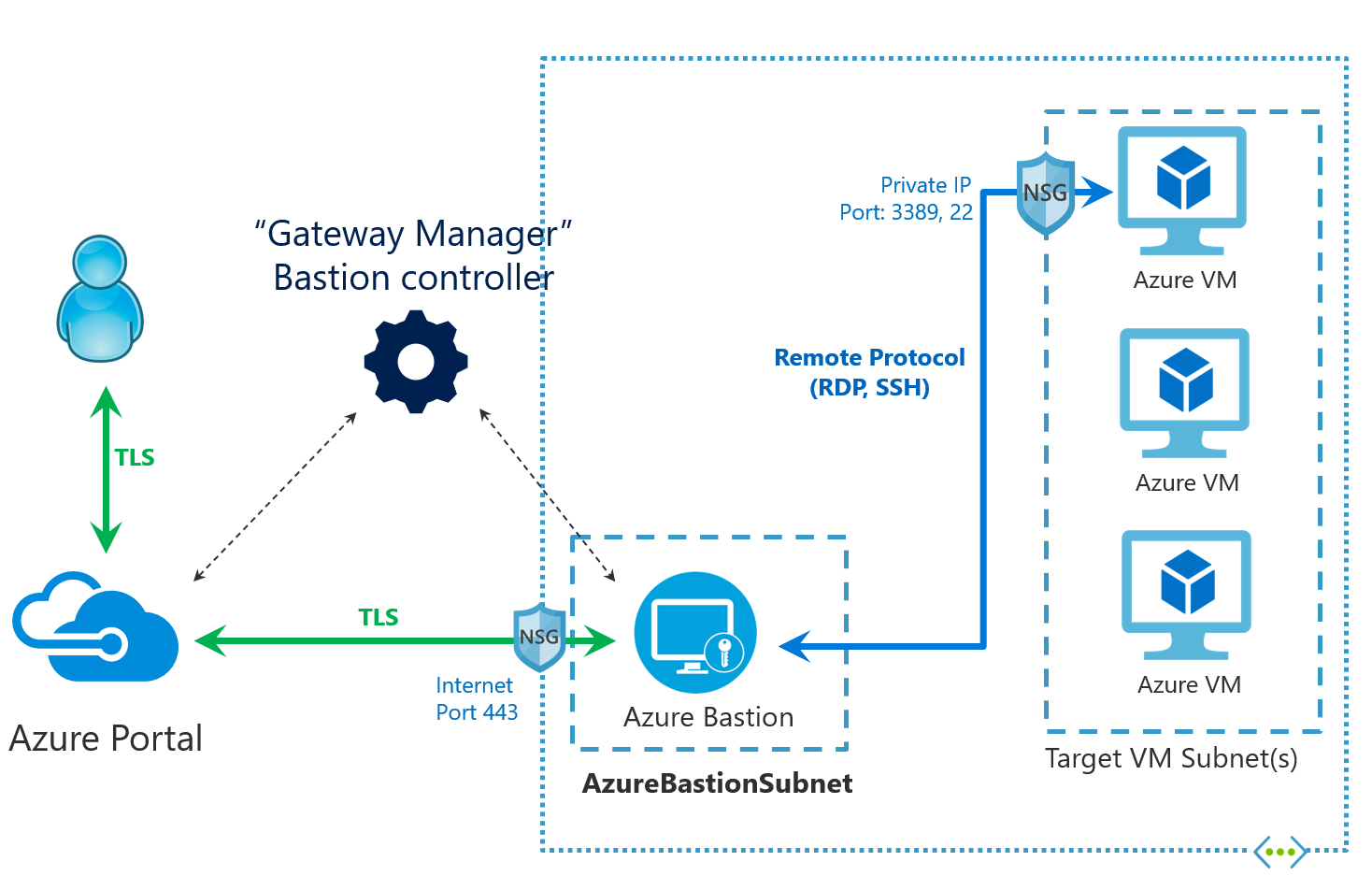
What is Bastion connection? Azure Bastion is a service you can use to connect to your VMs without needing a public IP address for each VM. It works at the VNet level.
-
What is difference between ASR(Azure Site Recovery) and ASM(Azure Server Migration)? ASM is used to migrate workloads from On-Prem to Azure. ASR is used to create a secondary site for your workloads in case of a disaster.
-
are the IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS models all part of Hybrid Cloud systems? You can use any of those models in a Hybrid Cloud environment
-
What's the difference between "High Availability" and "Fault Tolerance". Same thing with Elasticity and Scalability? High Availability is the capacity of running your workloads with le least amount of disruptions. Fault Tolerance is the ability to tolerate a certain amount of failures in the different components of your workload without service interruption.
-
Would a Hybrid Cloud require a backbone connection like Azure ExpressRoute? A Hybrid Cloud would require a connection between On-Prem and Azure. You can use a VPN or ExpressRoute.
-
Can we choose older vesions of SQL Server to work with? Only if you're using SQL Server running in Azure VMs. For the Managed Instances and Azure SQL DB, you always use the latest stable version
-
Once i delete my VM, will I be able to recover it? You can't recover a VM after it was deleted. We´ll talk about protecting resources by using locks tomorrow
-
What Hypervisor is used in Azure? The Azure hypervisor system is based on Windows Hyper-V
-
Do you recommend taking AZ-900 exam after day 2, or should we complete the Online Free Learning Paths from Microsoft first? Everyone's studying and test taking habits are different. My recommendation is that you utilize the free learning path at https://aka.ms/azfunpath to review the material and ensure that you are comfortable with all the material.


.png)