A simple fizz-buzz REST server in Golang (LeBonCoin's technical test).
Table of Contents generated with DocToc
The original fizz-buzz consists in writing all numbers from 1 to 100, and just replacing all multiples of 3 by "fizz", all multiples of 5 by "buzz", and all multiples of 15 by "fizzbuzz".
The output would look like this: "1,2,fizz,4,buzz,fizz,7,8,fizz,buzz,11,fizz,13,14,fizzbuzz,16,...".
-
Your goal is to implement a web server that will expose a REST API endpoint that:
- Accepts five parameters : three integers int1, int2 and limit, and two strings str1 and str2.
- Returns a list of strings with numbers from 1 to limit, where: all multiples of int1 are replaced by str1, all multiples of int2 are replaced by str2, all multiples of int1 and int2 are replaced by str1str2.
-
Add a statistics endpoint allowing users to know what the most frequent request has been.
This endpoint should:
- Accept no parameter
- Return the parameters corresponding to the most used request, as well as the number of hits for this request
-
The server needs to be:
- Ready for production
- Easy to maintain by other developers
To build and run this server, the following must be installed:
- make version 3.81
- git version 2.26.2
- docker version 20.10.0
- docker-compose version 1.27.4
- gommit (only if you want to contribute to the project) version 2.2.0
⚠Important note: The specified versions are for information purposes only. They are the versions used to develop the project and not the minimum required to run it.
Clone the project:
git clone https://github.com/Geoffrey42/fizzBuzz.git
cd fizzBuzzProduction branch is main, but default is develop. Choose accordingly to your needs.
git checkout mainCreate an .env file based on this .env.sample:
HTTP_PROXY= # Your corporate proxy if applicable
HTTPS_PROXY= # Your corporate proxy if applicable
API_PORT= # Any available port for your API e.g my-redis
REDIS_HOSTNAME= # Any string to identify your Redis instance
REDIS_PORT= # Any available port for your Redis instance
REDIS_EXP_PORT= # Any available port for redis_exporter
PROMETHEUS_PORT= # Any available port for Prometheus
GRAFANA_PORT= # Any available port for GrafanaFill it according to your configuration needs.
To build and run the server:
make # for productionor
make dev # for dev (no restart always and log rotation)Depending on your connection, those above commands can take some time.
Once it's done, check that everything is correct by running:
$ make ps
docker-compose ps
Name Command State Ports
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
fb-api /bin/sh -c ./fizzbuzz-serv ... Up 0.0.0.0:5000->5000/tcp
fb-grafana /run.sh Up 0.0.0.0:3000->3000/tcp
fb-prometheus /bin/prometheus --config.f ... Up 0.0.0.0:9090->9090/tcp
fb-redis docker-entrypoint.sh redis ... Up 0.0.0.0:6368->6379/tcp
fb-redis_exporter ./redis_exporter -redis.ad ... Up 0.0.0.0:9121->9121/tcppThe fizzbuzz server exposes two endpoints:
- /api/fizzbuzz: Hitting this endpoint and the server will perform a fizzbuzz according to the specified query parameters (to learn more about the parameters see the Swagger UI info in the Swagger section).
- /api/stats: This endpoint returns the top fizzbuzz request, its query parameters and the number of hits.
To perform some tests on your running configuration you can still use curl but here is a Postman collection gathering the most important requests with some example:
You will have to change the API port number (5000 in the Postman collection) by the API_PORT from your .env file.
You can also perform some tests on your Swagger UI. See Swagger section.
The server was built using go-swagger. It's a Golang implementation of Swagger 2.0 specification. The server source code has been generated from this swagger.yml.
A Swagger UI documentation available at http://127.0.0.1:[API_PORT]/docs.
At the heart of the server lies a simple DoFizzBuzz function defined as the following:
package fb
import (
"errors"
"strconv"
"strings"
)
const start int64 = 1
const max int64 = 100
const base int = 10
func DoFizzBuzz(int1, int2, limit int64, str1, str2 string) ([]string, error) {
result := ""
separator := ""
if limit < start || limit > max {
return nil, errors.New(
"limit must be between" + strconv.FormatInt(start, base) + " and " + strconv.FormatInt(max, base))
}
for i := start; i <= limit; i++ {
if i > start {
separator = ","
}
if i%int1 == 0 && i%int2 == 0 {
result += separator + str1 + str2
} else if i%int1 == 0 {
result += separator + str1
} else if i%int2 == 0 {
result += separator + str2
} else {
result += separator + strconv.FormatInt(i, base)
}
}
return strings.Split(result, ","), nil
}⚠Important note: limit must be between 1 and 100.
See actual function in fizzbuzz.go
The statistics endpoint relies heavily on Redis Sorted Set data structure. When a request hits the above /api/fizzbuzz endpoint:
- A Sorted Set member is created in the form of a string "int1-int2-limit-str1-str2" e.g "3-5-16-fizz-buzz" would be created for the assignment's example.
- Its score is increaseb by one.
A http middleware being a perfect fit to intercept incoming requests, here the snippet in configure_fizzbuzz.go
func increaseCounterMiddleware(handler http.Handler) http.Handler {
return http.HandlerFunc(func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
limit, err := strconv.Atoi(r.URL.Query()["limit"][0])
if err == nil && limit >= 1 && limit <= 100 {
member := utils.BuildMemberFromParams(r.URL.Query())
client.ZIncrBy(utils.Key, 1, member)
}
handler.ServeHTTP(w, r)
})
}Then, when a client request the /api/stats endpoint, it returns the first element of the go-redis equivalent of ZREVRANGE.
Here is the model for the Stat struct returned by /api/stats in stat.go:
type Stat struct {
Hit int64 `json:"hit,omitempty"`
Int1 int64 `json:"int1,omitempty"`
Int2 int64 `json:"int2,omitempty"`
Limit int64 `json:"limit,omitempty"`
Str1 string `json:"str1,omitempty"`
Str2 string `json:"str2,omitempty"`
}And here is the http.handler in configure_fizzbuzz.go:
api.StatsGetAPIStatsHandler = stats.GetAPIStatsHandlerFunc(func(params stats.GetAPIStatsParams) middleware.Responder {
ok, err := client.Exists(utils.Key).Result()
if err != nil {
errorMessage := models.Error{Code: 500, Message: "Database isn't available: " + err.Error()}
return stats.NewGetAPIStatsInternalServerError().WithPayload(&errorMessage)
} else if ok == 0 {
errorMessage := models.Error{Code: 404, Message: "No stored request can be found."}
return stats.NewGetAPIStatsNotFound().WithPayload(&errorMessage)
}
topRequests, _ := client.ZRevRangeWithScores(statistics.Key, 0, -1).Result()
topRequest, errorMessage := statistics.GetTopRequestFromList(topRequests)
if errorMessage != nil {
return stats.NewGetAPIStatsNotFound().WithPayload(errorMessage)
}
return stats.NewGetAPIStatsOK().WithPayload(topRequest)
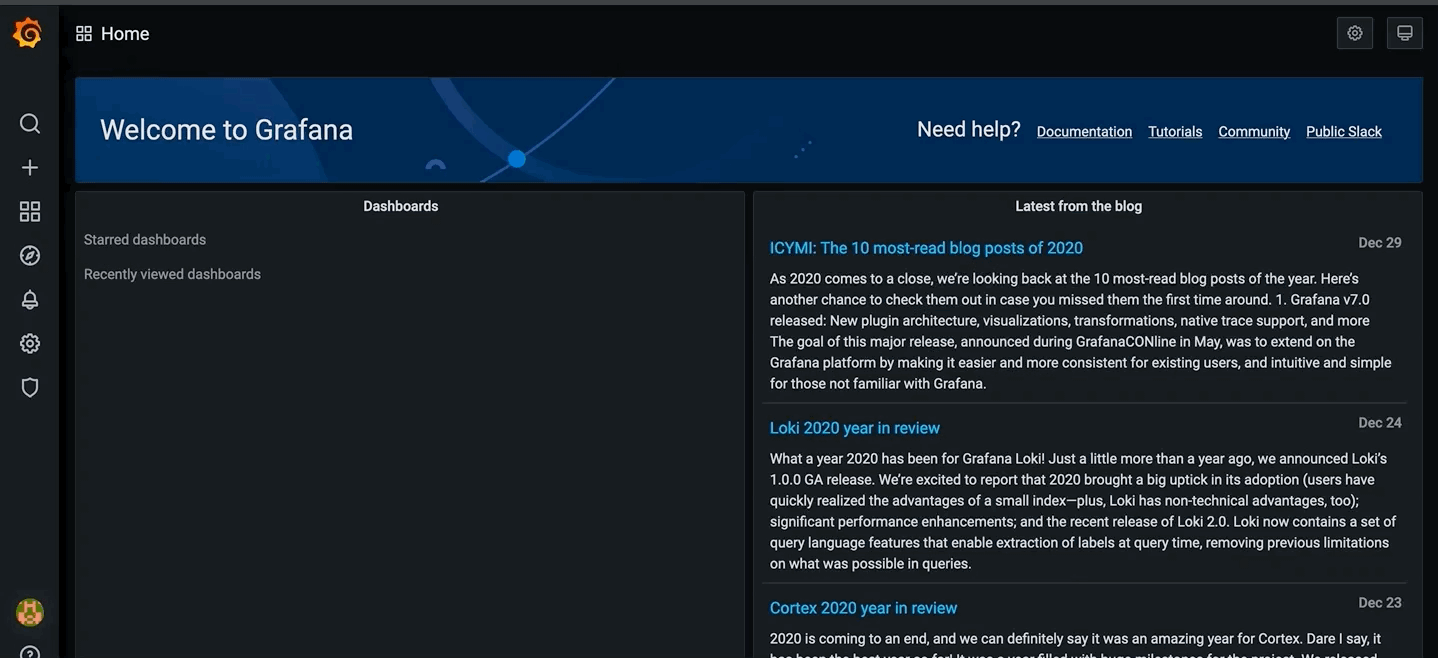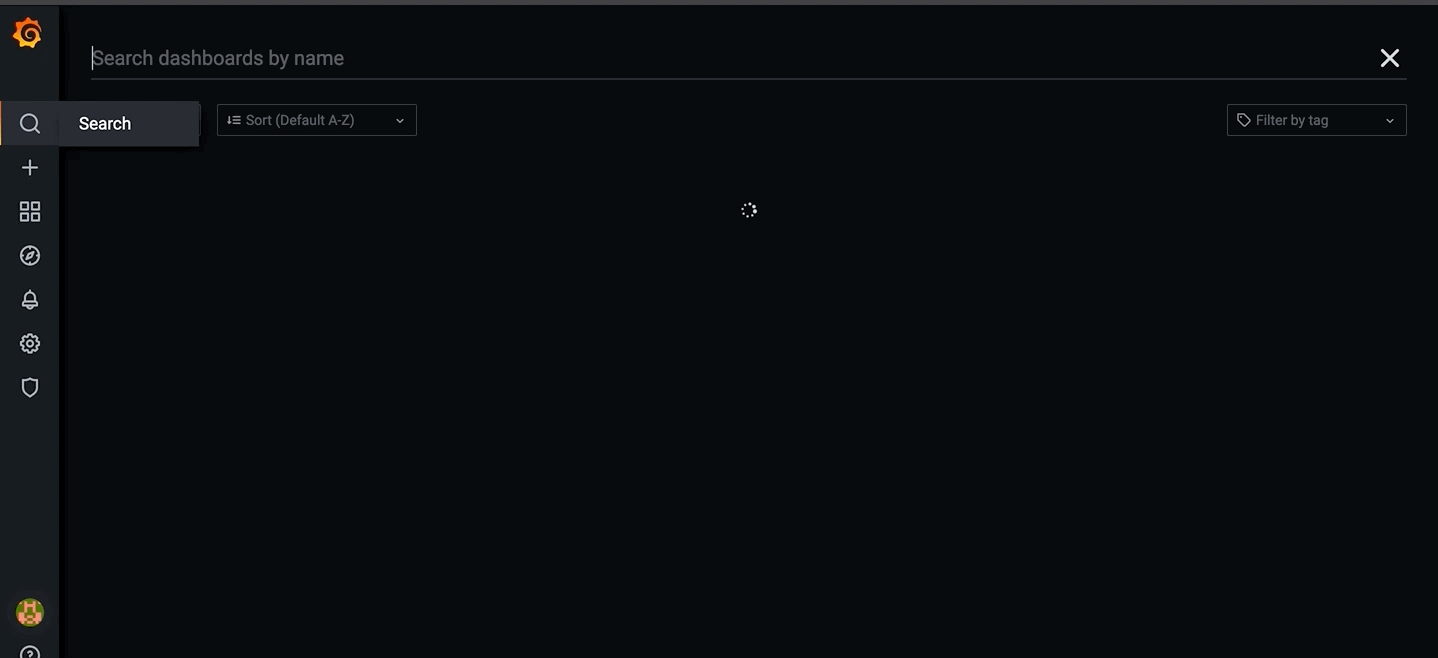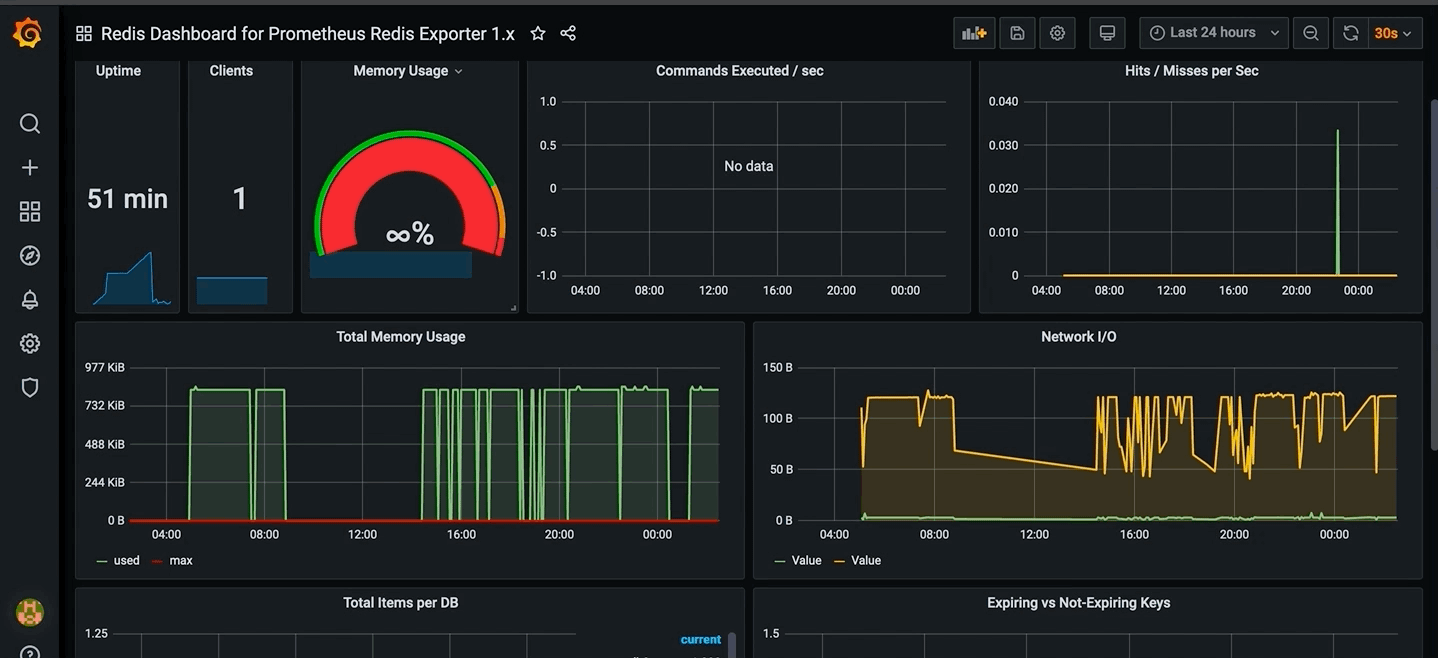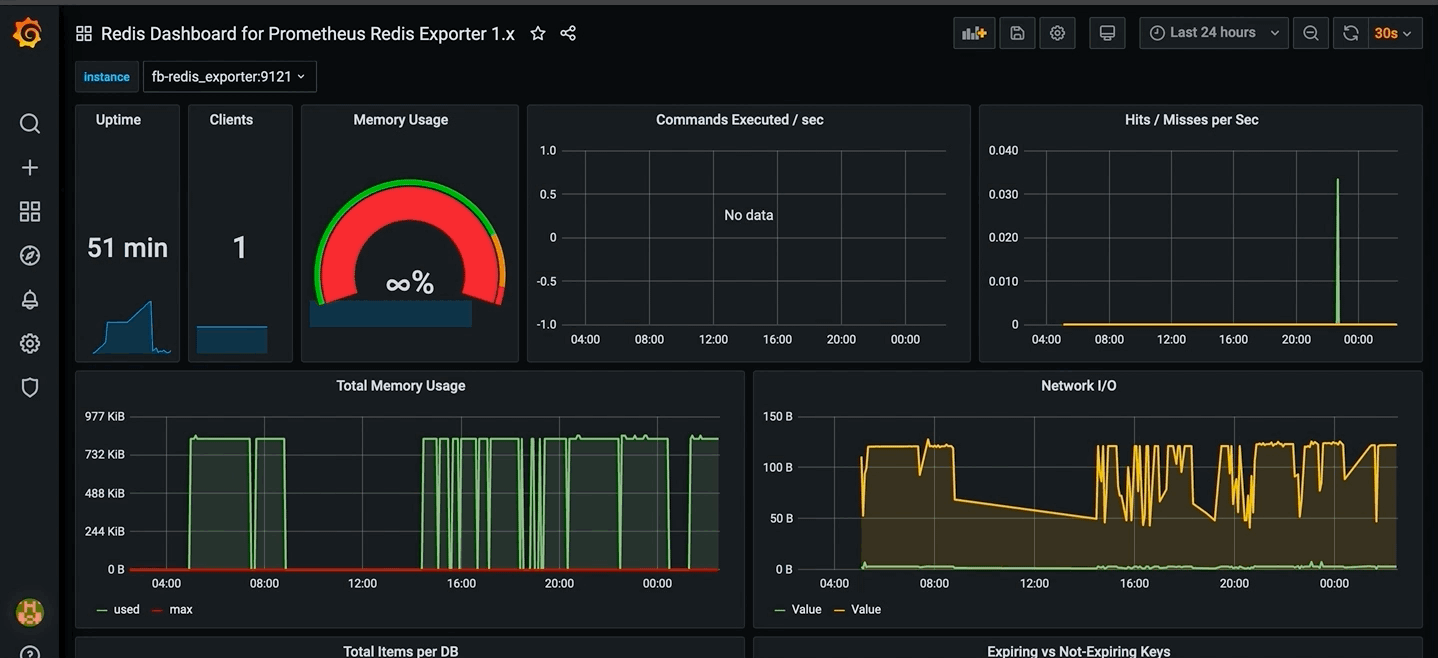
})The redis container is essential to get /api/stats endpoint working. Thus, a monitoring stack composed of a Prometheus instance, a redis_exporter and a Grafana dashboard is available to monitor the database.
Go to your grafana instance (http://127.0.0.1:[GRAFANA_PORT]) to see the metrics exposed by redis_exporter. Be aware that on first log-in, both default username and password are admin.
Then search for Redis Dashboard for Prometheus Redis Exporter 1.x dashboard. See capture below:
Pull requests are welcomed. For more details, please refers to our contributing file.