-
Using Google Colab (fastest performance, recommended) -
- Open Google Colab
- Switch to GPU for faster performance
- Upload the datasets in the repository to the /content/ of colab disk (note mentioned folder is default folder in colab disk, so no need to change any directory)
- Run the notebook as it is
-
On local machine
- Clone this repository on your local machine
- Change directory to the root of the cloned repository
- Run
pip3 install -r requirements.txtto install dependencies - Run the code on terminal as
python3 task.py .
-
Using Google Colab, without any uploads (slower performance) -
- Add shortcut of Shared folder on Google Drive to your drive
- Set
use_colab_disk = Falseon the first line of the Google Colab notebook - Run the Google Colab notebook
Input dataset contains binary images of characters and digits of resolution 1100 x 900. These training images are too large to be given as input, so as a preprocessing step we do the following -
- Find the contour of the characters
- Crop out these characters so as to remove the extra white background
- Resize the characters while maintaining aspect raio
- Paste these characters on a new image of size 28 x 28 with padding of 4 px
- Invert the colors to make the dataset in accordance with the MNIST dataset
- Save this modified dataset
Note - We are saving our processed dataset over here so as to fasten up the training and reduce the redundant work over the epochs, but this step can be added easily as a part of the transform pipeline.
Given dataset was normalized with mean 0.5 and standard deviation 0.5 before passing through the network.
After reading through a couple of architectures, I thought of starting with the most basic one LeNet-5 since this is easier to code and has been used in past on MNIST dataset. However the accuracy of this model does not come out to be good as the number of parameters are very low. So, finally I settled with a hybrid of VGG-NET and LeNet-5. I went over a couple of architectures like ResNet and Inception too but they are a bit complex to code in the time I had for the submission, and the suggested network gives a decent performance on the train and validation splits.
The layers in the suggested architecture are as follows -
- 64 3 x 3 filters with no padding
- 64 3 x 3 filters with no padding
- 2 x 2 max pooling layer
- 128 3 x 3 filters with no padding
- 128 3 x 3 filters with no padding
- 2 x 2 max pooling layer
- fully connected layer of 1024 neurons for 62 char recognition and of 512 neurons for 10 char recognition
- fully connected layer of 512 neurons for 62 char recognition and of 128 neurons for 10 char recognition
- fully connected layer of 62 neurons for 62 char recognition and of 10 neurons for 10 char recognition
Activation functions used in each of the intermediate layer is ReLU, with batch normalization being applied before every layer for faster convergence and dropout with p=0.25 being applied before every fc layer to prevent overfitting. AdamW was used as the optimizer to achieve faster convergence.
The provided dataset contains 55 images for each of the 62 classes. Since the number of datapoints in the dataset are low a random rotation of 20 degrees is also applied to artificially inflate the dataset a bit. Also dataset contains some confusing images too, like some images of s can be confused with that of 8.
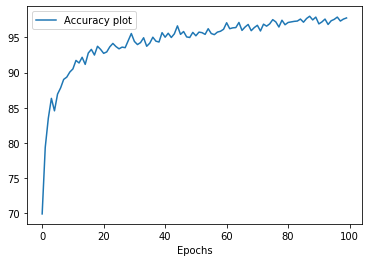
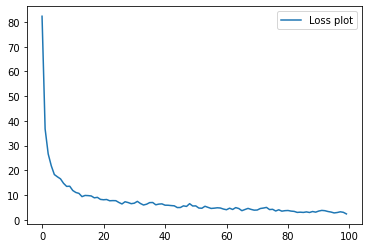
Training was first done with a 9:1 split of the train dataset into train and validation set. The model was able to achieve a validation accuracy of 97% and test accuracy of 98%. After this the model was fully trained over the entire dataset for 100 epochs.
Final accuracy on train dataset - 97.78225806451613%
We create another zip file from the given training dataset but with data points only consisting of 0 - 9 characters. This additional zip file has been included in the repository. Pre-processing as mentioned above is also applied to this dataset.
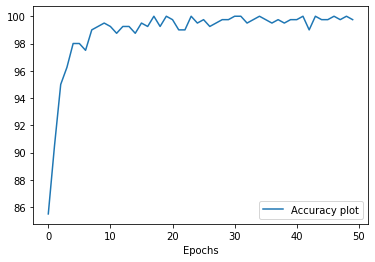
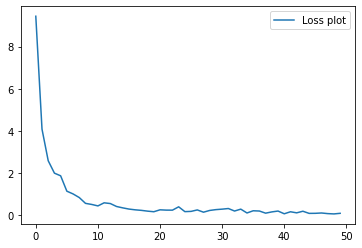
This time the cnn architecture is modified a bit and the number of parameters in the last fc layers are decreased as mentioned above in the CNN architecture. Finally the model is trained for 50 epochs.
Final accuracy on train dataset - 99.75%
Next we use this pretrained model and train on the MNIST dataset for 50 epochs.
Final accuracy on train dataset - 99.86833333333334%
Final accuracy on test dataset - 99.34%
Another cnn network with the same architecture with random initialization was taken and trained on the MNIST dataset for 50 epochs.
Final accuracy on train dataset - 99.91333333333333%
Final accuracy on test dataset - 99.56%
The pretrained network is able to obtain a higher accuracy and lower loss in the initial epochs, but on further training the randomly initialized network is able to achieve better final results. This signals that the pretrained network is not being able to escape the local minima. An effort to escape local minima can be seen with intermediate dips in the accuracy as the training progresses however the model is not able to converge to the global minima after 50 epochs (probably increasing number of epochs may lead to convergence).
First of all pretrained model from 2 is used and trained on this dataset for 50 epochs. The following results are observed -
Final accuracy on train dataset - 21.253333333333334%
Final accuracy on test dataset - 0.15%
Using a randomly initialized network and training for 50 epochs the following results are observed -
Final accuracy on train dataset - 21.591666666666665%
Final accuracy on test dataset - 0.2%
The dataset is shuffled with a lot of data points belonging to incorrect classes, so the pre-trained network will initially try to predict the correct classes. However since the loss function used is cross entropy loss, there is a high penalty for incorrect classification and the pre trained network is supposed to be off by a higher margin, since it understands the distinction between incorrect classes. Therefore in the final result we can observe that the training loss is higher for the pre-trained network and consequently the accuracy is lower for this model.