The project IoT@VET ("Gamification-Based Teaching Materials for IoT Education in VET Schools" | www.iotvet.eu), supported by the EU Erasmus+ funding program, aims to develop digital teaching materials and a gamification-based platform for Internet of Things (IoT) education in vocational education and training (VET) schools.
This repository contains the practical exercise modules developed by GT-ARC in the scope of IoT@VET project, focusing on the smart factory use cases.
The modules were curated by Dr. Fikret Sivrikaya and co-implemented with students at TU Berlin / GT-ARC.
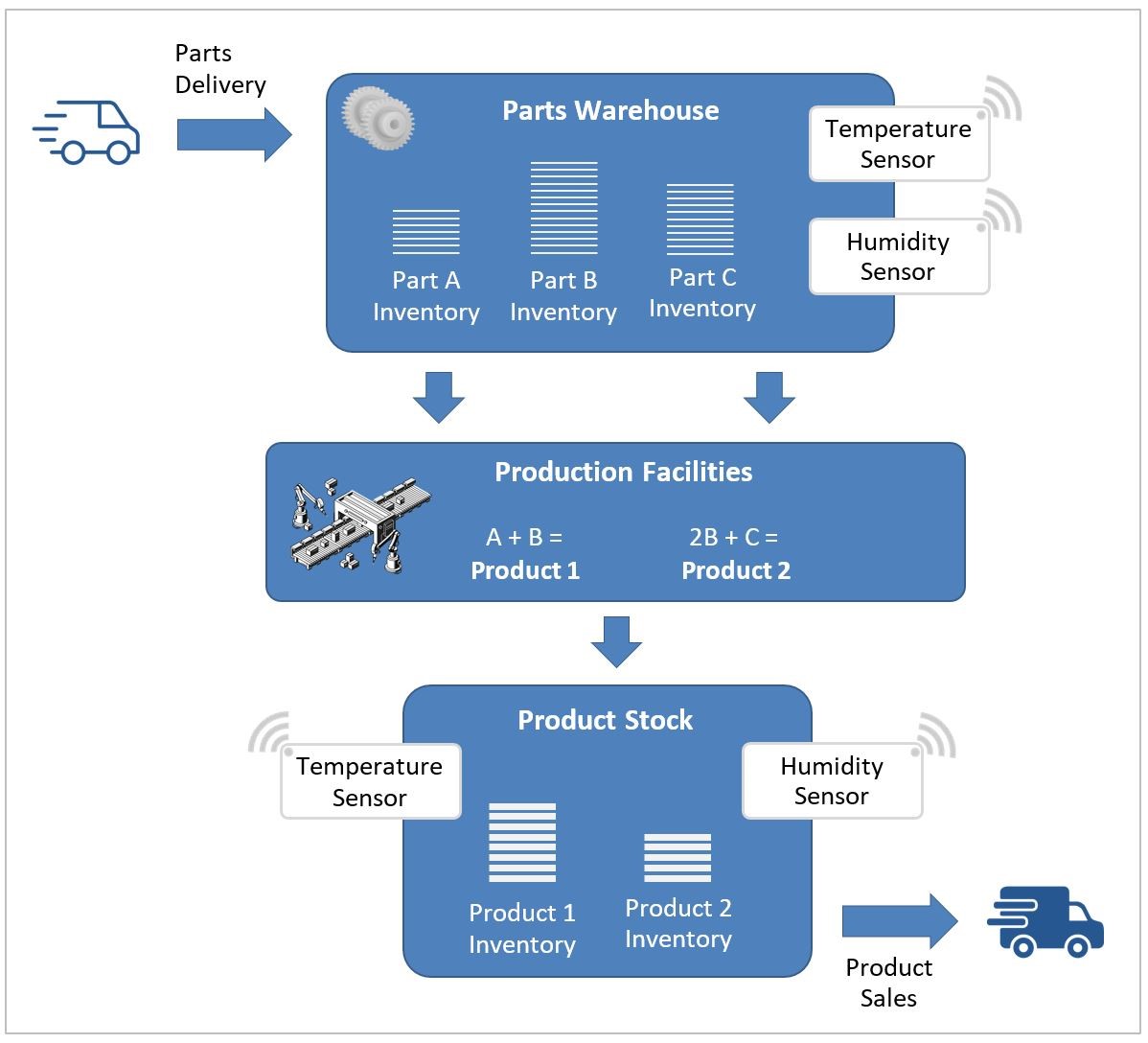
10 training modules are designed as an interconnected set of hands-on exercises in the domain of factories. The individual modules can be developed by different students or student groups in a class to collectively realize a "smart factory" IoT scenario, as depicted in the following figure.
- In our scenario, there is a warehouse, where different parts are delivered and stored. These parts have specific temperature and humidity requirements for long-term storage. Therefore, sensors are deployed in the warehouse to monitor the environment.
- The production facilities in the smart factory include conveyor belts and robotic systems for production. It is also supported by automated systems to pick up and deliver the required parts from the warehouses into the production facilities. For simplification, each product in our scenario is a combination of certain parts, as shown in the figure.
- The product stock serves as a warehouse for finished products and facilitates their automated delivery based on sales orders. As in the parts warehouses, the product stock is also equipped with temperature and humidity sensors to ensure proper storage conditions for the products.
- Finally, the smart factory has an automated inventory tracking system to monitor the amount of available parts and products in real time. Whenever there is a new delivery of certain parts, the production of a product, or sales and delivery of a product, the inventories are updated accordingly.
The next section provides a summary of the 10 modules within the scenario.
The first two training modules in this collection are common for all students and aim to set up the common development environment and baseline for the remaining lab sessions.
- Docker as a Virtualization Platform for Cloud and Edge: This module aims to introduce one of the virtualization concepts, containers, as an enabler of cloud and edge computing. It introduces Docker as a container technology and provides hands-on experience on the creation and management of containerized applications in the Docker environment, focusing on Node-RED as an example application running in Docker.
- Getting started with Docker
- Installing an application as a Docker container
- Running & configuring a container/app from an existing local image
- Node-RED as an IoT Application Development Tool: This module aims to provide basic understanding of Node-RED as a visual flow programming tool that can support IoT application design and development.
- Installing and running Node-RED (as a docker container)
- "Nodes" and “Flows” in Node-RED
- Creating your first flow / application in Node-RED
- Implementing the Parts Warehouse Sensors: This module implements simulated temperature and humidity sensors to keep track of the environmental conditions in the parts warehouse.
- Using the inject and function nodes in Node-RED to create virtual sensors
- Generating random numbers to emulate sensor data
- Using an MQTT-out node to send the sensor data to a remote MQTT Broker
- Implementing the Product Stock Sensors: Similar to the previous module, this module implements a pair of temperature and humidity sensors, but instead of creating them from scratch, we will see how to create a copy of the warehouse sensors and edit them easily for the product stock.
- Exporting and importing flows in Node-RED
- Editing the properties of existing flows and nodes
- Monitoring and Visualization of Sensor Data: This module implements a visual dashboard to monitor the sensor data from the parts warehouse and the product stock.
- Reading sensor data by subscribing to an MQTT topic
- Plotting sensor data by using node-red-dashboard nodes
- Understanding and adapting the user interface (UI) layout in Node-RED
- Implementing an Inventory Service API – GET Method: This module introduces how to implement an inventory database service in Node-RED and to develop a Web API for reading the current inventory/stock amount for any given part or product (e.g., "retrieve the number of part A units available in the warehouse").
- Using “flow variables” in Node-RED to store values persistently across different nodes
- Learning to implement a web service with a REST API
- Implementing a GET method for external software modules to read the inventory/stock states
- Implementing an Inventory Service API – POST Method: This module continues with the implementation of an inventory database service by developing a Web API for updating the inventory/stock for parts and products (e.g., "add two more units of Product 1 to the stock").
- Implementing a POST method for external software modules to update the inventory/stock states
- Observing the context data and variable values to test the application functionality
- Simulation of Parts Delivery and Product Sales: This module implements a web-based UI to simulate the delivery of parts to the warehouse and the sale of products from the available product stock. It utilizes the inventory/stock API of the web service from the last two modules.
- Implementing a client that uses the POST method of the web service API
- Using forms in Node-RED to retrieve and process user input
- Simulation of Production: This module implements a web-based UI to simulate the production in the smart factory, resulting in an increase in product stock values and decrease in the inventory of the associated parts. It also relies on the inventory/stock web service.
- Implementing a client that uses a combination of the GET and POST methods of the web service API
- Checking for sufficient amount of the required parts for production
- Dashboard for Monitoring Inventory/Stock status: This module implements a visual dashboard to monitor the number of available parts in the warehouse and products in the stock, utilizing the inventory/stock web service API from the previous modules.
- Creating web UI with multiple data series in a single plot
- Using bar charts for data visualization