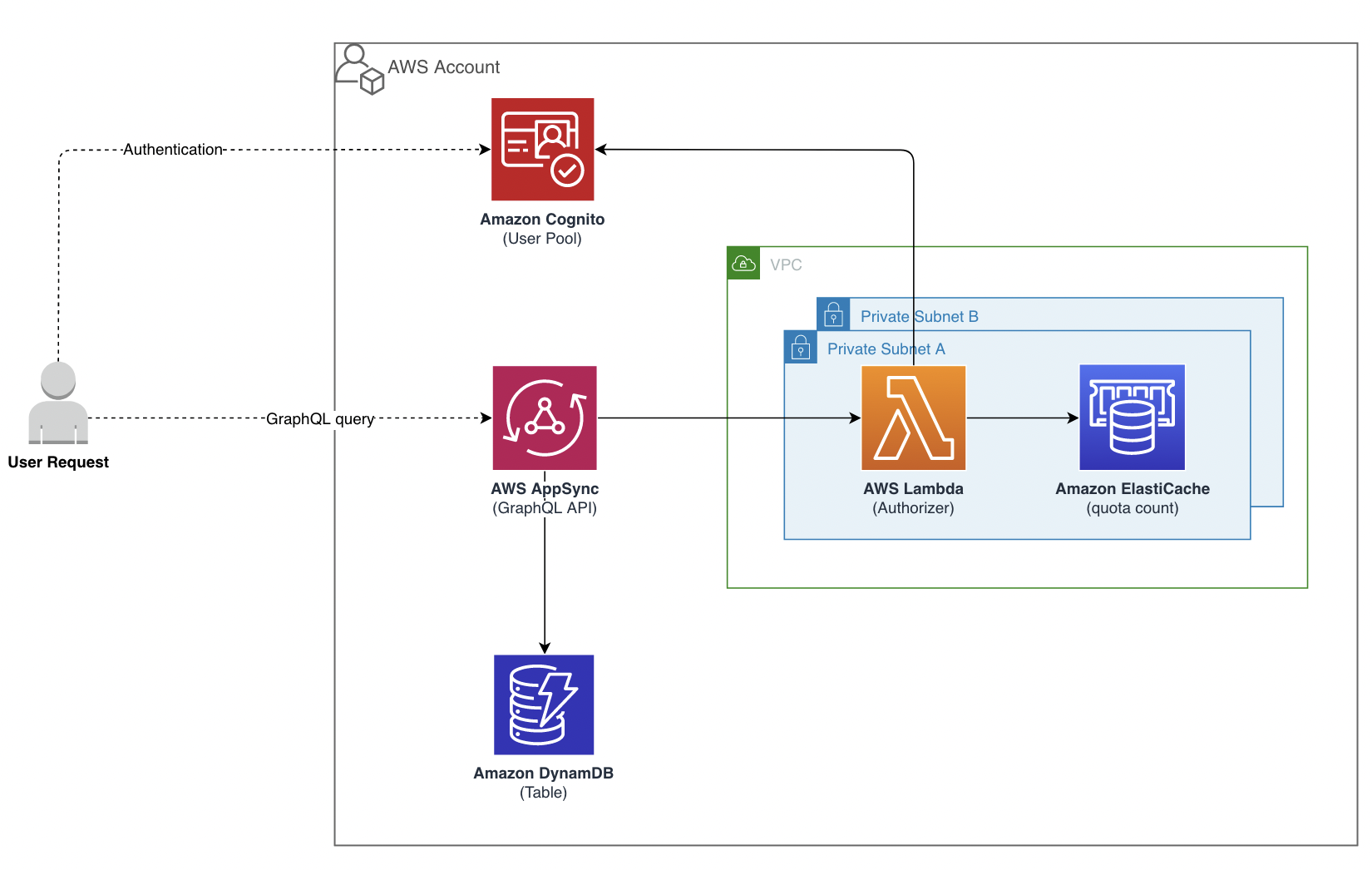
API Quotas define the valid amount of calls available for a consumer during a specific amount of time. Enforcing quotas protects your API from unintentional abuse, minimizes data exfiltration and protects your resources from excessive usage. Beyond the mentioned security benefits, it can also unlock your capabilities to monetize the digital assets sitting behind the API. This project showcases building blocks for applying daily user quotas on AWS AppSync using the Lambda Authorizer. ElastiCache for Redis, thanks to it's sub-millisecond latency, is used to track the call count in real time.
The backend is hosted on Amazon AppSync and uses GraphQL as the connector to the DynamoDB database where the data will live. Amazon Cognito User Pool serves as the OIDC identity provider. The Lambda authorizer provides authentication, authorization and quota enforecement per user at the AppSync API. The authentication logic is provided by a Lambda Layer where Cognitojwt library and the auth method are hosted. Current call count is tracked via ElasticCache for Redis. Both the Lambda functions and Redis cluster sit in a VPC on a private subnet. Once deployed, this solution will allow Cognito user pool users to log in and consume the data.
How to enforce user quota on AWS AppSync with Lambda authorizer
The cloudformation stack will create the following resources:
- AppSync GraphQL API
- DynamoDB Table
- Cognito User Pool
- Lambda Authorization function
- Lambda Layer containing authentication logic
- Redis Cluster
- Security Groups
- IAM Roles & Policies
- STACK_NAME - CloudFormation stack name
- AWS_REGION - AWS region where the solution will be deployed
- AWS_PROFILE - Named profile that will apply to the AWS CLI command
- ARTEFACT_S3_BUCKET - S3 bucket where the infrastructure code will be stored. (The bucket must be created in the same region where the solution lives)
- VPC - VPC id where the Lambda function and redis cluster will be deployed
- SUBNET_A - Private subnet id where the Lambda function and redis node will be deployed
- SUBNET_B - Private subnet id where the Lambda function and redis node will be deployed
- GraphQLUrl
- CognitoUserPoolId
- CognitoAppClientId
- CognitoAccesstokenUrl
- CognitoAuthUrl
- DynamoDBTableName
All deployments are done using bash scripts, in this case we use the following commands:
-
./deployment_scripts/deploy.sh- Packages, builds and deploys the local artifacts that your AWS CloudFormation template (e.g: cfn_template.yaml) is referencing./deployment_scripts/deploy.sh STACK_NAME \ ARTEFACT_S3_BUCKET \ AWS_PROFILE AWS_REGION \ SUBNET_A SUBNET_B \ VPC
-
./deployment_scripts/destroy.sh- Destroys the CloudFormation Stack you created in the deployment above (e.g: cfnstackdeployment)./deployment_scripts/destroy.sh STACK_NAME \ AWS_PROFILE AWS_REGION
Run the python script batch_upload_ddb.py to upload the sample data moviedata.json into the DynamoDB Table
python batch_upload_ddb.py -t DynamoDBTableName \
-p AWS_PROFILE -r AWS_REGION \
-f moviedata.jsonYou may test the solution via postman. In test you can find the postman collection json file with all the necessary configurations to authenticate and perform the GraphQL query. Once imported make sure to fill the variables in the collection. All values will be outputted from ./deployment_scripts/deploy.sh except for the CognitoAppClientSecret which you have to fetch from the Cognito console in the app client after the deployment.
- Cognito
- Make sure the stack name is all lowercase otherwise it will fail deployment. This comes due to the following configuration:
Domain: Fn::Sub: ${AWS::StackName}-${CognitoDomain}
- Make sure the stack name is all lowercase otherwise it will fail deployment. This comes due to the following configuration:
- Network:
- Select SubnetA and SubnetB as private subnets
- Have a Public NAT GW as endpoint for the 0.0.0.0/0 in your Subnet(s) routing table(s)
See CONTRIBUTING for more information.
This library is licensed under the MIT-0 License. See the LICENSE file.