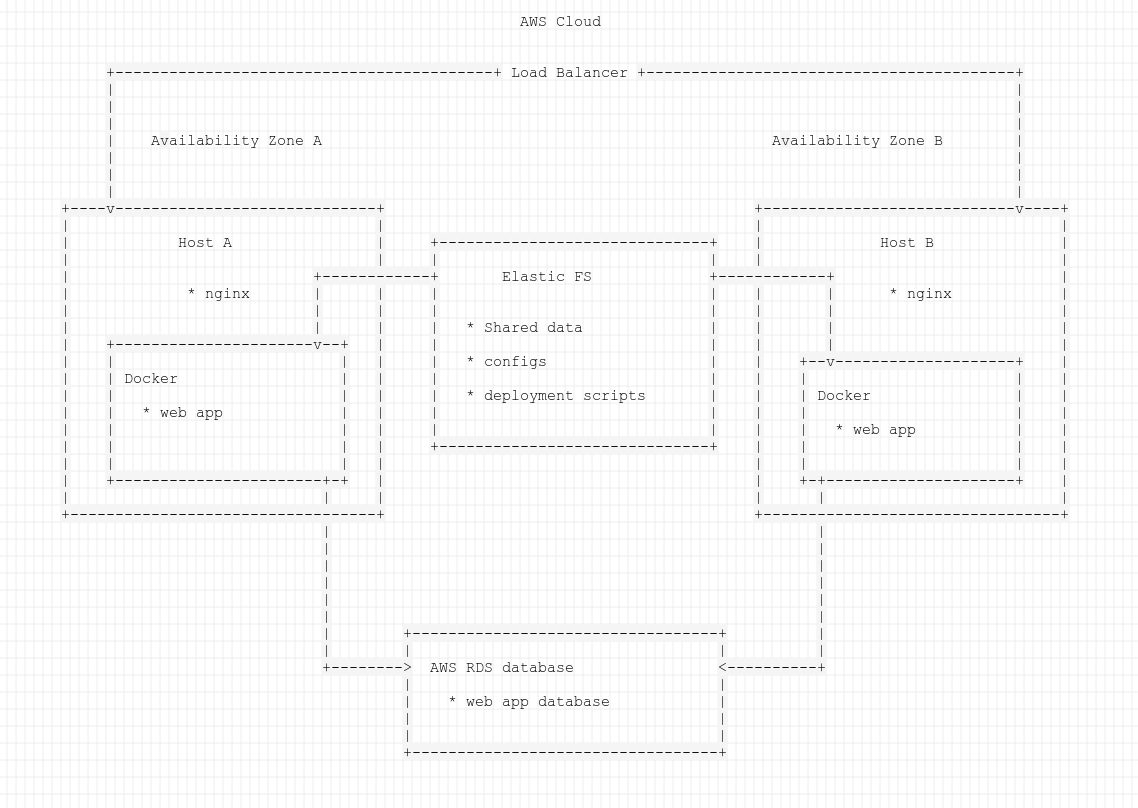
High Availability Setup Example
Initial estimation: 20h
Time spent: 21h 55m during 1 week
Playing with python Vibora: 4h 40m
Whats going on?!
We'll implement high availability setup for a web app, so your site or even business always would be available for customers with 99.99% SLA* and zero downtime updates**
*According to AWS SLA
**At least while you don't wanna do the sql database schema update
Requirements:
- Terraform
- Ansible
- Existed AWS account with admin api credentials
- Understanding that applying this setup will cost you money for used aws resources
- Understanding what we are doing here :)
Stack:
- AWS ec2 load balancer & instances, efs, rds
- Nginx as frontend web server with cache and static content serving
- Docker containers and compose for running application
- Terraform for configuring AWS infra
- Ansible for configuring everything on the hosts
Out of scope:
- Security: ssl, access control including VPC and Basition host, waf
- Infra: multisite setup, internal LB for app, dns
- Terraform: remote backend
- Ansible: dynamic inventory
- Dev env: docker registry, CD & CI env and system
How to do the same without AWS cloud:
- Load Balancer:
- you still can use some external lb like aws or cloudflare
- or you should setup it yourself, maybe with keepalived and haproxy or nginx
- Sync between hosts:
- some sync script like lsync or syncthing
- any cluster fs lile ceph or glusterfs
- some ntfs like aws efs
- Database:
- you still can use some external db like aws rds
- Mysql Galera
- Mariadb master-master
Anyway you should use keepalived or haproxy or glbd for HA for all except first one
- Hosts: can be any :)
Before we start :)
We would use some sensitive data that should never be stored in git repo, especially in public git repo
Data like:
- private aws ssh key
- private ssh key for app deployment
- mysql root password
- mysql app password
Lucky that I already generated strongly passwords and keys for you and stored it in the encrypted vault :)
You can store encrypted files like this in git repos with minimum risks
Vault file is ansible/group_vars/all/vault.yml and password is my_vault_password
(don't use so weaked passwords like this at home)
So first of all, do this for preventing ansible asking vault password at each execution
cd ansible
echo 'my_vault_password' > .vault_pass
ansible-vault decrypt group_vars/all/vault.yml
Next step: terraform also require own variables, so we'll convert our ansible yaml file into terraform json
python -c 'import json, sys, yaml ; \
y=yaml.safe_load(open("group_vars/all/vault.yml").read()) ; \
open("../terraform/ansible.auto.tfvars", "w").write(json.dumps(y))'
And we also need aws ssh private key for applying ansible setup into hosts
python -c 'import json, sys, yaml ; \
y=yaml.safe_load(open("group_vars/all/vault.yml").read()) ; \
open("id_rsa_aws", "w").write(y["ssh_privkey"])'
chmod 600 id_rsa_aws
ssh-add id_rsa_aws
Finally close the vault file and change directory to the main
ansible-vault encrypt group_vars/all/vault.yml
cd ..
Now we are ready to go! :)
Create infra with Terraform
cd terraform
terraform init
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID="XXX"
export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY="YYY"
export AWS_DEFAULT_REGION="us-west-2"
terraform plan
terraform apply
After dozen of minutes (thanks to rds db creation) you'll finally get something like this:
Apply complete! Resources: 12 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
Outputs:
efs = fs-80a57228.efs.us-west-2.amazonaws.com
web-a = 34.219.137.185
web-b = 34.221.216.70
web-db = web-db.cylt5xazlrm6.us-west-2.rds.amazonaws.com
web-lb = web-elb-1230834140.us-west-2.elb.amazonaws.com
Terrafrom also updated ansible variables:
diff --git a/ansible/group_vars/all/vars.yml b/ansible/group_vars/all/vars.yml
index 853eb00..df57033 100644
--- a/ansible/group_vars/all/vars.yml
+++ b/ansible/group_vars/all/vars.yml
@@ -1,9 +1,9 @@
ansible_port: 22
# separate aws rds variable as it can be used in multiple apps
-aws_rds_host: ''
+aws_rds_host: web-db.cylt5xazlrm6.us-west-2.rds.amazonaws.com
-app_efs: ''
-app_lb: ''
+app_efs: fs-80a57228.efs.us-west-2.amazonaws.com
+app_lb: web-elb
app_mysql_host: "{{ aws_rds_host }}"
mysql_root_password: "{{ rds_root_password }}"
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/ansible/inventory b/ansible/inventory
index eee5423..4be85db 100644
--- a/ansible/inventory
+++ b/ansible/inventory
@@ -1,2 +1,2 @@
-web-a
-web-b
+web-a ansible_host=34.219.137.185
+web-b ansible_host=34.221.216.70
For serious setup better use Ansible dynamic inventory but for now it's fine :)
Setup services and configs with Ansible
cd ../ansible
First of all we'll install python2 into servers as ansible require it
ansible-playbook playbooks/ansible-bootstrap-ubuntu.yml
After that we'll install basic packages, hostname and small fixes
ansible-playbook playbooks/common.yml
And finally we'll setup our app environment
ansible-playbook playbooks/setup_application.yml
Latest playbook do almost all the magic:
- install necessary soft like nginx, docker & docker-compose
- create directories for shared file system and docker logs
- mount aws efs into shared directory
- copy nginx and compose configs
- copy deployment script with ssh keys
- create app user and database
Finally run the app
ssh ubuntu@$(cd ../terraform; terraform output web-a)
We'll use dummy web app as an our setup payload.
I played a little with python vibora framework
and created docker container for you and uploaded it to the hub.
Most of the time I struggled with installing process or outdated documentation,
so I advise you to use it only for experiments and nothing more =\
However this framework looks promisingly.
You can find sources in the app directory in this repo.
This app would rerutn hello world to the / request and pong to the /ping request.
We'll run it in the docker container with our docker-compose config file:
cat /shared/configs/docker-compose.yml.
Ansible created it from roles/app/templates/docker-compose.yml.j2 template.
Don't forget to commit this config into git for history!
cd /shared/configs/ && git commit -a -m"add docker-compose.yml"
Deployment script will help us with first deployment (and with later updates).
You can check it before execution:
cat /shared/scripts/deploy.sh
It was also created by Ansible from roles/app/templates/deploy.sh.j2 template.
So, just run it:
sudo bash /shared/scripts/deploy.sh all
If all was fine and you didn't see something like 'I'm aborting deployment',
then you can log off with exit command and finally check your setup:
curl -v $(cd ../terraform; terraform output web-lb)
Hooray, we did it!
Don't forget to clean all in the end!
cd ../terraform
terraform destroy
cd ../
git reset --hard HEAD
What's next?
Tools:
- https://www.terraform.io
- https://aws.amazon.com/ru/blogs/apn/terraform-beyond-the-basics-with-aws/
- https://checklyhq.com/blog/2018/08/an-in-depth-look-at-100-zero-downtime-deployments-with-terraform/
- https://github.com/leucos/ansible-tuto
- https://docs.docker.com/compose/
Understanding: