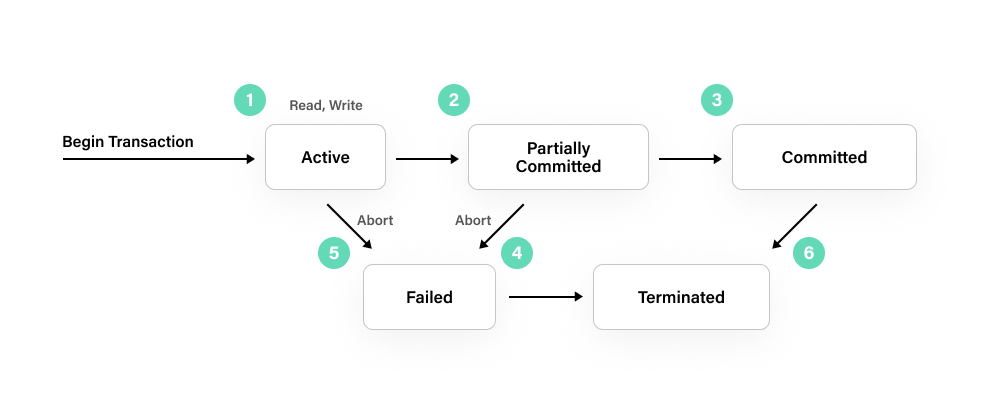
A database transaction is a sequence of operations that are executed as a single unit of work, ensuring that either all of the operations are completed successfully or none of them are. This ensures data consistency and integrity and is a fundamental aspect of database management systems.
Transactions are typically used in multi-user environments where multiple users are accessing the same database simultaneously. Transactions can help prevent conflicts between different users accessing the same data at the same time, and ensure that each user sees a consistent view of the data.
- Atomicity: All operations within a transaction must be completed successfully, or the transaction is rolled back to its initial state.
- Consistency: A transaction must leave the database in a consistent state, meaning that all integrity constraints and business rules are satisfied.
- Isolation: Each transaction must be executed in isolation from other transactions, so that each transaction sees a consistent view of the data.
- Durability: Once a transaction is committed, its changes must be permanent and survive any subsequent failures or system crashes. These properties ensure that transactions are reliable and consistent, and that the database is always in a valid state.
- Active: The transaction is currently executing its operations.
- Committed: The transaction has completed successfully and its changes have been permanently saved to the database.
- Rolled back: The transaction has been aborted due to an error or other issue, and its changes have been undone.
To control transactions, most databases provide commands to begin, commit, or rollback a transaction:
- BEGIN TRANSACTION: Starts a new transaction.
- COMMIT TRANSACTION: Commits the changes made in the current transaction to the database.
- ROLLBACK TRANSACTION: Rolls back the changes made in the current transaction and ends the transaction.
- It's important to note that transactions can also be implicitly started and committed by the database management system, such as when executing a single SQL statement.