picostack
A super lightweight KVM virtualization manager suitable for single linux-based host system. A motivation to write yet another VM manager is simple - picostack is
- open source (MIT license)
- is written to be minimalistic
- has little overhead, only control over instances
- can be installed as a python package, i.e.
pip install picostack - has a KVM (qemu) back-end
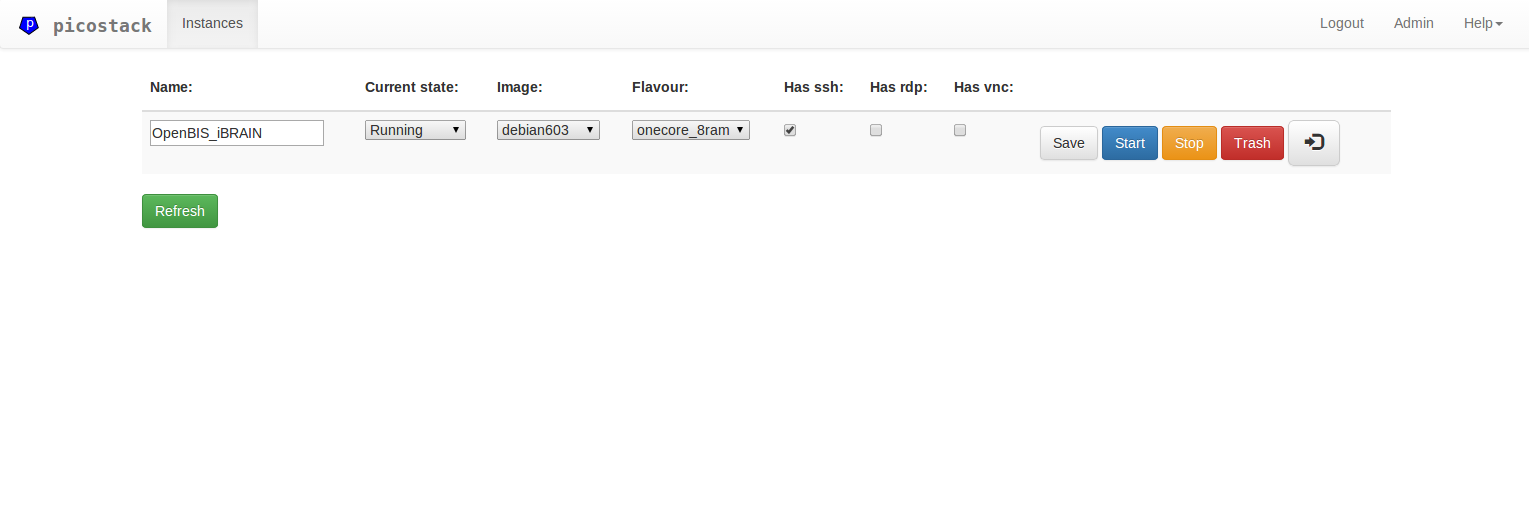
- has web-interface to manipulate execution of VMs (in a fashion motivated by OpenStack)
- powered by django framework
- allows mapping of network ports from guest system into the host system
Note that picostack is conceived as a virtualization manager - not a cloud service provider' software, but a single server split of available resources.
Copyright (c) 2014 Yauhen Yakimovich
Licensed under the MIT License (MIT). Read a copy of LICENSE distributed with this code.
Creating VM instances by cloning
To produce a new VM instance one should always clone a previously registered image disk. Machine starts with "In cloning" and transits to "Stopped" once done. Such a machine can be "launched" using web-interface with //host/instances overview. As soon as the VM is started it obtains state "Running" and continues to boot. After some period of time one can connect to mapped ports over the network to check if the guest has complete booting.
Adding new images
picostack init jeos Will attempt to use vmbuilder to create an example ubuntu JeOS image, which can be copied and registered in the DB.
In practice, anything supported by KVM can be used as long as you can convert the disk image into qcow2 format (e.g. virtual box machines can be converted to be run by KVM).
Currently, in order to register a new image one should use an admin part of the web interface (which is a usual django-based ORM editing interface).
Installation
Create a dedicated pstk user
Start by creating a new separate user for dedicated to run picostak daemon.
adduser pstk
sudo usermod -a -G www-data pstk
sudo usermod -a -G kvm pstkwhere www-data is your apache user.
Debian prerequisites
sudo apt-get install python-devGet a copy of picostack
Installation starts with obtaining a copy of picostack code either from github and perform a developer's installation like this:
git clone https://github.com/ewiger/picostack.git
cd picostack
pip install -e .or just give it a try your luck and directly pick a PyPI package:
pip install picostackConfiguration
Two consoles
Picostack has two controlling scripts that can be used in a command line to operate the program.
whereis picostk
picostk: /usr/local/bin/picostkand
whereis picostk-django
picostk-django: /usr/local/bin/picostk-djangoFirst one provides controlling interface over the picostack daemon as well as instances and images of the application.
Second one is a django-admin interface to access functionality pf the django system.
Default configuration
You should use a (sudoer) user to run the application. Currently the configuration folder is located in ~/.picostack
Calling
picostk init config
sudo picostk init dbwill populate the configuration folder with some default settings. Please navigate there and adjust it if you need to.
You would also need to init the database. Make sure to add you picostack user () or in any other way make access to the DB file shared with apache user. Default location is:
/var/picostack/db/picostk.sqlite3
Running at boot time
First, make sure you have the service script placed at /etc/init.d/pstk.
Second, to install picostack service as a boot time script to be run by debian-like system one has to register it with:
update-rc.d pstk defaultsRemoving is achieved by:
update-rc.d -f pstk removeConfiguring apache as the webinterface
It is not recommended to use picostk-django runserver for production
environment. Instead one should use something more reliable and production
ready, e.g. apache web server.
This should install and enable WSGI module in your apache: aptitude install libapache2-mod-wsgi.
Once module is installed, you can adopt the following example configuration of the virtual host:
# picostack virtual host:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin i@am.admin
DocumentRoot /usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/picostack
ServerName picostack.mysite.org
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/picostack.error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/picostack.access.log combined
WSGIScriptAlias / /usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/picostack/wsgi.py
WSGIDaemonProcess picostack.mysite.org python-path=/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/picostack:/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/:/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages
WSGIProcessGroup picostack.mysite.org
<Directory "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/picostack/">
<Files wsgi.py>
Require all granted
# For apache <= 2.4 uncomment and use lines below instead
# Order allow,deny
# Allow from all
</Files>
</Directory>
Alias /static/admin/ /usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/django/contrib/admin/static/admin/
<Directory "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/django/contrib/admin/static/admin/">
Require all granted
# For apache <= 2.4 uncomment and use lines below instead
# Order allow,deny
# Allow from all
</Directory>
Alias /static/ /usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/picostack/static/
<Directory "/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/picostack/static/">
Require all granted
# For apache <= 2.4 uncomment and use lines below instead
# Order allow,deny
# Allow from all
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>where /usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/picostack/ is the path to user's home folder and picostack.mysite.org is the website URL to be installed to.
For further details follow modwsgi documantaion on django page.
Running tests
There are a bunch of nose tests inside tests folder. A quick start to run them:
pip install nose
cd tests/
nosetestswbr, yy