A general purpose memory allocator must do at least three tasks: allocating a block of memory of a given size,\n freeing the allocated memory block and resizing the allocated memory block. These functions constitute a general purpose memory allocator interface.
In this task basic functions of page allocator will be implemented. The algorithm suggests we have a continuous part of memory which is divided into "pages". The pages have a constant size of some of the powers of 2.
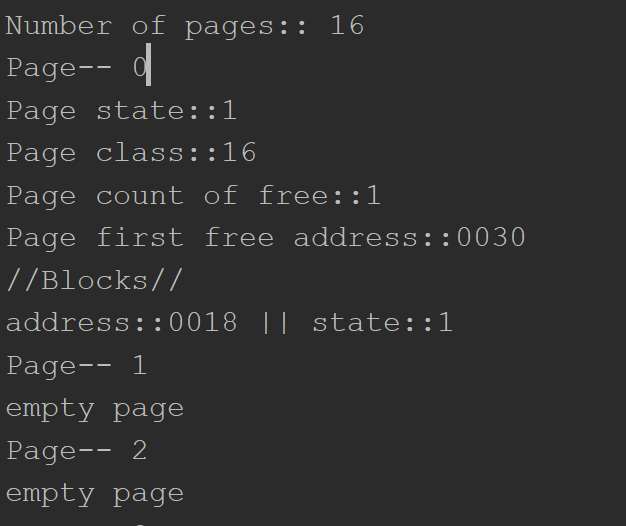
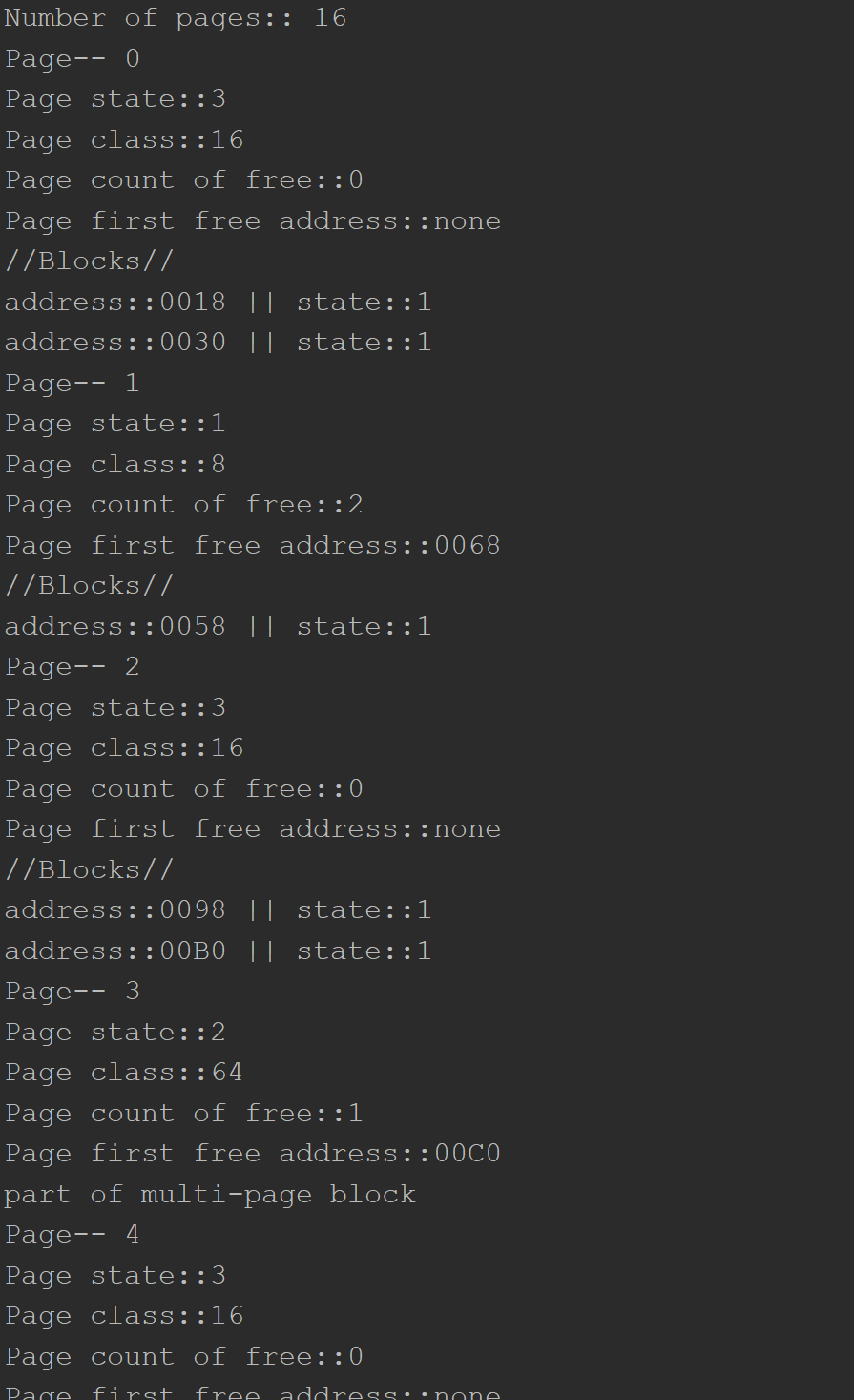
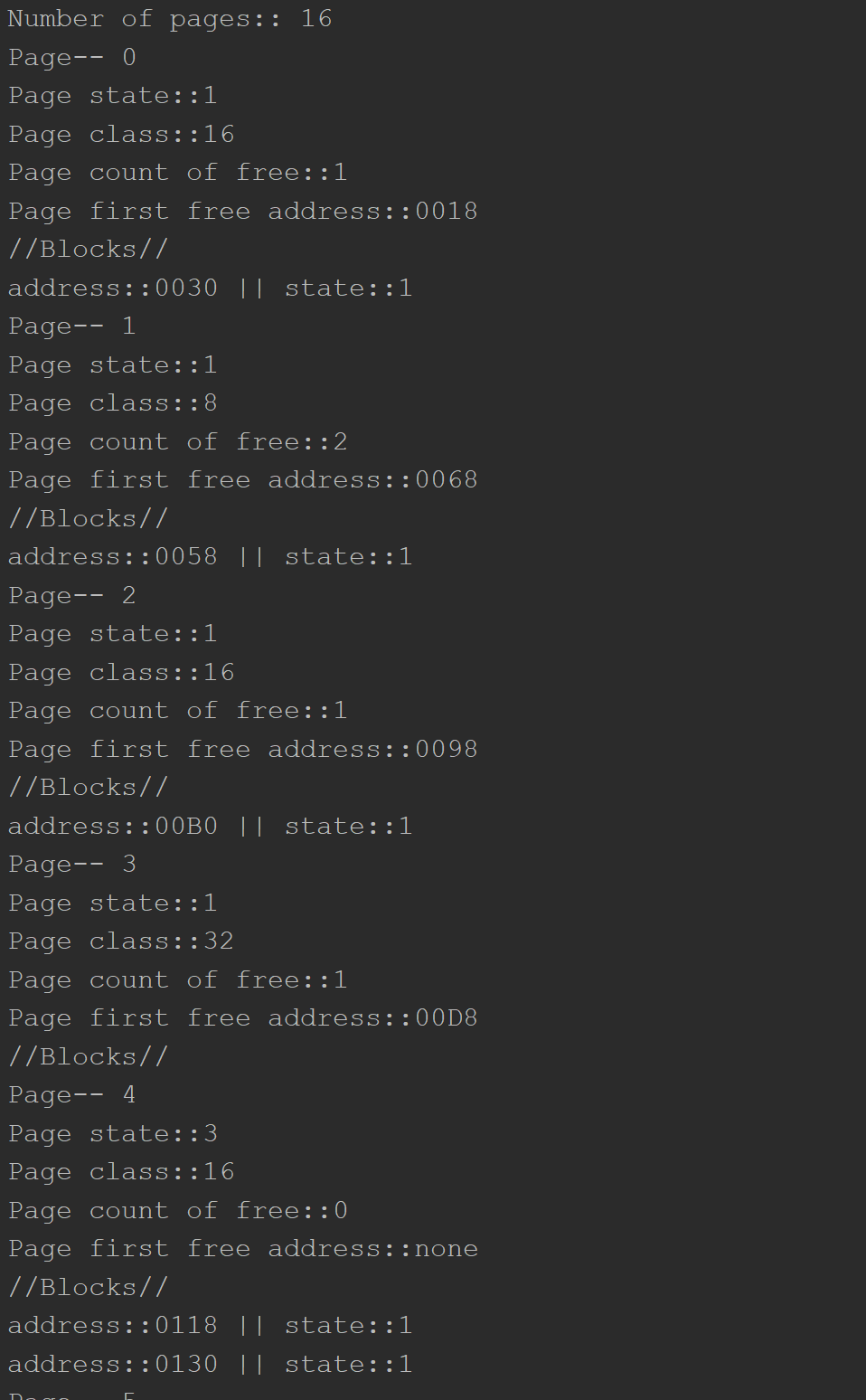
Each page has a descriptor. It always has fixed size of 16 bytes and consist of:
[state_of_the_page][class_of_the_page][counter_of_the_page][first_free_address] (4 bytes each)
There are 4 types of pages( depends on page state value).
- Free pages. Actually free pages, without any division into the blocks.
[state_of_the_page] ~ 0
- Pages divided into small blocks(small blocks have size lesser of equal to the half size of DEFAULT_PAGE_SIZE)
[state_of_the_page] ~ 1
This type of pages contains blocks consisted of header and data, where header
- Pages that are taken by multi-page blocks.
[state_of_the_page] ~ 2
- Pages with no free space, divided into small blocks.
[state_of_the_page] ~ 3
Each block has a header and the data. Header always has a fixed size of 9 bytes. The structure of header:
[previous_block_size] (4 bytes); [current_size] (4 bytes); [indicator_is_Empty] (1 byte);
-
void *mem_alloc(size_t size);
When function mem_alloc has called, it looks throw selected memory area for free blocks,
acceptance criteria: the size of the free block has to be at least size + HEADER_SIZE (default size of the header). Switch option:
- found free block properly size -> call function divide_into to divide founded area into two blocks (if it is possible);
- no empty module -> return null;
-
void mem_free(void *addr);
When function mem_free has called, it gets block by its address, flags it as empty and performs garbige_collection function that merges free blocks in memory area if they are adjacent.
-
void *mem_realloc(void *addr, size_t size);
There are two types of purposes to call this function: make the block bigger or smaller;
First of all, allocator creates a backup of the memory area to avoid deleting info from the current block and not updating it for new data if an error occurs. Second, it calls mem_free with and then find_next function that returns an address of the next block if it exists, otherwise, it returns a null value. If the new size of the block fits into the memory area between previous and next blocks -> execute writing into it, else: return null and set memory area value as the back up created at the first step.
// allocate memory block sized to 4 bytes
System.out.println(alloc.memAlloc(4));
// print sate of memory for address on 0008
alloc.memDamp("0008");
System.out.println(alloc.memAlloc(8));
System.out.println(alloc.memAlloc(6));
// free memory for current adresses
alloc.memFree("0014");
alloc.memFree("0008");
System.out.println("...");
// create blocks with size 8 and 6 bytes
System.out.println(alloc.memAlloc(8));
System.out.println(alloc.memAlloc(6));
System.out.println("...");
//resize block with address "0x08" to 4 bytes
System.out.println(alloc.memRealloc("0008", 4));
System.out.println(alloc.memAlloc(2));
//resize block with address "0x08" to 200 bytes
System.out.println(alloc.memRealloc("0008", 200));