Repository for plugins to let new NoSQL document databases leverage the Hackolade data modeling engine, if they're not natively supported in Hackolade (yet.)
The plugin architecture of Hackolade lets you create your own NoSQL database ‘targets’, following its terminology, attributes, and storage model through the customization of the following modules:
-
properties panes
-
localization
-
data types
-
connection and authentication parameters
-
reverse-engineering parameters for sampling and schema inference (TBD)
This guide walks you through the steps necessary to create your own plugin in your github repository and test it. Once you’re ready to make your plugin public, you may create a pull request for your entry in the registry file in this repo.
Each NoSQL document database has its own personality: terminology, storage approach, primary keys, indexing, partionning/sharding, data types, API, etc... At Hackolade, after adapting our engine to a couple of rather different NoSQL vendors, we quickly realized that we were going to have a hard time keeping up with the frequent appearance of new databases on the market. So, in order to unleash the power of our data modeling engine, we decided to rewrite the application and open up our features through a plugin architecture.
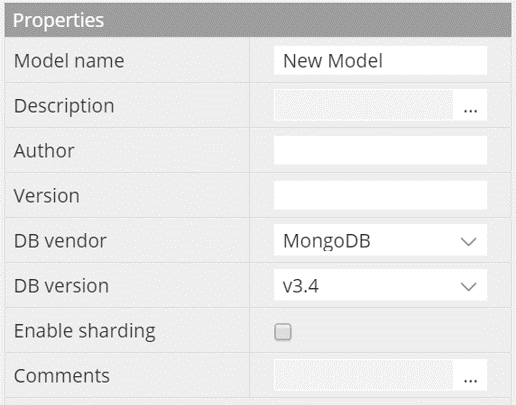
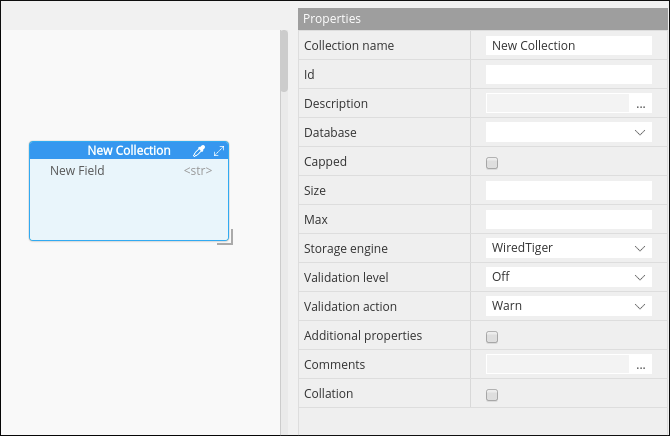
With the customization of the properties pane, you're able to control attributes specific to each DB at the following levels: model, container, collection, attribute, indexing, sharding, etc...
You can add the necessary property labels and control the input types.
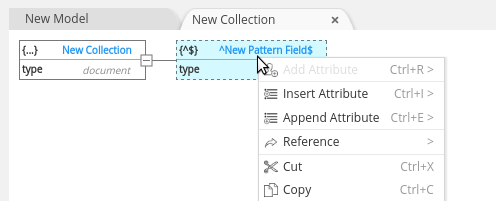
You can also define the entity hierarchy of the database:
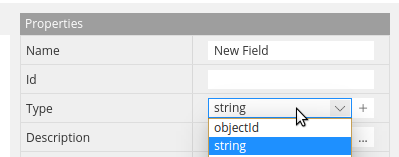
Each data type has its own set of properties and behaviour described in the configurations. Type changes affect UI of ERD (model view), DTD (collection tree view) and behaviour of the contextual menu:
The easiest way to create a new plugin is to copy an existing one as a starting point, and to edit it progressively, verifying along the way that the desired behavior gets reflected in the application. When choosing an existing plugin, make sure to take one with a storage model as cole as possible to yours.
Plugins are stored in the ~/.hackolade/plugins directory. The plugin folder name should be the same as the name property in package.json file of your plugin.
The package.json file is the plugin entry point. This file is required and contains initial info about plugin such as name, version, author, target name etc.. It should be placed in the root of your plugin folder. Package.json should contain several required properties that guarantee its uniqueness:
-
Name
-
Contributes
-
Author
See more details about each field of package.json file.
logo.jpg - the plugin logo image that will be displayed in the list of plugins. Name and extension of the file cannot be changed. The file is placed in the root folder next to the package.json file. If not set - the first letter from name property in package.json file will be used instead of logo.
Properties pane visual structure depends on the selected item (entity). There are several entity types in Hackolade that change the structure:
-
model
-
container
-
collection
-
view
-
field
Each entity can have several tabs. Current version supports customizing details tab only.
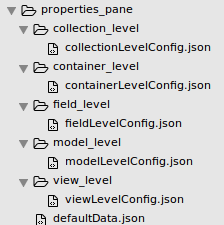
All configurations are stored in properties_pane folder and situated in the root of plugin folder. Each entity has own folder with corresponding naming:
-
model_level
-
container_level
-
collection_level
-
view_level
-
field_level
Inside each folder there’s a [ENTITYNAME]LevelConfig.json file which contains configurations for PP.
You can add defaultData.json file to a properties_pane folder to define default values that will be displayed in the PP. Here’s an example of properties pane folder structure:
Each *.json file represents an array with objects. Each object has configurations for a particular tab. Tab name is defined in lowerTab property. All properties are defined as array and have the same structure across all PP configurations. Here’s an example of details tab with one property comments:
[
{
"lowerTab": "Details",
"structure": [
{
"propertyName": "Comments",
"propertyKeyword": "comments",
"shouldValidate": false,
"propertyTooltip": "comments",
"propertyType": "details",
"propertyDefault": "Some comment",
"template": "textarea",
"valueType": "string"
}
]
}
]
For detailed information about each property see Property Pane Structure API.
containerLevelConfig contains description of collection keys for detailed see Container Level Keys.
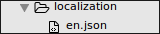
Localization folder contains files for language / target localization of your application. Language localization can be implemented by creating *.json files inside localization folder. File name for localization should correspond to ISO naming convention (e.g. en for English localization)
Each localized item inside *.json file is represented by a key/value pair e.g.:
"MAIN_MENU___ADD_COLLECTION": "Add Collection"
If you delete any predefined property from this file - default text will be displayed.
There are 7 basic types in Hackolade:
-
String
-
Boolean
-
Numeric
-
Document
-
Array
-
Binary
-
Null
If you don’t need to change name and behaviour of basic types - you can skip this configuration block. If you want to customize basic type or create a custom type - you can create your own configuration. The only condition is that new type must be INHERITED from the basic type.
For example in order to create custom type <list> on the base of the <array> type it is necessary to perform several steps:
-
Create list.json file inside types folder situated in the root of plugin folder (notice that file name should be the same as type name)
-
Set name, parent type (one out of list of 7 base types) and abbreviations for your custom type in the properties object inside list.json file:
{
"name": "list",
"erdAbbreviation": "<list>",
"dtdAbbreviation": "[...]",
"parentType": "array"
}
To learn more about all properties take a look at Field types API
All configurations for Reverse Engineering are stored in folder reverse_engineering. Connection and authentication params and connection settings modal configuration are defining in the connectionSettingsModalConfig.json file.
[
{
"lowerTab": "Connection",
"structure": [
{
"inputLabel": "Disable SSl Authentication",
"inputKeyword": "disableSSL",
"inputType": "checkbox",
"inputTooltip": "Disable SSl Authentication for local instance"
}
]
}
]
For detailed information about each property see Reverse Engineering API.
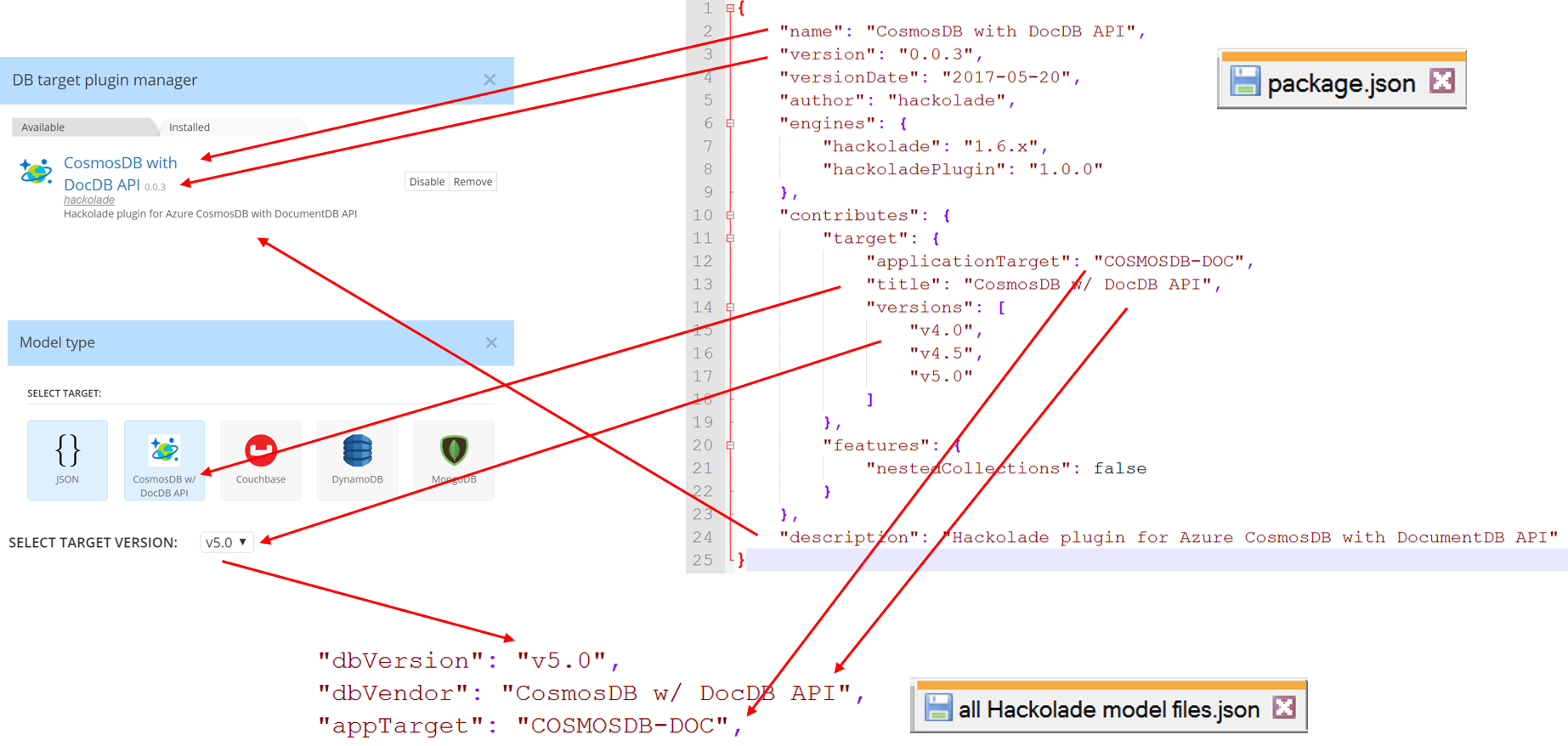
The package.json file is the plugin entry point. The mapping below shows how the information is used throughout the application.
name (string) - required; unique plugin name
version (string) - required; used to compare versions and provide possibility to update plugin
versionDate (string) - optional; value will be displayed in the plugins list;
author (string) - required; defines plugin author
engines (object) - required; used to define which Hackolade version supports plugin;
Example:
"engines": {
"hackolade": "1.6.x",
}
contributes (object) - required; provides information about the database target and available features.
Example:
"contributes": {
"target": {
"applicationTarget": "MONSTOR",
"title": "MonStor",
"versions": [
"v1.0"
]
},
"features": {
"nestedCollections": true
}
}
target (object) - provides information about target name for which the plugin was created; applicationTarget value should be uppercase.
features (object) - optional; object which defines what features will be enabled or disabled; Key is the name of feature. Value - true or false;
Available features:
- nestedCollections
description - optional; this data will be displayed in the list of plugins;
disabled - optional; used to mark the plugin as disabled; by default - false
Property pane structure is represented by array of objects with two properties:
-
lowerTab
-
structure
lowerTab is used to define type of tab for the entity. There are several modes of tabs in the application:
-
Details
-
Collection level users
-
Indexes
-
Sharding
-
Relationships
-
Model level users
structure property represents a collection of objects, each describing field type and behaviour.
[
{
"lowerTab": "Details",
"structure": [
{
"propertyName": "Comments",
"propertyKeyword": "comments",
"shouldValidate": false,
"propertyTooltip": "comments",
"propertyType": "details",
"propertyDefault": "Some comment",
"template": "textarea",
"valueType": "string"
}
]
}
]
propertyName (string) - required; used to display label in the Properties Panes for a property;
propertyKeyword (string) - required; used in the main code as a keyword; no whitespaces are allowed; should be lowercase;
shouldValidate (string) - optional; defines whether field should be validated or any value is allowed. Validation ruels are defined in validationRegularExpressions.json;
propertyType (string) - required; field types; can be simple or complex; simple types are select inputs or text inputs. Complex types usually use modal windows; Available field types to use when customizing PP properties are:
- text
"propertyType": "text"
- details (used to add a description or comments with defined template property, cfr below)
"propertyType": "details",
"template": "textarea"
- select (used with options property)
"propertyType": "select",
"options": [
"Public",
"Restricted",
"Confidential",
"Internal"
]
- number (used to add a numeric property)
"propertyType": "text",
"valueType": "number"
- checkbox (used to add description or comments with defined template property
"propertyType": "checkbox"
template (string) - optional; template that is used in the modal window if fieldtype is complex
- Textarea
valueType (string) - optional; type (one out of 7 basic types) to define validation rules
options (array) - optional; used to define options in the select input if fieldType is selected
propertyDefault (string|number|boolean) - optional; contains default value of property. Type of value dependent on propertyType.
"propertyType": "checkbox"
"propertyDefault": true
name (string) - required; type name
erdAbbreviation (string) - optional; abbreviation that is used to display in the ERD table
dtdAbbreviation (string) - optional; abbreviation used to define field visually on DTD
parentType (string) - optional; one out of 7 base types (used if custom type should be created)
sample (string) - optional; value that is used to display it in the corresponding input in PP by default
useSample (boolean) - optional; defines whether to use default value for sample or not
mode (array) - required for numeric fields; there are 4 base modes for numeric types:
-
Integer32
-
Integer64
-
Decimal128
-
Double
It is possible to define own mode with custom name that inherits base mode behaviour (esp. validation). For example here’s how a new mode int will be created:
{
"name": "int"
"parentType": "integer32",
"sample": 12
}
defaultValues (array) - optional; used to define properties in PP; can be different and custom for each type
Container Level Keys - fields which are the keys at the container level and automatically added to the collections when they are created. They are defining at containerLevelConfigюоыщт by property containerLevelKeys. For example:
{
"cotnainerLevelKeys": [...],
"structure": [...],
"lowerTab": "..."
}
Setting container level keys has the similar structure to Property Pane Structure API. For example key with name "Index":
{
"cotnainerLevelKeys": [{
"labelName": "Index",
"defaultName": "_index",
"propertyPrimaryKey": true,
"typeName": "Data type",
"typeOptions": ["string"],
"defaultType": "string",
"disabledFieldOption": true,
"sampleGen": "&containerName",
"propertyName": "Index",
"propertyKeyword": "index",
"propertyType": "text"
}]
}
labelName (string) - required; name of property in properties pane
propertyPrimaryKey (boolean) - required; whether the field is a primary key
typeName (string) - required; label name of selector type
typeOptions (array) - required; variant of types for field
defaultType (string) - optional; default field type
defaultName (string) - optional; default name of field
sampleGen (string) - optional; generate sample for field in preview, can contains next variants:
-
&random - will generate random value
-
&entityName - link to entity name
-
&containerName - link to container name
-
constant - some constant value
disabledFieldOption (boolean) - optional; disable options of field
Reverse Engineering structure is represented by several blocks and include:
- configuration for connection settings modal and authentication
- file with Database API functionality
- configuration for RE process
- package file for define npm modules for RE
Connection and authentication params and connection settings modal configuration are defining in the connectionSettingsModalConfig.json file.
[
{
"lowerTab": "Connection",
"structure": [
{
"inputLabel": "Disable SSl Authentication",
"inputKeyword": "disableSSL",
"inputType": "checkbox",
"inputTooltip": "Disable SSl Authentication for local instance"
}
]
}
]
This config contain a list of templates (tabs) for different part of connection settings split by categories and has the next structure:
lowerTab (string) - required; tab name in connection settings modal
structure (array) - required; list of inputs for connection settings modal
inputLabel (string) - required; connection settings input label
inputKeyword (string) - required; keyword for connection settings param which is used in the RE process
inputType (string) - required; type of connection settings input. Available input types to use when customizing connection settings template are:
- text
- checkbox
- password
inputTooltip (string) - optional; connection settings input tooltip message
inputPlaceholder (string) - optional; placeholder for connection settings input
isHiddenKey (string) - optional; flag that defines values which would be replaced by ****** in the log file
defaultValue (string) - optional; default value for connection settings param
File api.js it is an adapter between a database and a Hackolade application that allows you to perform RE and process data using the API methods:
- connect()
- disconnect()
- testConnection()
- getDatabases()
- getDocumentKinds()
- getDbCollectionsNames()
- getDbCollectionsData()
The file config.js consist error messages list and property excludeDocKind
errors (object) - list of error messages
excludeDocKind (array) - list of props which would be excluded from select docType modal
{
"errors": {
"NO_DATABASES": "There are no databases in CosmosDB instance",
"WRONG_CONNECTION": "Can not connect to CosmosDB instance"
},
"excludeDocKind": ["id"]
}
The file package.json contains a list of dependencies that are required to execute RE via api.js
TODO: Write usage instructions
-
Fork it!
-
Create your feature branch:
git checkout -b my-new-feature -
Commit your changes:
git commit -am 'Add some feature' -
Push to the branch:
git push origin my-new-feature -
Submit a pull request :D
TODO: Write history
TODO: Write credits
TODO: Write license