Tensorflow_MNIST_CNN
Summary
Python의 Tensorflow를 활용하여 MNIST 데이터 셋을 학습시키는 것이 목표이다.
이미지 학습에 뛰어난 성능을 가진 CNN(Convolution Neural Network)를 활용할 것이다.
MNIST Data
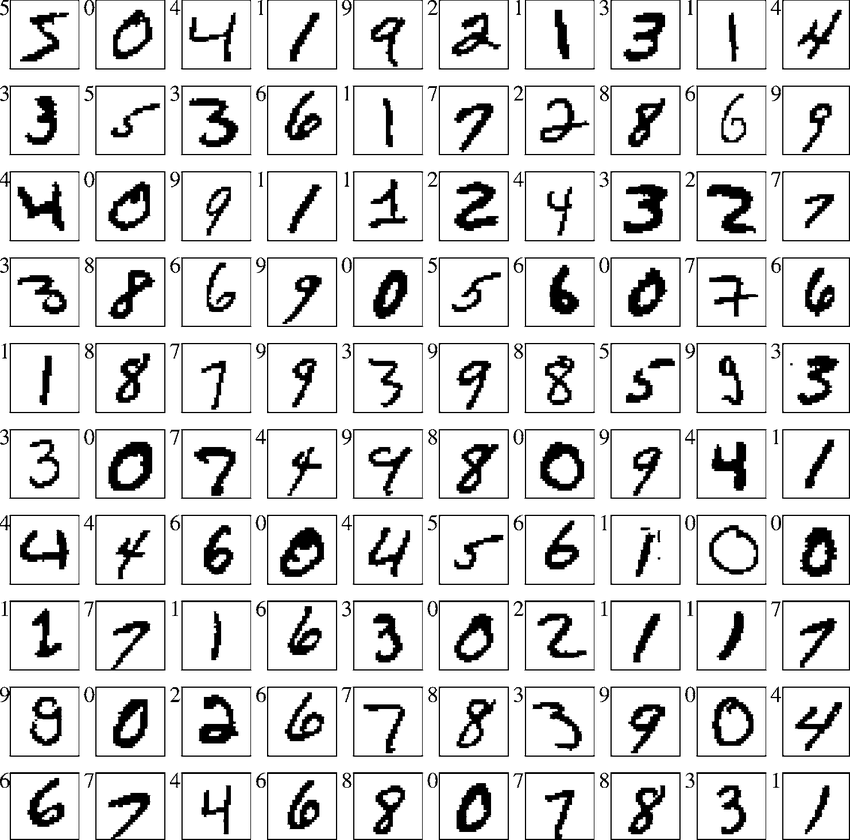
MNIST는 사람들의 손글씨가 그려져 있는 데이터이다. MNIST의 데이터는 28x28x1의 형태로 주어지며 Train과 Test 데이터로 나뉘게 된다. Train과 Test에는 라벨이 달려있어 그 손글씨가 어떤 숫자인지를 알려준다. Train 데이터는 학습에 사용할 계획이고 Test 데이터는 학습 후에 테스트를 해보는 용도로 사용할 것이다.
Source Code
Iibrary
tensorflow를 사용할 것이다.
MNIST를 사용하기 위해서 tensorflow의 예제를 이용한다.
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_dataFunction
shape으로 배열 모양의 입력을 받으면 truncated_normal 함수로 절단정규분포의 난수로 배열을 채워서 상수로 만들어준다.
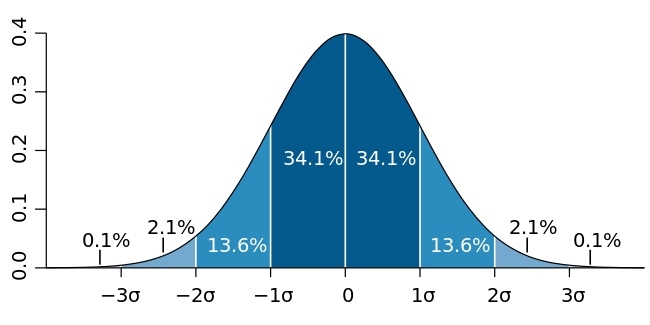
tf.truncated_normal에서 stddev는 정규분포에서 표준편차를 나타낸다.
stddev는 시그마에 들어간다.
def weight_variable(shape):
initial = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=shape, stddev=0.1))
return tf.Variable(initial)def bias_variable(shape):
initial = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=shape, stddev=0.1))
return tf.Variable(initial)합성곱을 해주는 함수이다.tf.nn.conv2d를 사용하여 (1, 1)칸씩을 이동하면서 x와 w를 합성곱 해주고 padding 설정을 통해 출력은 입력한 사진 즉 28x28의 크기로 출력을 해준다. 그리고 마지막으로 bias를 더해준다.
def conv2d(x, w, bias):
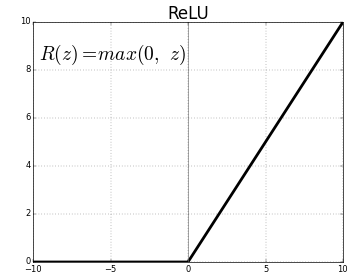
return tf.nn.conv2d(x, w, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME') + biasrelu함수는 0보다 작은 값은 0으로 0보다 큰 값은 그대로 출력한다.
def relu(x):
return tf.nn.relu(x)Pooling 레이어 사이즈를 2x2로 정했다. 그리고 strides를 (2, 2)로 설정하였다. 2x2에서 가장 큰 값이 Pooling 된다.
def max_pool_2x2(x):
return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')Input Layer(MNIST Data Set)
Moist 데이터를 불러와 이미지를 28x28 사이즈로 모양을 설정하여 X에 저장하였다. Y_Label에 이미지의 손글씨가 나타내는 숫자를 저장하였다.
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("data/MNIST_data/", one_hot=True, reshape=False)
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 28, 28, 1])
Y_Label = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 10])Hidden Layer
Hidden Layer 를 2개로 정했다.
Layer 1개에 Convolution -> Relu -> Pooling 과정이다.
첫 번째 Layer는 14x14 사이즈로 두 번째 Layer에 넘겨준다. 두 번째 레이어는 7x7 사이즈로 Output Layer에 넘겨주게 된다.
Conv1 = conv2d(X, weight_variable([4, 4, 1, 4]), bias_variable([4]))
Relu1 = relu(Conv1)
Pool1 = max_pool_2x2(Relu1)
Conv2 = conv2d(Pool1, weight_variable([4, 4, 4, 8]), bias_variable([8]))
Relu2 = relu(Conv2)
Pool2 = max_pool_2x2(Relu2)Output Layer
Hidden Layer에서 넘겨준 값을 [392] 1차원으로 펴준다. 그리고 W1과 합성곱을 한 후 b1(bias)를 더해준다.
W1 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=[8*7*7, 10]))
b1 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=[10]))
Pool2_flat = tf.reshape(Pool2, [-1, 8*7*7])
OutputLayer = tf.matmul(Pool2_flat, W1) + b1
Softmax_cross_entropy를 하고 값 평균을 구한후 Loss에 담는다.
Loss를 Gradient Descent(Learning rate=0.005)하여 학습시킨다.
Loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=Y_Label, logits=OutputLayer))
train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(0.005).minimize(Loss)tf.arg_max를 사용하여 가장 큰 값의 위치를 나타낸다 즉 모델이 예측한 숫자를 말한다.
tf.equal를 사용하면 비교하여 같은 값이면 True, 다른 값이면 False를 출력한다.
Tf.cast를 사용하여 correct_prediction을 float32 형으로 바꾸고 tf.reduce_mean 을 사용하여 평균 값을 구한다.
Accuracy(평균 값)은 모델의 예측 성공률을 나타낸다.
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.arg_max(OutputLayer, 1), tf.arg_max(Y_Label, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))Learning And Test
64개 데이터를 1000번 학습시킨다.
X에 이미지가 주어지고 Y_Lable에 이미지 정답이 주어진다.
100번 마다 Test를 하는데 X에 테스트 이미지를 주고 Y_Label에 테스트 이미지의 정답을 준다.
학습률인 accuracy를 줄력한다.
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for i in range(1000):
trainingData, Y = mnist.train.next_batch(64)
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={X: trainingData, Y_Label: Y})
if i % 100 == 0:
print(sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={X: mnist.test.images, Y_Label: mnist.test.labels}))Full Sources
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
def weight_variable(shape):
initial = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=shape, stddev=0.1))
return tf.Variable(initial)
def bias_variable(shape):
initial = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=shape, stddev=0.1))
return tf.Variable(initial)
def conv2d(x, w, bias):
return tf.nn.conv2d(x, w, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME') + bias
def relu(x):
return tf.nn.relu(x)
def max_pool_2x2(x):
return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
# 데이터 셋 블러오기
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("data/MNIST_data/", one_hot=True, reshape=False)
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 28, 28, 1])
Y_Label = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 10])
Conv1 = conv2d(X, weight_variable([4, 4, 1, 4]), bias_variable([4]))
Relu1 = relu(Conv1)
Pool1 = max_pool_2x2(Relu1)
Conv2 = conv2d(Pool1, weight_variable([4, 4, 4, 8]), bias_variable([8]))
Relu2 = relu(Conv2)
Pool2 = max_pool_2x2(Relu2)
W1 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=[8*7*7, 10]))
b1 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=[10]))
Pool2_flat = tf.reshape(Pool2, [-1, 8*7*7])
OutputLayer = tf.matmul(Pool2_flat, W1) + b1
Loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=Y_Label, logits=OutputLayer))
train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(0.005).minimize(Loss)
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.arg_max(OutputLayer, 1), tf.arg_max(Y_Label, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for i in range(1000):
trainingData, Y = mnist.train.next_batch(64)
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={X: trainingData, Y_Label: Y})
if i % 100 == 0:
print(sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={X: mnist.test.images, Y_Label: mnist.test.labels}))Resources
http://coderkoo.tistory.com/13
http://cs231n.github.io/convolutional-networks/
https://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/정규_분포
http://pythonkim.tistory.com/69
https://gist.github.com/haje01/202ac276bace4b25dd3f
https://legacy.gitbook.com/book/tensorflowkorea/tensorflow-kr/details