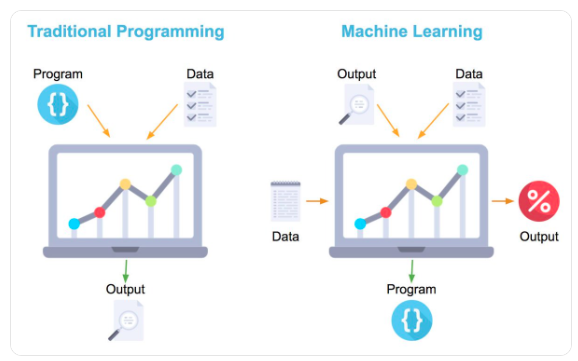
Machine learning is an application of artificial intelligence (AI) that provides systems the ability to automatically learn and improve from experience without being explicitly programmed. Machine learning focuses on the development of computer programs that can access data and use it learn for themselves.
- It uses the data to detect patterns in a dataset and adjust program actions accordingly.
- It focuses on the developement of computer program that can teach themselves to grow and change when exposed to new data.
- It enables computers to find hidden insights using iterative alogrith without being explicitly programmed.
- Machine Learning is a method of data analysis that automates analytical model building.
Machine learning algorithms are often categorized as supervised or unsupervised.
-
Supervised machine learning algorithms can apply what has been learned in the past to new data using labeled examples to predict future events. Starting from the analysis of a known training dataset, the learning algorithm produces an inferred function to make predictions about the output values. The system is able to provide targets for any new input after sufficient training. The learning algorithm can also compare its output with the correct, intended output and find errors in order to modify the model accordingly.
-
Unsupervised machine learning algorithms are used when the information used to train is neither classified nor labeled. Unsupervised learning studies how systems can infer a function to describe a hidden structure from unlabeled data. The system doesn’t figure out the right output, but it explores the data and can draw inferences from datasets to describe hidden structures from unlabeled data.
-
Semi-supervised machine learning algorithms fall somewhere in between supervised and unsupervised learning, since they use both labeled and unlabeled data for training – typically a small amount of labeled data and a large amount of unlabeled data. The systems that use this method are able to considerably improve learning accuracy. Usually, semi-supervised learning is chosen when the acquired labeled data requires skilled and relevant resources in order to train it / learn from it. Otherwise, acquiringunlabeled data generally doesn’t require additional resources.
-
Reinforcement machine learning algorithms is a learning method that interacts with its environment by producing actions and discovers errors or rewards. Trial and error search and delayed reward are the most relevant characteristics of reinforcement learning. This method allows machines and software agents to automatically determine the ideal behavior within a specific context in order to maximize its performance. Simple reward feedback is required for the agent to learn which action is best; this is known as the reinforcement signal.
It learns from given data and find insights. According to data it makes changes in program.
- Collecting Data: Collecting data from various sources
- Data Wrangling: Formatting raw data.
- Analyse Data: Analysis on data
- Train Algorithm: Fit model
- Test Algorithm: Test model
- Deployment: Deploy in real system
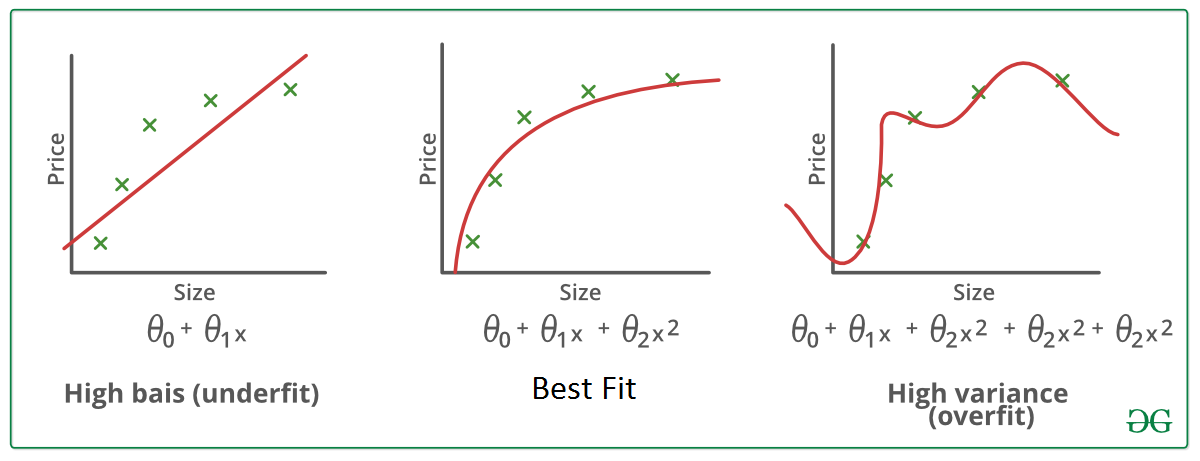
Fitting is a measure of how well a machine learning model generalizes to similar data to that on which it was trained. A model that is well-fitted produces more accurate outcomes, a model that is overfitted matches the data too closely, and a model that is underfitted doesn’t match closely enough.
Each machine learning algorithm has a basic set of parameters that can be changed to improve its accuracy. During the fitting process, you run an algorithm on data for which you know the target variable, known as “labeled” data, and produce a machine learning model. Then, you compare the outcomes to real, observed values of the target variable to determine their accuracy. Next, you use that information to adjust the algorithm’s standard parameters to reduce the level of error, making it more accurate in uncovering patterns and relationships between the rest of its features and the target. You repeat this process until the algorithm finds find the optimal parameters that produce valid, practical, applicable insights for your practical business problem.
Underfit- By looking at the graph on the left side we can predict that the line does not cover all the points shown in the graph. Such model tend to cause underfitting of data .It also called High Bias.
Overfit- Where as the graph on right side, shows the predicted line covers all the points in graph. In such condition you can also think that it’s a good graph which cover all the points. But that’s not actually true, the predicted line into the graph covers all points which are noise and outlier. Such model are also responsible to predict poor result due to its complexity. It is also called High Variance.
Good Fit- Looking at the middle graph it shows a pretty good predicted line. It covers majority of the point in graph and also maintains the balance between bias and variance.
Solving the issue of bias and variance is really about dealing with over-fitting and under-fitting. Bias is reduced and variance is increased in relation to model complexity. As more and more parameters are added to a model, the complexity of the model rises and variance becomes our primary concern while bias steadily falls.
Bias:It gives us how closeness is our predictive model’s to training data after averaging predict value. Generally algorithm has high bias which help them to learn fast and easy to understand but are less flexible. That looses it ability to predict complex problem, so it fails to explain the algorithm bias. This results in underfitting of our model.
Getting more training data will not help much.
Variance:It define as deviation of predictions, in simple it is the amount which tell us when its point data value change or a different data is use how much the predicted value will be affected for same model or for different model respectively. Ideally, the predicted value which we predict from model should remain same even changing from one training data-sets to another, but if the model has high variance then model predict value are affect by value of data-sets.
The Graph below shows the path when a learning algorithm suffers from High Variance. This show getting more training data will help to deal with it.
There are two ways to avoid this overfitting, getting more data and regularization.
-
Getting more data is usually the best solution, a model trained on more data will naturally generalize better.
-
Regularization is done when the latter is not possible, it is the process of modulating the quantity of information that the model can store or to add constraints on what information it is allowed to keep. If the model can only memorize a small number of patterns, the optimization will make it to focus on the most relevant ones, improving the chance of generalizing well.
Regularization is done mainly by the following techniques:
-
Reducing the model’s size: Reducing the number of learnable parameters in the model, and with them its learning capacity. The goal is to get to a sweet spot between too much and not enough learning capacity. Unfortunately, there aren’t any magical formulas to determine this balance, it must be tested and evaluated by setting different number of parameters and observing its performance.
-
Adding weight regularization: In general, the simpler the model the better. As long it can learn well, a simpler model is much less likely to overfit. A common way to achieve this, is to constraint the complexity of the network by forcing its weights to only take small values, regularizating the distribution of weight values. This is done by adding to the loss function of the network a cost associated with having large weights. The cost comes in two ways-
-
L1 regularization: The cost is proportional to theabsolutethe value of the weights coefficients (L1 norm of the weights).
-
L2 regularization: The cost is proportional to the square of the value of the weight coefficients (l2 norm of the weights)
-
- Google Maps: Find your historical patterns etc.
- Uber: Find location, find your patterns etc.
- Social Media (Tagging): Facebook dface project for tagging people on image.
- Virtual Assistant: Google Assistant, Alexa, Cortana etc
- Product Recommendations: Amazon
- Self Driving Car: Tesla
- Applications using ML: Netfilx, Amazon, Hulu etc.
-
Supervised Learning-
1.1. Classification
1.2. Regression
-
Unsupervised Learning
2.1. Clustering
2.2. Association
Lets Understand in Detail-
Supervised learning problems can be further grouped into regression and classification problems.
Supervised learning is where you have input variables (x) and an output variable (Y) and you use an algorithm to learn the mapping function from the input to the output.
Y = f(X)
The goal is to approximate the mapping function so well that when you have new input data (x) that you can predict the output variables (Y) for that data.
It is called supervised learning because the process of an algorithm learning from the training dataset can be thought of as a teacher supervising the learning process. We know the correct answers, the algorithm iteratively makes predictions on the training data and is corrected by the teacher. Learning stops when the algorithm achieves an acceptable level of performance.
- Classification: A classification problem is when the output variable is a category, such as “red” or “blue” or “disease” and “no disease”.
- Regression: A regression problem is when the output variable is a real value, such as “dollars” or “weight”.
Unsupervised learning is where you only have input data (X) and no corresponding output variables.
The goal for unsupervised learning is to model the underlying structure or distribution in the data in order to learn more about the data.
These are called unsupervised learning because unlike supervised learning above there is no correct answers and there is no teacher. Algorithms are left to their own devises to discover and present the interesting structure in the data.
Unsupervised learning problems can be further grouped into clustering and association problems.
- Clustering: A clustering problem is where you want to discover the inherent groupings in the data, such as grouping customers by purchasing behavior.
- Association: An association rule learning problem is where you want to discover rules that describe large portions of your data, such as people that buy X also tend to buy Y.
We wil talk about following algorithm. We will also talk about Mathematics behind it and Implementation in Python.
-
Supervised Learning-
1.1. Linear Regression
1.2. Logistic Regression
1.3. Decision Tree
1.4. Random Forest
1.5. Naive Bayes Classifier
1.6. Support vector machines for classification problems.
-
Unsupervised learning-
2.1. k-means for clustering problems
2.2. Apriori algorithm for association rule learning problems
-
Semi-Supervised Learning
-
Reinforcement Learning