LockedList is an NSIS plug-in written by Afrow UK. It displays or gets a list of programs that are locking selected files that are to be uninstalled or overwritten.
The changelog can be found here.
Further information about the plug-in can be found on the Winamp forum.
This is not an "official repository", as that doesn't seem to exist. The plug-in had not been updated since 2015, and there were a couple of known issues with it, which has been addressed. This repository has been created so that there is a place where bug fixes can be submitted, and updated builds downloaded. There are no plans for "active development" of the plug-in.
Extract x86-unicode\LockedList.dll to your NSIS\Plugins\x86-unicode
folder.
Extract x86-ansi\LockedList.dll to your NSIS\Plugins\x86-ansi folder.
To be able to find 64-bit modules from a 32-bits NSIS installer, in addition to the above file, extract LockedList64.dll to somewhere and copy it to the NSIS\Plugins folder from the NSIS script. The same 64-bit DLL is used for both ANSI and Unicode. See LockedListKernel32.nsi for an example.
Extract LockedList64.dll to your NSIS\Plugins\x64-unicode
folder and rename it to LockedList.dll.
See Examples\LockedList for examples of use.
The main plug-in functions loop through system handles and process modules to find a file that your installer has to overwrite or delete.
As of 0.4, LockedList supports listing of currently open applications.
As of 0.7, the plug-in also supports listing of applications from window classes and captions.
As of 0.9, a Unicode build is included.
As of 3.0.0.0, 64-bit module enumeration (for ::AddModule) is now supported. Simply extract a copy of LockedList64.dll to $PLUGINSDIR on 64-bit machines (see the LockedListKernel32.nsi example script). The same LockedList64.dll is used for both ANSI and Unicode installers.
For the LockedList dialog, processes on the list will be removed when they have been closed or terminated, enabling the Next button if the list becomes empty.
LockedList also has support for silent installers with NSIS stack interaction as opposed to using a dialog. Silent searching can also be performed asynchronously so that other tasks can be performed while the plug-in searches (such as a progress bar).
The plug-in uses API's only available on Windows XP and upwards and therefore you cannot use the plug-in on a version of Windows that is older than Windows XP.
WinVer.nsh can be used to handle this:
!include WinVer.nsh
…
${If} ${AtLeastWinXP}
; Call LockedList plugin.
${EndIf}These functions must be called before displaying the dialog or performing a silent search.
LockedList::AddFile "path\to\myfile.ext"This adds an ordinary file. These files are searched case-insensitively by enumerating open file handles.
String matching is done from the end of the string, therefore you can also specify just the file name (with a leading backslash) like so: "\myfile.ext".
See LockedListTest.nsi for an example.
LockedList::AddModule "path\to\mylibrary.dll"
LockedList::AddModule "path\to\mycontrol.ocx"
LockedList::AddModule "path\to\myapp.exe"This adds a module file. This includes DLL, OCX and EXE files. These files are searched for case-insensitively by enumerating running process modules. To enumerate 64-bit DLL and OCX files from a 32-bit installer, you must extract LockedList64.dll to $PLUGINSDIR first.
String matching is done from the end of the string, therefore you can also specify just the file name (with a leading backstroke) like so: "\mylibrary.dll"
See LockedListShell32.nsi for an example.
LockedList::AddFolder "path\to\myfolder"This adds a folder, causing both files and modules to be enumerated. Please use carefully as this can result in many processes being found.
See LockedListFolder.nsi for a (bad) example.
LockedList::AddClass "class_with_wildcards"This adds an application by window class. You can use wildcards such as * and ? for searching.
See LockedListClasses.nsi for an example.
LockedList::AddCaption "caption_with_wildcards"This adds an application by window caption/title. You can use wildcards such as * and ? for searching.
See LockedListCaptions.nsi for an example.
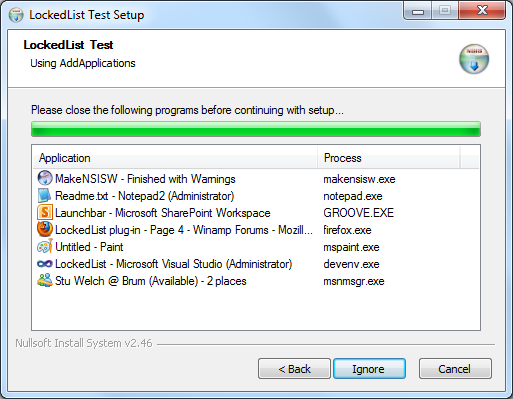
LockedList::AddApplicationsAdds all applications currently running.
See LockedListApplications.nsi for an example.
GetFunctionAddress $CallbackFunctionAddress AddCustomCallback
LockedList::AddCustom [/icon "path\to\file.ext"] "application_name" \
"process_name" $CallbackFunctionAddressAdds a custom item to the list with a callback function. The callback function is used to check if the custom item should remain listed or not.
/icon specifies the full path to an icon to use on the list. It can be an icon file (.ico) or resource (.exe, .dll).
"application_name" is what will be displayed in the Application list box column for the custom item. "process_name" will be displayed in the Process column.
$CallbackFunctionAddress is any variable containing the callback function's address, which is retrieved by using GetFunctionAddress.
The plug-in will push "process_name" onto the stack before calling the callback function. The callback function must push "true" if the custom item should remain listed or "false" otherwise. You can also use the LockedList::IsFileLocked function inside your callback which pushes the correct stack values.
See LockedListCustom.nsi for an example.
LockedList::Dialog [optional_params]
Pop $VarThis is the normal way to display the dialog.
LockedList::InitDialog [optional_params]
Pop $HWNDVar
LockedList::Show
Pop $VarThis method allows you to modify controls on the dialog with SendMessage, SetCtlColors etc., by using the $HWNDVar between the InitDialog and Show calls and also in the page's leave function.
At this point, regardless of which of the above methods that is used, $Var will contain "error" on display error, "next" if the next button was pressed, "back" if the back button was pressed or "cancel" if the cancel button was pressed.
These [optional_params] apply to both LockedList::Dialog and LockedList::InitDialog. The parameter names are case-insensitive.
| Parameter | Argument(s) | Description |
|---|---|---|
/heading |
"text" |
Set page heading text. |
/caption |
"text" |
Set dialog caption text. |
/colheadings |
"application_text", "process_text" |
Set the column heading texts in the processes list. An empty string will use the default text. |
/noprograms |
"text" |
Item text when no programs to be closed are running. |
/searching |
"text" |
Item text while search is in progress. |
/endsearch |
"text" |
Item text when user clicks back or cancel during a search. |
/endmonitor |
"text" |
Item text when user clicks back or cancel after a search (at which point the list of programs is being monitored for closing). |
/usericons |
Icons search.ico and info.ico in the current working directory will be used instead of icons from shell32.dll for the searching list. If no icons are found, the installer icon is used. |
|
/ignore |
"next_button_text" |
Allow the user to click Next even if there are items on the list. "next_button_text" sets the Next button text. Use "" to use the default Next button text. This parameter is ignored if /autoclose or /autoclosesilent is used. |
/autoclose |
"close_text", "kill_text", "failed_text", "next_button_text" |
Close all running processes on exit with the confirmation message box "close_text". Processes that cannot be closed safely with WM_CLOSE are killed with the confirmation message box "kill_text". If processes are still running, the "failed_text" message box is displayed. An empty string will use the default text. "next_button_text" sets the Next button text. Use "" to use the default Next button text. |
/autoclosesilent |
"failed_text", "next_button_text" |
Same as the above switch, except that the close and kill confirmation boxes are not displayed. If some processes cannot be killed, the "failed_text" message is still displayed and the user is prevented from continuing with setup. An empty string will use the default text. "next_button_text" sets the Next button text. Use "" to use the default Next button text. |
/menuitems |
"close_text", "copy_list_text" |
Sets the list context menu item texts. |
/autonext |
Moves to the next page automatically if no processes are found. |
LockedList::Dialog /caption `I like cheese` /heading `I do really`
Pop $VarLockedList::Dialog /autoclose `` `` `Couldn't kill 'em all, oops!`
Pop $VarGetFunctionAddress $AddrVar SilentSearchCallback
LockedList::SilentSearch [/async] $AddrVar
Pop $VarBegins the search silently using the given callback function. Specify /async to allow the search to commence asynchronously. You can then check the progress of the asynchronous search with the SilentWait and SilentPercentComplete functions listed below.
$Var will contain "ok" if /async was used and the search started successfully. If not using /async, $Var will contain "done" on search completion or "cancel" on search cancellation.
The callback function is given 3 stack items: Process ID, full path, description.
The callback function must push "true" to continue enumeration or
"false" to cancel the search. Pushing "autoclose" will close the
current process before continuing the search.
Function SilentSearchCallback
Pop $R0 ; process ID
Pop $R1 ; file path
Pop $R2 ; description
; do stuff here
Push true ; continue enumeration
FunctionEndNote: If "autoclose" was pushed and the auto-close failed, the callback function will be called again with a process ID of -1. This can be used to display a message to the user, if required.
See LockedListTest.nsi for a full example. See LockedListAutoCloseSilent.nsi for an auto-close example.
These can only be used after calling SilentSearch with /async (see above).
LockedList::SilentWait [/time #]
Pop $VarIf SilentSearch /async was used, this function will wait until the
thread has finished, or optionally, return in # milliseconds when
using /time #.
$Var will contain either "wait", "done" or "cancel" depending on whether the search has finished. If the search was cancelled (by pushing "false" in the callback function or call LockedList::SilentCancel), $Var will be "cancel".
LockedList::SilentPercentComplete
Pop $Var$Var will contain the current completion percentage, i.e. 65 for 65%. This can be used in a progress message.
LockedList::SilentCancel
Pop $VarCancels the current asynchronous silent search and waits for it to complete.
$Var will contain either "wait", "done" or "cancel" depending on whether the search has finished.
LockedList::IsFileLocked "file_path"
Pop $VarAt this point, $Var is "true" or "false". This function can for example be used in the AddCustom callback function.
GetFunctionAddress $AddrVar EnumProcessesCallback
LockedList::EnumProcesses $AddrVar
Pop $VarEnumerates all running processes using a callback function.
The callback function is given 3 stack items: Process ID, full path, description.
The callback function must push "true" to continue enumeration or "false" to cancel enumeration. $Var will contain "done" on search
completion or "cancel" on search cancellation.
See LockedListEnumProcesses.nsi for an example.
LockedList::FindProcess [/yesno] process.exe
Pop $Var
[Pop $Var2
Pop $Var3]Finds a process by executable name (you must include the .exe). If you specify /yesno then the function will push "yes" or "no" onto the stack. Otherwise, by default, the function will place an empty string on the stack if no processes are found, or 3 stack items otherwise: Process ID, full path, description.
See LockedListFindProcess.nsi for an example.
LockedList::CloseProcess [/kill] process.exe
Pop $VarCloses a process by executable name (you must include the .exe) by sending WM_CLOSE to the application main window. Specify /kill to terminate the process forcefully instead.
See LockedListCloseProcess.nsi for an example.