Xu Jing
关于Paper的解读相对于同类型的paper较容易,作者在以自身实验的角度,在paper中重述了如何从YOLOv3找到YOLOX,细节可以参考上述提供的paper连接。
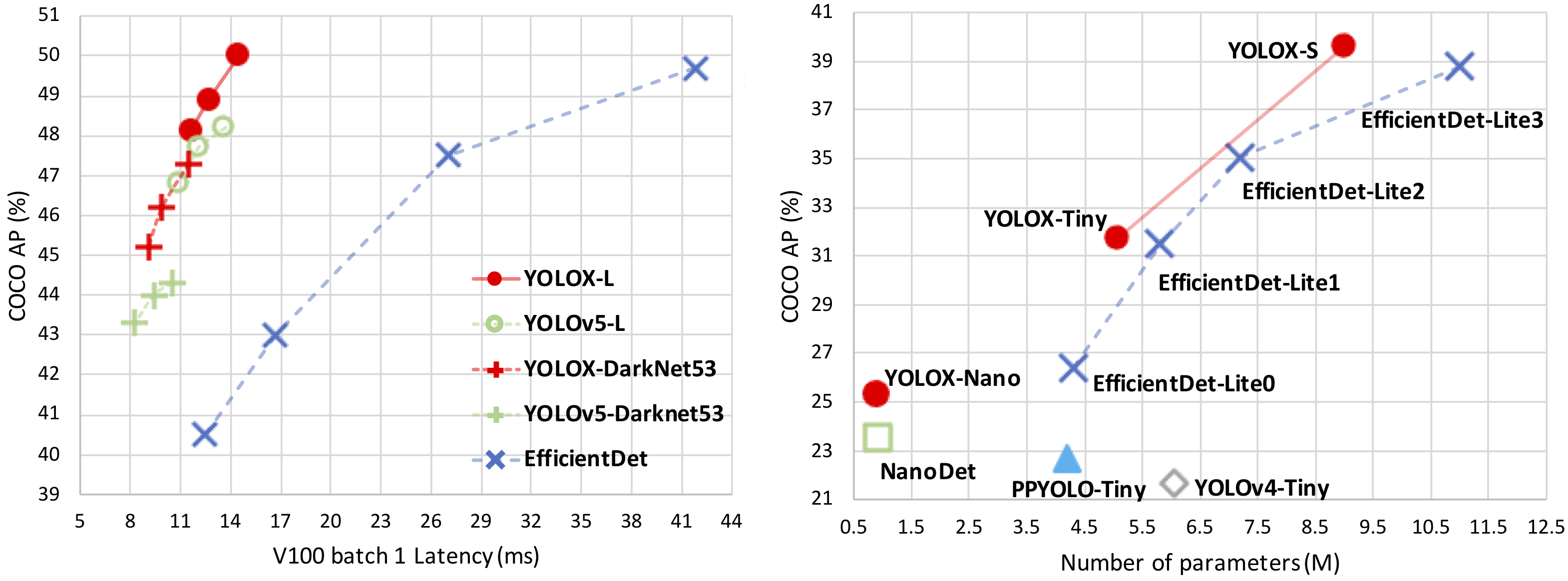
| Model | size | mAPtest 0.5:0.95 |
Speed V100 (ms) |
Params (M) |
FLOPs (G) |
weights |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOX-s | 640 | 39.6 | 9.8 | 9.0 | 26.8 | onedrive/github |
| YOLOX-m | 640 | 46.4 | 12.3 | 25.3 | 73.8 | onedrive/github |
| YOLOX-l | 640 | 50.0 | 14.5 | 54.2 | 155.6 | onedrive/github |
| YOLOX-x | 640 | 51.2 | 17.3 | 99.1 | 281.9 | onedrive/github |
| YOLOX-Darknet53 | 640 | 47.4 | 11.1 | 63.7 | 185.3 | onedrive/github |
| Model | size | mAPval 0.5:0.95 |
Params (M) |
FLOPs (G) |
weights |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOX-Nano | 416 | 25.3 | 0.91 | 1.08 | onedrive/github |
| YOLOX-Tiny | 416 | 31.7 | 5.06 | 6.45 | onedrive/github |
1.创建虚拟环境
git clone https://github.com/Megvii-BaseDetection/YOLOX
cd YOLOX
virtualenv -p /usr/bin/python3.7 yoloxenv
source yoloxenv/bin/activate2.安装必要的package
pip install -r requirements.txt 3.安装YOLOX
#pip install -v -e .
# 建议的安装方式
python setup.py develop4.安装apex
# 用于Pytorch的混合精度训练
# skip this step if you don't want to train model.
git clone https://github.com/NVIDIA/apex
cd apex
# pip install -v --disable-pip-version-check --no-cache-dir --global-option="--cpp_ext" --global-option="--cuda_ext" ./
# 建议安装方式
python setup.py install
5.安装pycocotools
pip install cython; pip3 install 'git+https://github.com/cocodataset/cocoapi.git#subdirectory=PythonAPI'YOLOX的训练支持COCO和VOC的数据格式,这里我们以VOC数据格式的数据集为例,详细讲解,如何自定义数据集训练自己的YOLOX模型!
1.数据标注
通过一些通用的数据标注工具标注数据比如:LabelImg, Labelme, CVAT,标注数据过程中注意标注精度,标签的一致性,注意对训练图像的审核等,尽量确保标注数据是干净合规的。
2.VOC数据集样式
将数据集存放在datasets文件夹下,其文件结构如:
./datasets/eus #数据集存放在datasets文件夹,数据集的名字:eus
├─Annotations #VOC标注文件存放的文件夹
│ test1.xml #具体的标注文件
│ test2.xml
├─JPEGImages #Image存放的文件夹
│ test1.jpg #具体的图片
│ test2.jpg
│─ImageSets #训练,验证图片列表:注意每一行存放的是文件名字比如:test1
│────Main
│ train.txt
│ val.txt
└
恭喜你,按照上述文件结构,数据集就做好了!!!
3.修改DataLoader类加载自定义VOC格式数据集
- 新建
voc_classes_eus.py
# 这里存放了训练集中所有的类别,其顺序即是label id,你也可以在代码中重新指定classes
VOC_CLASSES = ( #<------------不应该包含背景类别,类别个数中也不应该加入背景类别!
"Lioxxx",
"Lipxxx",
"Pancxxx",
"GIxx",
"Cyxx",
"Nxx",
"Canxxx",
"Normal"
)- 新建
voc_eus.py:基于自定义VOC格式的数据集修改该py文件
# 该部分代码主要是通过Pytorch加载标注文件和图片,计算detector的评价指标coco AP和 VOC mAP
# 关于数据增强部分,在其他文件中存放主要用到了mosiac和mixup,建议小模型不要使用数据增强,大模型或小数据集建议使用数据增强
# 线下验证,医学数据及的数据增强意义不是很大
import cv2
import numpy as np
from yolox.evaluators.voc_eval import voc_eval
import os
import os.path
import pickle
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
from .datasets_wrapper import Dataset
from .voc_classes_eus import VOC_CLASSES # <----------------自定义的 clas label
class AnnotationTransform(object):
"""Transforms a VOC annotation into a Tensor of bbox coords and label index
Initilized with a dictionary lookup of classnames to indexes
Arguments:
class_to_ind (dict, optional): dictionary lookup of classnames -> indexes
(default: alphabetic indexing of VOC's 20 classes)
keep_difficult (bool, optional): keep difficult instances or not
(default: False)
height (int): height
width (int): width
"""
def __init__(self, class_to_ind=None, keep_difficult=True):
self.class_to_ind = class_to_ind or dict(zip(VOC_CLASSES, range(len(VOC_CLASSES))))
self.keep_difficult = keep_difficult
def __call__(self, target):
"""
Arguments:
target (annotation) : the target annotation to be made usable
will be an ET.Element
Returns:
a list containing lists of bounding boxes [bbox coords, class name]
"""
res = np.empty((0, 5))
for obj in target.iter("object"):
difficult = int(obj.find("difficult").text) == 1
if not self.keep_difficult and difficult:
continue
# name = obj.find("name").text.lower().strip() # <-------------不需要变小写
name = obj.find("name").text.strip()
bbox = obj.find("bndbox")
pts = ["xmin", "ymin", "xmax", "ymax"]
bndbox = []
for i, pt in enumerate(pts):
cur_pt = int(bbox.find(pt).text) - 1
# scale height or width
# cur_pt = cur_pt / width if i % 2 == 0 else cur_pt / height
bndbox.append(cur_pt)
label_idx = self.class_to_ind[name]
bndbox.append(label_idx)
res = np.vstack((res, bndbox)) # [xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, label_ind]
# img_id = target.find('filename').text[:-4]
return res # [[xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, label_ind], ... ]
class VOCDetection(Dataset):
"""
VOC Detection Dataset Object
input is image, target is annotation
Args:
root (string): filepath to VOCdevkit folder.
image_set (string): imageset to use (eg. 'train', 'val', 'test')
transform (callable, optional): transformation to perform on the
input image
target_transform (callable, optional): transformation to perform on the
target `annotation`
(eg: take in caption string, return tensor of word indices)
dataset_name (string, optional): which dataset to load
(default: 'VOC2007')
"""
def __init__(
self,
data_dir,
# image_sets=[('eus', 'train'), ('eus', 'val')], #<-----------没有年份的需求
img_size=(416, 416),
preproc=None,
target_transform=AnnotationTransform(),
dataset_mode="train", # Main/train.txt / val.txt # <----------------训练模式
):
super().__init__(img_size)
self.root = data_dir # ./datasets/eus
# self.image_set = image_sets
self.img_size = img_size
self.preproc = preproc
self.target_transform = target_transform
self.name = dataset_mode
self._annopath = os.path.join(self.root, "Annotations", "%s.xml")
self._imgpath = os.path.join(self.root, "JPEGImages", "%s.jpg")
self._classes = VOC_CLASSES
self.ids = list()
# for (year, name) in image_sets: # <-------------这一部分不需要,调整为注释下方代码
# self._year = year
# rootpath = os.path.join(self.root + year)
# for line in open(
# os.path.join(rootpath, "ImageSets", "Main", name + ".txt")
# ):
# self.ids.append((rootpath, line.strip()))
for line in open(
os.path.join(self.root, "ImageSets", "Main", self.name + ".txt")
):
# self.ids.append((rootpath, line.strip()))
self.ids.append(line.strip()) # <-------------只存文件名
def __len__(self):
return len(self.ids)
def load_anno(self, index):
img_id = self.ids[index]
if os.path.exists(self._annopath % img_id):
target = ET.parse(self._annopath % img_id).getroot()
if self.target_transform is not None:
target = self.target_transform(target)
else: # <--------------------不存在标注文件
target = None
return target
def pull_item(self, index):
"""Returns the original image and target at an index for mixup
Note: not using self.__getitem__(), as any transformations passed in
could mess up this functionality.
Argument:
index (int): index of img to show
Return:
img, target
"""
img_id = self.ids[index]
img = cv2.imread(self._imgpath % img_id, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
height, width, _ = img.shape
target = self.load_anno(index)
# <---------------------------没有标注怎么办?
if target is None:
target = np.array([[10,10,width-10,height-10,7]],dtype=np.float32)
img_info = (height, width)
return img, target, img_info, index
@Dataset.resize_getitem
def __getitem__(self, index):
img, target, img_info, img_id = self.pull_item(index)
if self.preproc is not None:
img, target = self.preproc(img, target, self.input_dim)
return img, target, img_info, img_id
def evaluate_detections(self, all_boxes, output_dir=None):
"""
all_boxes is a list of length number-of-classes.
Each list element is a list of length number-of-images.
Each of those list elements is either an empty list []
or a numpy array of detection.
all_boxes[class][image] = [] or np.array of shape #dets x 5
"""
self._write_voc_results_file(all_boxes)
IouTh = np.linspace(0.5, 0.95, int(np.round((0.95 - 0.5) / 0.05)) + 1, endpoint=True)
mAPs = []
for iou in IouTh:
mAP = self._do_python_eval(output_dir, iou)
mAPs.append(mAP)
print("--------------------------------------------------------------")
print("map_5095:", np.mean(mAPs))
print("map_50:", mAPs[0])
print("--------------------------------------------------------------")
return np.mean(mAPs), mAPs[0]
def _get_voc_results_file_template(self):
filename = "comp4_det_test" + "_{:s}.txt"
filedir = os.path.join(self.root, "results", "Main")
if not os.path.exists(filedir):
os.makedirs(filedir)
path = os.path.join(filedir, filename)
return path
def _write_voc_results_file(self, all_boxes):
for cls_ind, cls in enumerate(VOC_CLASSES):
cls_ind = cls_ind
if cls == "__background__":
continue
print("Writing {} VOC results file".format(cls))
filename = self._get_voc_results_file_template().format(cls)
with open(filename, "wt") as f:
for im_ind, index in enumerate(self.ids):
index = index[1]
dets = all_boxes[cls_ind][im_ind]
if dets == []:
continue
for k in range(dets.shape[0]):
f.write(
"{:s} {:.3f} {:.1f} {:.1f} {:.1f} {:.1f}\n".format(
index,
dets[k, -1],
dets[k, 0] + 1,
dets[k, 1] + 1,
dets[k, 2] + 1,
dets[k, 3] + 1,
)
)
def _do_python_eval(self, output_dir="output", iou=0.5):
# rootpath = os.path.join(self.root, "VOC" + self._year)
rootpath = self.root
# name = self.image_set[0][1] # train_val
name = self.name
annopath = os.path.join(rootpath, "Annotations", "{:s}.xml")
imagesetfile = os.path.join(rootpath, "ImageSets", "Main", name + ".txt")
cachedir = os.path.join(
self.root, "annotations_cache")
if not os.path.exists(cachedir):
os.makedirs(cachedir)
aps = []
# The PASCAL VOC metric changed in 2010
# use_07_metric = True if int(self._year) < 2010 else False
use_07_metric = True # False (2010 metric)
print("Eval IoU : {:.2f}".format(iou))
if output_dir is not None and not os.path.isdir(output_dir):
os.mkdir(output_dir)
for i, cls in enumerate(VOC_CLASSES):
if cls == "__background__":
continue
filename = self._get_voc_results_file_template().format(cls)
rec, prec, ap = voc_eval(
filename,
annopath,
imagesetfile,
cls,
cachedir,
ovthresh=iou,
use_07_metric=use_07_metric,
)
aps += [ap]
if iou == 0.5:
print("AP for {} = {:.4f}".format(cls, ap))
if output_dir is not None:
with open(os.path.join(output_dir, cls + "_pr.pkl"), "wb") as f:
pickle.dump({"rec": rec, "prec": prec, "ap": ap}, f)
if iou == 0.5:
print("Mean AP = {:.4f}".format(np.mean(aps)))
print("~~~~~~~~")
print("Results:")
for ap in aps:
print("{:.3f}".format(ap))
print("{:.3f}".format(np.mean(aps)))
print("~~~~~~~~")
print("")
print("--------------------------------------------------------------")
print("Results computed with the **unofficial** Python eval code.")
print("Results should be very close to the official MATLAB eval code.")
print("Recompute with `./tools/reval.py --matlab ...` for your paper.")
print("-- Thanks, The Management")
print("--------------------------------------------------------------")
return np.mean(aps)🍼注意:如果使用数据增强:Mosiac 和 MixUp,还需要修改上面代码中的pull_item和load_anno函数,这里我们不做任何数据增强,因为我们发现对于我们的数据集不做数据增强效果反而更好。这里要明白的是为什么做数据增强需要修改这两个方法,因为对于图像做了相应的数据增强,标注的bounding box也要做相同的操作才可以,这样才能保证数据的一致性!
- 修改
__init__.py
from .coco import COCODataset
from .coco_classes import COCO_CLASSES
from .datasets_wrapper import ConcatDataset, Dataset, MixConcatDataset
from .mosaicdetection import MosaicDetection
# from .voc import VOCDetection
from .voc_eus import VOCDetection # <--------加载自己的类别
from .voc_classes_eus import VOC_CLASSES # <--------加载自己的类别4.修改./evaluators/voc_eval.py
def parse_rec(filename):
""" Parse a PASCAL VOC xml file """
objects = []
tree = ET.parse(filename)
for obj in tree.findall("object"):
obj_struct = {}
obj_struct["name"] = obj.find("name").text
obj_struct["pose"] = obj.find("pose").text
# obj_struct["truncated"] = int(obj.find("truncated").text) # <---------VOC标注是字符串不能转int,并且这个字段在这里没用用到
obj_struct["difficult"] = int(obj.find("difficult").text)
bbox = obj.find("bndbox")
obj_struct["bbox"] = [
int(bbox.find("xmin").text),
int(bbox.find("ymin").text),
int(bbox.find("xmax").text),
int(bbox.find("ymax").text),
]
objects.append(obj_struct)
return objectsdef voc_eval(
detpath,
annopath,
imagesetfile,
classname,
cachedir,
ovthresh=0.5,
use_07_metric=False,
):
# first load gt
if not os.path.isdir(cachedir):
os.mkdir(cachedir)
cachefile = os.path.join(cachedir, "annots.pkl")
# read list of images
with open(imagesetfile, "r") as f:
lines = f.readlines()
imagenames = [x.strip() for x in lines]
if not os.path.isfile(cachefile):
# load annots
recs = {}
for i, imagename in enumerate(imagenames):
# 没有xml标注文件不做统计!!! # <--------------------有些图像没有标注文件,没有标注文件的辅助类别不计算mAP!
if not os.path.exists(annopath.format(imagename)):
continue
recs[imagename] = parse_rec(annopath.format(imagename))
if i % 100 == 0:
print("Reading annotation for {:d}/{:d}".format(i + 1, len(imagenames)))
# save
print("Saving cached annotations to {:s}".format(cachefile))
with open(cachefile, "wb") as f:
pickle.dump(recs, f)
else:
# load
with open(cachefile, "rb") as f:
recs = pickle.load(f)
# extract gt objects for this class
class_recs = {}
npos = 0
for imagename in imagenames:
R = [obj for obj in recs[imagename] if obj["name"] == classname]
bbox = np.array([x["bbox"] for x in R])
difficult = np.array([x["difficult"] for x in R]).astype(np.bool)
det = [False] * len(R)
npos = npos + sum(~difficult)
class_recs[imagename] = {"bbox": bbox, "difficult": difficult, "det": det}
# read dets
detfile = detpath.format(classname)
with open(detfile, "r") as f:
lines = f.readlines()
if len(lines) == 0:
return 0, 0, 0
splitlines = [x.strip().split(" ") for x in lines]
image_ids = [x[0] for x in splitlines]
confidence = np.array([float(x[1]) for x in splitlines])
BB = np.array([[float(z) for z in x[2:]] for x in splitlines])
# sort by confidence
sorted_ind = np.argsort(-confidence)
BB = BB[sorted_ind, :]
image_ids = [image_ids[x] for x in sorted_ind]
# go down dets and mark TPs and FPs
nd = len(image_ids)
tp = np.zeros(nd)
fp = np.zeros(nd)
for d in range(nd):
R = class_recs[image_ids[d]]
bb = BB[d, :].astype(float)
ovmax = -np.inf
BBGT = R["bbox"].astype(float)
if BBGT.size > 0:
# compute overlaps
# intersection
ixmin = np.maximum(BBGT[:, 0], bb[0])
iymin = np.maximum(BBGT[:, 1], bb[1])
ixmax = np.minimum(BBGT[:, 2], bb[2])
iymax = np.minimum(BBGT[:, 3], bb[3])
iw = np.maximum(ixmax - ixmin + 1.0, 0.0)
ih = np.maximum(iymax - iymin + 1.0, 0.0)
inters = iw * ih
# union
uni = (
(bb[2] - bb[0] + 1.0) * (bb[3] - bb[1] + 1.0)
+ (BBGT[:, 2] - BBGT[:, 0] + 1.0) * (BBGT[:, 3] - BBGT[:, 1] + 1.0)
- inters
)
overlaps = inters / uni
ovmax = np.max(overlaps)
jmax = np.argmax(overlaps)
if ovmax > ovthresh:
if not R["difficult"][jmax]:
if not R["det"][jmax]:
tp[d] = 1.0
R["det"][jmax] = 1
else:
fp[d] = 1.0
else:
fp[d] = 1.0
# compute precision recall
fp = np.cumsum(fp)
tp = np.cumsum(tp)
rec = tp / float(npos)
# avoid divide by zero in case the first detection matches a difficult
# ground truth
prec = tp / np.maximum(tp + fp, np.finfo(np.float64).eps)
ap = voc_ap(rec, prec, use_07_metric)
return rec, prec, ap5.修改exp配置文件使用YOLOX-x训练自定义数据集的配置文件
该配置文件主要配置了YOLOX的训练的超参数,比如数据集的加载路径,训练周期,学习率调整策略,评价指标,模型的backbone等等。
- 在
exps文件夹下新建eus_voc文件夹,并在该文件夹下新建yolox_voc_x.py
# encoding: utf-8
import os
import random
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.distributed as dist
from yolox.exp import Exp as MyExp
from yolox.data import get_yolox_datadir
class Exp(MyExp):
def __init__(self):
super(Exp, self).__init__()
self.num_classes = 8 # <----------------添加了辅助类别normal
self.depth = 1.33 # <-------------------YOLOX-x
self.width = 1.25
self.exp_name = os.path.split(os.path.realpath(__file__))[1].split(".")[0]
self.input_size = (640,640) # <-----------------图像大小
self.test_size = (640,640)
self.max_epoch = 300 # <--------------训练周期
# <---------------注意这里还有其他超参数,比如学习率相关的,可以参考exp_base!
def get_data_loader(self, batch_size, is_distributed, no_aug=False):
from yolox.data import (
VOCDetection,
TrainTransform,
YoloBatchSampler,
DataLoader,
InfiniteSampler,
MosaicDetection,
)
dataset = VOCDetection( # <---------------要和我们修改的参数对应起来
data_dir=os.path.join(get_yolox_datadir(), "eus"),
# image_sets=[('2007', 'trainval'), ('2012', 'trainval')],
img_size=self.input_size,
preproc=TrainTransform(
rgb_means=(0.485, 0.456, 0.406),
std=(0.229, 0.224, 0.225),
max_labels=50,
),
)
# <-------------马赛克数据增强,我在训练过程中是关闭的!
dataset = MosaicDetection(
dataset,
mosaic=not no_aug,
img_size=self.input_size,
preproc=TrainTransform(
rgb_means=(0.485, 0.456, 0.406),
std=(0.229, 0.224, 0.225),
max_labels=120,
),
degrees=self.degrees,
translate=self.translate,
scale=self.scale,
shear=self.shear,
perspective=self.perspective,
enable_mixup=self.enable_mixup,
)
self.dataset = dataset
if is_distributed:
batch_size = batch_size // dist.get_world_size()
sampler = InfiniteSampler(
len(self.dataset), seed=self.seed if self.seed else 0
)
batch_sampler = YoloBatchSampler(
sampler=sampler,
batch_size=batch_size,
drop_last=False,
input_dimension=self.input_size,
mosaic=not no_aug,
)
dataloader_kwargs = {"num_workers": self.data_num_workers, "pin_memory": True}
dataloader_kwargs["batch_sampler"] = batch_sampler
train_loader = DataLoader(self.dataset, **dataloader_kwargs)
return train_loader
def get_eval_loader(self, batch_size, is_distributed, testdev=False):
from yolox.data import VOCDetection, ValTransform
valdataset = VOCDetection(
data_dir=os.path.join(get_yolox_datadir(), "eus"),
# image_sets=[('2007', 'test')],
img_size=self.test_size,
preproc=ValTransform(
rgb_means=(0.485, 0.456, 0.406),
std=(0.229, 0.224, 0.225),
),
dataset_mode="val", # <----------验证集做验证!
)
if is_distributed:
batch_size = batch_size // dist.get_world_size()
sampler = torch.utils.data.distributed.DistributedSampler(
valdataset, shuffle=False
)
else:
sampler = torch.utils.data.SequentialSampler(valdataset)
dataloader_kwargs = {
"num_workers": self.data_num_workers,
"pin_memory": True,
"sampler": sampler,
}
dataloader_kwargs["batch_size"] = batch_size
val_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(valdataset, **dataloader_kwargs)
return val_loader
def get_evaluator(self, batch_size, is_distributed, testdev=False):
from yolox.evaluators import VOCEvaluator
val_loader = self.get_eval_loader(batch_size, is_distributed, testdev=testdev)
evaluator = VOCEvaluator(
dataloader=val_loader,
img_size=self.test_size,
confthre=self.test_conf,
nmsthre=self.nmsthre,
num_classes=self.num_classes,
)
return evaluator🎉 恭喜你,可以开始训练了!!!
🚑训练我们使用NVIDIA的计算卡,你最好能拥有一台类似V100这样的显卡!!!
python tools/train.py -f exps/default/yolox-s.py -d 8 -b 64 --fp16 -o
exps/default/yolox-m.py
exps/default/yolox-l.py
exps/default/yolox-x.py- -d: GPU设备的数
- -b: 总的batch size,推荐num-gpu * 8
- --fp16: 混合精度训练
- -c: 预训练模型路径
- -o: 先占用GPU进行训练
🪲:训练模型的一些Tricks:
1.YOLOX是anchor-free的模型仅有若干超参数,最好的方式是使用我们提供的默认参数。
2.默认参数得不到好的训练效果可以采取下面策略:
- 模型选择,这里提供了YOLOX-Nano,YOLOX-Tiny, YOLOX-S作为移动端的模型,YOLOX-M/L/X作为云端模型
- 推荐使用YOLOX-DarkNet53
- 如果训练过程过早出现overfitting,可以降低
max_epochs,减小base_lr和min_lr_ratio
# -------------- training config --------------------- #
self.warmup_epochs = 5
self.max_epoch = 300
self.warmup_lr = 0
self.basic_lr_per_img = 0.01 / 64.0
self.scheduler = "yoloxwarmcos"
self.no_aug_epochs = 15
self.min_lr_ratio = 0.05
self.ema = True
self.weight_decay = 5e-4
self.momentum = 0.9- 调整数据增强策略
- 对于小模型应该减少使用数据增强,对于大模型和数据量较小的数据集应该增加使用数据增强的策略
# --------------- transform config ----------------- #
self.degrees = 10.0
self.translate = 0.1
self.scale = (0.1, 2)
self.mscale = (0.8, 1.6)
self.shear = 2.0
self.perspective = 0.0
self.enable_mixup = True- 设计自己的检测器,参考作者的paper设计网络的策略,设计自己的detector!
我们使用的训练命令:
python tools/train.py -n yolox-x -f exps/eus_voc/yolox_voc_x.py -c ./pretrain/yolox_x.pth.tar -d 1 -b 8 -o 🍼注意:
1.训练过程中,你可能会发现l1_loss一直是0,作者的回复是: we only adopt l1 loss in the last 15 epoch when mosaic and mixup are closed
2.训练数据默认不支持无标注的辅助类别,即一个图片必须有对应的标注文件,但经过我们修改后无需满足该条件!
为了更好的实现训练后模型的推断,方便部署,我们基于demo.py实现了基于图像和视频的推断程序,分别存放在./tools/test_imgs.py和./tools/test_video.py
# 图像推断
python tools/test_imgs.py2021-08-15 18:36:24.871 | INFO | __main__:main:137 - 加载exp文件...
2021-08-15 18:36:29.596 | INFO | __main__:main:150 - 模型导入...
2021-08-15 18:36:30.461 | INFO | __main__:main:156 - 模型权重...
2021-08-15 18:36:30.461 | INFO | __main__:main:166 - 开始测试...
2021-08-15 18:36:30.565 | INFO | __main__:inference:91 - Infer time: 0.0487s
2021-08-15 18:36:30.566 | INFO | __main__:image_demo:128 - Saving detection result in ./vis_res/2021_08_15_18_36_30/20200813_caseid_205_imgid_4906.jpg
2021-08-15 18:36:30.652 | INFO | __main__:inference:91 - Infer time: 0.0327s
2021-08-15 18:36:30.653 | INFO | __main__:image_demo:128 - Saving detection result in ./vis_res/2021_08_15_18_36_30/20200813_caseid_205_imgid_4907.jpg
2021-08-15 18:36:30.736 | INFO | __main__:inference:91 - Infer time: 0.0325s
2021-08-15 18:36:30.737 | INFO | __main__:image_demo:128 - Saving detection result in ./vis_res/2021_08_15_18_36_30/20200813_caseid_205_imgid_4908.jpg
2021-08-15 18:36:30.821 | INFO | __main__:inference:91 - Infer time: 0.0326s
2021-08-15 18:36:30.822 | INFO | __main__:image_demo:128 - Saving detection result in ./vis_res/2021_08_15_18_36_30/20200813_caseid_205_imgid_4910.jpg
2021-08-15 18:36:30.907 | INFO | __main__:inference:91 - Infer time: 0.0326s
2021-08-15 18:36:30.908 | INFO | __main__:image_demo:128 - Saving detection result in ./vis_res/2021_08_15_18_36_30/20200813_caseid_205_imgid_4911.jpg
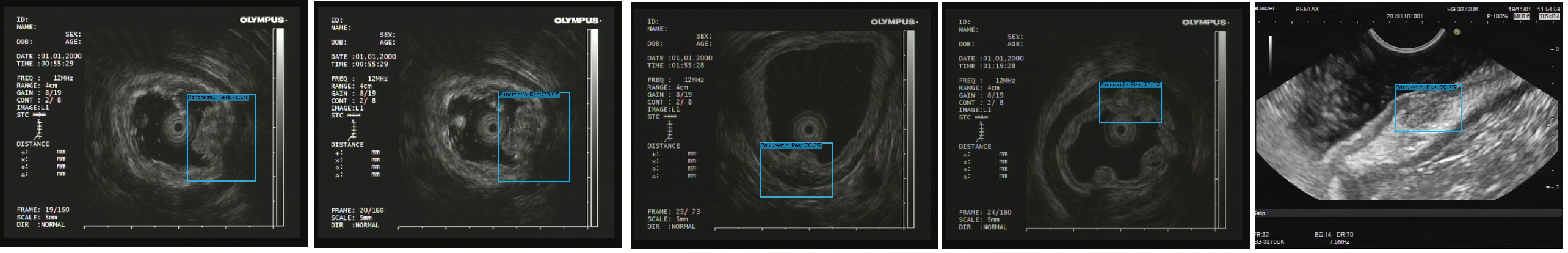
2021-08-15 18:36:30.916 | INFO | __main__:main:168 - 测试结束...其测试结果如下图所示:
# 视频测试
python tools/test_video.py2021-08-15 20:33:37.904 | INFO | __main__:inference:90 - Infer time: 0.0329s
2021-08-15 20:33:37.997 | INFO | __main__:inference:90 - Infer time: 0.0329s
2021-08-15 20:33:38.089 | INFO | __main__:inference:90 - Infer time: 0.0329s
2021-08-15 20:33:38.176 | INFO | __main__:inference:90 - Infer time: 0.0329s
2021-08-15 20:33:38.270 | INFO | __main__:inference:90 - Infer time: 0.0328s
识别后的视频保存在了vis_res/时间/视频名字
基于TensorRT 7.2.4实现在Win10和Linux下的TensorRT的C++调用,其主要包括:前处理,模型序列化,模型反序列化,后处理,模型推断等几部分。
1. win10
假设您已经在Win10下安装配置好了TensorRT,并且安装了OpenCV和VS等工具。
# step 1 转onnx
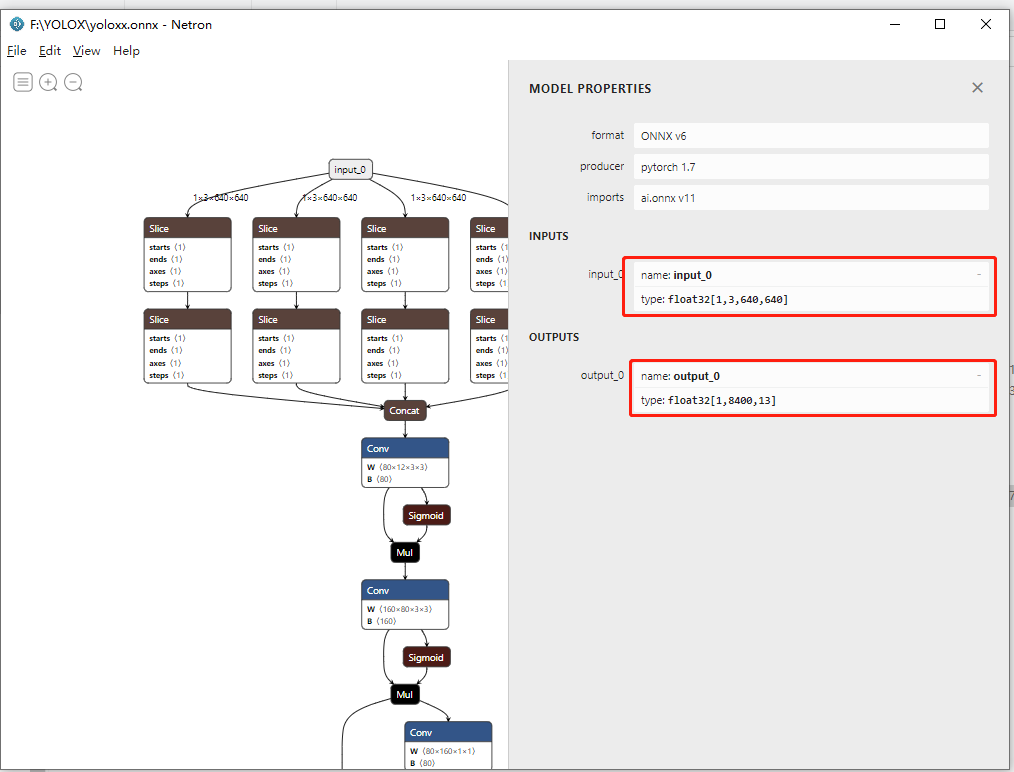
python tools/export_onnx.py --output-name yoloxx.onnx --input input_0 --output output_0 --no-onnxsim -n yolox-x -f exps/eus_voc/yolox_voc_x.py -c YOLOX_outputs/yolox_voc_x/best_ckpt.pth.tar(yolov4_env) myuser@ubuntu:~/xujing/YOLOX$ python tools/export_onnx.py --output-name yoloxx.onnx --input input_0 --output output_0 --no-onnxsim -n yolox-x -f exps/eus_voc/yolox_voc_x.py -c YOLOX_outputs/yolox_voc_x/best_ckpt.pth.tar
2021-08-16 11:53:33.313 | INFO | __main__:main:56 - args value: Namespace(ckpt='YOLOX_outputs/yolox_voc_x/best_ckpt.pth.tar', exp_file='exps/eus_voc/yolox_voc_x.py', experiment_name=None, input='input_0', name='yolox-x', no_onnxsim=True, opset=11, opts=[], output='output_0', output_name='yoloxx.onnx')
2021-08-16 11:53:35.296 | INFO | __main__:main:80 - loading checkpoint done.
2021-08-16 11:53:53.153 | INFO | __main__:main:90 - generated onnx model named yoloxx.onnx
# step 2 序列化enginetrtexec --verbose --onnx=yoloxx.onnx --saveEngine=yoloxx.engine[08/16/2021-13:11:15] [I] Host Latency
[08/16/2021-13:11:15] [I] min: 64.0759 ms (end to end 114.172 ms)
[08/16/2021-13:11:15] [I] max: 208.799 ms (end to end 208.846 ms)
[08/16/2021-13:11:15] [I] mean: 70.7899 ms (end to end 133.57 ms)
[08/16/2021-13:11:15] [I] median: 66.6198 ms (end to end 131.152 ms)
[08/16/2021-13:11:15] [I] percentile: 208.799 ms at 99% (end to end 208.846 ms at 99%)
[08/16/2021-13:11:15] [I] throughput: 0 qps
[08/16/2021-13:11:15] [I] walltime: 2.66215 s
[08/16/2021-13:11:15] [I] Enqueue Time
[08/16/2021-13:11:15] [I] min: 1.63184 ms
[08/16/2021-13:11:15] [I] max: 174.015 ms
[08/16/2021-13:11:15] [I] median: 1.94141 ms
[08/16/2021-13:11:15] [I] GPU Compute
[08/16/2021-13:11:15] [I] min: 63.4412 ms
[08/16/2021-13:11:15] [I] max: 208.289 ms
[08/16/2021-13:11:15] [I] mean: 70.0063 ms
[08/16/2021-13:11:15] [I] median: 65.8401 ms
[08/16/2021-13:11:15] [I] percentile: 208.289 ms at 99%
[08/16/2021-13:11:15] [I] total compute time: 2.66024 s
&&&& PASSED TensorRT.trtexec # trtexec --verbose --onnx=yoloxx.onnx --saveEngine=yoloxx.engineWin10下TensorRT调用YOLOx的C++代码存放在项目下:tensorrt_cpp\yolox下
# step 3 TensorRT C++ 调用
F:\YOLOX\tensorrt_cpp\yolox\x64\Debug\yolox.exe F:\YOLOX\tensorrt_cpp\yolox\model\yoloxx.engine -i F:\YOLOX\test\20200813_caseid_217_imgid_5337.jpgblob image
7884ms
num of boxes before nms: 7
num of boxes: 1
2 = 0.76585 at 303.19 329.67 169.75 x 126.05
save vis file运行后在项目下生成det_res.jpg文件,其测试结果如下图所示.
2.Linux
为了简化在Linux上TensorRT的安装,我们使用 TensorRT的Docker镜像作为测试环境,使用的TensorRT的镜像为nvcr.io/nvidia/tensorrt:21.03-py3 ,读者可以在NVIDIA NGC pull相应的镜像,在该镜像内我们安装了必要的库比如: make, opencv等。
# step 1 运行tensorrt镜像
sudo docker pull nvcr.io/nvidia/tensorrt:21.03-py3
sudo docker images # 查看镜像是否拉取成功
sudo nvidia-docker run -it nvcr.io/nvidia/tensorrt:21.03-py3
# 这里假设已经在容器内被指和安装了必要的库比如 make, opencv# step 2 将host的tensorrt linux项目copy到容器内
# 关于TensorRT的Linux下的CPP的代码我们存放在项目下的 tensorrt_cpp/yilox_linux下
sudo docker cp yolox_linux 8d80a7f44e59:/workspace
# 注意这里的8d80a7f44e59需要替换为自己的容器的id# step 3 在Linux下编译 TensorRT yolox
cd yolox_linux
cmake .
make
# 将在项目下生成yolox可执行文件# cmake .
root@8d80a7f44e59:/workspace/yolox_linux# cmake .
-- The C compiler identification is GNU 9.3.0
-- The CXX compiler identification is GNU 9.3.0
-- Check for working C compiler: /usr/bin/cc
-- Check for working C compiler: /usr/bin/cc -- works
-- Detecting C compiler ABI info
-- Detecting C compiler ABI info - done
-- Detecting C compile features
-- Detecting C compile features - done
-- Check for working CXX compiler: /usr/bin/c++
-- Check for working CXX compiler: /usr/bin/c++ -- works
-- Detecting CXX compiler ABI info
-- Detecting CXX compiler ABI info - done
-- Detecting CXX compile features
-- Detecting CXX compile features - done
-- Found OpenCV: /workspace/opencv-4.5.2/build (found version "4.5.2")
-- Looking for pthread.h
-- Looking for pthread.h - found
-- Looking for pthread_create
-- Looking for pthread_create - not found
-- Looking for pthread_create in pthreads
-- Looking for pthread_create in pthreads - not found
-- Looking for pthread_create in pthread
-- Looking for pthread_create in pthread - found
-- Found Threads: TRUE
-- Found CUDA: /usr/local/cuda (found version "11.2")
-- cmake success!!! yolovx by xj
-- Configuring done
-- Generating done
-- Build files have been written to: /workspace/yolox_linux
# make
root@8d80a7f44e59:/workspace/yolox_linux# make
Scanning dependencies of target yolox
[ 50%] Building CXX object CMakeFiles/yolox.dir/src/yolox.cc.o
[100%] Linking CXX executable yolox
[100%] Built target yolox
# 测试
./yolox ./model/yoloxx.engine -i ./20200813_caseid_217_imgid_5337.jpg
# 需要注意的是TensorRT的engine对于TensorRT的版本和显卡是有一致性要求的,即不同显卡下序列化的engine是不同的!blob image
27ms
num of boxes before nms: 7
num of boxes: 1
2 = 0.76585 at 303.19 329.67 169.75 x 126.05
save vis file
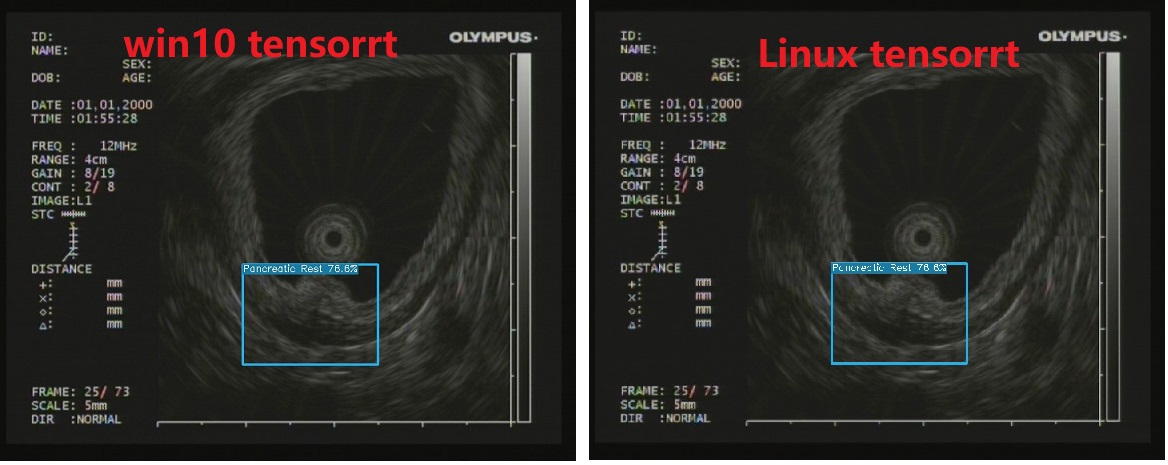
TensorRT调用成功,并在项目下生成det_res.jpg预测文件,其结果与Pytorch的调用和TensorRT在Win10下的调用测试结果是一致的。
🐤TODO
-
YOLOX ncnn,TNN框架的调用
-
YOLOX OpenCV调用
-
YOLOX OpenVINO调用
-
YOLOX INT8量化
If you use YOLOX in your research, please cite our work by using the following BibTeX entry:
@article{yolox2021,
title={YOLOX: Exceeding YOLO Series in 2021},
author={Ge, Zheng and Liu, Songtao and Wang, Feng and Li, Zeming and Sun, Jian},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2107.08430},
year={2021}
}