The instruction applies only to the European version of the gateway mieu01 from Xiaomi, with a European plug, as well as a version of the gateway from Aqara ZHWG11LM with a Chinese or European plug. For xiaomi gateway2 version with Chinese plug DGNWG02LM it will not work, it has other hardware components installed.
This instruction assumes that you already have ssh access to the gateway. If you have not done this, use the following instruction
Do make a back-up copy. If you decide to return to the stock firmware,
to revert to the original firmware you need the tar.gz backup from your
device with an archive of your root filesystem.
You cannot use a generic backup because every firmware contains unique
IDs and keys.
tar -cvpzf /tmp/lumi_stock.tar.gz -C / . --exclude='./tmp/*' --exclude='./proc/*' --exclude='./sys/*'After backup is done, download it to your local computer.
scp root@*GATEWAY_IP*:/tmp/lumi_stock.tar.gz .or using WinScp in scp mode (dropbear on the gateway doesn't support sftp
mode)
If you already have a rootfs image made with dd, make an archive anyway. During the boot phase of the dd image, nand flash or ubifs errors usually occur. Option with tar.gz does not have these drawbacks because it formats the flash before writing the files.
It is the easiest and recommended way that can be used either with a serial console or via ssh. It doesn't require additional soldering but works only on the stock firmware.
Double-check you don't have any redundant archives in the /tmp directory.
You'll need space to download firmware binaries. The gateway must be connected
to the internet too.
Run the command:
echo -e "GET /openlumi/owrt-installer/main/install.sh HTTP/1.0\nHost: raw.githubusercontent.com\n" | openssl s_client -quiet -connect raw.githubusercontent.com:443 2>/dev/null | sed '1,/^\r$/d' | bashThis command will stop all the processes on the gateway. It is a normal
behavior if your ssh connection is dropped. The flashing process takes a few
minutes. After it is done the gateway will create an open Wi-Fi network
with OpenWrt name.
If, for some reason, the Over-the-Air method did not work for you, you can bring the gateway back to life by soldering usb and uart and flashing it through mfgtools
After flashing, the gateway will create an open Wi-Fi network with the name OpenWrt. To connect the gateway to your router you have to connect to this network and go to http://192.168.1.1/
Default credentials to the gateway are: login 'root' without a password.
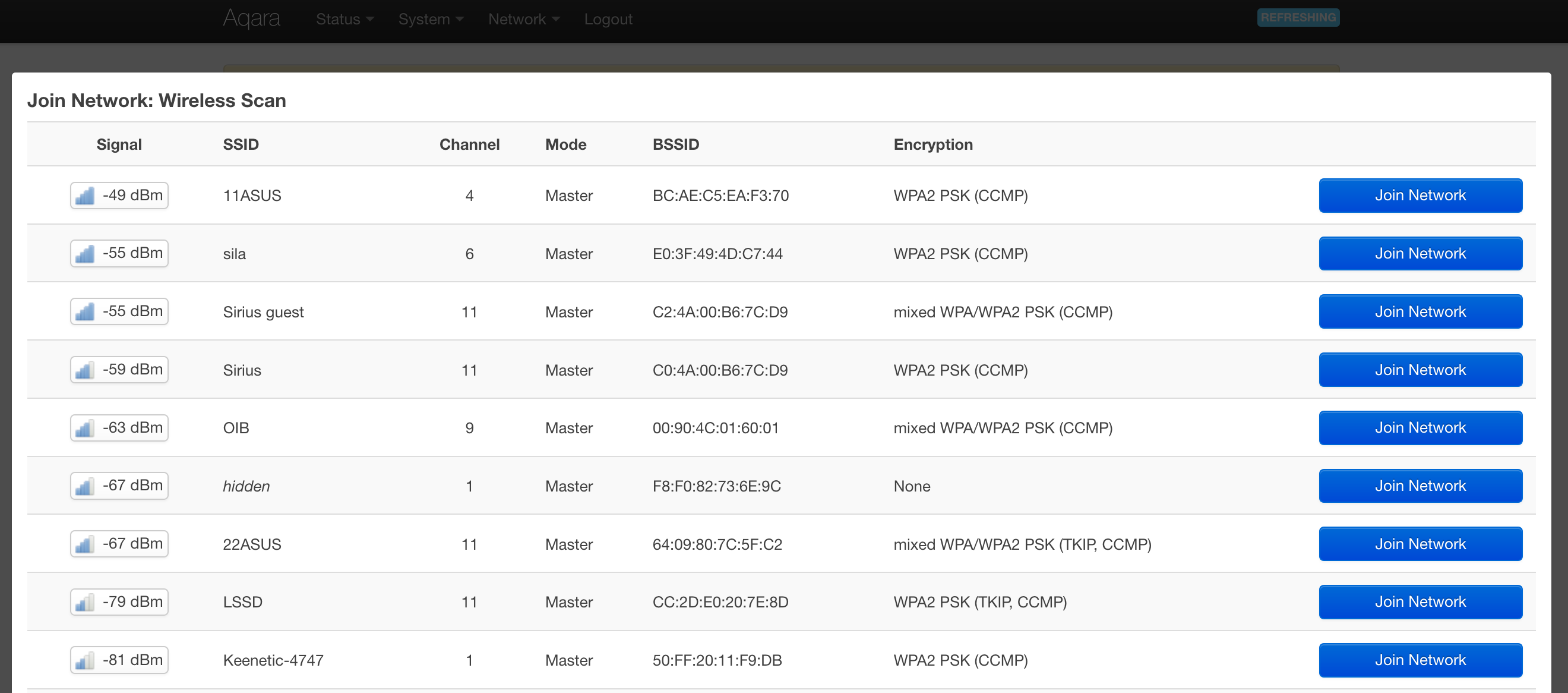
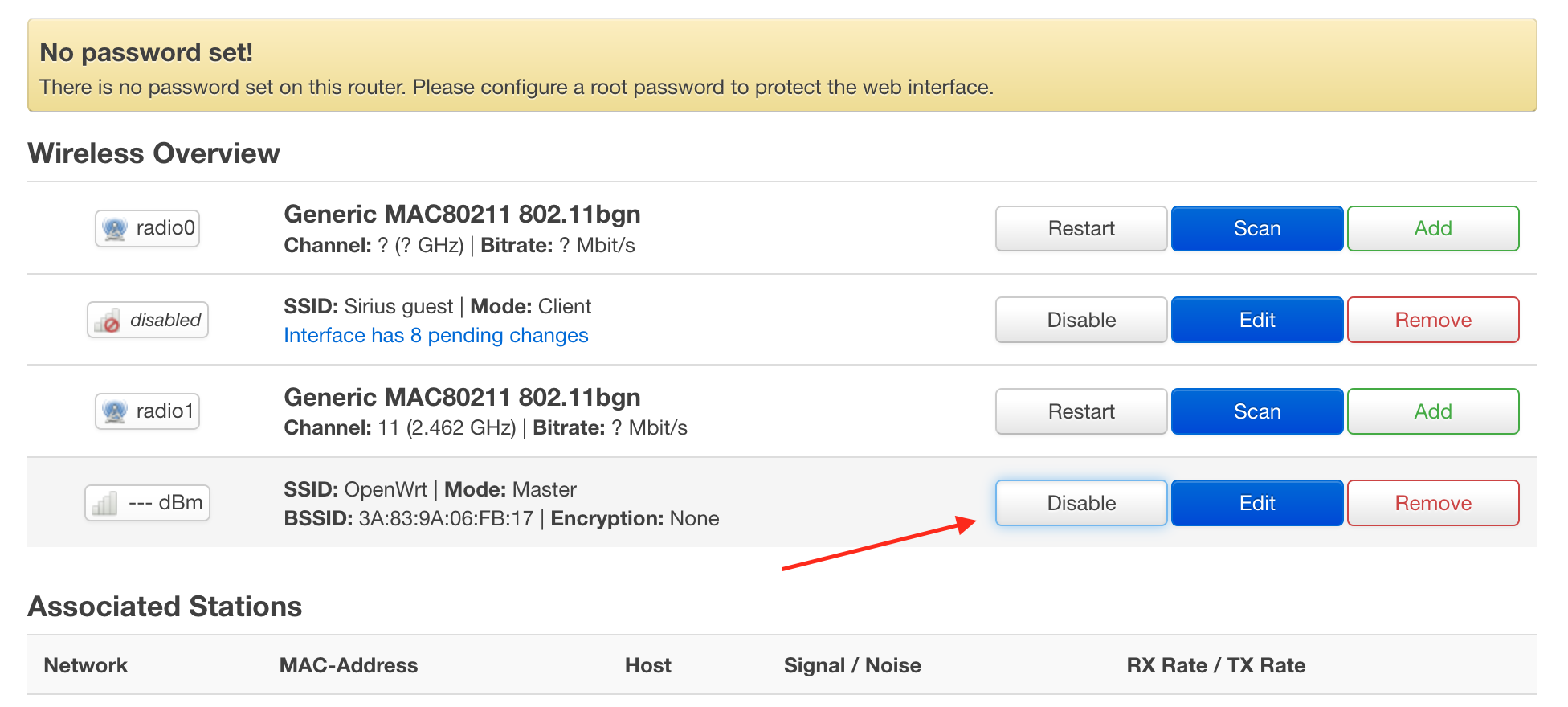
Go to the section Network -> Wireless
Press the Scan button against the first interface radio0 After a few seconds, you will see a list of networks. Find your network and press Join Network
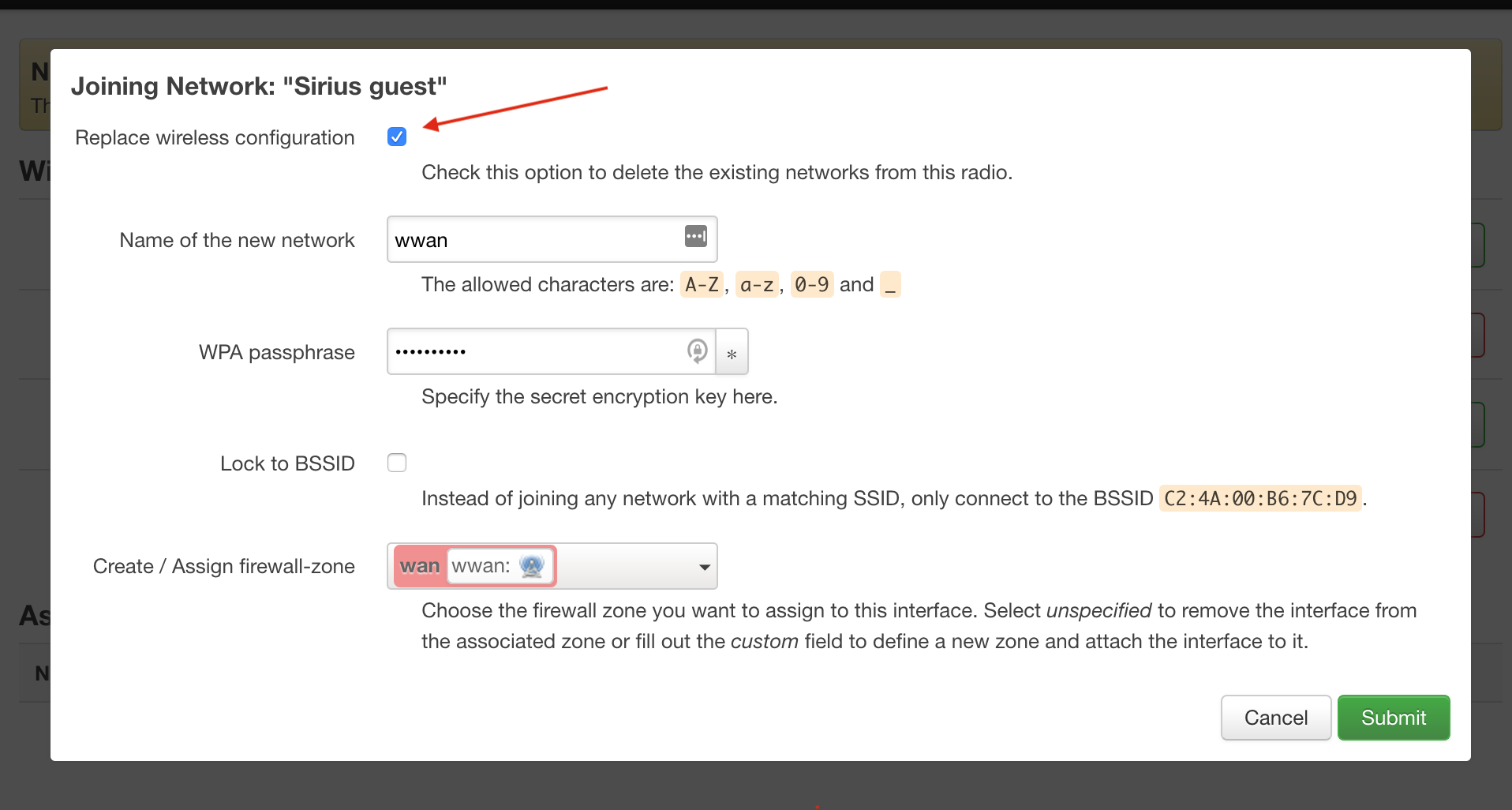
In the pop-up window set the "Replace wireless configuration" checkbox. Enter the passphrase from your Wi-Fi network below
Confirm the settings on the next window, press the Save button.
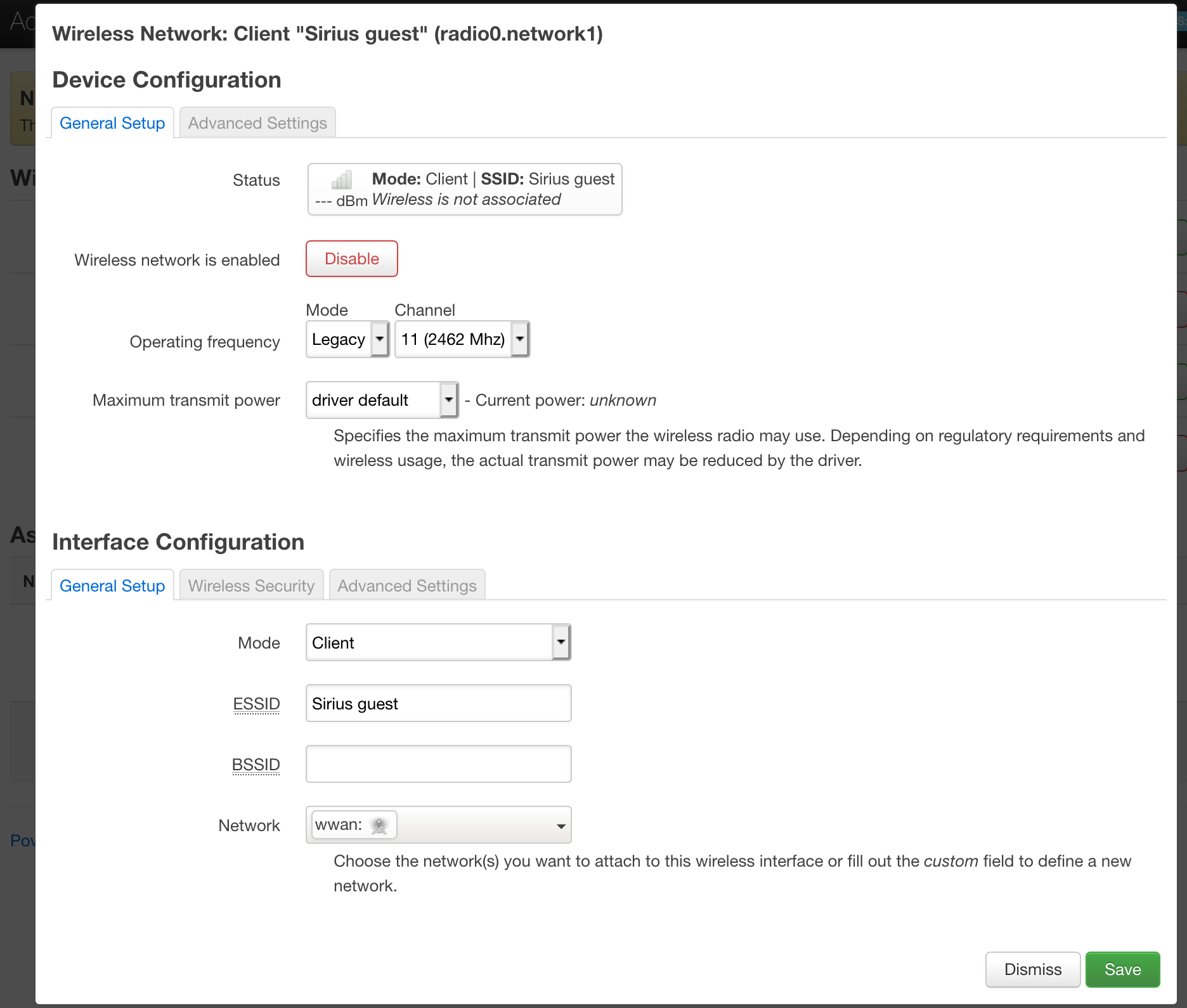
To apply the changes correctly, you should disable Access Poing by pressing "Disable" button against connection for the second interface.
The gateway will disconnect you from AP and will apply the changes. After the firmware, the mac address of the gateway changes, because the ip address is also most likely will change. Check it in the router or in the gateway itself.
The gateway is pre-installed:
- OpenWrt LuCi GUI on port 80 http
- command utility for flashing zigbee module jn5169
- Web plugin for LuCi to flash a firmware
Do not enable Wi-Fi AP + Station modes on the gateway at the same time. The driver that is used in the system cannot work in two modes at the same time. If you changed the LuCi settings and after that the gateway stopped connecting to the network, press the button on the gateway for 10 seconds. It will blink yellow 3 times and with start the initial network configuration mode with creating Wi-Fi Access Point.
Zigbee chip can work only with a single system, therefore you have to choose a program you'd like to use. But at the same time, you can use zigbee2mqtt to work with zigbee and domoticz for other automations.
- https://github.com/openlumi/lumimqtt/ - a service that allow managing the gateway devices over the MQTT
- https://flows.nodered.org/node/node-red-contrib-xiaomi-gateway - a package for node red
To erase data on the OpenWrt firmware and go to the initial set up (like you just flashed the gateway), you must hold the gateway button for 20 seconds. The gateway will blink red 3 times and will reset to the initial set up with creating Wi-Fi Access Point. Be careful with resetting, all programs and settings will be erased. Use it in case of emergency, when resetting Wi-Fi credentials not help.
To return to the stock firmware you have to flash original kernel, dtb and rootfs from your backup. Kernel and DTB are the same for all gateways and to keep the Mi Home working, you'll need your tar.gz backup.
mfgtools to return to the stock firmware
Put your backup with the namelumi_stock.tar.gz to directory
Profiles/Linux/OS Firmware/files overwriting the empty file
lumi_stock.tar.gz
Then again put the gateway into the boot mode via usb and via mfgtools flash the original firmware.
Kudos to @Clear_Highway и @lmahmutov
opkg update
opkg install gpioctl-sysfs
opkg install kmod-spi-gpio
opkg install kmod-spi-dev
opkg install kmod-spi-gpio-customControl
echo "69" > /sys/class/gpio/export
echo "70" > /sys/class/gpio/export
echo "out" > /sys/class/gpio/gpio69/direction
echo "out" > /sys/class/gpio/gpio70/direction
echo "1" > /sys/class/gpio/gpio70/value
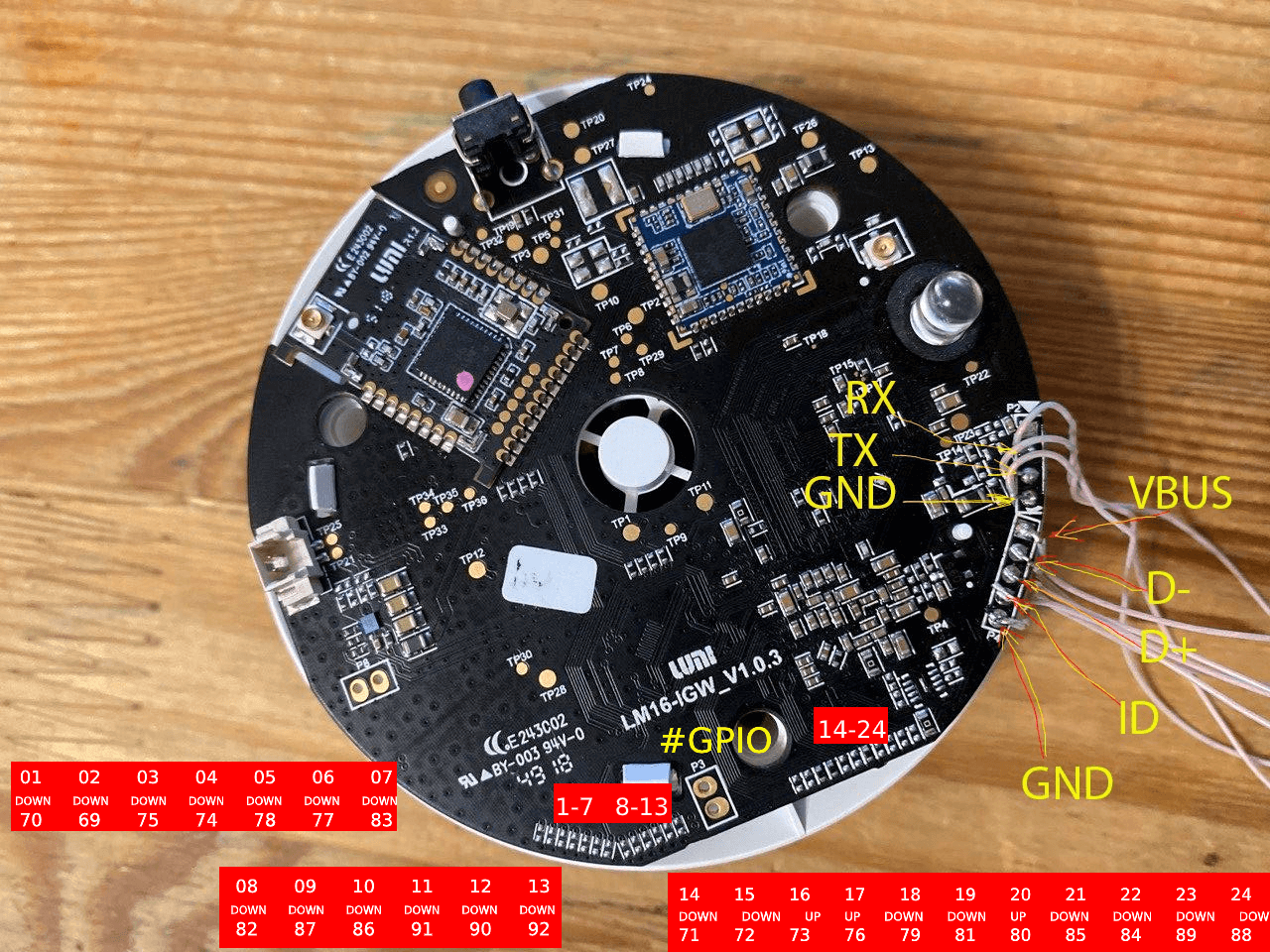
echo "0" > /sys/class/gpio/gpio70/valueGPIO numbers. Contact numbers start from the lowest on the photo and go up. DOWN and UP represents the type of pulling. Down to GND, UP - 3.3v
| Num | PULL | GPIO |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | DOWN | 69 |
| 1 | DOWN | 70 |
| 14 | DOWN | 71 |
| 15 | DOWN | 72 |
| 16 | UP | 73 |
| 4 | DOWN | 74 |
| 3 | DOWN | 75 |
| 17 | UP | 76 |
| 6 | DOWN | 77 |
| 5 | DOWN | 78 |
| 18 | DOWN | 79 |
| 20 | UP | 80 |
| 19 | DOWN | 81 |
| 8 | DOWN | 82 |
| 7 | DOWN | 83 |
| 22 | DOWN | 84 |
| 21 | DOWN | 85 |
| 10 | DOWN | 86 |
| 9 | DOWN | 87 |
| 24 | DOWN | 88 |
| 23 | DOWN | 89 |
| 12 | DOWN | 90 |
| 11 | DOWN | 91 |
| 13 | DOWN | 92 |
- An article that details the changes and technical modifications: [Xiaomi Gateway (eu version - Lumi.gateway.mieu01) Hacked] (https://habr.com/ru/post/494296/)
- Collection of information on hardware and software modding of Xiaomi Gateway https://github.com/T-REX-XP/XiaomiGatewayHack
- Telegram channel with discussion of modifications https://t.me/xiaomi_gw_hack