Self-Attentive BiLSTM-CRF wIth with Transferred Embeddings for Causality Extraction
Code and data for:
Li, Z., Li, Q., Zou, X., & Ren, J. (2021). Causality extraction based on self-attentive BiLSTM-CRF with transferred embeddings. Neurocomputing.
DOI: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.08.078.
(Table 6 in this version does not appear to have been edited correctly; please see arXiv for a correctly formatted paper.)
- A novel causality tagging scheme has been proposed to serve the causality extraction
- Transferred embeddings dramatically alleviate the problem of data insufficiency
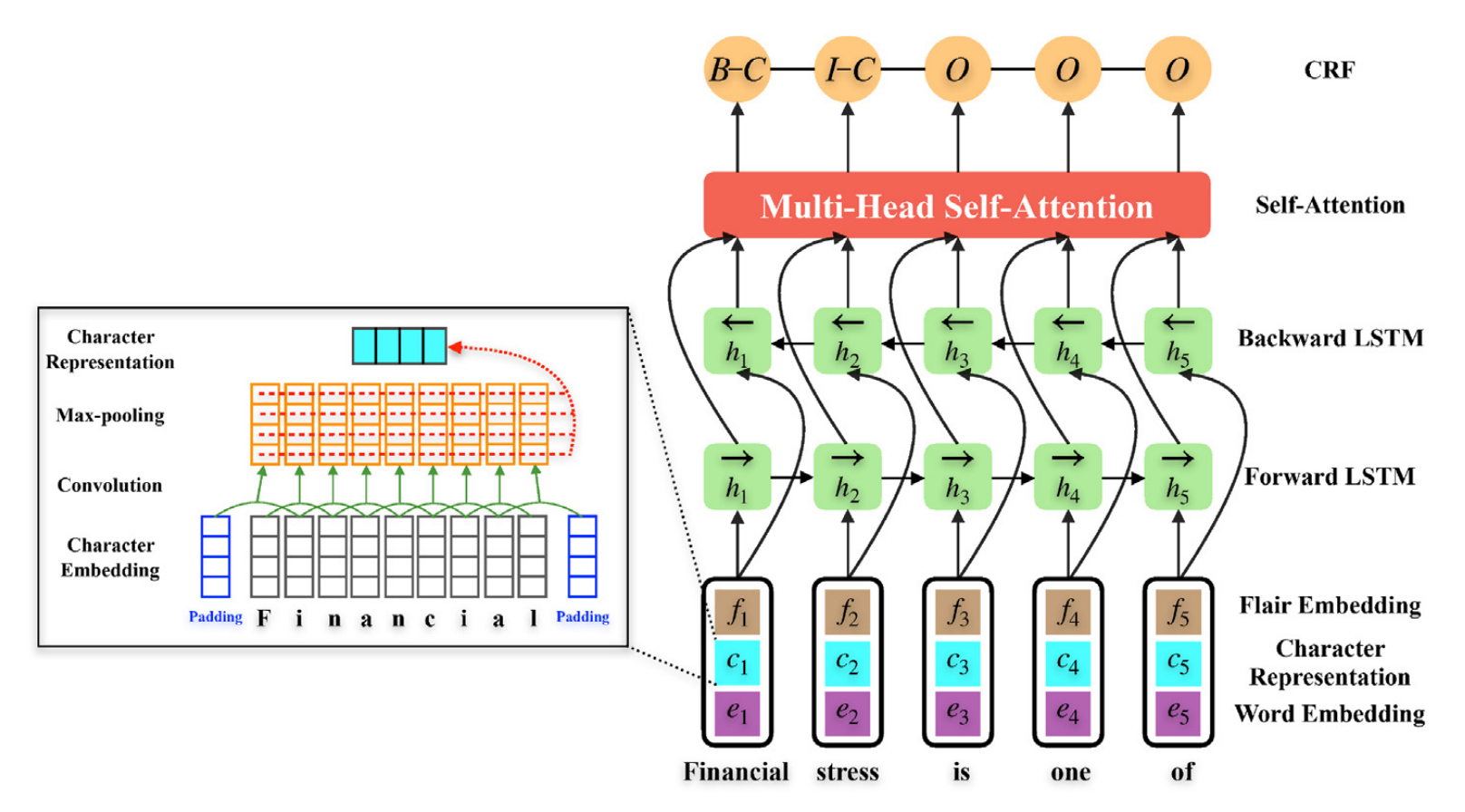
- The self-attention mechanism can capture long-range dependencies between causalities
- Experimental results show that the proposed method outperforms other baselines
Causality extraction from natural language texts is a challenging open problem in artificial intelligence. Existing methods utilize patterns, constraints, and machine learning techniques to extract causality, heavily depending on domain knowledge and requiring considerable human effort and time for feature engineering. In this paper, we formulate causality extraction as a sequence labeling problem based on a novel causality tagging scheme. On this basis, we propose a neural causality extractor with the BiLSTM-CRF model as the backbone, named SCITE (Self-attentive BiLSTM-CRF wIth Transferred Embeddings), which can directly extract cause and effect without extracting candidate causal pairs and identifying their relations separately. To address the problem of data insufficiency, we transfer contextual string embeddings, also known as Flair embeddings, which are trained on a large corpus in our task. In addition, to improve the performance of causality extraction, we introduce a multihead self-attention mechanism into SCITE to learn the dependencies between causal words. We evaluate our method on a public dataset, and experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves significant and consistent improvement compared to baselines.
Causality extraction, Sequence labeling, BiLSTM-CRF, Flair embeddings, Self-attention
- Baidu Netdisk: https://pan.baidu.com/s/18CfLFFQ3IRPGLX8QDJdSlg password: v5c2
- Google Drive: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1qJRYF3RZ2Fc4kLSXHZ5weNgC11BjWDGK/view?usp=sharing
Please cite the following paper when using SCITE.
@article{Li2021,
author = {Li, Zhaoning and Li, Qi and Zou, Xiaotian and Ren, Jiangtao},
doi = {10.1016/j.neucom.2020.08.078},
URL = {http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925231220316027},
issn = {18728286},
journal = {Neurocomputing},
pages = {207-219},
title = {Causality extraction based on self-attentive BiLSTM-CRF with transferred embeddings},
volume = {423},
year = {2021}
}
For bug reports, please contact Zhaoning Li (yc17319@umac.mo, or @lizhn7).
Thanks to shields.io.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License, which gives you the right to re-use and adapt, as long as you note any changes you made, and provide a link to the original source.