A Washington Trails Association Hike Recommender
Galvanize Data Science Program - Summer 2016 - Capstone Project - Jade Tabony
While the Washington Trails Association (WTA) provides a great resource for people to find hikes in their area that fit their specifications, the site does not have a recommender system to suggest hikes to people based on hikes that they have liked in the past. I built Rec The Trail to fill exactly that gap.
Web Application: recthetrail.com
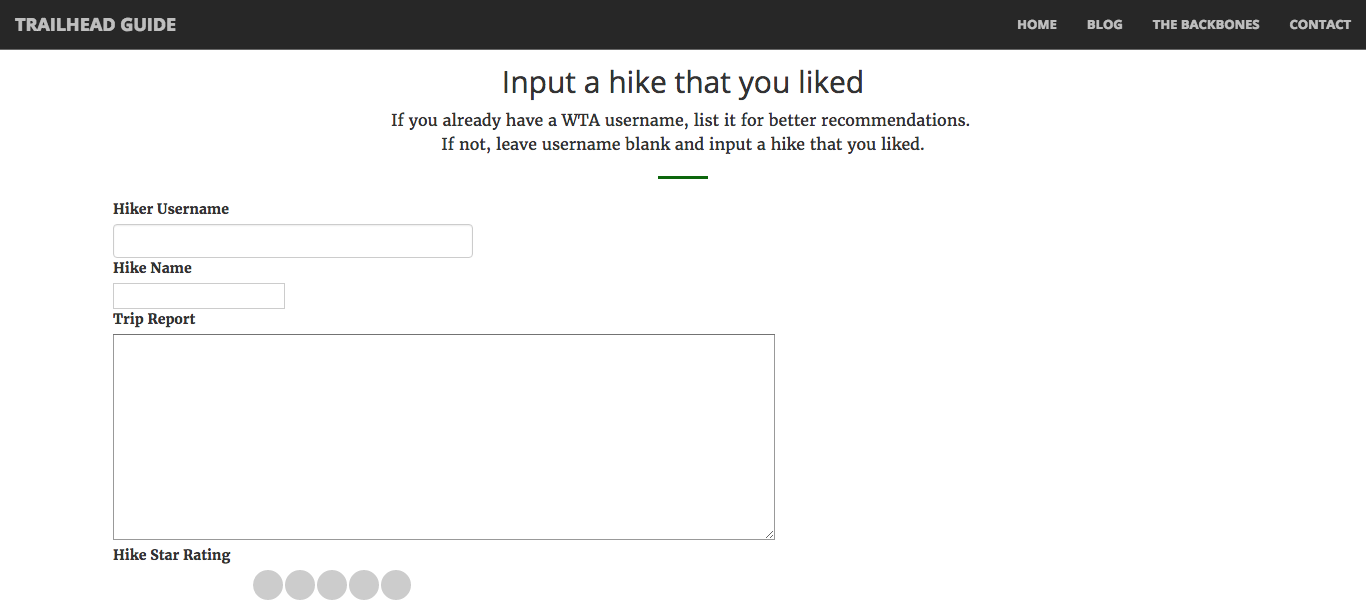
At recthetrail.com, you can input a hike that you like along with either a rating or a trip report and it will give you five hike recommendations!
If you already have a WTA username, you can provide that for tailored refined hike recommendations.
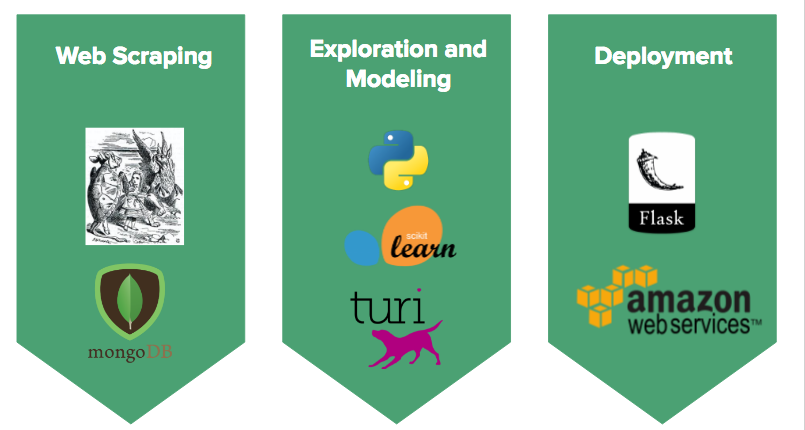
Recthetrail.com is created using Flask and self-hosted on AWS.
All of my data is scraped from the WTA website using requests and BeautifulSoup. For each hike, I scraped the hike meta data, the trail description and all of the corresponding trip reports. Since the website only provides an overall average rating, instead of individual user ratings, I used sentiment analysis on trip reports in order to create a rating system.
All of the data was stored in MongoDB.
For every hike, I scraped the provided longitude and latitude and used the Google API to calculate the drive time from Seattle.
From the hike description, I vectorized all of the text using TF-IDF. I then performed k-means clustering to group hikes based on similar keywords. Some of the groups produced were:
- Loop hikes
- Summits
- Waterfalls
- Rivers
Due to the lack of individual ratings for each hike, I decided to apply sentiment analysis to each trip report to create a rating system. I tried a variety of sentiment analysis method, including built-in algorithms such as the TextBlob Polarity and Turi Sentiment Analysis. After searching for some relevant training data, I found that reviews on everytrail.com all had both text and rating data. Unfortunately, the data is highly unbalanced and messy (some entries were in Turkish).
Following data cleaning, I tried building my own sentiment analysis models using the following models:
- Random Forests
- Gradient Boosting
- Adaboosting
- With the following base estimators:
- Multinomial bayes
- Decision tree
- With the following base estimators:
The recommendation system is implemented using Turi GraphLab (now owned by Apple). I tried three different types of recommendation systems:
- Factorization Recommender
- Item Content Recommender
- Ranking Factorization Recommender with Item Data
The models were each evaluated using RMSE, Recall and Precision at N and A/B testing. The final web app is built using ranking factorization with item data and item content recommenders in absence of preexisting user data.
├── code
| ├── ider_pickler.py (functions for pickling hike identification)
| ├── recommender.py (builds final recommendation systems and pickles it)
| └── sentiment_analysis.py (functions for sentiment analysis and rating system)
|
├── EDA
| ├── EDA.ipynb (hike feature exploration and visualization)
| ├── Recommender.ipynb (recommender exploration and comparisons)
| └── sentimentAnalysis.ipynb (Sentiment analysis model comparison)
|
├── scraper
| ├── dataCleaning.py (parses scraped data, extracts meta data and uses Google API)
| ├── trainingDataScraper.py (everytrail.com trip review scraper)
| ├── tripReportScraper.py (wta.org trip report scraper)
| └── wtaScraper.py (wta.org hike scraper)
|
├── web_app
| ├── pickle (all pickled models used in the app)
| ├── static
| ├── templates
| └── root.py (runs application)
|
├── CrispDM.md (write-up of Crisp-DM methodology used for this project)
├── Install.txt
└── README.md
- Use more advanced techniques on the trip report text to improve sentiment analysis based rating system
- Refine the web application (add weather report, add gear recommendations such as microspikes if snow is present).
- Incorporate more filtering options for the use. (Ex. Limit drive time, less popular hike)
-
"Washington Trails Association." WTAs Blog. N.p., n.d. Web. 09 Aug. 2016.
-
"EveryTrail - Travel Community, IPhone Guides for Sightseeing, Hiking, Walking Tours and More." EveryTrail - Travel Community, IPhone Guides for Sightseeing, Hiking, Walking Tours and More. N.p., n.d. Web. 09 Aug. 2016.
-
Andy Bromberg. (n.d.). Retrieved August 09, 2016, from http://andybromberg.com/sentiment-analysis-python/
-
Debnath, S., Ganguly, N., & Mitra, P. (2008). Feature weighting in content based recommendation system using social network analysis. Proceeding of the 17th International Conference on World Wide Web - WWW '08. doi:10.1145/1367497.1367646
-
Machine Learning Blog & Software Development News. (n.d.). Retrieved August 09, 2016, from http://blog.datumbox.com/machine-learning-tutorial-the-naive-bayes-text-classifier/
-
Silva, Nádia, Estevam Hruschka, and Eduardo Hruschka. "Biocom Usp: Tweet Sentiment Analysis with Adaptive Boosting Ensemble." Proceedings of the 8th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval 2014) (2014): n. pag. Web.
-
Sobhanam, H., & Mariappan, A. K. (2013). Addressing cold start problem in recommender systems using association rules and clustering technique. 2013 International Conference on Computer Communication and Informatics. doi:10.1109/iccci.2013.6466121
-
Turi Machine Learning Platform User Guide. (n.d.). Retrieved August 09, 2016, from https://turi.com/learn/userguide/recommender/choosing-a-model.html