This project is the implementation of distributed synchronization methods for the research project at Santa Clara University COEN 283 Operating Systems.
/DistributedSyncSimulator/
│
├─bin
│ └─distributedsyncsimulator
│ ├─ifc
│ ├─leadnode
│ ├─shared
│ ├─utilities
│ └─worknode
├─Interface
│ └─src
│ ├─main/java/distributedsyncsimulator/interface
│ |-LeaderIFC.java
│ |-WorkerIFC.java
├─LaunchScript
│ │ -StartLead2PL.bat
│ │ -StartLeadTS.bat
│ │ -StartRMI.bat
│ │ -StartWorkeNodes.bat
│ │ -StartWorkeNodesNoConflic.bat
│ │
│ └─log
│
├─LeadNode
│ └─src
│ ├─main/java/distributedsyncsimulator/leadnode
│ |-LeadNode.java
│ |-SanpshotIsolationManager.java
│ |-SyncManagerBase.java
│ |-TimeStampOrderingManager.java
│ |-TwoPhaseLockManager.java
├─SampleLog
│ ├─2 Phase Lock
│ │ |-LeadNode_20220528_22-20-0575.log
│ │ |-WorkerNode001_20220528_22-20-19269.log
│ │ |-WorkerNode002_20220528_22-20-19269.log
│ │
│ └─Timestamp Ordering
│ |-LeadNode_20220528_22-21-25462.log
│ |-WorkerNode001_20220528_22-21-30256.log
│ |-WorkerNode002_20220528_22-21-30255.log
│
├─Shared
│ └─src
│ ├─main/java/distributedsyncsimulator/shared
│ |-MyAction.java
│ |-MyConfiguration.java
│ |-MyDatabase.java
│ |-MyLock.java
│ |-MyLog.java
│ |-MyTransaction.java
│
├─Transactions
│ |-test.txt
│ |-trans1.txt
│ |-trans2.txt
│
├─Utilities
│ └─src
│ ├─main/java/distributedsyncsimulator/utilities
│ |-Constants.java
│ |-MyUtils.java
└─WorkNode
└─src
├─main/java/distributedsyncsimulator/worknode
|-WorkNode.java
Java Remote Method Invocation (RMI)
- Server
- Client
Though the distributed environment is designed based on the distributed database system, the focus is on the Synchronization Algorithm simulation. Thus, it is not necessary to implement a middleware to communicate with real database. Instead, we can abstact the concpet of database by simulated it with a key-value in memory DB.
- Designed as a singleton, such that one worker node can only monitor/operate one databse
- Use a hashmap to simulate the key-value db
- key - String
- value - integer
- It support 4 operations
- read
- write
- add
- minus
A transaction can contains multiple operations, and each action is seperated by delimeter -. The allowed actions typs are as follow:
- read - r
- write - w
- plus - p
- minus - m
The pattern for read and write operations are <r/w>-<key>. For example, r-Apple means read Apple's value.
The pattern for plus and minus operations are: <p/m>-<key>-<value>. For example, p-Apple-9 means add 9 to Apple.
A typical transaction example is as follow:
r-Apple,p-Apple-9,w-Apple,r-Orange,p-Orange-9,w-Orange
There are two sets of input Transactions:
- trans<#>.txt
- the number means the worker number. e.g. trans1.txt will be consumed by worker1
- It is generate by script.
- Currentlt, trans1.txt and trans2.txt are designed by purpose to avoid deadlock when run together.
- test.txt
- this short transaction lists are design for sanity check
- It is used to check if the program is running as designed.
- A singleton
- use synchornous queue to save logs
- A thread object called LogHandler to fetch messages from sync_queue continously
- print to screen
- write to log file
The log file will be saved in ./log, that is created in the running directory. For example, if you execute running script in ./DistributedSyncSimulator/LaunchScript, then the log directory will be created at ./DistributedSyncSimulator/LaunchScript/log.
Each node will generated its own logs. For example, if the test runs with 1 LeadNode and 2 WorkerNode, the log files will be created like something similiar to the following:
- LeadNode Log
- Pattern: LeadNode_timestamp.log
- Example: LeadNode_20220527_00-52-13265.log
- WorkerNode Log
- Pattern: WorkerNodeNNN_timestamp.log
- Example:
- WorkerNode001_20220527_00-52-32456.log
- WorkerNode002_20220527_00-52-32457.log
Install gradle and Java, and set the environment proper. You can verify the installation by enter the following command in cmd. It should be able to show the verison infomations for both.
> gradle --version
------------------------------------------------------------
Gradle 7.4.2
------------------------------------------------------------
Build time: 2022-03-31 15:25:29 UTC
Revision: 540473b8118064efcc264694cbcaa4b677f61041
Kotlin: 1.5.31
Groovy: 3.0.9
Ant: Apache Ant(TM) version 1.10.11 compiled on July 10 2021
JVM: 17.0.2 (Eclipse Adoptium 17.0.2+8)
OS: Windows 10 10.0 amd64
> java --version
openjdk 17.0.2 2022-01-18
OpenJDK Runtime Environment Temurin-17.0.2+8 (build 17.0.2+8)
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM Temurin-17.0.2+8 (build 17.0.2+8, mixed mode, sharing)
-
Launch CMD and naviagte to SyncSimulator\DistributedSyncSimulator
> cd SyncSimulator\DistributedSyncSimulator
-
Build project using gradle
> gradle build -
The compiled class file is located at
binfile at _SyncSimulator\DistributedSyncSimulator\bin_
-
Launch CMD and naviagte to ./DistributedSyncSimulator/
-
Launch LeadNode
- Manually enter command in cmd with argument to choose Sync Methods:
- 0 -> 2 Phase Lock
- 1 -> Time Ordering Algorithm
# using 2PL > java -classpath bin -Djava.rmi.server.hostname=localhost distributedsyncsimulator.leadnode.LeadNode 0 # or using Time Ordering > java -classpath bin -Djava.rmi.server.hostname=localhost distributedsyncsimulator.leadnode.LeadNode 1
- In windows, you can run script StartLeadNode{methodName}.bat
# using 2PL > StartLead2PL.bat # using Time Ordering > StartLeadTS.bat
- Manually enter command in cmd with argument to choose Sync Methods:
-
Launch Worker Node
- Launch a single worker node by using command
# launch worker node name WorkerNode001, and comsumes transaction test.txt > start cmd.exe /k java -classpath bin distributedsyncsimulator.worknode.WorkNode 001 Transactions\test.txt
- In windows, you can run script StartWorkeNodes.bat to launch 2 WorkerNodes:
- WorkerNode001
- consumes test.txt
- WorkerNode001
- consumes test.txt
- Since they use the same Transactions, it will cause
deadlock.> StartLeadNodes.bat
- WorkerNode001
- In windows, you can run script StartWorkeNodesNoConflic.bat to launch 2 WorkerNodes:
- WorkerNode001
- consumes trans1.txt
- WorkerNode001
- consumes trans2.txt
- Since they use the two different designed Transactions, no dead lock will happen.
> StartWorkeNodesNoConflict.bat
- WorkerNode001
- Launch a single worker node by using command
- RMI Service
- If the error messages show that the RMI service is not running, you can start the RMI service manually with correct bin directory path by
> start rmiregistry -J-Djava.rmi.server.codebase=file:<bin_file_path> - In Windows, You can also use script StartRMI.bat to launch RMI services
> StartRMI.bat
- If the error messages show that the RMI service is not running, you can start the RMI service manually with correct bin directory path by
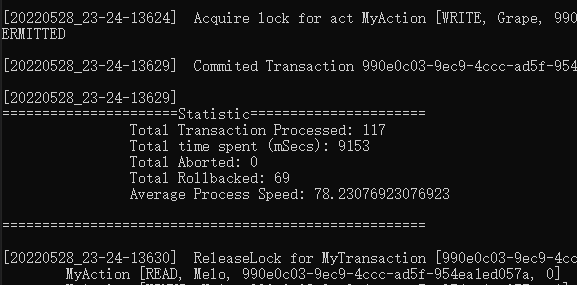
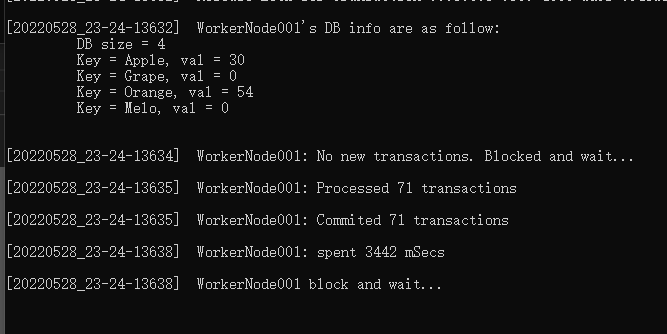
The log file is generated with a certain pattern when an event is occur and labeled with key words and timestamps. A log analyze tool could be developed to read log and parse the key words to do log analysis, profile benchmark, etc.
As of 05/28/2022, there is no bandwidth for me to implement this tool. I used some in-program variables to do simple statistic collection. The simple benchmark will be showned as follow:
- Programming Language:
- Java 17
- Python 3
- Batch
- 3rd Party Library: N/A
- Build Tool
- Gradle 7.4
- OS tested
- build envrionment
- win10
- ubuntu
- macos
- run envrionment
- Windows 10 x64
- build envrionment