This repository provides an implementation of age prediction from images of faces using CNN models.
Age prediction project allows to use two base CNN models (MobileNetV2 and ResNet50) from Keras. The models are trained via transfer learning, where ImageNet pre-trained CNNs are used and fine-tuned for the classification task.
Age prediction CNN is compatible with Python 3.6 and is distributed under the MIT license.
# Python3.5+
# Keras 2.2.5+
# create age_prediction_cnn folder
mkdir age_prediction_cnn
cd age_prediction_cnn
# clone and install prerequisites locally
git clone git@github.com:vovaekb/age_prediction_cnn.git
cd age_prediction_cnn
pip install -r requirements.txt
# create a folder for saving model
mkdir -p data/model
Use some preprocessing script to crop out faces in images and obtain a person age. You should have a batch of image files with faces named in following format:
<id>_<age>_<gender>.jpg
You can use UTKFace. This dataset was used to train models in the Age prediction CNN. UTKFace dataset provides labels for both age and gender.
For UTKFace dataset you can use the script transform_dataset_names.py in root folder of the project. This script allows to prepare face crops in required format. To run this script:
python transform_dataset_names.py --sample_dir <path_to_utkface_data> --output_dir <path_to_save_utkface_training_dataset>
When you are going to train the age predictor you just need to run python.
python train_model.py --type <model_type> --range_mode True --train_sample_dir <train_sample_dir> --test_sample_dir <test_sample_dir> --model_path <model_path> --base_model <base_model_name> --img_dim <img_dim> --batch_size <batch_size> --lr_scheduler <lr_scheduler> --age_deviation <age_deviation> --load --predict_gender --fine_tuning --lr_find
Here --type denotes the type of NN model and can have two values ("classification" and "regression").
Parameters --train_sample_dir and --test_sample_dir specify path to train and test datasets accordingly.
--model_path specifies the path where model will be saved after training so predictor can load model from h5 file later.
--base_model means CNN architecture used (two values: MobileNetV2 and ResNet50).
--img_dim means dimension of input images for training (width, height), 128 on default.
--batch_size specifies the size of batch to use for training.
--lr_scheduler allows to specify learning rate scheduler to use (reduce_lr_on_plateau, cyclic_lr).
--age_deviation specifies the deviation in age vector (in years), 5 on default
Optional parameters:
--load means that trained model will be loaded from h5 file rather than trained from scratch.
--predict_gender allows to apply gender classification in addition to age prediction.
--fine_tuning applies fine tuning of CNN model (freezing layers in base models and unzfreezing Conv layers).
--lr_find specifies whether or not to find optimal learning rate (value 0 or 1).
If you run the application in training mode you should see something like this:
Using TensorFlow backend.
Initializing CNN model ...
Starting training ...
Epoch 1/13
1/2 [==============>...............] - ETA: 8s - loss: 0.0947
2/2 [==============================] - 13s 6s/step - loss: 0.0668 - val_loss: 0.1144
Epoch 2/13
...
If you run the application with gender classification turned in you should see similar output with accuracy and loss for both age and gender.
Training accuracy and loss as well as validation accuracy will be printed in terminal.
If you run the application in loading mode you should see something like this:
Using TensorFlow backend.
Initializing CNN model ...
Predicting for image 20170110224238891_10_0.jpg
Predicted age: 0, true age: 10
Predicted gender: M, true gender: M
...
If you run the application with gender classification turned on you should see similar output with predictions for both age and gender.
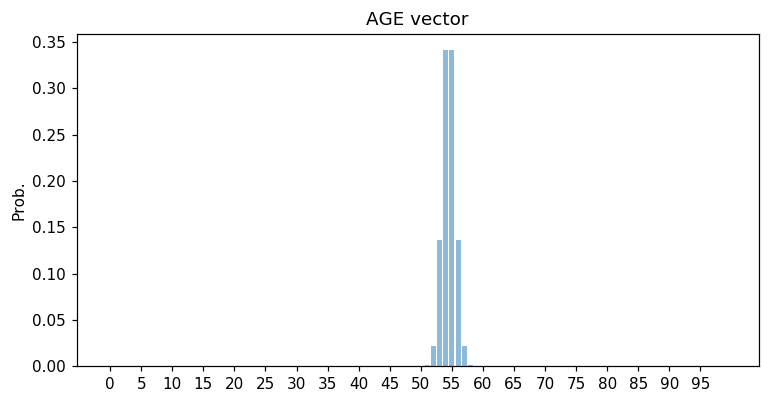
Unlike regular image classification age prediction should not be strictly discriminative. In this case soft decision making can be applied through predicting histogram of normal probability around the age value. Here we build a AGE vector represented as a histogram of a normal probability with mean in the age value with deviation 5 years. This is inspired by image aesthetics quantification problem.
We have no statistic data about ages so AGE vectors were generated manually. For generating AGE vectors we used method build_age_vector() in script utils.py locating in folder facematch/age_prediction/utils.
In the CNN model output layer is represented by a fully connected layer with 100 nodes and softmax activation.
As loss and accuracy metrics Earth mover's distance and Mean Absolute Error are used respectively. Earth mover's distance measures the histogram similarity.
To run training in age classification mode use command:
python train_model.py --type classification <options>
To run loading model from file and predicting age:
python train_model.py --type classification <options> --load True
We also predict a range the age belongs to from following ranges: 0-5,5-10,10-15,15-20,20-25,25-30,...,75-80,80+. Here we use regular classification model where each class is represented by an age range.
To run training in age classification mode use command:
python train_model.py --type classification --range_mode True <options>
To run loading model from file and predicting age use command with option --load True.
In regression mode chosen predictor outputs single floating point value in range 0 to 1.0 representing age. Mean squared error is used as loss. In regression model output layer is represented by a fully connected layer with the only node and linear activation.
We applied scaling target age values to range [0, 1] and multiplying predictions by 100 when presenting results to user as it gives better accuracy results.
To run training in age classification mode use command:
python train_model.py --type regression <options>
To run loading model from file and predicting age use command with option --load True.
We also apply gender classification of a person on image. You can include this option using parameter --predict_gender:
python train_model.py --type <model_type> <options> --predict_gender True
To run loading model from file and predicting age and gender use command with option --load True.
In training optimization we use learning rate schedules to optimize finding best learning rate. We use ReduceLROnPlateau and CyclicLR methods from keras.callbacks module.
Parameter --lr_scheduler allows to set one of these LR schedulers.
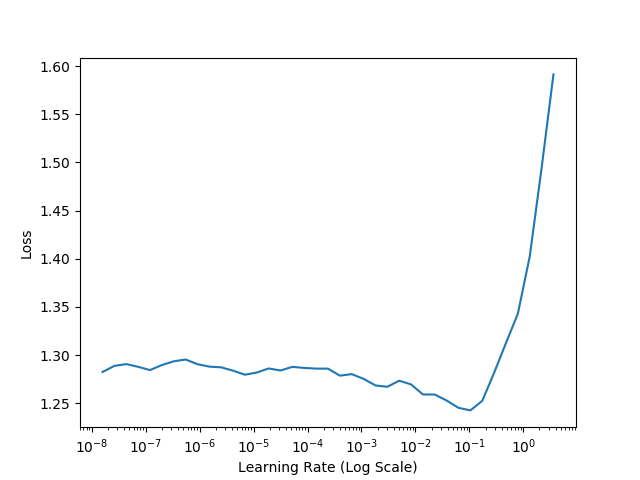
There is an option to automatically find optimal learning rates. Learning Rate Finder starts training in 3 epochs exponentially increasing the learning rate from min_lr (1e-10) to max_lr (1e+1) after each batch update and plot Loss vs. Learning rate. The final plot will be saved in the folder output.
Use parameter --lr_find to run Learning Rate Finder.
Optionally we include applying fine tuning for all modes of age and gender prediction. We freeze layers of base model, train the model, then unfreeze last convolutional layer in the base model and retrain the model again.
To run the training model with fine tuning use this command
python train_model.py <options> --fine_tuning True
We use TerminateOnNan callback which terminates the training once NaN (Not-a-Number) values appear in loss. It checks results when batch ends, retrieves loss from logs and stops training if it is Nan.
We using TrainingMonitor and ModelCheckpoint for monitoring performance of training. TrainingMonitor allows to record loss and accuracy metrics after each epoch and build a plot Loss/Accuracy vs Epochs. This plot allows us to spot overfitting earlier during the training and find out whether the learning rate found is optimal.
ModelCheckpoint is tracking particular metric (accuracy, loss) after each epoch and prints out whether the metric has improved. It can also be setup to save the network weights only when there is an improvement in classification accuracy (e.g. on validation dataset: monitor='val_acc').
This project uses this dataset to train the prediction model:
- Abhimanyu Dubey, Otkrist Gupta, Ramesh Raskar, Nikhil Naik. "Maximum-Entropy Fine-Grained Classification." Proceedings of the 32Nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (2018).
- Talebi, Hossein, and Peyman Milanfar. "NIMA: Neural Image Assessment." IEEE Transactions on Image Processing (2018).
- Mark Sandler, Andrew Howard, Menglong Zhu, Andrey Zhmoginov, Liang-Chieh Chen. "MobileNetV2: Inverted Residuals and Linear Bottlenecks." The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2018
- Kaiming He, Xiangyu Zhang, Shaoqing Ren, Jian Sun. "Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition." 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)
- Adrian Rosebrock (2017) "Deep Learning for Computer Vision with Python" [ebook].
- Keras, Regression, and CNNs
- Fine Tuning with Keras and Deep Learning
- Keras learning rate schedules and decay
See LICENSE for details.