Common Image segmentation utilities
Training deep neural networks for Image segmentation usually involves training models on small patches rather than full images due to memory constraints. This repo provides some common utilities for patch generation, recombination and simple segmentation mask conversion.
Utilities
Patch generation
Patch generation is one of the most important part in input-output pipeline of segmentation task where the whole high resoltion image is divided into small tiles 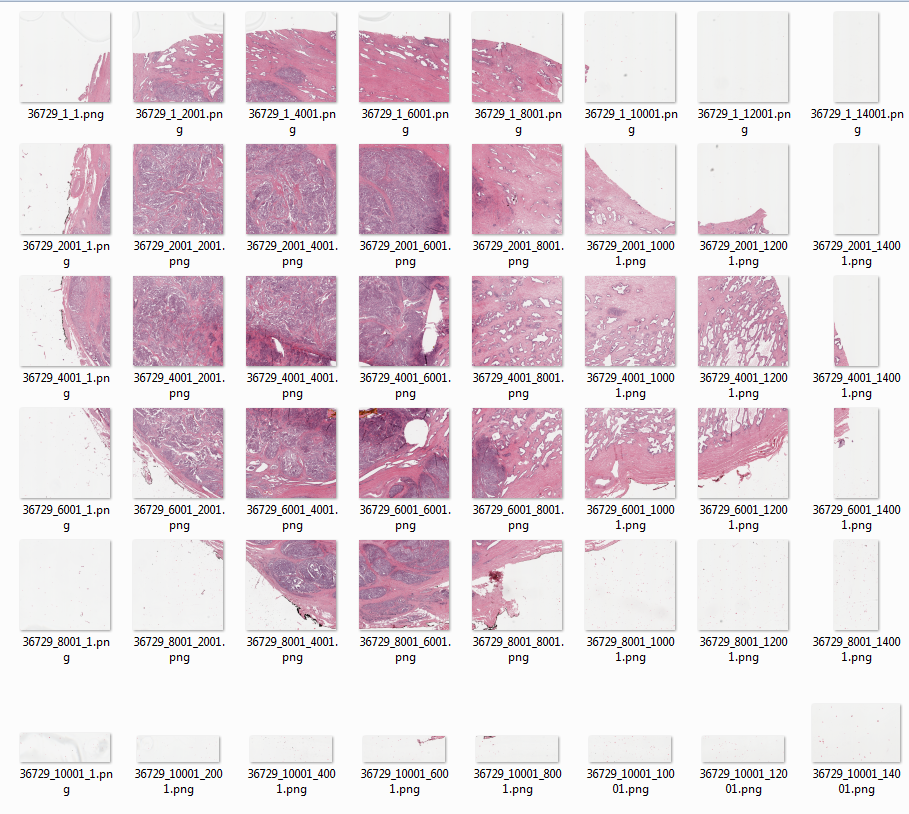
Also, the corresponding mask is also divided into small tiles 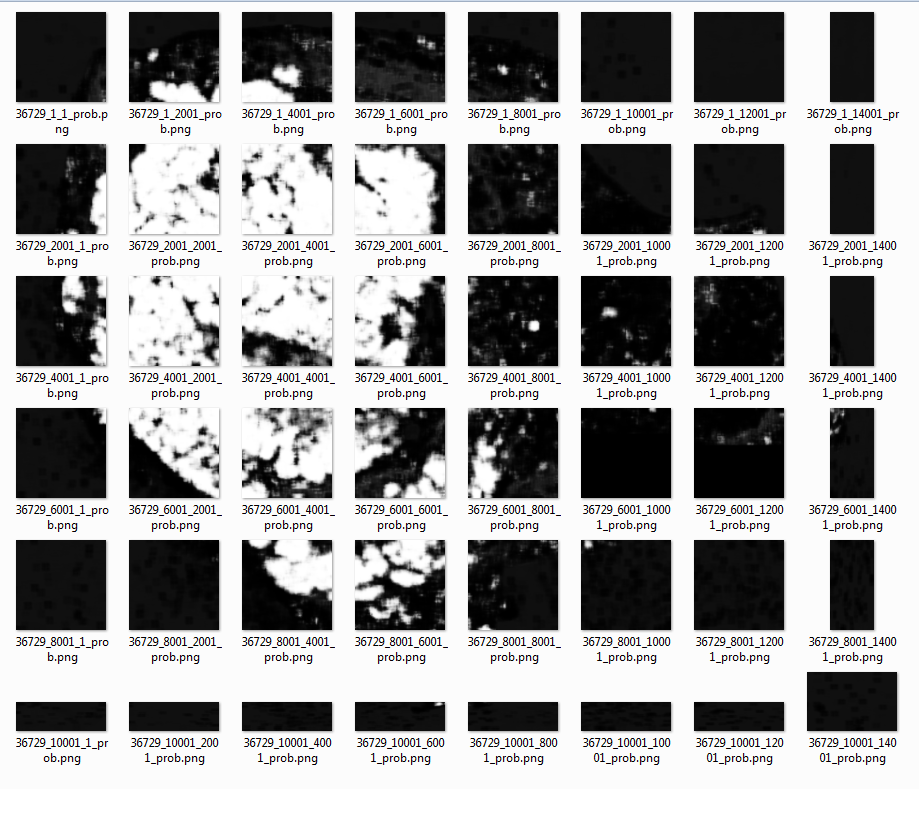
You can use function create_patches in utils.py to create patches with or without overlap. For further information look into the help string of the function.
Patch recombination
After training segmentation model on patches as a final step all the predictions on patches has to be combined to get image segmentation mask 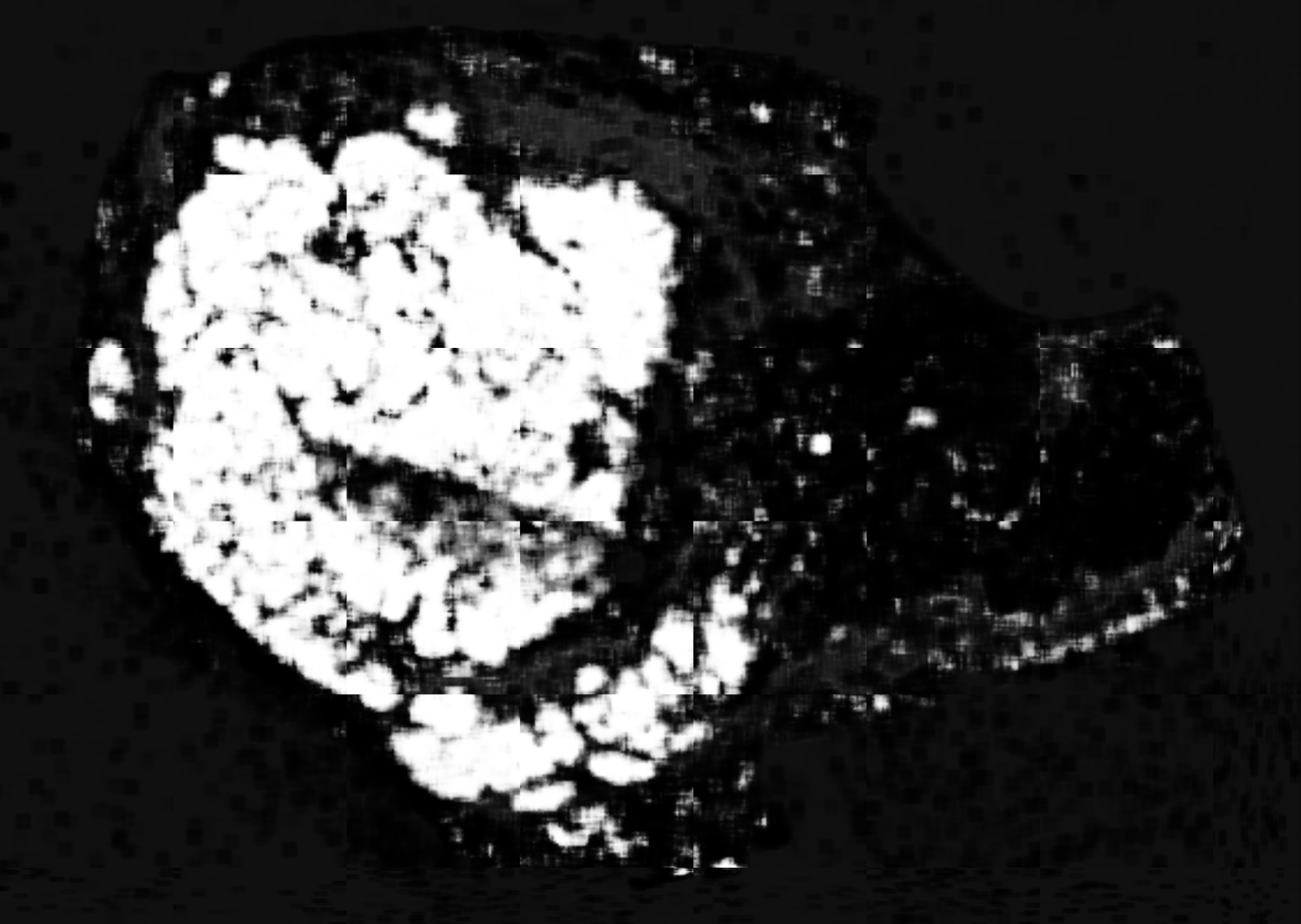 Usually, any Segmentation DL model output dense class probability mask instead of discrete class mask. Hence, it is reccomended that first probability patches be stitched together to get final probability mask which can be thresholded to get final dense prediction.
Usually, any Segmentation DL model output dense class probability mask instead of discrete class mask. Hence, it is reccomended that first probability patches be stitched together to get final probability mask which can be thresholded to get final dense prediction.
This repo provides two methods for patch recombination
-
Naive method
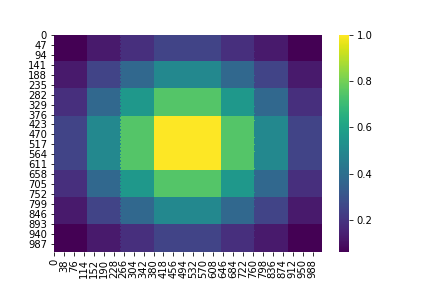
Naive method assumes linear recombination of patches and gives relative weightage to patches with twice overlap(i.e. stride = 0.5*patch_size) as shown
Usually, segmentation models like U-Net take image patches and make predictions on those small local windows, without data near the border of the patches, so there might first be a high error on the predictions made near the outside of the window, in plus of the fact that predictions may be just concatenated, so it looks even more jagged. Therfore, predicting on overlapping patches and recombination through naive method helps in preventing jagged predictions.
You can use
stitch_patchfunction inutils.pyto recombine the patches using naive method. For more information look into the help string of the functionIn practice this method works pretty well but still there may still be some boundary effects if receptive field of model is extremely small. Therefore, for more smooth predictions another ecombination method is provided.
-
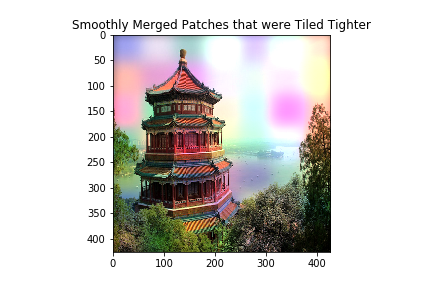
Smoothing-spline method
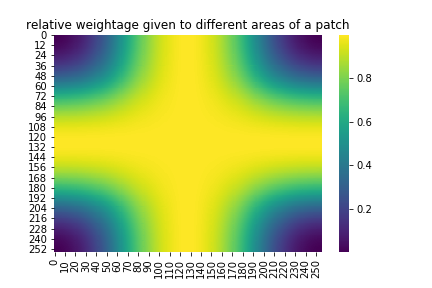
This method use smoothing splines interpolation and Dihedral group rotation averaging of patches to reduce variance in stitched image. It gives smoothly varying weightage to different areas in patches
For eg. if following test image
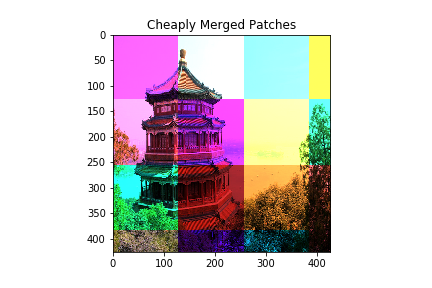
is broken into patches with some added noise then simply concatenating the patches together would result in following recombined image
but if combined through smoothing-spline method then the same combined image would look like this:
You can either see demo of this method by directly running
smooth_stitch.pyor can import window function in your code to directly predict on large input image
from smooth_stitch import predict_img_with_smooth_windowing
from your_code import your_model
# Instanciate a U-Net CNN (or any similarly-behaved neural network) in the variable named `model`. We use a Keras model but it can be anything:
model = your_model()
# CNN's receptive field's border size: size of patches
window_size = 160
# Amount of categories predicted per pixels.
nb_classes = 10
# Load an image. Convention is channel_last, such as having an input_img.shape of: (x, y, nb_channels), where nb_channels is of 3 for regular RGB images.
input_img = ...
# Use the algorithm. The `pred_func` is passed and will process all the image 8-fold by tiling small patches with overlap, called once with all those image as a batch outer dimension.
# Note that model.predict(...) accepts a 4D tensor of shape (batch, x, y, nb_channels), such as a Keras model.
predictions_smooth = predict_img_with_smooth_windowing(
input_img,
window_size=window_size,
subdivisions=2, # Minimal amount of overlap for windowing. Must be an even number.
nb_classes=nb_classes,
pred_func=(
lambda img_batch_subdiv: model.predict(image_to_neural_input(img_batch_subdiv))
)
)
# For more details, refer to comments and code in smooth_tiled_predictions.pyRBG segmentation mask to Multi channel one hot encoded mask
Often in Multi class segmentation target masks are provided as RGB mask in which one unique pixel value represents one class but for tarining of DL models one-hot encoded masks are required as per any DL framework api.
You can use function rgb_to_mask in utils.py for converting rgb mask to multi channel one hot encoded mask and mask_to_rgb for vice-versa
RGB segmentation mask to binary encoded mask
Sometimes, it is also required to train binary models on indivdual class in multi-class segmentation. In such a case binary segmentation masks are required for each class.
You can use function create_binary_mask in utils.py for this purpose
This repo is inspired by this work