This guide walks you through the process of building an application that uses Spring Data JPA to store and retrieve data in a relational database.
What You Will build
You will build an application that stores Customer POJOs (Plain Old Java Objects) in a memory-based database.
What You need
Starting with Spring Initializr
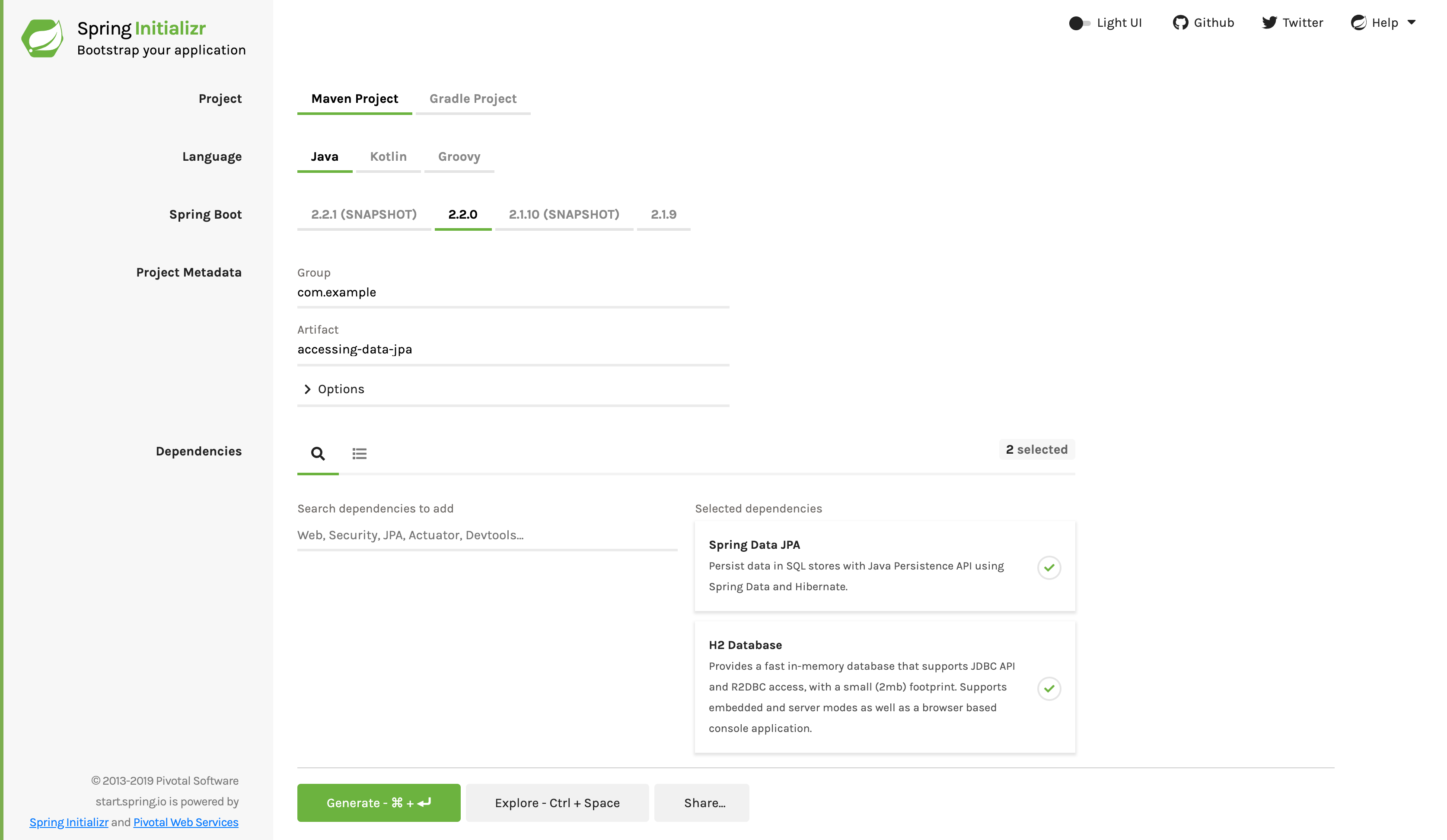
For all Spring applications, you should start with the Spring Initializr. The Initializr offers a fast way to pull in all the dependencies you need for an application and does a lot of the set up for you. This example needs the JPA and H2 dependencies. The following image shows the Initializr set up for this sample project:
|
Note
|
The preceding image shows the Initializr with Maven chosen as the build tool. You
can also use Gradle. It also shows values of com.example and accessing-data-jpa as the
Group and Artifact, respectively. You will use those values throughout the rest of this sample.
|
The following listing shows the pom.xml file created when you choose Maven:
link:complete/pom.xml[]
The following listing shows the build.gradle file created when you choose Gradle:
link:complete/build.gradle[]
Define a Simple Entity
In this example, you store Customer objects, each annotated as a JPA entity. The
following listing shows the Customer class (in
src/main/java/com/example/accessingdatajpa/Customer.java):
link:complete/src/main/java/com/example/accessingdatajpa/Customer.java[]Here you have a Customer class with three attributes: id, firstName, and lastName.
You also have two constructors. The default constructor exists only for the sake of JPA.
You do not use it directly, so it is designated as protected. The other constructor is
the one you use to create instances of Customer to be saved to the database.
The Customer class is annotated with @Entity, indicating that it is a JPA entity.
(Because no @Table annotation exists, it is assumed that this entity is mapped to a
table named Customer.)
The Customer object’s id property is annotated with @Id so that JPA recognizes it as
the object’s ID. The id property is also annotated with @GeneratedValue to indicate
that the ID should be generated automatically.
The other two properties, firstName and lastName, are left unannotated. It is assumed
that they are mapped to columns that share the same names as the properties themselves.
The convenient toString() method print outs the customer’s properties.
Create Simple Queries
Spring Data JPA focuses on using JPA to store data in a relational database. Its most compelling feature is the ability to create repository implementations automatically, at runtime, from a repository interface.
To see how this works, create a repository interface that works with Customer entities
as the following listing (in src/main/java/com/example/accessingdatajpa/CustomerRepository.java) shows:
link:complete/src/main/java/com/example/accessingdatajpa/CustomerRepository.java[]CustomerRepository extends the CrudRepository interface. The type of entity and ID
that it works with, Customer and Long, are specified in the generic parameters on
CrudRepository. By extending CrudRepository, CustomerRepository inherits several
methods for working with Customer persistence, including methods for saving, deleting,
and finding Customer entities.
Spring Data JPA also lets you define other query methods by declaring their method
signature. For example, CustomerRepository includes the findByLastName() method.
In a typical Java application, you might expect to write a class that implements
CustomerRepository. However, that is what makes Spring Data JPA so powerful: You need
not write an implementation of the repository interface. Spring Data JPA creates an
implementation when you run the application.
Now you can wire up this example and see what it looks like!
Create an Application Class
Spring Initializr creates a simple class for the application. The following listing shows
the class that Initializr created for this example (in
src/main/java/com/example/accessingdatajpa/AccessingDataJpaApplication.java):
link:initial/src/main/java/com/example/accessingdatajpa/AccessingDataJpaApplication.java[]Now you need to modify the simple class that the Initializr created for you. To get output
(to the console, in this example), you need to set up a logger. Then you need to set up
some data and use it to generate output. The following listing shows the finished
AccessingDataJpaApplication class (in
src/main/java/com/example/accessingdatajpa/AccessingDataJpaApplication.java):
link:complete/src/main/java/com/example/accessingdatajpa/AccessingDataJpaApplication.java[]Application includes a demo() method that puts the CustomerRepository through a few tests. First, it fetches the CustomerRepository from the Spring application context. Then it saves a handful of Customer objects, demonstrating the save() method and setting up some data to work with. Next, it calls findAll() to fetch all Customer objects from the database. Then it calls findOne() to fetch a single Customer by its ID. Finally, it calls findByLastName() to find all customers whose last name is "Bauer". The demo() method returns a CommandLineRunner bean that automatically runs the code when the application launches.
The AccessingDataJpaApplication class includes a main() method that puts the
CustomerRepository through a few tests. First, it fetches the CustomerRepository from
the Spring application context. Then it saves a handful of Customer objects,
demonstrating the save() method and setting up some data to use. Next, it calls
findAll() to fetch all Customer objects from the database. Then it calls findOne()
to fetch a single Customer by its ID. Finally, it calls findByLastName() to find all
customers whose last name is "Bauer".
|
Note
|
By default, Spring Boot enables JPA repository support and looks in the package (and
its subpackages) where @SpringBootApplication is located. If your configuration has
JPA repository interface definitions located in a package that is not visible, you can
point out alternate packages by using @EnableJpaRepositories and its type-safe
basePackageClasses=MyRepository.class parameter.
|
When you run your application, you should see output similar to the following:
== Customers found with findAll():
Customer[id=1, firstName='Jack', lastName='Bauer']
Customer[id=2, firstName='Chloe', lastName='O'Brian']
Customer[id=3, firstName='Kim', lastName='Bauer']
Customer[id=4, firstName='David', lastName='Palmer']
Customer[id=5, firstName='Michelle', lastName='Dessler']
== Customer found with findById(1L):
Customer[id=1, firstName='Jack', lastName='Bauer']
== Customer found with findByLastName('Bauer'):
Customer[id=1, firstName='Jack', lastName='Bauer']
Customer[id=3, firstName='Kim', lastName='Bauer']
Summary
Congratulations! You have written a simple application that uses Spring Data JPA to save objects to and fetch them from a database, all without writing a concrete repository implementation.
|
Note
|
If you want to expose JPA repositories with a hypermedia-based RESTful front end with little effort, you might want to read Accessing JPA Data with REST. |