- the description of the project task
- datasets overview
- description of methods
- the code structure
- how to run the code
- perspectives
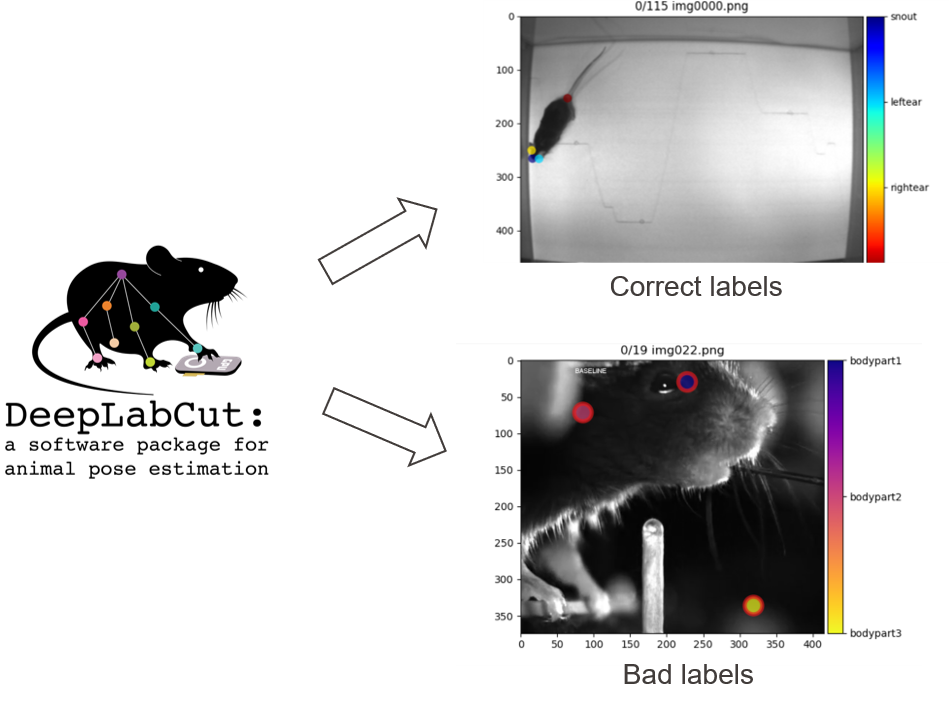
This project focuses on implementation of unsupervised Machine Learning methods for outlier detection to avoid mistakes when manually labeling data using deeplabcut GUI before the training process.
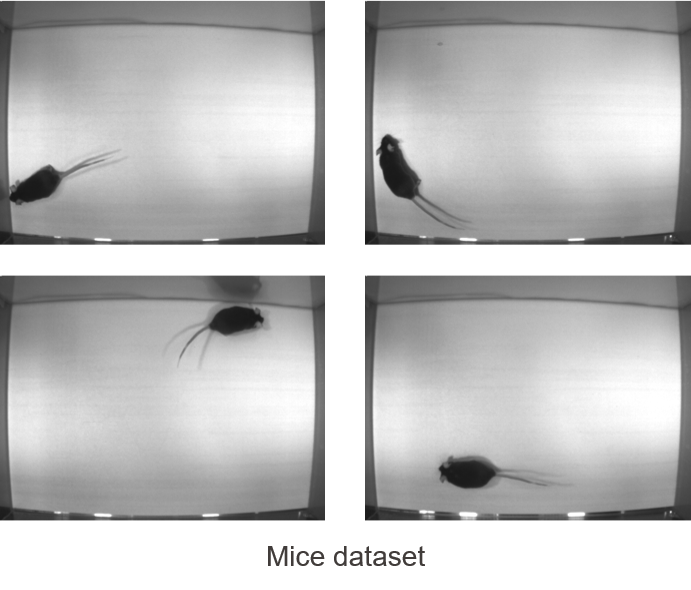
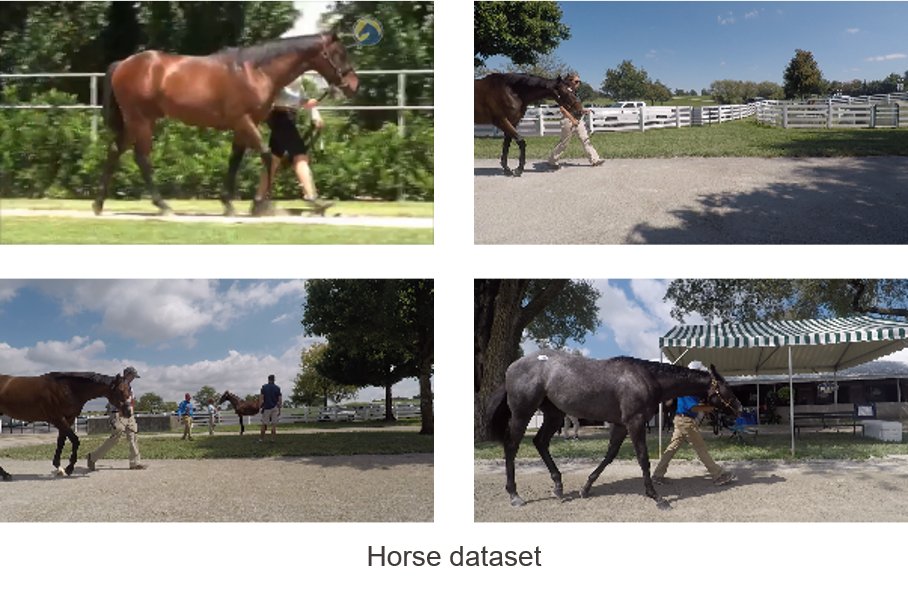
For this project we used the following datasets:
- Mice dataset: 1178 images
- Horse dataset: 3069 images
The main idea is to obtain the geometric features of labels on images, cluster labels using unsupervised Machine Learning methods, and identify images with bad labels.
You can see the general pipeline below:
- Data visualization.
- Computing features:
- the distance between every two body parts;
- angle and angle sign between three points (e. g. left ear, snout, right ear).
- PCA.
- Clustering.
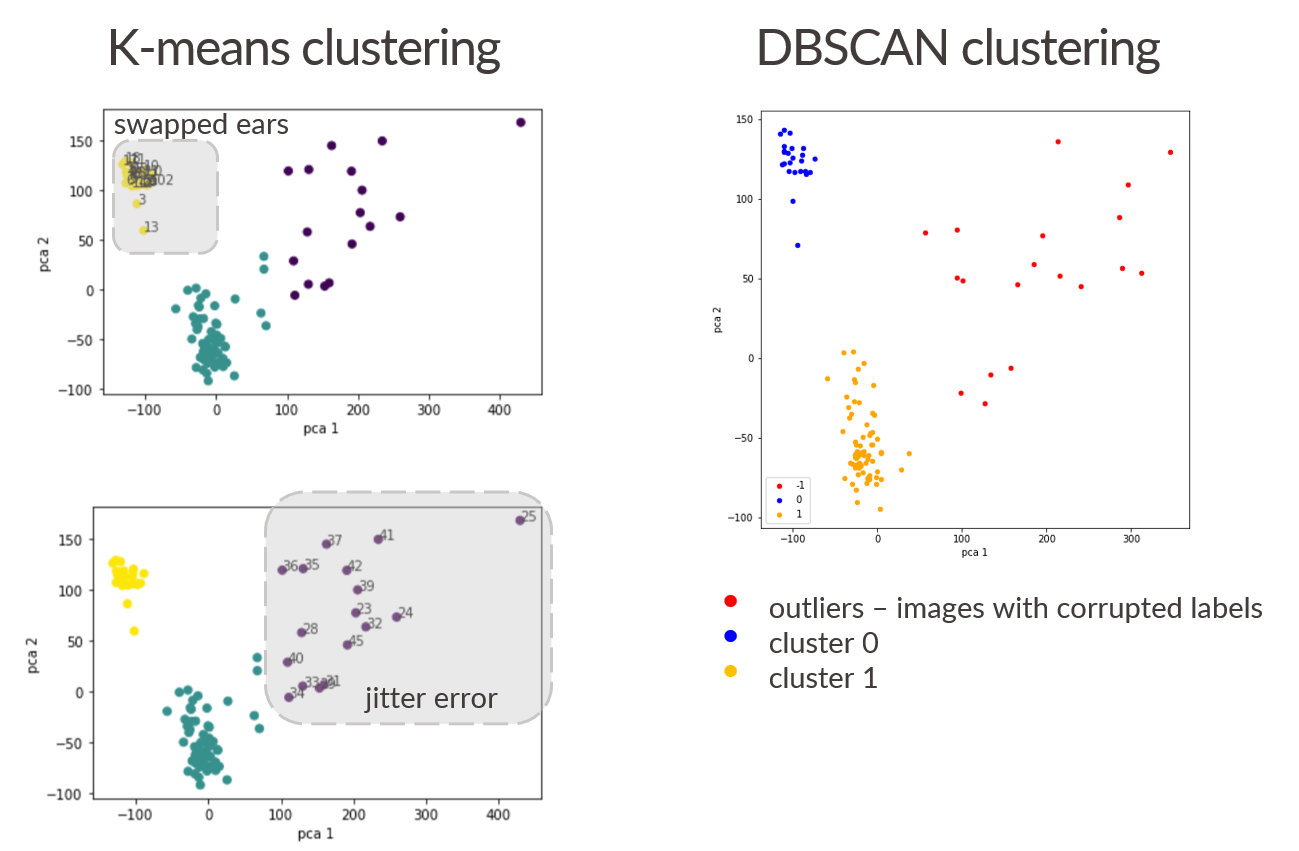
You can see the results of k-means and dbscan clustering method applied to mice dataset with 40% of corrupted images below:
The same clustering methods doesn't allow to indicate all corruted images for horse data. The main challenge of horse data is that images are very different:
- more body parts
- different quality of images
- sometimes only part of the horse is visible
To understand how the swap ears error affect the performance of the DLC algorithm we conducted the following experiment. Here we consider the mice dataset.
Firstly, we add swap ears error on image in the mice dataset in 6 different proportions: 0 (without corrupted images), 0.2 (20% of images have ears swap error), 0.4, 0.6, 0.8 and 1 (all images have ears swap error).
Then we train the network with the DLC algorithm and run 6 different experiments to see how many images with errors are identified.
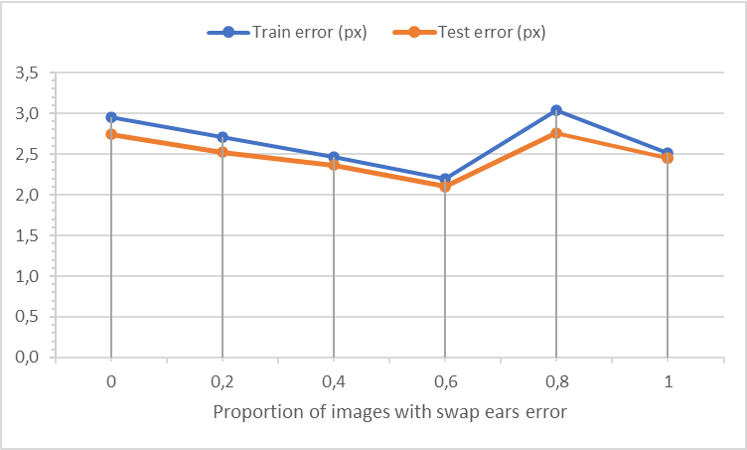
In the graph below, you can see the error of the DLC algorithm in pixels on train and test samples depending on the number of corrupted images.
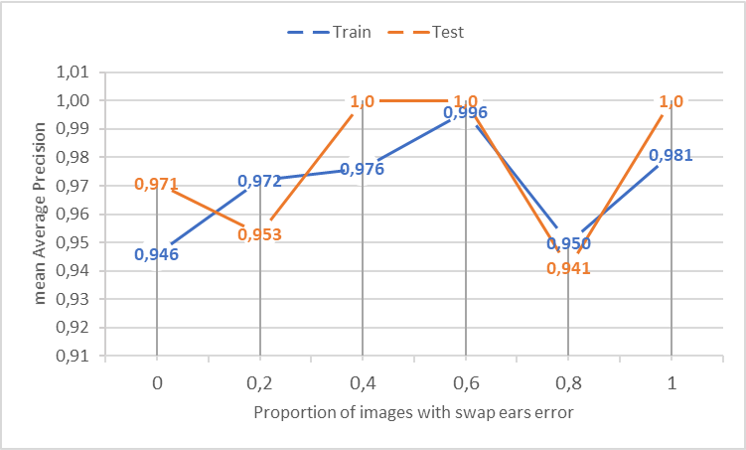
In the graph below, you can see the mean Average Precision of the DLC algorithm on train and test samples depending on the number of corrupted images.
As we can see from these graphs, the DLC algorithm makes the most mistakes on the test sample when 80% of the images contain a swap ears error. The expected training error graph is Gaussian function but the main limitation of used method is that we used dataset of 116 images where the test sample contains only 6 images. For a better understanding of the effect, more data should be used in the future experiments.
In the folder horse_dataset contains horse-10 data set.
In the folder scripts you can find two files:
clustering_and_LRtest_mice.ipynb- consisting the code for mice data setclustering_and_LRtest_horse.ipynb- consisting the code for horse-10 data set
Clone the repository to your preferred location using the following command:
git clone https://github.com/AnnaPaulish/Unsupervised_detection_methods.git
Then open the code using Jupyter notebook.
We can see that the geometric features for horse data not sufficient for solving the problem.
The horse data is much more complex than mice data because they have more body parts and different types of images, sometimes only part of the horse is visible.
If we want to detect bad labels in real-life images we need to consider other features or methods.
Future steps:
- Find impact of other errors on the performance of the DLC algorithm
- Explore already existing methods with visual transformers and apply them to our data set