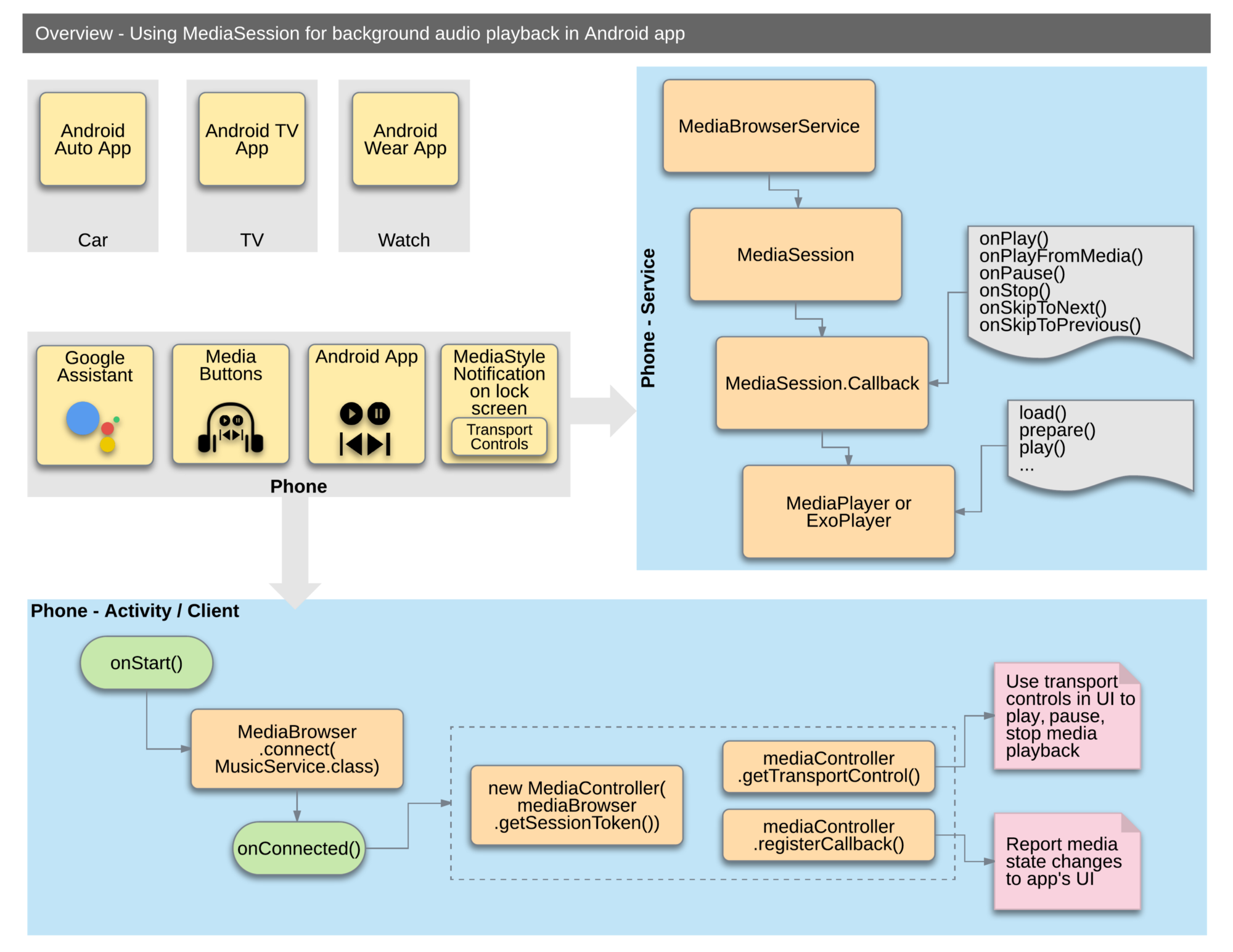
This sample shows how to implement a media app that allows background playback of audio, and provide a media library that is exposed to other apps.
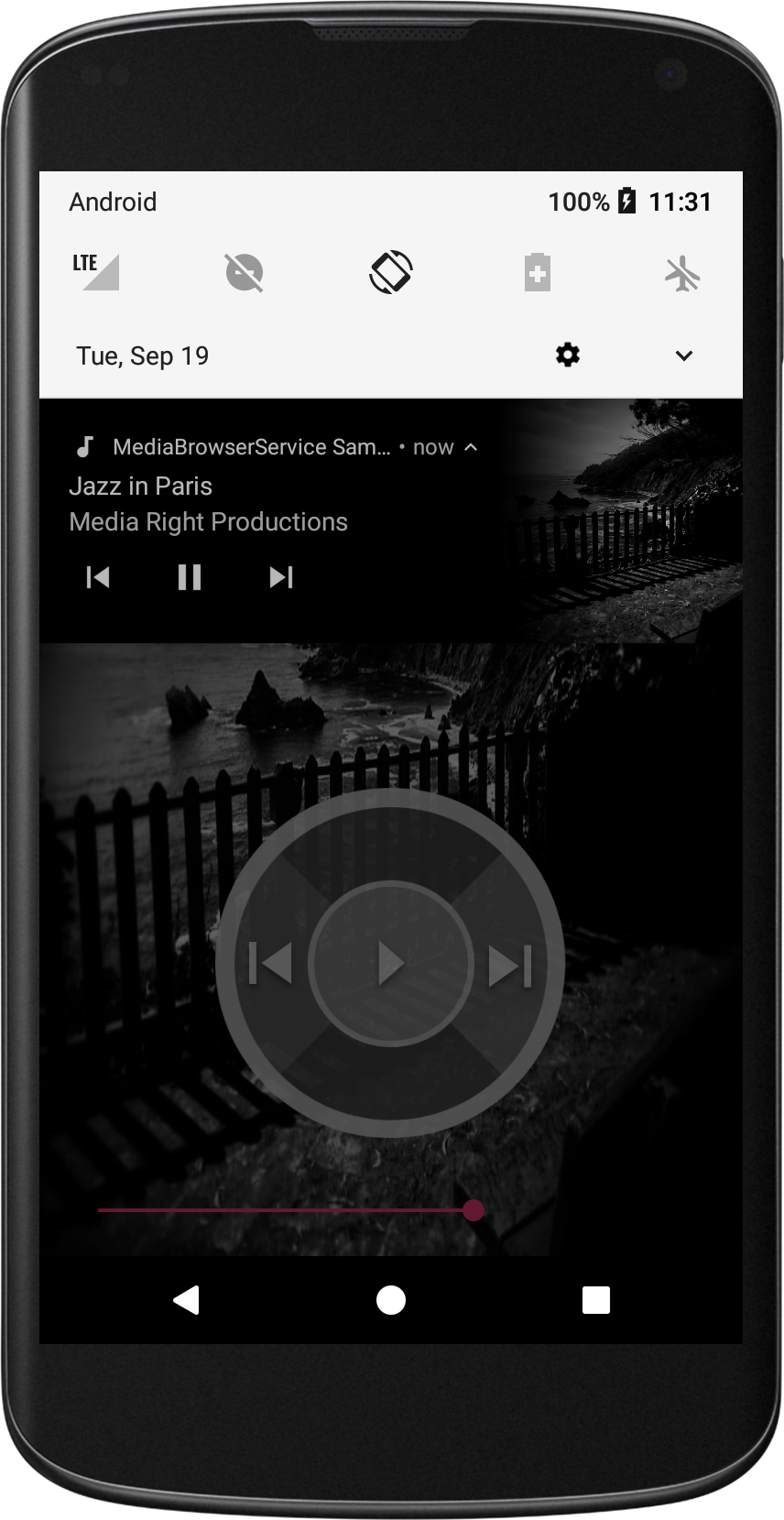
- It allows other apps control media playback externally using MediaSession. This allows playback to be controlled by the Google Assistant, for example.
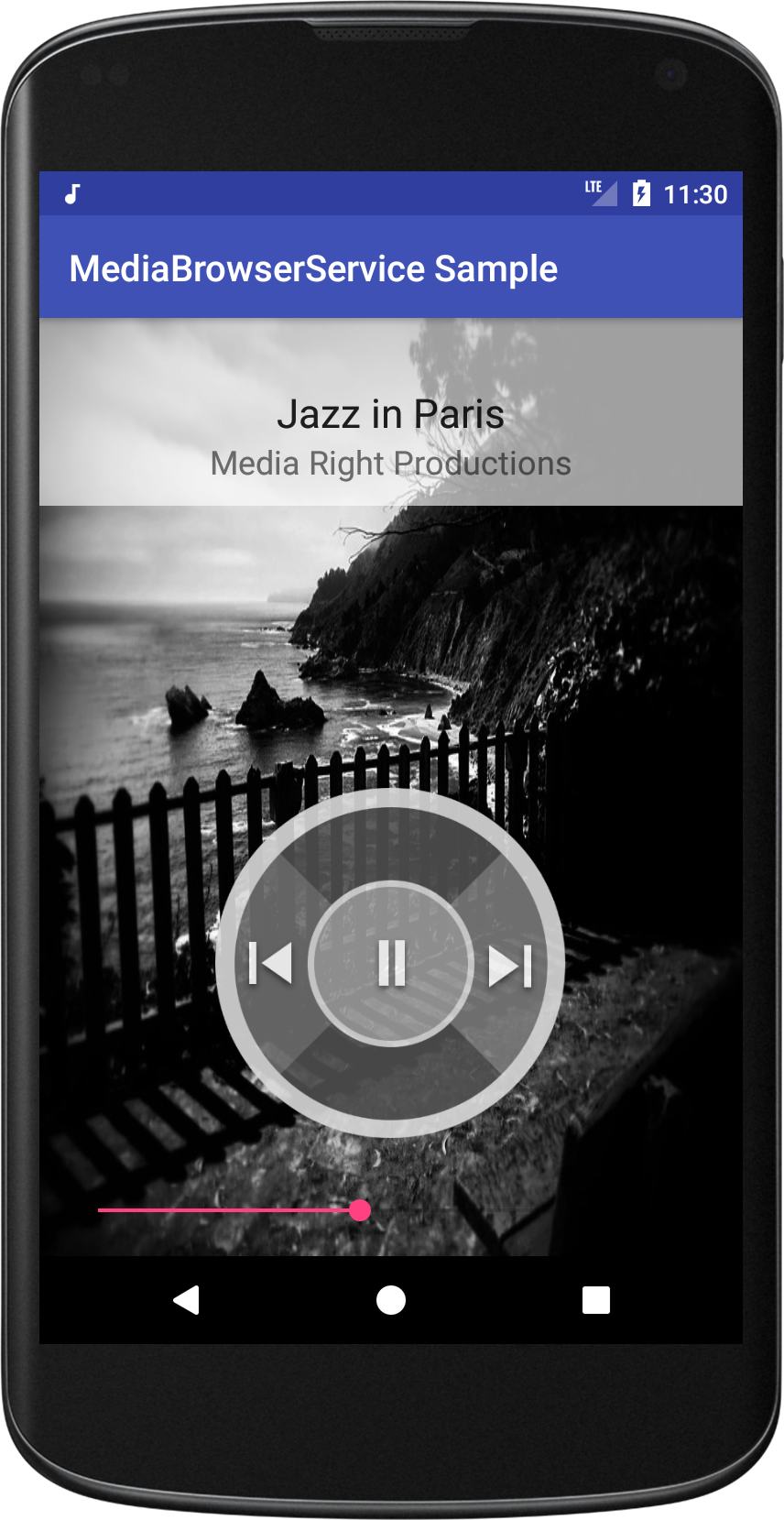
- It exposes a simple music library through MediaBrowserService. And it provides MediaSession callbacks. This allows it to be used by Android Auto, for example. When not connected to a car, the app has a very simple UI that allows for playback as well as skip to previous and next tracks. To learn more about MediaSession and MediaBrowserService, read this article on Medium that goes into the architectural details of these APIs.
To implement a MediaBrowserService, you need to:
-
Extend MediaBrowserServiceCompat, implementing the media browsing related methods onGetRoot and onLoadChildren;
-
In onCreate, start a new MediaSession and call super.setSessionToken() with this MediaSession's token;
-
Set a MediaSession.Callback class on the MediaSession. The callback class will receive all the user's actions, like play, pause, etc;
-
Handle all the actual music playing using any method your app prefers (for example, the Android MediaPlayer class)
-
Whenever it changes, update info about the playing item and the playing queue using MediaSession corresponding methods (setMetadata, setPlaybackState, setQueue, setQueueTitle, etc)
-
Handle AudioManager focus change events and react appropriately (e.g. pause when audio focus is lost)
To make it compatible with Android Auto, you also need to:
-
Declare a meta-data tag in AndroidManifest.xml linking to a xml resource with a automotiveApp root element. For a media app, this must include an <uses name="media"/> element as a child.
For example, in AndroidManifest.xml:
<meta-data android:name="com.google.android.gms.car.application"
android:resource="@xml/automotive_app_desc"/>
And in res/xml/automotive_app_desc.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<automotiveApp>
<uses name="media"/>
</automotiveApp>
- Declare and export the service in AndroidManifest.xml:
<service
android:name=".service.MusicService"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.media.browse.MediaBrowserService" />
</intent-filter>
</service>
- Android SDK 26
- Android Build Tools v26.0.1
- Android Support Repository
This sample uses the Gradle build system. To build this project, use the "gradlew build" command or use "Import Project" in Android Studio.
- Google+ Community: https://plus.google.com/communities/105153134372062985968
- Stack Overflow: http://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/android
If you've found an error in this sample, please file an issue: https://github.com/googlesamples/android-MediaBrowserService
Patches are encouraged, and may be submitted by forking this project and submitting a pull request through GitHub. Please see CONTRIBUTING.md for more details.
Copyright 2017 The Android Open Source Project, Inc.
Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.