catr is a command-line utility similar to the Unix cat command but with enhanced functionality. It allows users to
extract specific portions of text from a file by defining start and either end or length, offering extra flexibility and
precision in text extraction.
catr is licensed under GLWTS. For more information, please refer to the LICENSE file.
catr enhances the traditional Unix cat command, offering targeted text extraction capabilities. With catr, users
can effortlessly extract character or line ranges from a file.
- Character Count from a Character: Extract 10 characters starting from the 50th character from
file.txt:
catr file.txt 50 10- Character Range: Extract characters 50 to 100 from
file.txt:
catr file.txt -r 50 100- Line Range: Extract lines 10 to 20 from
file.txt:
catr file.txt -rl 10 20- Line Count from a Line: Extract 5 lines starting at line 3 from
file.txt:
catr file.txt -l 3 5Follow these steps to install the catr command-line tool on your system. This guide assumes you have gcc installed
and are using a Unix-like operating system.
While both catr and cat can display text from files, catr provides additional capabilities for more specific text
extraction without the need for combining multiple commands.
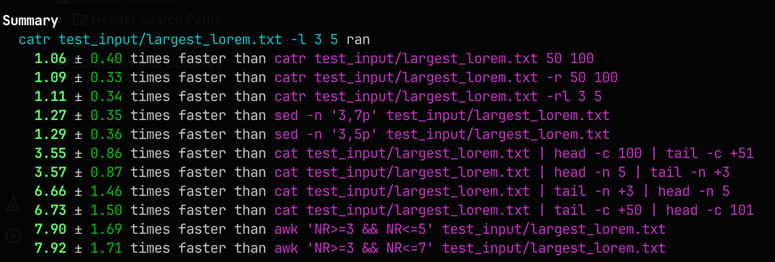
All the following examples are ran with hyperfine to measure the time it takes to run each command. The tests were run on a MacBook Pro M2 Pro chip, 16GB RAM, and macOS 14.3.1.
For more information on the tests, please refer to the hyperfine results.
Here is an overview of the results:
catr is more concise and easier to use for these tasks. And it also provides a more intuitive way to extract text
which could be useful for users who are not familiar with Unix commands and all the intricacies.
- Ensure you have
gccinstalled on your system to compile the source code. You can check this by runninggcc --versionin your terminal. - This script is designed to work with
zsh. If you are using a different shell, you might need to adjust the script or the instructions accordingly.
- Clone the repository or download the source code:
If you have
gitinstalled, you can clone the repository using the following command:
git clone https://github.com/Andree37/catr.gitAlternatively, download the source code to your local machine.
- Run the installation script:
Execute the installation script with the following command:
./install.shThis script will compile the catr program, create a directory at $HOME/bin (if it doesn't already exist), and place
the catr executable there. It will also ensure that the $HOME/bin directory is added to your PATH by updating
the .zshrc file.
If you encounter any permissions errors while running the script, you might need to grant execution permissions to the script:
chmod +x install.shand then rerun the script.
- Restart your terminal or source your profile:
For the changes to take effect, either restart your terminal or source your profile with the following command:
source ~/.zshrcIf you are using a different shell, source the corresponding configuration file for your shell.
- Verify the installation:
Once the installation is complete and your terminal is restarted (or your profile is sourced), you can verify the
installation of
catrby running:
catr --helpThis command should display the usage information for catr.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed catr on your system.