- Author : Langlois Quentin
- Promotor : Dupont Pierre
- Academic year : 2021-2022
- Overleaf link : link
The objective of this master thesis is to provide a new way to give question / contexts to limit the current constraints and allow to give more knowledge to the model.
├── custom_architectures/ : custom architectures
├── custom_layers/ : custom layers
├── custom_train_objects/ : custom objects for training
│ ├── callbacks/ : custom callbacks
│ ├── generators/ : custom data generators
│ ├── losses/ : custom losses
│ ├── optimizers/ : custom optimizers / lr schedulers
├── datasets/ : utilities for dataset loading / processing
│ ├── custom_datasets/ : where to save custom datasets processing
├── hparams/ : utility class to define modulable hyper-parameters
├── loggers/ : some logging utilities
├── models/ : main `BaseModel` subclasses directory
│ ├── classification/ : directory for `BaseClassifier` classes
│ ├── qa/ : main directory of Q&A models
├── pretrained_models/ : saving directory for pretrained models
├── unitest/ : custom unitest framework to test models' consistency
├── utils/ : utilities for data processing
├── experiments_mag.py : main file to run multiple experiments (build / train / test / pred)
├── main.py : main file to build or train or test or pred (single model)
├── Makefile / Dockerfile-maggie / docker-compose-maggie.yml : files to build / run bot container
└── maggie.py : code for the discord bot
See README.original for more information on the original project.
- Clone this repository :
git clone https://github.com/Ananas120/mag.git - Go to the root of this repository :
cd mag - Install requirements :
pip install -r requirements.txt - Open an example notebook and follow the instructions !
You must have docker and docker-compose installed and NVIDIA drivers (to allow Docker to use GPU)
- Clone this repository :
git clone https://github.com/Ananas120/mag.git - Go to the root of this repository :
cd mag - Build container :
make build - Run container :
make - Stop the bot :
make down(or CTRL + C aftermakeif you are in the container's console)
- Make the TO-DO list.
- Make the
READMEfile. - Add references and citations (done in the report).
- Make a
BERT-based span retriever model. - Make a
BART-based answer generator. - Make a
Retriever Augmented Generator (RAG)-style answer generator. - Write the final report
- Write the
introductionpart - Write the
backgroundpart - Write the
experimentspart - Write the
resultspart - Write the
conclusionpart - Send it to promotor and perform modifications proposed
- Write the
- Allow to give separately the answer and the context to the
Encoderpart and concat them before giving them to theDecoderpart. - Allow to subsample each part (encoded question / context) to a given factor.
- Allow to concat encoded question / context before the
Encoder's end. - Add
type embeddingto each different contexts given at once. - Add the possibility to add a context offset for the contexts'
positional encoding index - Add the
batch-merging mode for contexts (give multiple contexts during training). - Add the
document-mode for contexts (give an entirewikipediaparagraph at once). - Allow to split context and pass it as separated sentences
- Perform Google / Bing search to get best results
- Perform Q&A based on a google-search result
- Create a Discord bot
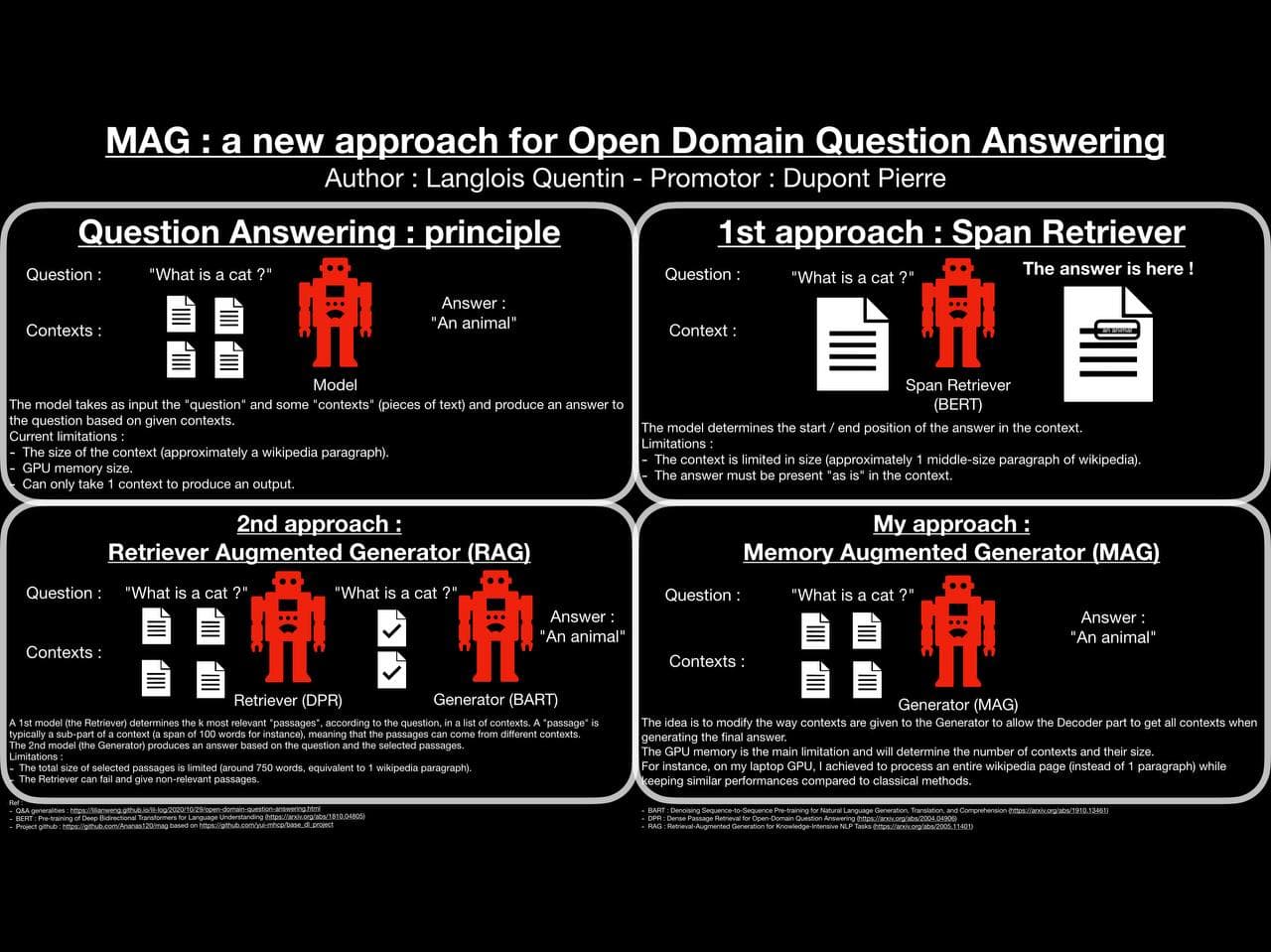
There exists multiple approaches of Q&A :
- Answer Span Retriever
- Multiple Choice Q&A
- Answer Generation :
- Open-book answer generation : the model has question and context containing the answer.
- Closed-book answer generation : only give question without context and the model has to keep knowledge in its parameters.
This master thesis will focus on the Open-book answer generation and try to improve its capabilities by giving more and more knowledge at once.
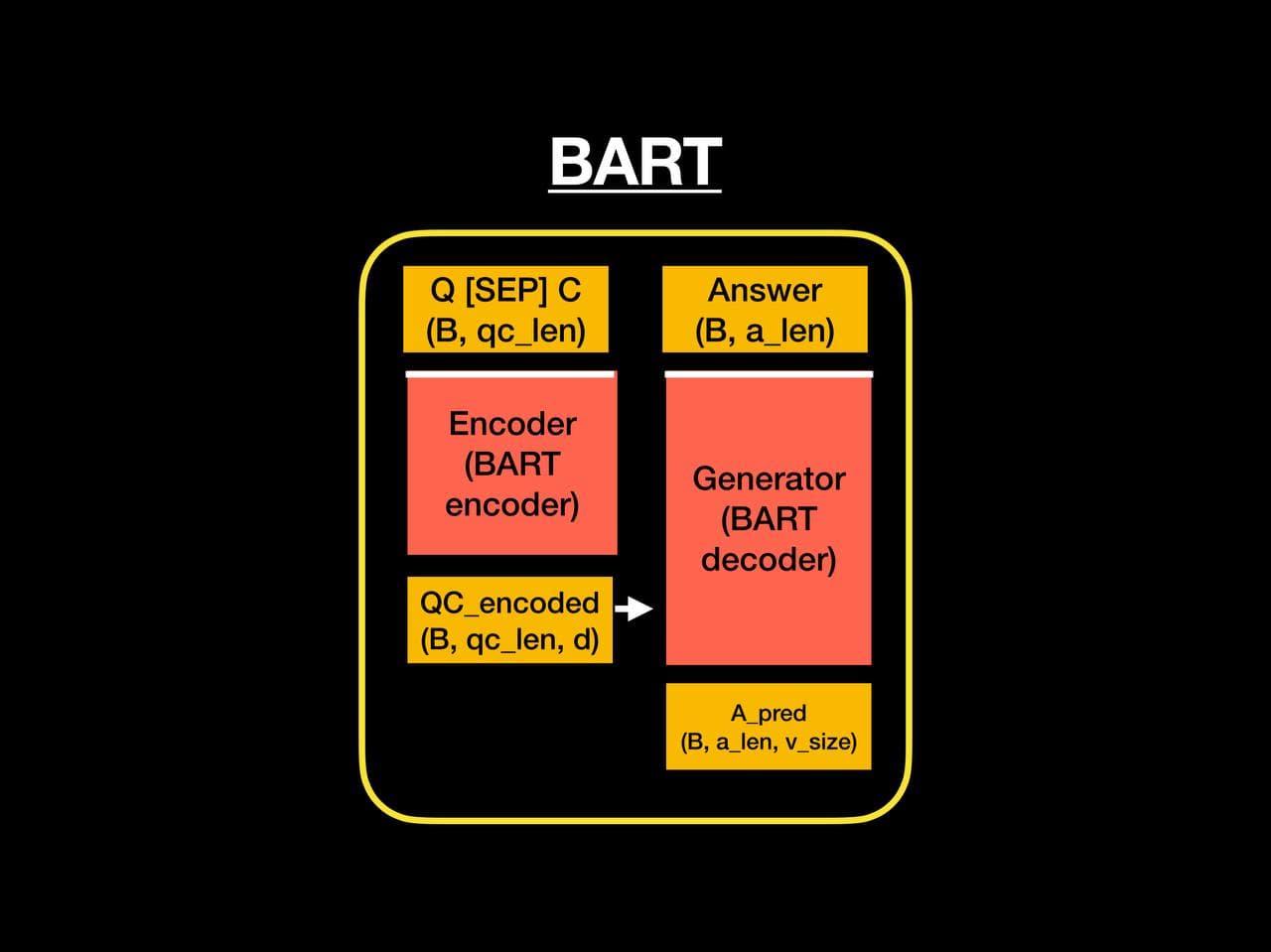
The MAG architecture is a classical BART architecture with some additional features to modify the way data are given to the model.
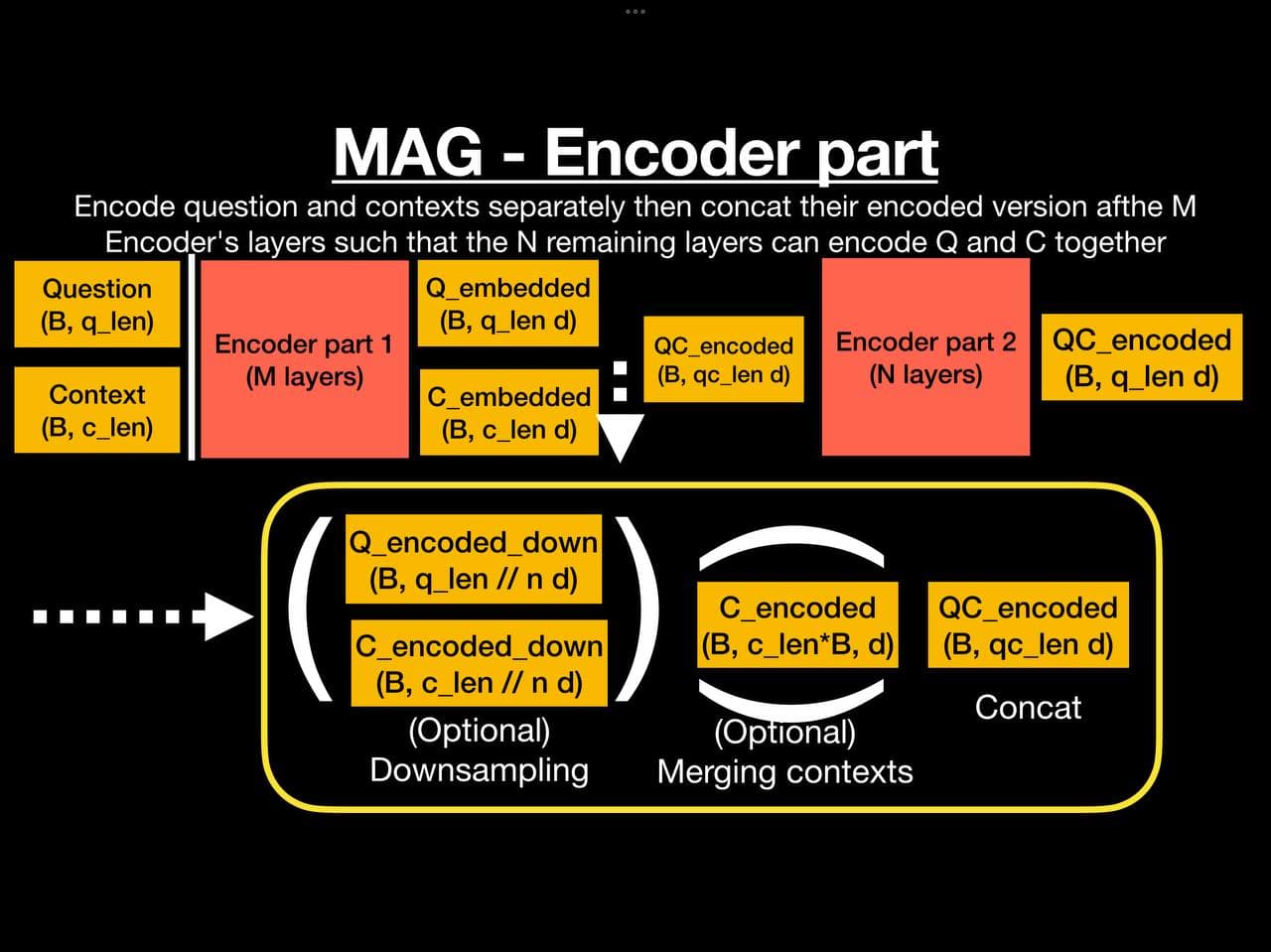
These layers are classical BART encoder's N first layers. They first embed the input (Embedding + positional encoding) then pass it though the N first layers.
Notation : n is the subsampling_step and d is the model's embedding size.
Once inputs have been encoded by the N first layers, I optionnally subsample them. Differents modes are supported :
select: simply keep vectors with a step of n (subsampled = encoded[:,::subsampling_step], where the 1st dimension isbatchand 2nd isseq_len)mean: keep the mean between the n consecutive embeddings such thate[i] = mean(e[i*n : i*n + n])dense: apply aDenselayer to a reshaped version such that theDenselayer takes as input the n tokens at once (sized * n) and produces a single vector of lengthd*
* the best initialization I found was to 1st train the model with a mean mode then initialize Dense's weights to perform the same mean-gehavior then train it.
Check the report for full analysis and results
Current parameters and their explaination :
question_format: the way to give questioncontext_format: the way to give context (for instance'{title}{sep_token}{context}'means to give the title and its context separated by a special token).max_{input/output}_length: maximum length of input / output *context_offset: the offset of contexts' positional encoding **subsample_question: whether to subsample the question or not (before the concatenation).encoder_repeat_pos_idx: whether to repeat subsampled indexes' positional index (for instance ifsubsample_step = 3, the 3 first tokens will have index 0 and the 3 next ones will have index 1 etc).encoder_subsample_at: the number of layers at which to concatenate all encoded question / contexts.encoder_subsample_after: whether to concat before / after the ithEncoderlayer (allow to concat before the 1st layer or after the last one).encoder_subsampling_step: the subsampling factor.encoder_subsampling_offset: how many tokens to skip before subsampling.encoder_subsampling_mode: the way to subsampleencoder_use_type_embedding: whether to addEmbeddingto contexts or not.encoder_max_types: the maximum number of contexts we can give at once.
* Important : in classical models, the max input length is the maximum length of question and context concatenated while in MAG it is the maximum length for each part individually (the total length can be much larger !).
** In classical model, question and context are given together so the context's start position is equal to the length of the question + 1. In MAG, they are given separately so, in theory, start position of both should be 0 but it can produce confusion to the model while this offset allow to remove positional overlap between question and context.
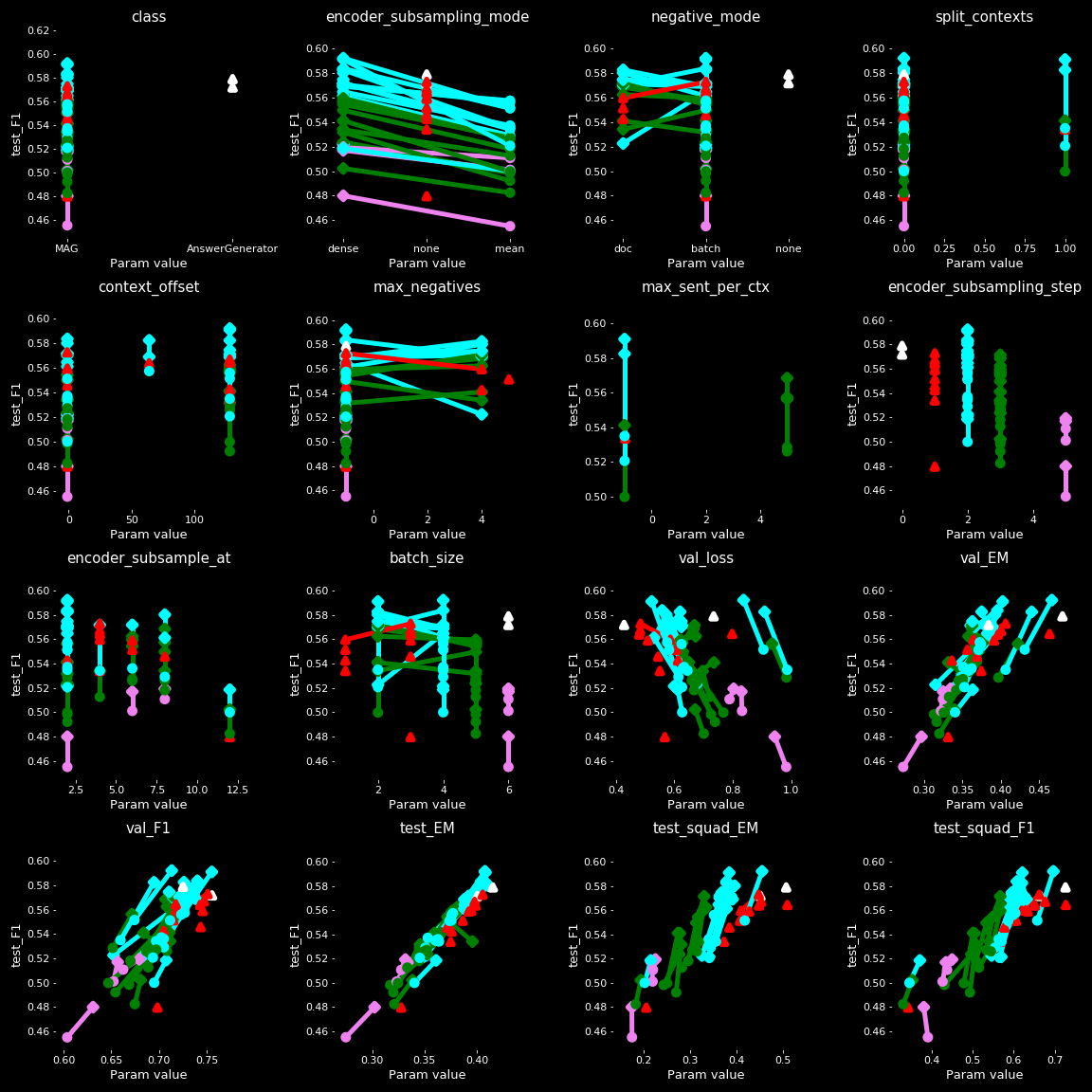
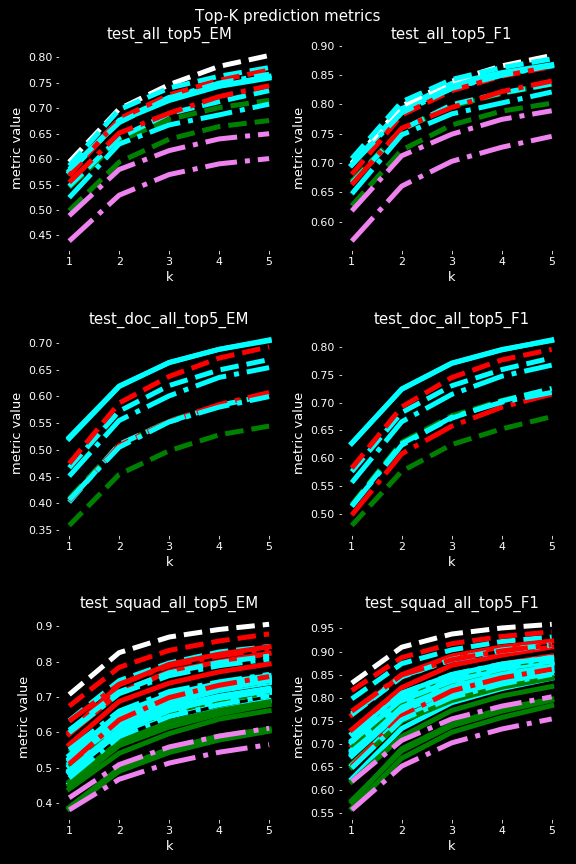
Each point represent a trained model, each subplot represents a parameter where x-axis is the parameter's value and y-axis is the val_loss of the model.
Each model has been trained and validated on NaturalQuestions and tested on SQUAD1.0 dev-set (test_squad_...) and on NaturalQuestions (test_...)
Note that some parameters are not relevant as dependant of other parameters (shuffle_size = 32 * batch_size) while some others are memory-dependant (batch_size)
Check the report for the legend
Important note on validation / testing : models have been evaluated the same way they have been trained, meaning that a batch-merging model has been validated with batch_size * 2 paragraphs and a doc-based model has been validated with max_negatives + 1 paragraphs (from the same wikipedia page). This is not the case during testing where all models have been tested with 1 paragraph (the relevant one) to have comparable results.
- Baseline, the classical approach :
In below graphes, the classical model is represented by the single green dot : the AnswerGenerator class which takes as input {question}{sep_token}{context} (Q and C separated by a token).
Its loss is much better than other (0.4 while others are between 0.53 and 0.65) but its Exact Match (EM) and F1 are comparable and even a bit lower than some MAG models ! Proving that my approach can give comparable / slighly better results while giving much more data to the model.
- Subsampling step impact :
The batch_size shows the impact of subsampling_step on memory usage : the higher the step is, the higher the batch_size can be.
The batch merge mode merges all paragraphes from a single batch to give them to the decoder. It means that the model does not get a question with its associated relevant paragraph (like in classical methods) but get the question with its corresponding paragraph and batch_size -1 other non-relevant paragraphs ! It is the reason why the subsampling_step has a big impact on memory usage.
The subsampling_step therefore allows to give much more data to the model (instead of 3 * 512, it allows 4 or 5 * 512 tokens at once at training time, during validation it is twice more) ! *
It is interesting to see that even by subsampling tokens, results do not decrease dramatically and are still comparable even with a subsampling of 3 (white points) ! It can be observed in test_F1 where white dots (subsample = 3) have even better results than blue dots (no subsampling) and comparable to red points (subsample = 2).
* The 512 is an arbitrary choice, in theory BART can handle 1024 tokens maximum but in practice, the wide majority of paragraphs is smaller than 512 and it is more convenient for the GPU memory I have access to (16Go).
- Subsampling mode impact :
We can observe that the dense mode always perform better results than its associated mean model. It is normal as the dense mode is a fine-tuned version of the mean model. However, this mechanism of fine-tuning with a mean-based initialization is required to achieve good results : if not, results are really poor (loss > 3).
- N and M impact (subsample at) :
I should make more tests to have a better view of this parameter's impact to better observe its impact on extreme values (0 and 12).
You can contact me via my student mail : quentin.langlois@student.uclouvain.be
You can contact me at yui-mhcp@tutanota.com or on discord at yui#0732
The objective of these projects is to facilitate the development and deployment of useful application using Deep Learning for solving real-world problems and helping people. For this purpose, all the code is under the Affero GPL (AGPL) v3 licence
Furthermore, you cannot use any of these projects for commercial purpose without my permission. You can use, modify, distribute and use any of my projects for production as long as you respect the terms of the licence and use it for non-commercial purposes (i.e. free applications / research).
If you use this project in your work, please cite this project to give it more visibility ! 😄
@misc{yui-mhcp
author = {yui},
title = {A Deep Learning projects centralization},
year = {2021},
publisher = {GitHub},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/yui-mhcp}}
}
TO-DO