- 洪熠佳 520021910598
- 罗皓天 520030910325
- 蒋林希 520030910328
- 三人共同完成代码及报告
- user
| user_id | password | balance | token | terminal |
|---|
- store:
| store_id | stock_level |
|---|
- book:
| _id | id | title | author | publisher | originate_title | translator | pub_year | pages | price | currency_unit | binding | isbn | author_intro | book_intro | book_intro | content | tags | picture |
|---|
- user_store:
| user_id | store_id |
|---|
- new_order:
| order_id | user_id | store_id |
|---|
- new_order_detail:
| order_id | book_id | count | price |
|---|
Use pymongo to implement the backend logic (Only show the Important Parts)
-
user.py
-
register
Add a new info of user into the database "user"
new_user = { "user_id" : user_id, "password" : password, "balance" : 0, "token" : token, "terminal" : terminal } self.db['user'].insert_one(new_user)
-
check_password
Find the password of the user in the database and check whether it matches
result = self.db['user'].find_one({'user_id': user_id}, {'password':1})
-
login
Invoke check_password to check the user's password and update the token in the database to store the timestamp of the time when the user login
result = self.db['user'].update_one({'user_id': user_id}, {'$set': {'token': token, 'terminal': terminal}})
-
logout
Update the token in the database (dummy_token)
If the duration has been more than 3,600 s, the user will logout automatically
result = self.db['user'].update_one({'user_id': user_id}, {'$set': {'token': dummy_token, 'terminal': terminal}})
-
unregister
Delete the infomation of the user from the database
result = self.db['user'].delete_one({'user_id': user_id})
-
change_password
Fisrt, invoke check_password to check the user's password and then updata the new password in the database
result = self.db['user'].update_one({'user_id': user_id}, {'$set': {'password': new_password, 'token': token, 'terminal': terminal}})
-
-
buyer.py
-
new_order
Fisrt, check the whether the bookstore and the book exist
Then, check the stock_level of the book
Update the new stock_level and create a new order in the database
order = { "order_id" : uid, "store_id" : store_id, "user_id" : user_id, "status" : 0, "create_time" : datetime.datetime.now() } self.db['new_order'].insert_one(order)
-
payment
First, cheak the user's password and the order id
Then check the balance of the user
If the balance is enough, then update the status of order to paid and the new balance of the user in the database.
// some code bookresult = self.db['store'].update_one({'store_id': store_id, 'book_id': book_id}, {'$inc': {'stock_level': count}}) // some code result = self.db['user'].update_one({'user_id': buyer_id, 'balance': {'$gte': total_price}}, {'$inc': {'balance': -total_price}}) if result.modified_count == 0: return error.error_not_sufficient_funds(order_id) result = self.db['user'].update_one({'user_id': seller_id}, {'$inc': {'balance': total_price}}) if result.modified_count == 0: return error.error_non_exist_user_id(seller_id) result = self.db['new_order'].update_one({'order_id': order_id}, {'$set': {'status': 1}}) if result.modified_count == 0: return error.error_invalid_order_id(order_id)
-
add_funds
First, cheak the password of the user. Then update the balance.
order = { "order_id" : uid, "store_id" : store_id, "user_id" : user_id, "status" : 0, "create_time" : datetime.datetime.now() } self.db['new_order'].insert_one(order)
-
-
seller.py
-
add_book
Check the store_id and book_id and update the info of book in the database
new_book = { "store_id" : store_id, "book_id" : book_id, "book_info": book_json_str, "stock_level": stock_level } result = self.db['store'].insert_one(new_book)
-
add_stock_level
Check the store_id and book_id and update the stock_level of book in the database
self.db['store'].update_one({'store_id': store_id, 'book_id': book_id}, {'$inc': {'stock_level': add_stock_level}})
-
create_store
Check the store_id and add a new info of store in the database.
new_store = { "store_id" : store_id, "user_id" : user_id } self.db['user_store'].insert_one(new_store)
-
-
store.py
-
init_tables_mongo
Init the database (create the index)
def init_tables_mongo(self): try: user_col = self.db['user'] user_col.create_index([("user_id", 1)], unique=True) user_store_col = self.db['user_store'] user_store_col.create_index([("user_id", 1), ("store_id", 1)], unique=True) store_col = self.db['store'] store_col.create_index([("store_id", 1), ("book_id", 1)], unique=True) store_col.create_index([("book_id", 1)]) new_order_col = self.db['new_order'] new_order_col.create_index([("order_id", 1)], unique=True) new_order_detail_col = self.db['new_order_detail'] new_order_detail_col.create_index([("order_id", 1), ("book_id", 1)], unique=True) except pymongo.errors.PyMongoError as e: logging.error(e)
-
-
db_coon.py
Some utils to check whether the _id exists
- user_id_exist && book_id_exist && store_id_exist
def user_id_exist(self, user_id): result = self.db['user'].find_one({'user_id': user_id}) if result is None: return False else: return True def book_id_exist(self, store_id, book_id): result = self.db['store'].find_one({'store_id': store_id, 'book_id': book_id}) if result is None: return False else: return True def store_id_exist(self, store_id): result = self.db['user_store'].find_one({'store_id': store_id}) if result is None: return False else: return True
- user_id_exist && book_id_exist && store_id_exist
- buyer.py
-
send_out_delivery
First check the order_id and user_id
Then update the status of the order (status = 2)
result = self.db['new_order'].update_one({'order_id': order_id}, {'$set': {'status': 2}}) if result.matched_count == 0: return error.error_invalid_order_id(order_id)
-
take_delivery
First check the order_id and user_id
Then update the status of the order (status = 3)
result = self.db['new_order'].update_one({'order_id': order_id}, {'$set': {'status': 3}}) if result.matched_count == 0: return error.error_invalid_order_id(order_id)
-
-
fe/access/book.py
Create text index for search
self.bookCollection = DBConn().db['book'] self.bookCollection.create_index( [("$**", TEXT)] ) self.bookCollection.create_index([("id", 1)], unique=True)
-
user.py
-
search_for_book
def search_for_book(self, user_id:str, target: str ,store_id: str = '-1') -> (int, str, list)
If the value of store_id is 1, we search in all stores.
If the results of search is too large, we will return only 10 results once
result = self.db['book'].find({'$text':{'$search': target}},{'score':{'$meta':'textScore'},'id':1}).sort('score',pymongo.DESCENDING).skip(int(10*i)).limit(10)
-
- buyer.py
-
order_cancel
Cancle the order and update the information accroding to the status of order(paid or not paid)
-
order cancel automatically
-
be/server.py
Check the order every 15 seconds (a short time to test easily)
scheduler = APScheduler() scheduler.add_job('regular_inspection', regular_inspection, trigger='interval', seconds=15) scheduler.start()
-
be/times.py A function to check the status of orders. If the order is not paid, then cancel the order automatically
def regular_inspection(): b = Buyer() result = b.db['new_order'].find({'status': 0}, {'order_id':1, 'store_id':1, 'create_time':1}) for row in result: order_id = row['order_id'] duration = (datetime.datetime.now() - row['create_time']).total_seconds() if duration > b.duration_limit: store_id = row['store_id'] booklist = b.db['new_order_detail'].find({'order_id': order_id}, {'book_id':1, 'count':1}) for row in booklist: book_id = row['book_id'] count = row['count'] b.db['store'].update_one({'store_id': store_id, 'book_id': book_id}, {'$inc': {'stock_level': count}}) b.db['new_order'].update_one({'order_id': order_id}, {'$set': {'status': 4}})
Check the duration: if the time is longer than the pre-defined value and the order is not paid, then cancel the order.
duration = (datetime.datetime.now() - order['create_time']).total_seconds() for row in booklist: book_id = row['book_id'] count = row['count'] if order['status'] <= 1 and duration > self.duration_limit: bookresult = self.db['store'].update_one({'store_id': store_id, 'book_id': book_id}, {'$inc': {'stock_level': count}}) if bookresult.matched_count == 0: return 536, "invalid store_id and book_id", "" order_details.append(row)
-
-
order_query
Search all order and show their status.
-
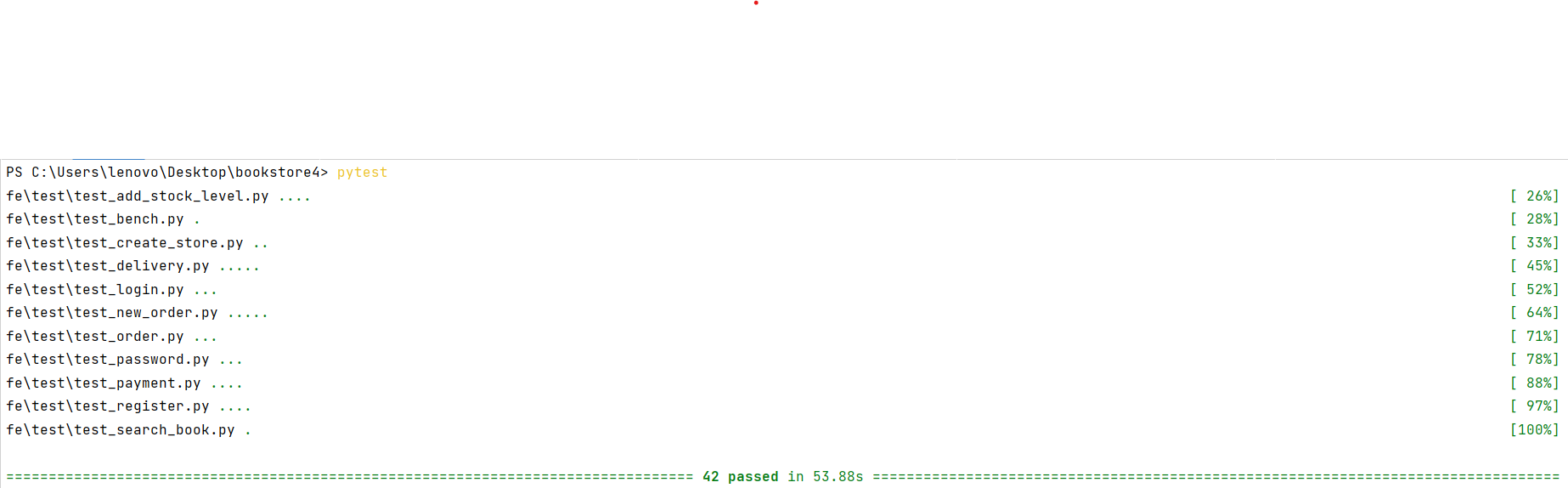
All 42 pass (contains our own tests) in 53.88s (contains 15s sleep for our own test)
For the additional function, we write three more test.py:
-
test_delivery.py
First, create an order and test the delivery and take delivery.
We test some unallowed behaviors
- deliver before payment
- take delivery before deliver
- repeat deliver
- repeat take delivery
-
test_search_book.py
First, we create two book stores and add some books(a part of these books are same)
We test the function search in one certain store and all stores.
-
test_order.py
First, we create some orders.
We test the delivery and take delivery. (For testing some unallowed behaviors)
We test some unallowed behaviors
- deliver before payment
- auto cancel
- deliver after cancel
We test auto cancel by sleep 15s (a short time to test easily)
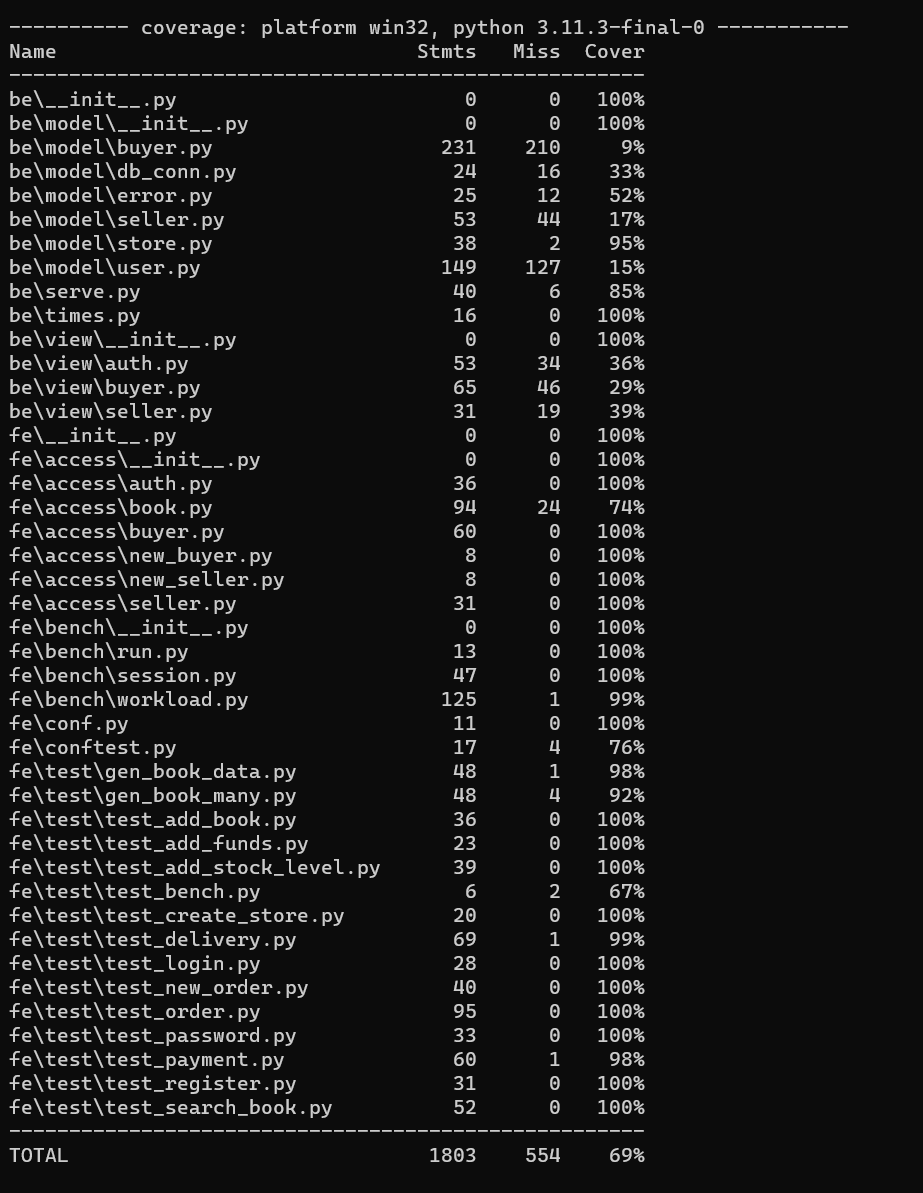
All our test programs have cover all the error number which we write. We also test some unallowed behaviors to ensure. So we believe our code coverage is high.
We use coverage to test
Our total coverage is 69%
In function search_for_book(), we use text index and control search results with weights
Text search assigns a score to each document that contains the search term in the indexed fields. The score determines the relevance of a document to a given search query.
For a text index, the weight of an indexed field denotes the significance of the field relative to the other indexed fields in terms of the text search score.
For each indexed field in the document, MongoDB multiplies the number of matches by the weight and sums the results. Using this sum, MongoDB then calculates the score for the document.
self.bookCollection = DBConn().db['book']
self.bookCollection.create_index(
[("$**", TEXT)]
,
weights={
'title': 10,
'author': 5,
'publisher': 5,
'original_title': 10,
'translator': 5,
'tags': 3
}
)We find that there do not exist some access control between the owner of the store and the buyers.
Owing to the lack of access control, any user who knows the store_id can modify the info of books, so we add access control in the backend.
def is_my_store(self, user_id, store_id):
result = self.db['user_store'].find_one({'user_id': user_id, 'store_id': store_id})
if result is None:
return False
else:
return TrueAnd we will invoke this function to check access.
https://github.com/AegeanYan/DB_PJ1
Git and GitHub is used to manage the code version