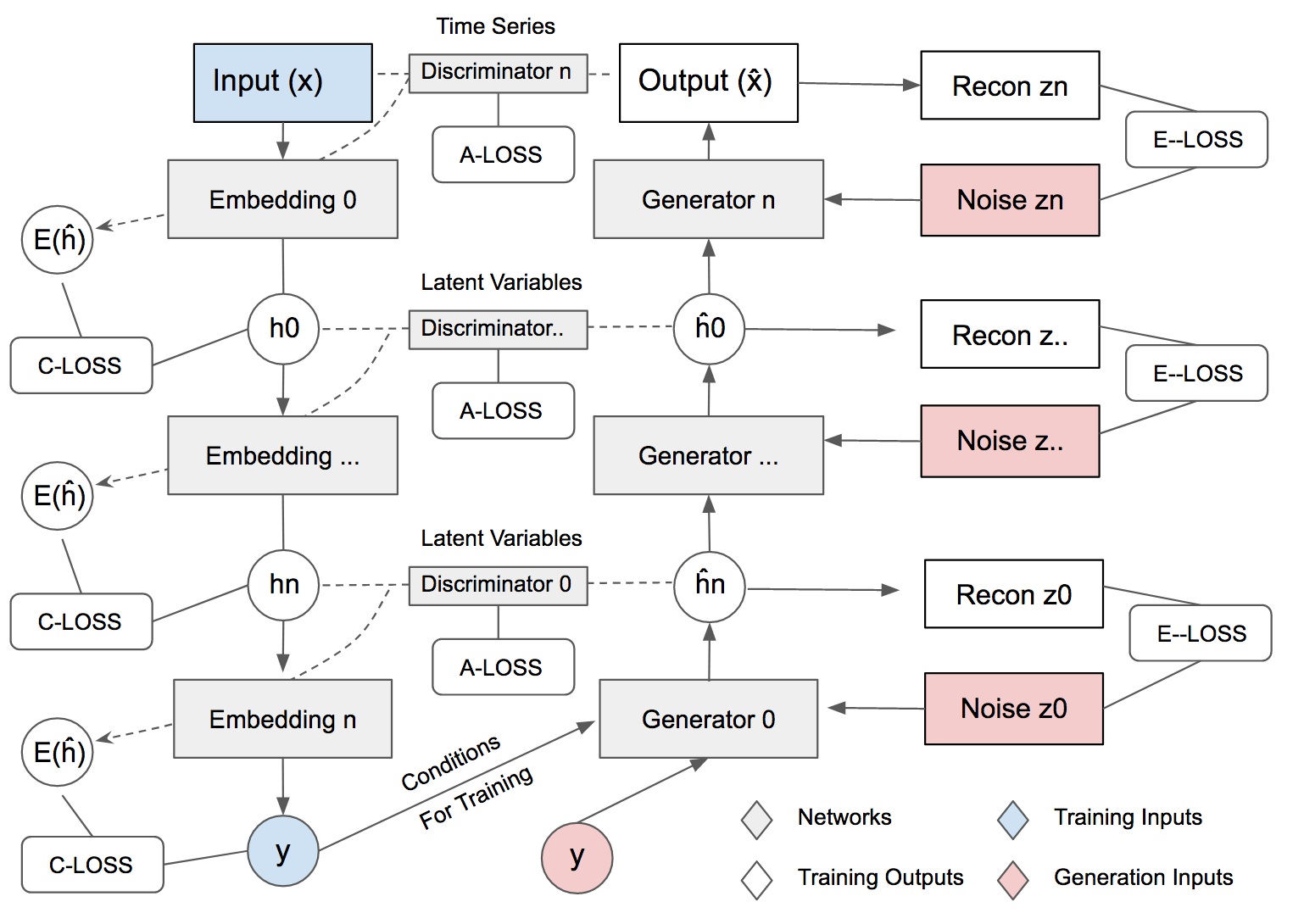
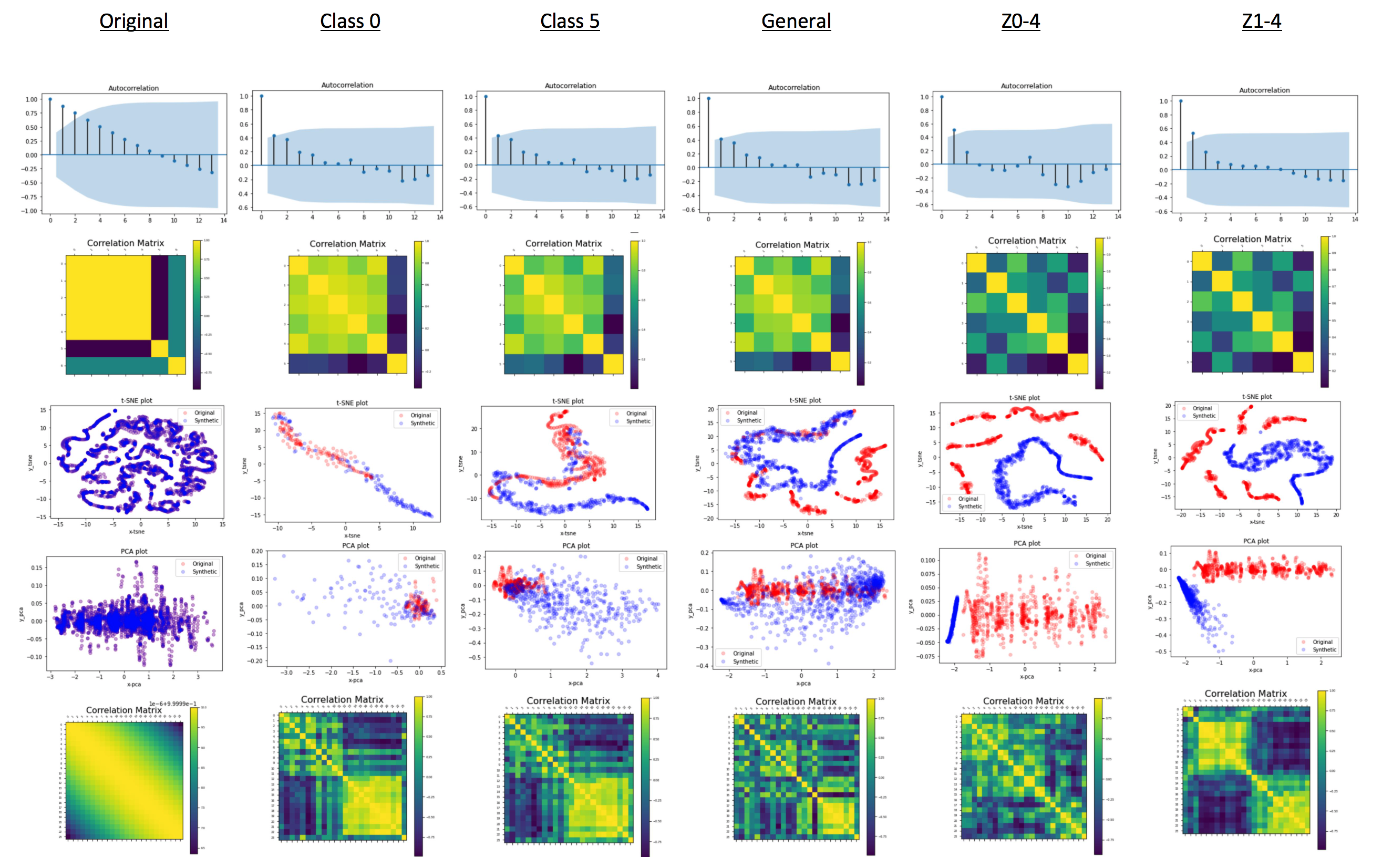
MTSS-GAN: Multivariate Time Series Simulation Generative Adversarial Networks
The model has been developed on a colaboratory notebook. Here I have added a few code snippets, if there is demand, I can build a package, please let me know in the issues tab. For some additional information, feel free to consult the paper.
Generator:
def generator(inputs,
activation='sigmoid',
labels=None,
codes=None):
"""
if codes is not None:
# generator 0 of MTSS
inputs = [inputs, codes]
x = concatenate(inputs, axis=1)
# noise inputs + conditional codes
else:
# default input is just a noise dimension (z-code)
x = inputs ##
x = Dense(SHAPE[0]*SHAPE[1])(x)
x = Reshape((SHAPE[0], SHAPE[1]))(x)
x = GRU(72, return_sequences=False, return_state=False,unroll=True)(x)
x = Reshape((int(SHAPE[0]/2), 6))(x)
x = Conv1D(128, 4, 1, "same")(x)
x = BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8)(x) # adjusting and scaling the activations
x = ReLU()(x)
x = UpSampling1D()(x)
x = Conv1D(6, 4, 1, "same")(x)
x = BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8)(x)
if activation is not None:
x = Activation(activation)(x)
# generator output is the synthesized data x
return Model(inputs, x, name='gen1')Discriminator
def discriminator(inputs,
activation='sigmoid',
num_labels=None,
num_codes=None):
ints = int(SHAPE[0]/2)
x = inputs
x = GRU(SHAPE[1]*SHAPE[0] , return_sequences=False, return_state=False,unroll=True, activation="relu")(x)
x = Reshape((ints, ints))(x)
x = Conv1D(16, 3,2, "same")(x)
x = LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(x)
x = Conv1D(32, 3, 2, "same")(x)
x = LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(x)
x = Conv1D(64, 3, 2, "same")(x)
x = LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(x)
x = Conv1D(128, 3, 1, "same")(x)
x = LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(x)
x = Flatten()(x)
# default output is probability that the time series array is real
outputs = Dense(1)(x)
if num_codes is not None:
# MTSS-GAN Q0 output
# z0_recon is reconstruction of z0 normal distribution
# eventually two loss functions from this output.
z0_recon = Dense(num_codes)(x)
z0_recon = Activation('tanh', name='z0')(z0_recon)
outputs = [outputs, z0_recon]
return Model(inputs, outputs, name='discriminator')Encoder
def build_encoder(inputs, num_labels=6, feature0_dim=6*24):
x, feature0 = inputs
y = GRU(SHAPE[0]*SHAPE[1], return_sequences=False, return_state=False,unroll=True)(x)
y = Flatten()(y)
feature0_output = Dense(feature0_dim, activation='relu')(y)
# Encoder0 or enc0: data to feature0
enc0 = Model(inputs=x, outputs=feature0_output, name="encoder0")
# Encoder1 or enc1
y = Dense(num_labels)(feature0)
labels = Activation('softmax')(y)
# Encoder1 or enc1: feature0 to class labels
enc1 = Model(inputs=feature0, outputs=labels, name="encoder1")
# return both enc0 and enc1
return enc0, enc1Build
def build_and_train_models():
"""Load the dataset, build MTSS discriminator,
generator, and adversarial models.
Call the MTSS train routine.
"""
dataX, _, _ = google_data_loading(seq_length)
dataX = np.stack(dataX)
train_n = int(len(dataX)*.70)
X = dataX[:,:,:-1]
y = dataX[:,-1,-1]
x_train, y_train = X[:train_n,:,:], y[:train_n]
x_test, y_test = X[train_n:,:,:], y[train_n:]
# number of labels
num_labels = len(np.unique(y_train))
# to one-hot vector
y_train = to_categorical(y_train)
y_test = to_categorical(y_test)
model_name = "MTSS-GAN"
# network parameters
batch_size = 64
train_steps = 10
#train_steps = 2000
lr = 2e-4
decay = 6e-8
z_dim = 50 ##this is the real noise input
z_shape = (z_dim, )
feature0_dim = SHAPE[0]*SHAPE[1]
feature0_shape = (feature0_dim, )
# [1] uses Adam, but discriminator converges easily with RMSprop
optimizer = RMSprop(lr=lr, decay=decay)
# build discriminator 0 and Q network 0 models
input_shape = (feature0_dim, )
inputs = Input(shape=input_shape, name='discriminator0_input')
dis0 = build_discriminator(inputs, z_dim=z_dim )
#Model(Dense(SHAPE[0]*SHAPE[1]), [f0_source, z0_recon], name='dis0')
# loss fuctions: 1) probability feature0 is real
# (adversarial0 loss)
# 2) MSE z0 recon loss (Q0 network loss or entropy0 loss)
# Because there are two outputs.
loss = ['binary_crossentropy', 'mse']
loss_weights = [1.0, 1.0]
dis0.compile(loss=loss,
loss_weights=loss_weights,
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
dis0.summary() # feature0 discriminator, z0 estimator
# build discriminator 1 and Q network 1 models
input_shape = (x_train.shape[1], x_train.shape[2])
inputs = Input(shape=input_shape, name='discriminator1_input')
dis1 = discriminator(inputs, num_codes=z_dim)
# loss fuctions: 1) probability time series arrays is real (adversarial1 loss)
# 2) MSE z1 recon loss (Q1 network loss or entropy1 loss)
loss = ['binary_crossentropy', 'mse']
loss_weights = [1.0, 10.0]
dis1.compile(loss=loss,
loss_weights=loss_weights,
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
dis1.summary() # time series array discriminator, z1 estimator
# build generator models
label_shape = (num_labels, )
feature0 = Input(shape=feature0_shape, name='feature0_input')
labels = Input(shape=label_shape, name='labels')
z0 = Input(shape=z_shape, name="z0_input")
z1 = Input(shape=z_shape, name="z1_input")
latent_codes = (labels, z0, z1, feature0)
gen0, gen1 = build_generator(latent_codes)
# gen0: classes and noise (labels + z0) to feature0
gen0.summary() # (latent features generator)
# gen1: feature0 + z0 to feature1
gen1.summary() # (time series array generator )
# build encoder models
input_shape = SHAPE
inputs = Input(shape=input_shape, name='encoder_input')
enc0, enc1 = build_encoder((inputs, feature0), num_labels)
# Encoder0 or enc0: data to feature0
enc0.summary() # time series array to feature0 encoder
# Encoder1 or enc1: feature0 to class labels
enc1.summary() # feature0 to labels encoder (classifier)
encoder = Model(inputs, enc1(enc0(inputs)))
encoder.summary() # time series array to labels encoder (classifier)
data = (x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test)
print(x_train.shape)
print(y_train.shape)
# this process would train enco, enc1, and encoder
train_encoder(encoder, data, model_name=model_name)
# build adversarial0 model =
# generator0 + discriminator0 + encoder1
# encoder0 weights frozen
enc1.trainable = False
# discriminator0 weights frozen
dis0.trainable = False
gen0_inputs = [labels, z0]
gen0_outputs = gen0(gen0_inputs)
adv0_outputs = dis0(gen0_outputs) + [enc1(gen0_outputs)]
# labels + z0 to prob labels are real + z0 recon + feature1 recon
adv0 = Model(gen0_inputs, adv0_outputs, name="adv0")
# loss functions: 1) prob labels are real (adversarial1 loss)
# 2) Q network 0 loss (entropy0 loss)
# 3) conditional0 loss (classifier error)
loss_weights = [1.0, 1.0, 1.0]
loss = ['binary_crossentropy',
'mse',
'categorical_crossentropy']
adv0.compile(loss=loss,
loss_weights=loss_weights,
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
adv0.summary()
# build adversarial1 model =
# generator1 + discriminator1 + encoder0
optimizer = RMSprop(lr=lr*0.5, decay=decay*0.5)
# encoder1 weights frozen
enc0.trainable = False
# discriminator1 weights frozen
dis1.trainable = False
gen1_inputs = [feature0, z1]
gen1_outputs = gen1(gen1_inputs)
print(gen1_inputs)
print(gen1_outputs)
adv1_outputs = dis1(gen1_outputs) + [enc0(gen1_outputs)]
# feature1 + z1 to prob feature1 is
# real + z1 recon + feature1/time series array recon
adv1 = Model(gen1_inputs, adv1_outputs, name="adv1")
# loss functions: 1) prob feature1 is real (adversarial0 loss)
# 2) Q network 1 loss (entropy1 loss)
# 3) conditional1 loss
loss = ['binary_crossentropy', 'mse', 'mse']
loss_weights = [1.0, 10.0, 1.0]
adv1.compile(loss=loss,
loss_weights=loss_weights,
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
adv1.summary()
# train discriminator and adversarial networks
models = (enc0, enc1, gen0, gen1, dis0, dis1, adv0, adv1)
params = (batch_size, train_steps, num_labels, z_dim, model_name)
gen0, gen1 = train(models, data, params)
return gen0, gen1Training
def train(models, data, params):
enc0, enc1, gen0, gen1, dis0, dis1, adv0, adv1 = models
# network parameters
batch_size, train_steps, num_labels, z_dim, model_name = params
# train dataset
(x_train, y_train), (_, _) = data # I can do this.
# the generated time series array is saved every 500 steps
save_interval = 500
# label and noise codes for generator testing
z0 = np.random.normal(scale=0.5, size=[SHAPE[0], z_dim])
z1 = np.random.normal(scale=0.5, size=[SHAPE[0], z_dim])
noise_class = np.eye(num_labels)[np.arange(0, SHAPE[0]) % num_labels]
noise_params = [noise_class, z0, z1]
# number of elements in train dataset
train_size = x_train.shape[0]
print(model_name,
"Labels for generated time series arrays: ",
np.argmax(noise_class, axis=1))
tv_plot = tv.train.PlotMetrics(columns=5, wait_num=5)
for i in range(train_steps):
# train the discriminator1 for 1 batch
# 1 batch of real (label=1.0) and fake feature1 (label=0.0)
# randomly pick real time series arrays from dataset
dicta = {}
rand_indexes = np.random.randint(0,
train_size,
size=batch_size)
real_samples = x_train[rand_indexes]
# real feature1 from encoder0 output
real_feature0 = enc0.predict(real_samples)
# generate random 50-dim z1 latent code
real_z0 = np.random.normal(scale=0.5,
size=[batch_size, z_dim])
# real labels from dataset
real_labels = y_train[rand_indexes]
# generate fake feature1 using generator1 from
# real labels and 50-dim z1 latent code
fake_z0 = np.random.normal(scale=0.5,
size=[batch_size, z_dim])
fake_feature0 = gen0.predict([real_labels, fake_z0])
# real + fake data
feature0 = np.concatenate((real_feature0, fake_feature0))
z0 = np.concatenate((fake_z0, fake_z0))
# label 1st half as real and 2nd half as fake
y = np.ones([2 * batch_size, 1])
y[batch_size:, :] = 0
# train discriminator1 to classify feature1 as
# real/fake and recover
# latent code (z0). real = from encoder1,
# fake = from genenerator10
# joint training using discriminator part of
# advserial1 loss and entropy0 loss
metrics = dis0.train_on_batch(feature0, [y, z0])
# log the overall loss only
log = "%d: [dis0_loss: %f]" % (i, metrics[0])
dicta["dis0_loss"] = metrics[0]
# train the discriminator1 for 1 batch
# 1 batch of real (label=1.0) and fake time series arrays (label=0.0)
# generate random 50-dim z1 latent code
fake_z1 = np.random.normal(scale=0.5, size=[batch_size, z_dim])
# generate fake time series arrays from real feature1 and fake z1
fake_samples = gen1.predict([real_feature0, fake_z1])
# real + fake data
x = np.concatenate((real_samples, fake_samples))
z1 = np.concatenate((fake_z1, fake_z1))
# train discriminator1 to classify time series arrays
# as real/fake and recover latent code (z1)
# joint training using discriminator part of advserial0 loss
# and entropy1 loss
metrics = dis1.train_on_batch(x, [y, z1])
# log the overall loss only (use dis1.metrics_names)
log = "%s [dis1_loss: %f]" % (log, metrics[0])
dicta["dis1_loss"] = metrics[0]
# adversarial training
# generate fake z0, labels
fake_z0 = np.random.normal(scale=0.5,
size=[batch_size, z_dim])
# input to generator0 is sampling fr real labels and
# 50-dim z0 latent code
gen0_inputs = [real_labels, fake_z0]
# label fake feature0 as real (specifies whether real or not)
# is it bypassing the discriminator?
y = np.ones([batch_size, 1])
# train generator0 (thru adversarial) by fooling
# the discriminator
# and approximating encoder1 feature0 generator
# joint training: adversarial0, entropy0, conditional0
metrics = adv0.train_on_batch(gen0_inputs,
[y, fake_z0, real_labels])
fmt = "%s [adv0_loss: %f, enc1_acc: %f]"
dicta["adv0_loss"] = metrics[0]
dicta["enc1_acc"] = metrics[6]
# log the overall loss and classification accuracy
log = fmt % (log, metrics[0], metrics[6])
# input to generator0 is real feature0 and
# 50-dim z0 latent code
fake_z1 = np.random.normal(scale=0.5,
size=[batch_size, z_dim])
gen1_inputs = [real_feature0, fake_z1]
# train generator1 (thru adversarial) by fooling
# the discriminator and approximating encoder1 time series arrays
# source generator joint training:
# adversarial1, entropy1, conditional1
metrics = adv1.train_on_batch(gen1_inputs,
[y, fake_z1, real_feature0])
# log the overall loss only
log = "%s [adv1_loss: %f]" % (log, metrics[0])
dicta["adv1_loss"] = metrics[0]
print(log)
if (i + 1) % save_interval == 0:
generators = (gen0, gen1)
plot_ts(generators,
noise_params=noise_params,
show=False,
step=(i + 1),
model_name=model_name)
tv_plot.update({'dis0_loss': dicta["dis0_loss"], 'dis1_loss': dicta["dis1_loss"], 'adv0_loss': dicta["adv0_loss"], 'enc1_acc': dicta["enc1_acc"], 'adv1_loss': dicta["adv1_loss"]})
tv_plot.draw()
# save the modelis after training generator0 & 1
# the trained generator can be reloaded for
# future data generation
gen0.save(model_name + "-gen1.h5")
gen1.save(model_name + "-gen0.h5")
return gen0, gen1