| Tracker | VOT15(A/R/EAO) | VOT16(A/R/EAO) | VOT17(A/R/EAO) | VOT18(A/R/EAO) | OTB2013(AUC/Prec.) | OTB2015(AUC/Prec.) | OTB50(AUC/Prec.) | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SINT | - | - | - | - | 0.625/0.848 | - | - | 4 |
| SINT+ | - | - | - | - | 0.655/0.882 | - | - | 4 |
| SiamFC | 0.53/0.88/0.29 | 0.53/0.46/0.24 | 0.50/0.59/0.19 | - | 0.61/0.81 | 0.58/0.77 | 0.516/0.692 | 65 |
| CFNet-conv1 | - | - | - | - | 0.578/0.714 | 0.536/0.658 | 0.488/0.613 | 83 |
| CFNet-conv2 | - | - | - | - | 0.611/0.746 | 0.568/0.693 | 0.530/0.660 | 75 |
| CFNet-conv5 | - | - | - | - | 0.611/0.736 | 0.586/0.711 | 0.539/0.670 | 43 |
| DSiam | 0.5414 | - | - | - | 0.642/0.860 | - | - | 45 |
| DSiamM | 0.5566 | - | - | - | 0.656/0.891 | - | - | 25 |
| RASNet | -/-/0.327 | - | -/-/0.281 | - | 0.670/0.892 | 0.642/- | - | 83 |
| SA-Siam | 0.59/-/0.31 | -/-/0.236 | - | 0.566/0.258/0.337 | 0.676/0.894 | 0.656/0.864 | 0.610/0.823 | 50 |
| SiamRPN | 0.58/1.13/0.358 | 0.56/0.26/0.3441 | 0.49/0.46/0.243 | 0.49/0.46/0.244 | - | 0.637/0.851 | - | 160 |
| SINT++ | - | - | - | - | - | 0.574/0.768 | 0.624/0.839 | <4 |
| DaSiamRPN | 0.63/-/0.446 | 0.61/-/0.411 | -/-/0.326 | 0.569/0.337/0.326 | - | 0.658/0.88 | - | 160 |
| Siam-BM | - | - | -/-/0.335 | - | 0.686/0.898 | 0.662/0.864 | - | 48 |
| C-RPN | - | 0.594/0.95/0.363 | -/-/0.289 | - | 0.675/- | 0.663/- | - | 36 |
| SiamDW_CIResNet22_FC | 0.57/-/0.31 | 0.54/0.38/0.30 | 0.50/0.49/0.23 | - | 0.67/0.88 | 0.64/0.85 | - | 70 |
| SiamDW_CIResNet22_RPN | 0.59/-/0.38 | 0.58/0.24/0.37 | 0.52/0.41/0.30 | - | 0.67/0.92 | 0.67/0.90 | - | 150 |
| SiamMask | - | - | - | 0.602/0.288/0.347 | - | - | - | 35 |
| SiamRPN++ | - | - | - | 0.600/0.234/0.414 | - | 0.696/0.910 | - | 35 |
- Note
- Ranked by publish time.
- Performance details are mainly gathered from original papers, not tested under the same platform.
- AUC: area under curve of success plot.
- OP: mean overlap precision at the threshold of 0.5.
- DP/Prec.: mean distance precision of 20 pixels.
- A: accuracy.
- R: robustness(i.e. failure).
- EAO: expected average overlap.
-
-
SINT:R. Tao, E. Gavves, and A. W. Smeulders. Siamese instance search for tracking. In IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2016[paper][code][project]
- Propose to learn a generic matching function for tracking, from external video data, to robustly handle the common appearance variations an object can undergo in video sequences.
- Present a tracker based on the learnt generic matching function which reaches state-of-the-art tracking performance.
- Design a two-stream Siamese network specifically for tracking to learn the matching function.
- Use the radius sampling strategy to generate candidate boxes. At each sample location, generate three scaled versions of the initial box with the scales being {√2/2, 1,√2}
-
Use Euclidean distance as similarity metric.
- The sampling range is adaptive to the image resolution, set to be 30/512 ∗ w in this experiment, where w is the image width.
- Given the pixels covered by the predicted box in the previous frame and the estimated optical flow, remove the candidate boxes that contain less than 25% of those pixels in the current frame.
-
-
-
SiameseFC: Luca Bertinetto, Jack Valmadre, João F. Henriques, Andrea Vedaldi, Philip H.S. Torr. "Fully-Convolutional Siamese Networks for Object Tracking." ECCV workshop (2016).[paper][project] [official-code-matlab][code-pytorch][code2-pytorch][code-tensorflow]
- Achieves competitive performance in modern tracking benchmarks at speeds that far exceed the realtime requirement.
- Present a novel Siamese architecture that is fully-convolutional with respect to the search image.
- The position of the maximum score relative to the centre of the score map, multiplied by the stride of the network, gives the displacement of the target from frame to frame.
- Function h is fully-convolutional if:
for integer stride k and any translation
.
- Train: discriminative approach, Logistic loss:
, where v is the real-valued score of a single exemplar-candidate pair and y ∈ {+1, −1} is its ground-truth label.
- Positive example: within radius R of the centre (accounting for the stride k of the network).
- Loss for a score map:
- Multiple scales are searched in a single forward-pass by assembling a mini-batch of scaled images(scales 1.03^{−1,0,1}), any change in scale is penalized.
- backbone network: AlexNet.
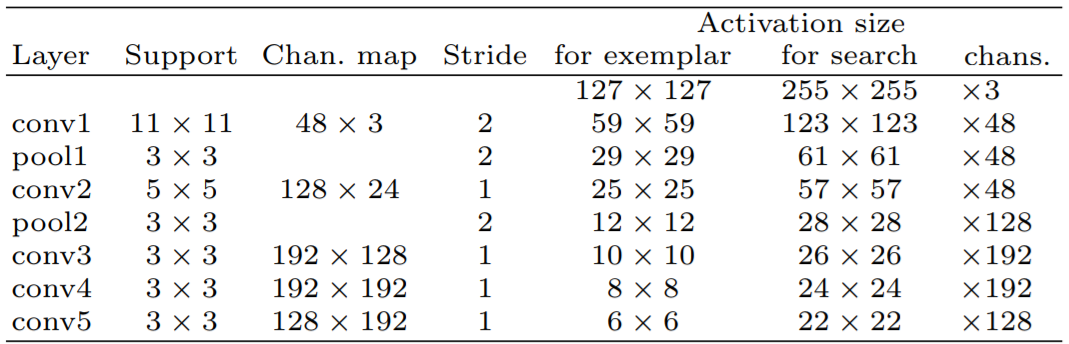
- elementary temporal constraints: search area(four times its previous size); a cosine window is added to the score map to penalize large displacements.
-
-
-
CFNet: Jack Valmadre, Luca Bertinetto, João F. Henriques, Andrea Vedaldi, Philip H. S. Torr."End-to-end representation learning for Correlation Filter based tracking." CVPR (2017). [paper][supp][project][official-code-matlab]
- Incorporating the Correlation Filter into the fully-convolutional Siamese framework(SiameseFC).
- Reveal that adding a Correlation Filter layer does not significantly improve the tracking accuracy.
-
-
-
DSiam: Qing Guo; Wei Feng; Ce Zhou; Rui Huang; Liang Wan; Song Wang."Learning Dynamic Siamese Network for Visual Object Tracking." ICCV (2017). [paper] [official-code-matlab]
- Propose a fast general transformation learning model that enables effective online learning of target appearance variation and background suppression from previous frames.
- Propose a elementwise multi-layer fusion, which adaptively integrates the multi-level deep features of DSiam network.
- Develop a complete joint training scheme, DSiam can be trained as a whole directly on labeled video sequences.
- Basic pipeline of our DSiam network (orange line) and that of SiamFC(black dashed line).f^l(·) represents a CNN to extract the deep feature at lth layer.
- Two transformations are rapidly learned from frame t−1. When the target at frame t (redbox) is entirely different from the template O1, SiamFC gets a meaningless response map, within which no target can be detected
- Establishing an efficient back-propagation map for the solution to a system of circulant equations.
- Replace
with
aims to encourage
being similar to
and is online learned from (t − 1)th frame by considering temporally smooth variation of the target
aims to highlight the deep feature of target neighborhood regions and alleviate the interference of irrelevant background features.
-
Response map for each layer l is
, elementwise weight map
and
, final response map
, where
denotes the elementwise multiplication.
-
Two real offline learned fusion weight maps:
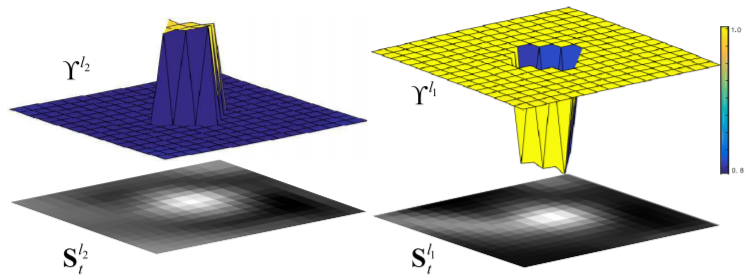
S: response map, layer (l1 = 5, l2=4) from AlexNet. Note , the response map of deeper layer l1 has higher weights in periphery and lower weights at central part within the searching region.
-
-
-
RASNet: Qiang Wang, Zhu Teng, Junliang Xing, Jin Gao, Weiming Hu, Stephen Maybank. "Learning Attentions: Residual Attentional Siamese Network for High Performance Online Visual Tracking." CVPR (2018).[paper]
- Different kinds of attention mechanisms are explored within the RASNet: General Attention, Residual Attention, and Channel Attention.
- Propose an end-to-end deep architecture specifically designed for the object tracking.
- Weighted cross correlation layer (WXCorr).
- Based on the exemplar features, three types of attentions are extracted. Exemplar and search features, along with the attentions as weights are inputed to WXCorr and finally transformed to a response map.
- Weighted Cross Correlation: not every constituent provides the same contribution to the cross correlation operation in the Siamese network.the object within the blue rectangular region should be reflected more to the cross correlation operation compared with the green rectangular region.
- Channel Attention: A convolutional feature channel often corresponds to a certain type of visual pattern. In certain circumstance some feature channels are more significant than the others.
- Baseline: SiamFC
-
-
-
SA-Siam: Anfeng He, Chong Luo, Xinmei Tian, Wenjun Zeng. "A Twofold Siamese Network for Real-Time Object Tracking." CVPR (2018).[paper][project]
- SA-Siam is composed of a semantic branch and an appearance branch, which are trained separately to keep the heterogeneity of the two types of features.
- Propose a channel attention mechanism for the semantic branch. Channel-wise weights are computed according to the channel activations around the target position.
- The network and data structures connected with dotted lines are exactly the same as SiamFC.
- A-Net(blue block) indicates the appearance network, which has exactly the same structure as the SiamFC network.
- S-Net(origin block) indicates the semantic network. The channel attention module determines the weight for each feature channel based on both target and context information.
- Symbols: z(the images of target), z^s(target with surrounding context, same size as search region), X(search region).
- The appearance branch:
response
- The semantic branch:
The S-Net is loaded from a pretrained AlexNet on ImageNet, last two convolution layers(conv4 and conv5) are used.
The concatenated multilevel features(denoted as fs ). Fusion module, implemented by 1×1 ConvNet.
response - final response:
,
where λ is the weighting parameter to balance the importance of the two branches, which can be estimated from a validation set. - Channel Attention in Semantic Branch:
Divide the feature map into 3 × 3 grids, Max pooling is performed within each grid, and then a two-layer multilayer perceptron(MLP) is used to produce a coefficient for this channel.
Finally, a Sigmoid function with bias is used to generate the final output weight ξi.
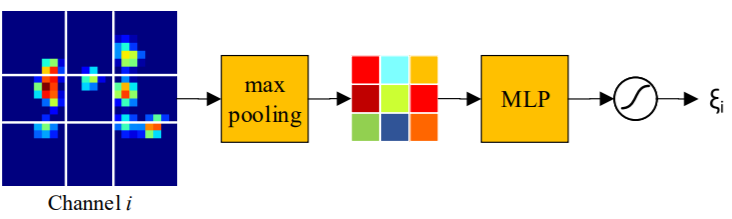
Note: this module is passed only once for the first frame of a tracking sequence. The computational overhead is negligible.
-
-
-
SiamRPN: Bo Li, Wei Wu, Zheng Zhu, Junjie Yan."High Performance Visual Tracking with Siamese Region Proposal Network." CVPR (2018 Spotlight).[paper][code-pytorch][code-pytorch]
- propose the Siamese region proposal network (SiameseRPN) which is end-to-end trained off-line with large-scale image pairs for the tracking task.
- During online tracking, the proposed framework is formulated as a local oneshot detection task, which can refine the proposal to discard the expensive multi-scale test.
- It achieves leading performance in VOT2015, VOT2016 and VOT2017 real-time challenges with the speed of 160 FPS, which proves its advantages in both accuracy and efficiency.
- Left: Siamese subnetwork for feature extraction
- Middle: Region proposal subnetwork, which has a classification branch and a regression branch. Pair-wise correlation is adopted to obtain the output of two branches.
- Right: Details of these two output feature maps.
- In classification branch, the output feature map has 2k channels which corresponding to foreground and background of k anchors.
- In regression branch, the output feature map has 4k channels which corresponding to four coordinates used for proposal refinement of k anchors.
- In the figure, ⋆ denotes correlation operator
- Loss Function:
- For classification(cross-entropy loss), for regression(smooth L1 loss), which is same as Faster R-CNN.
- Regression: Use normalized coordinates, Let Ax, Ay, Aw, Ah denote center point and shape of the anchor boxes and let Tx, Ty, Tw, Th denote those of the ground truth boxes, the normalized distance is:
- Smooth L1 loss:
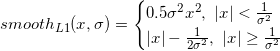
- Regression loss:
- Final loss: λ is hyper-parameter to balance the two parts.
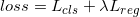
- RPN:
- Anchor: Only one scale with different ratios[0.33, 0.5, 1, 2, 3], less than detection task because the same object in two adjacent frames won’t change much.
- Training samples: Positive(IOU > 0.6) and Negative(IOU < 0.3)
At most 16 positive samples and totally 64 samples from one training pair.
- Tracking as one-shot detection:
- Because the local detection task is based on the category information only given by the template on initial frame, and the template branches’ outputs are regarded as the kernels for local detection, so it can be viewed as one-shot detection.
- Proposal selection:
- Non-maximum-suppression: NMS is performed afterwards to get the final tracking bounding box.
- Anchor ratios: 3 ratios are tried, [0.5, 1, 2], [0.33, 0.5, 1, 2, 3], [0.25, 0.33, 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4] (denoted as A3, A5, A7, respectively).
-
A5 performs better than A3, because it’s easier to predict the shape of target with large ratio of height and width through more anchors.
-
A7's performance drops by over-fitting.
ratios EAO(without Yuotube) EAO(with Yuotube) A3 0.279 0.311 A5 0.317 0.344 A7 0.304 0.337
-
- Anchor position:
-
-
-
SINT++: Xiao Wang, Chenglong Li, Bin Luo, Jin Tang. "SINT++: Robust Visual Tracking via Adversarial Positive Instance Generation." CVPR (2018). [paper]
- Propose a novel and general positive sample generation network(PSGN) to bridge the gap between data hunger deep neural networks and visual tracking task.
- Introduce the hard positive transformation network(HPTN) which can generate massive hard positive samples.
- Propose the SINT++ which improves tracking performance of the two streaming Siamese network.
- Three modules: PSGN, HPTN and two streaming Siamese network.
- The target object manifold is constructed by variational auto-encoder(VAE) , and the output can be directly input to the HPTN.
- The HPTN takes the reconstructed image as input, and learn to occlude the target which become hard for visual tracker to measure via deep reinforcement learning.
- PSGN:
- Traditional positive sampling strategy(based on IOU) lacks diversity, thus leading to under-fitting.
- Utilize the variational autoencoder (VAE) to learn the target object manifold.
- HPTN:
- Create occlusions on the target objects using image patch extracted from background.
-
-
-
DaSiamRPN: Zheng Zhu, Qiang Wang, Bo Li, Wu Wei, Junjie Yan, Weiming Hu. "Distractor-aware Siamese Networks for Visual Object Tracking." ECCV (2018). [paper][code]
- Find that the imbalance of the non-semantic background and semantic distractor in the training data is the main obstacle for the learning.
- Propose a novel Distractor-aware Siamese Region Proposal Networks(DaSiamRPN) framework to learn distractor-aware features in the off-line training, and explicitly suppress distractors during the inference of online tracking.
- Extend the DaSiamRPN to perform long-term tracking by introducing a simple yet effective local-to-global search region strategy, which significantly improves the performance of our tracker in out-of-view and full occlusion challenges.
- The non-semantic background occupies the majority, while semantic entities and distractor occupy less. This imbalanced distribution makes the training model hard to learn instance-level representation, but tending to learn the differences between foreground and background.
- Actively generate more semantics pairs in the offline training process.
- Response comparasion
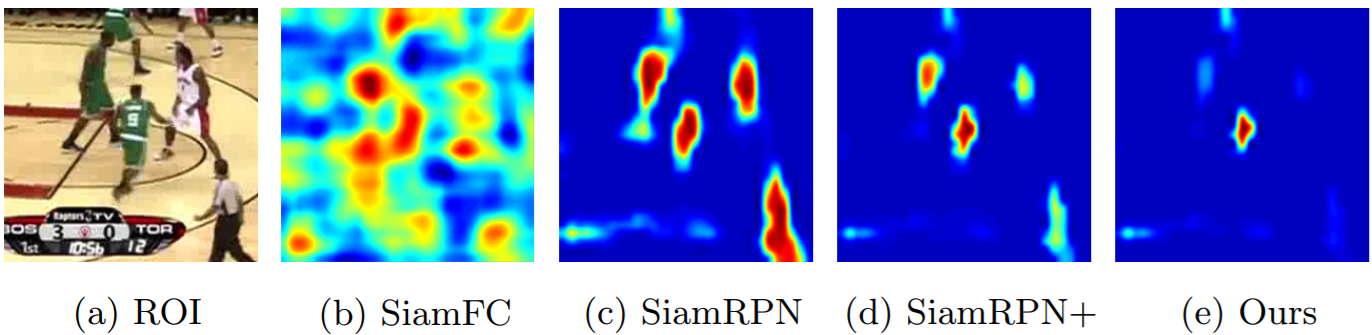
-
Distractor-aware Training:
- Diverse categories of positive pairs can promote the generalization ability.
- Semantic negative pairs can improve the discriminative ability.
- Customizing effective data augmentation for visual tracking.(Except the common translation, scale variations and illumination changes, introduce motion blur)
- Training pairs

-
Distractor-aware Incremental Learning:
- Use NMS to select the potential distractors d_i in each frames. Then collect a distractor set D := {∀ d_i ∈ D, f(z, d_i) > h ∩ d_i != z_t}, where h is the predefined threshold, z_t is the selected target in frame t and the number of this set |D| = n.
- Specifically, we get 17x17x5 proposals in each frame at first, and then we use NMS to reduce redundant candidates.
- The proposal with highest score will be selected as the target zt. For the remaining, the proposals with scores greater than a threshold are selected as distractors.
- Introduce a novel distractor-aware objective function to rerank the proposals P which have top-k similarities with the exemplar.
The weight factor α^hat control the influence of the distractor learning, the weight factor α_i is used to control the influence for each distractor d_i.
Final selected object:
SiamRPN:
-
-
-
Siam-BM: He A, Luo C, Tian X, et al. Towards a better match in siamese network based visual object tracker[C]. ECCV (2018). [paper][code]
- Propose to predict the angle of the target object.
- Propose to selectively apply a spatial mask to CNN feature maps when the possibility of distracting background objects is high.
- Adopt a simple template updating mechanism to cope with the gradual appearance change of the target object.
- Siamese network cannot properly handle large object rotation, because the CNN features are not invariant to large image transformations such as scaling and rotation.
- Tracking gets easily distracted when the background contains salient objects. It is hard to determine the spatial region from which DNN features should be extracted to represent the target object.
-
Angle Estimation:
- Siam-BM tracker adjusts the properties (scale or angle) of the tracked object only one at a time. With M scale choices and N angle choices, get M + N − 1 candidate patches.
- Similarly, the tracked object is determined by:
- Illustration: M=N=3, the highest response in the map with (1, −π/8) is significantly higher than the top values in other maps.
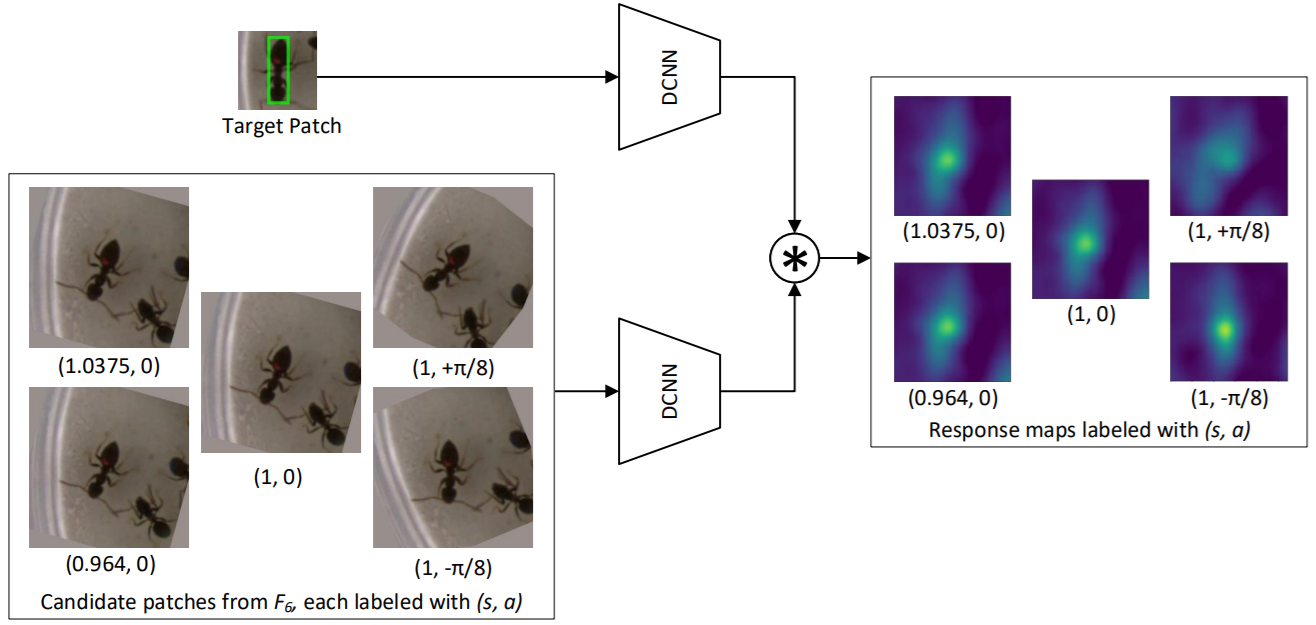
-
Spatial Mask:
- When the aspect ratio of the target object is far apart from 1 (vertical or horizontal), it is more likely to have salient objects in the background area.
- Spatial feature mask when the aspect ratio of target object exceeds a predefined threshold.
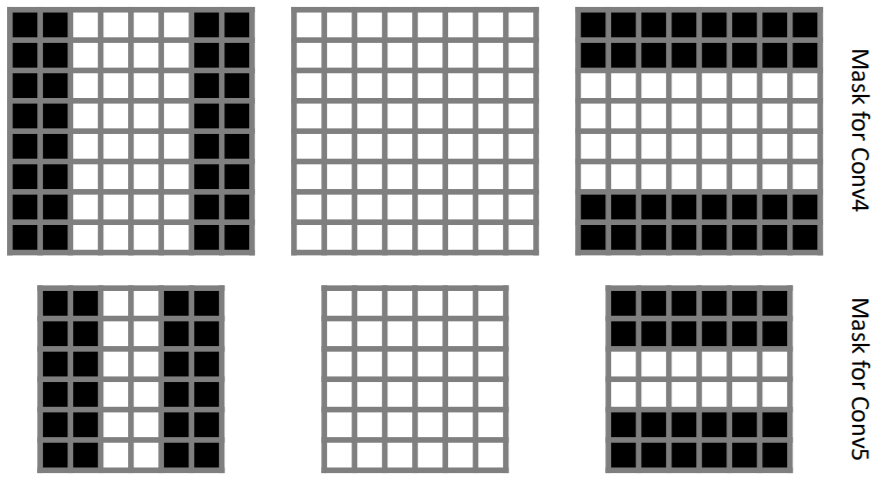
- Left two masks: h/w > threshold
- Right two masks: w/h > threshold
- Middle two masks: max{w/h, h/w} < threshold
- The white grids indicate a coefficient of 1 and the black grids indicate a coefficient of 0, threshold is set to 1.5.
-
-
-
C-RPN: Heng Fan, Haibin Ling. "Siamese Cascaded Region Proposal Networks for Real-Time Visual Tracking." CVPR (2019). [paper][supp]
- Present a novel multistage tracking framework, solve the problem of class imbalance by performing hard negative sampling. The easy negative anchors are then filtered out, and the rest, treated as hard examples, are utilized as training samples for the RPN of the next stage.
- C-RPN consists of multiple steps of regressions due to multiple RPNs. In each stage, the anchor boxes (including locations and sizes) are adjusted by the regressor.
- Design a novel feature transfer block(FTB), Instead of separately using features from a single layer in one RPN, FTB enables us to fuse the high-level features into low-level RPN.
- The distribution of training samples is imbalanced:
- Positive samples are far less than negative samples => ineffective training
- Most negative samples are easy negatives => non-similar nonsemantic background contribute little useful information.
- Low-level spatial features are not fully explored:
- Siamese-RPN (and other Siamese trackers), only features of the last layer, which contain more semantic information, are explored to distinguish target/background.
- Distractor have similar semantic features, the high-level semantic features are less discriminative in distinguishing these distractors.
- Propose a multistage tracking framework by cascading a sequence of RPNs to solve the class imbalance problem, and meanwhile fully explore features across layers for robust visual tracking.
- the Siamese network: To extract the features of the target template x and the search region z.
- cascaded RPN: Apply feature transfer block (FTB) to fuse the features from high-level layers for RPN. According to the classification scores and regression offsets, we filter out the easy negative anchors (e.g., an anchor whose negative confidence is larger than a preset threshold θ), and refine the locations and sizes of the rest anchors.
- To ensure classification and regression for each anchor, two convolution layers are utilized to adjust the channel to get ϕ(x)_cls, ϕ(x)_reg and ϕ(z)_cls, ϕ(z)_reg.
- Classification scores c_i and regression offsets r_i can be computed as:
- {c_i} = corr(ϕ(z)_cls, ϕ(x)_cls)
- {r_i} = corr(ϕ(z)_reg, ϕ(x)_reg)
- i is the anchor index, and corr(a, b) denotes correlation between a and b where a is served as the kernel.
- Each c_i is a 2d vector, representing for negative and positive confidences of the i-th anchor.
- Each r_i is a 4d vector which represents the offsets of center point location and size of the anchor to groundtruth.
- For l-th RPN, it receives fused features Φ(z)^l and Φ(x)^l of the conv-l layer and the highlevel layers from FTB, instead of features ϕ(z)^l and ϕ(x)^l from a single separate layer:
- Φ(z)^l = FTB(Φ(z)^(l-1), ϕ(z)^l)
- Φ(x)^l = FTB(Φ(x)^(l-1), ϕ(x)^l)
- For l = 1, Φ(z)^1 = ϕ(z)^1, Φ(x)^1 = ϕ(x)^1
- The anchors in C-RPN are progressively adjusted by the regressor in the previous stage.
- Feature Transfer Block:
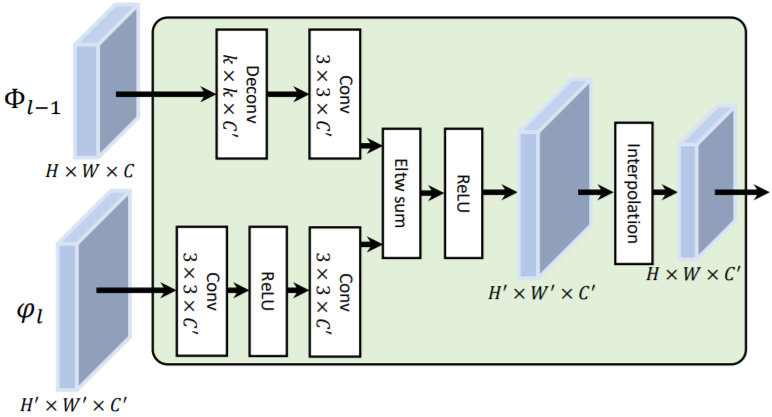
- A deconvolution layer is used to match the feature dimensions of different sources
- Different features are fused using element-wise summation + ReLU
- Apply the interpolation to rescale the fused features such that the output classification maps and regression maps have the same resolution for all RPN
-
LaSOT
- success(SUC): 0.459(protocol I) 0.455(protocol II, testing set)
- fps: 23
-
TrackingNet
- metrics: precision(PRE, 0.619), normalized precision (NPRE, 0.746) and success(SUC, 0.669)
- fps: 32
-
Number of stages
#Stages One stage Two stages Three stages SUC on LaSOT 0.417 0.446 0.455 Speed on LaSOT 48 fps 37 fps 23 fps EAO on VOT-2017 0.248 0.278 0.289 -
Negative anchor filtering(NAF)
Index C-RPN w/o NAF C-RPN w/ NAF SUC on LaSOT 0.439 0.455 EAV on VOT-2017 0.282 0.289 -
Feature transfer block(FTB)
Index C-RPN w/o FTB C-RPN w/ FTB SUC on LaSOT 0.442 0.455 EAV on VOT-2017 0.278 0.289
-
-
-
SiamDW: Zhipeng Zhang, Houwen Peng. "Deeper and Wider Siamese Networks for Real-Time Visual Tracking." CVPR (2019 oral).[paper][supp][code]
- Present a systematic study on the factors of backbone networks that affect tracking accuracy, and provides architectural design guidelines for the Siamese tracking framework.
- Design new deeper and wider network architectures for Siamese trackers, based on proposed nopadding residual units.
- Siamese trackers prefer a relatively small network stride
- Stride affects the overlap ratio of receptive fields for two neighboring output features, thus affect location precision.(prefer 4 or 8)
- The receptive field of output features should be set based on its ratio to the size of the exemplar image
- Each point of feature map captures the information of different spatial parts of a target object.(ratio prefer 60% ~ 80%)
- Network stride, receptive field and output feature size should be considered as a whole when designing a network architecture
- For a fully convolutional Siamese matching network, it is critical to handle the problem of perceptual inconsistency between the two network streams
- CIR Unit:
- The cropping operation removes features(a') whose calculation is affected by the zero-padding signals introduced in original residual unit(a).
- Downsampling CIR (CIR-D) Unit
- To reduce the spatial size of feature maps while doubling the number of feature channels.
- Change the convolutional stride from 2 to 1 within both the bottleneck layer and shortcut connection.
- Also insert Cropping to remove the padding-affected features.
- Max-pooling is employed to perform spatial downsampling of the feature map(b').
- CIR-Inception and CIR-NeXt Units
- Widen the CIR unit with multiple feature transformations(c', d')
-
-
- SiamMask: Qiang Wang, Li Zhang, Luca Bertinetto, Weiming Hu, Philip H.S. Torr. "Fast Online Object Tracking and Segmentation: A Unifying Approach." CVPR (2019).[paper][supp][project][code]
- Narrow the gap between arbitrary object tracking and video object segmentation(VOS)
- Simultaneously train a Siamese network on three tasks:
- Learn a measure of similarity between the target object and multiple candidates in a sliding window fashion(Localization)
- Bounding box regression using a Region Proposal Network
- Classagnostic binary segmentation
- Each task is represented by a different branch departing from a shared CNN and contributes towards a final loss
- three-branch(based on SiamRPN)
- two-branch(based on SiamFC)
- *d denotes depth-wise cross correlation
- SiamFC
- Mask
- Loss
- Each RoW is labelled with a ground-truth binary label yn ∈ {±1} and also associated with a pixel-wise ground-truth mask c_n of size w×h.
denote the label corresponding to pixel (i, j) of the object mask in the n-th candidate RoW.
- L_mask is considered only for positive RoWs (i.e. with y_n = 1, one of its anchor boxes has IOU with the ground-truth box of at least 0.6).
-
- SiamRPN++: Bo Li, Wei Wu, Qiang Wang, Fangyi Zhang, Junliang Xing, Junjie Yan. "SiamRPN++: Evolution of Siamese Visual Tracking with Very Deep Networks." CVPR (2019 oral).[paper][project]
- Provide a deep analysis of Siamese trackers and prove that when using deep networks the decrease in accuracy comes from the destroy of the strict translation invariance.
- Present a simple yet effective sampling strategy to break the spatial invariance restriction which successfully trains Siamese tracker driven by a ResNet architecture.
- Propose a layer wise feature aggregation structure for the cross-correlation operation, which helps the tracker to predict the similarity map from features learned at multiple levels.
- Propose a depth-wise separable correlation structure to enhance the cross-correlation to produce multiple similarity maps associated with different semantic meanings.
- Padding will destroy the strict translation invariance.
- First, targets are placed in the center with different shift ranges (0, 16 and 32) in three sepreate training experiments. After convergence, aggregate the heatmaps generated on test dataset and then visualize the results.
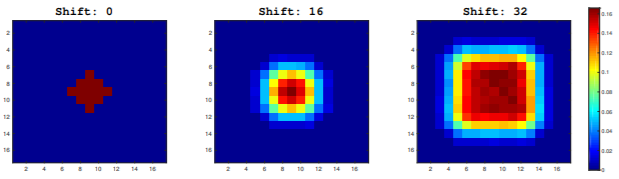
- Features from earlier layers will mainly focus on low level information such as color, shape, are essential for localization, while lacking of semantic information;
- Features from latter layers have rich semantic information that can be beneficial during some challenge scenarios like motion blur, huge deformation.
- A weighted-fusion layer combines all the outputs.
- XCorr: Predicts a single channel similarity map between target template and search patches in SiamFC
- UP-Corr: Outputs a multi-channel correlation features by cascading a heavy convolutional layer with several independent XCorr layers in SiamRPN
- DW-XCorr: Predicts multi-channel correlation features between a template and search patches
- UAV123
Trackers AUC Prec. SiamRPN++ 0.613 0.807 DaSiamRPN 0.586 0.796 SiamRPN 0.527 0.748 ECO 0.525 0.741 ECO-HC 0.506 0.725 - LaSOT
Trackers AUC Normalized Prec. SiamRPN++ 0.496 0.569 DaSiamRPN 0.415 0.496 SiamFC 0.336 0.420 ECO 0.324 0.338 ECO-HC 0.304 0.320 - TrackingNet
Index ECO SiamFC CFNet DaSiamRPN SiamRPN++ AUC(%) 55.4 57.1 57.8 63.8 73.3 P(%) 49.2 53.3 53.3 59.1 69.4 P_norm(%) 61.8 66.3 65.4 73.3 80.0
- 2017: R. Pflugfelder. An in-depth analysis of visual tracking with siamese neural networks. arXiv:1707.00569, 2017[paper]
- OTB2013 was proposed in the CVPR2013. (51 targets and 50 videos.[Jogging_1 + Jogging_2]) (Online Object Tracking: A Benchmark)
- TB-50 and TB-100 were proposed in the PAMI2015. (TB-50 is consisted by 50 difficult sequences among TB-100. The partition can be found in http://cvlab.hanyang.ac.kr/tracker_benchmark/datasets.html)
- Please note that TB-50 ≠ OTB2013 (Object Tracking Benchmark)
- add road trip figure
- add link for paper&code&project
- add core analyses
- add benchmark comparison
- finish all paper
MIT