This solution will help customers to create auditing and monitoring solution for cross accounts shared AWS AMI. This will also alert customers when any de-registered AMI is still getting used in any AWS Service. This pattern will help customers to provide insights about AMI usage and reduce any production issue in case any de-registered AMI is referred in customers production account.
-
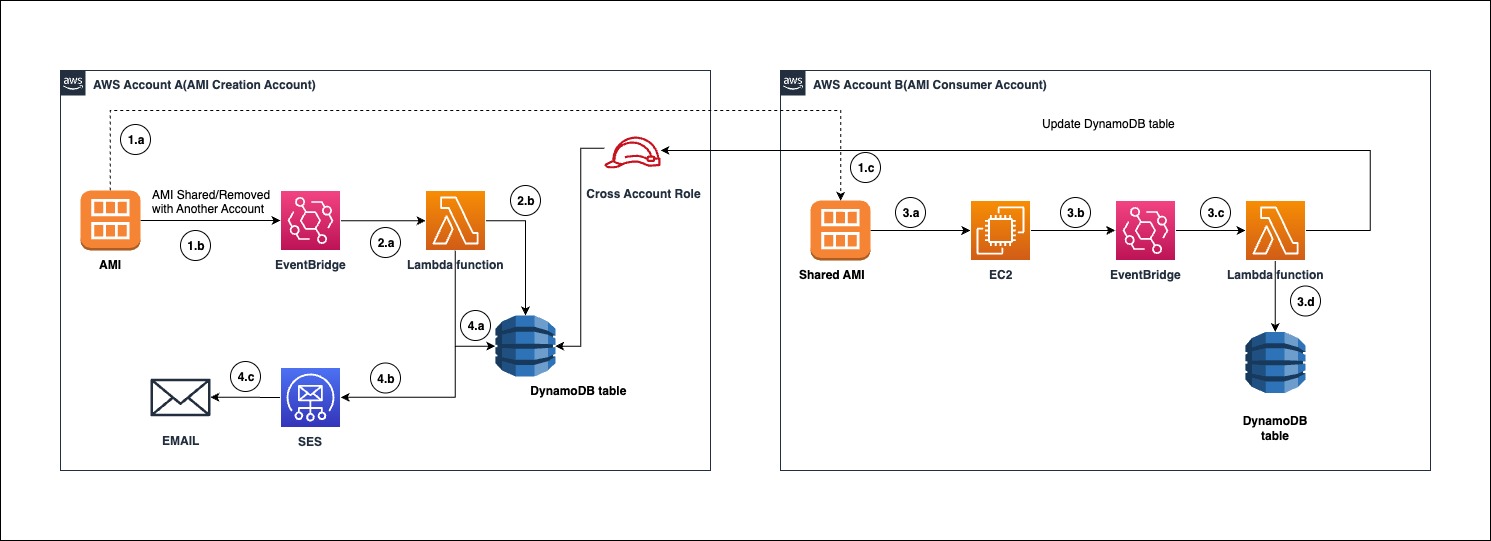
Share AMI with other AWS Accounts.
- AWS AMI is shared with another AWS Account.
- When AMI is shared, the ModifyImageAttribute event will be captured by an Amazon EventBridge event rule.
- The consumer AWS account can view the shared AMI as private image.
-
Trigger AWS Lambda function to store data in DynamoDB table.
- EventBridge will trigger Lambda function. This function will process the event.
- After processing the event, it will store the data related to the shared AMI in DynamoDB table.
-
Using shared AWS AMI in consumer AWS Account
- Shared AMI in consumer AWS Account will be referred/un-referred to create Launch Configuration, Launch Template, EC2 etc.
- When AMI is used/un-referred then its event will be captured by EventBridge rule.
- EventBridge will trigger the Lambda function, this Lambda function will update DynamoDB table item and add AMI usage details in Creator account with the help of a cross-account IAM role.
- This Lambda function will also update the AMI id and EC2/Launch template id in the Mapping DynamoDB table in the same AWS Account. This is needed when the AMI is deregistered from Launch templates or EC2 instances.
-
Un-register/Delete AMI in Creator account
- When ModifyImageAttribute has remove action, then the Lambda function will validate that the given AMI does not have any usage in DynamoDB table.
- If AMI is still being referenced, then Lambda function will trigger an email alert using SES.
- SES email subscriber will receive the event notification.
- At least 2 active AWS accounts.
- AWS AMI should be created in one of the AWS account.
- Terraform (Terraform version 1.2.0 or higher) installed and configured. Please follow this link for Terraform installation.
- AWS Lambda - AWS Lambda is a serverless compute service that runs your code in response to events and automatically manages the underlying compute resources for you.
- Amazon EventBridge - EventBridge is a serverless service that uses events to connect application components together, making it easier for you to build scalable event-driven applications.
- Amazon Dynamodb - Amazon Dynamodb is a fully managed NOSQL database.
- Amazon SNS - Amazon SNS is a fully managed service for pub-sub service.
- Python - Python is an interpreted, object-oriented, high-level programming language.
-
Setup AWS CLI profile's with help of this documentation for AMI creator and consumer accounts.
-
Update AWS Provider configurations in provider.tf to refer respective AWS CLI profiles for AMI Creator and Consumer account. This will create respective provider configuration block for creator and consumer AWS accounts. Please refer Terraform documentation on Provider for more help.
-
Update variable
account_email_mappingvalue present terraform.tfvars file to include account id and its corresponding email id. Terraform variableaccount_email_mappingcontains account id and email id mapping for AMI consumer accounts.Note: In case where AMI creator account is consuming the AMI then update details of AMI creator account in
account_email_mapping. Example:account_email_mapping = [ { "account" : "111111111111", "email" : "sample1@example.com" }, { "account" : "222222222222", "email" : "sample2@example.com" } ]
-
[Optional] Please refer this section for how to add a new Consumer Account for monitoring.
-
Run terraform commands to deploy these resources in following order:
- To initialize terraform directory
terraform init
- To format terraform configuration files
terraform fmt
- To validate terraform configuration syntax
terraform validate
- To generate terraform plan using the configuration file
terraform plan
- To apply terraform plan
terraform apply
- To initialize terraform directory
-
Validate Cross Account AMI Monitoring
To test and validate if Cross Account AMI Monitoring solution has been setup correctly please follow below steps:
a. AMI Creation Account
- Create a private AMI. Follow this documentation for more help.
- Share this AMI with one of the consumer AWS account. Follow this documentation for more help.
b. AMI Consumer Account
- Create an EC2 instance or Launch template using the shared AMI. This shared AMI will be present as a private image. Follow below reference documentations.
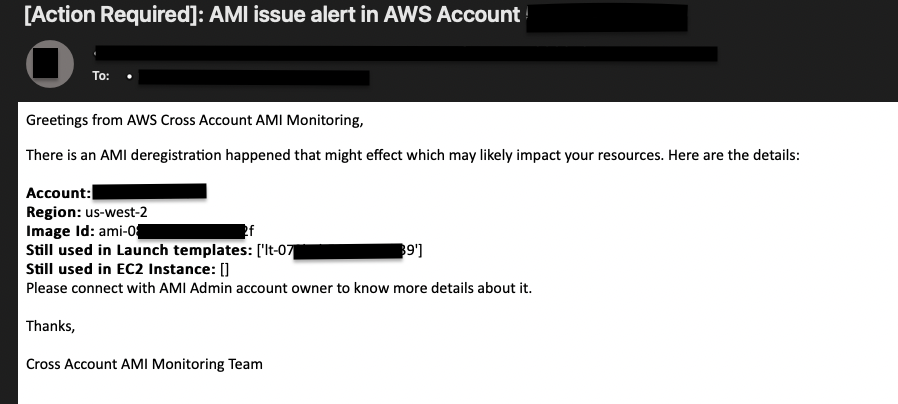
c. Test Cross Account AMI Monitoring in action Note: Please confirm the subscription of Amazon SES email service to successfully receive email alerts.
- To test this solution confirm if step 6.a and 6.b has been completed successfully.
- In AMI Creation account, remove AMI sharing with the consumer AWS Account. Follow this documentation for more help.
- As the shared AMI was still referenced in consumer AWS account(s), so AWS account owners whose details has been specified in terraform.tfvars will get email notification. Please find below sample email notification.
-
Setup a new AWS CLI profile with help of this documentation.
-
Setup a new Terraform AWS Provider in provider.tf and use the profile created in step above.
Example: Suppose you have created AWS CLI profile with name
new_consumerand you need to setup a provider forus-west-2region with alias namenew_aliasthen you will need to add terraform configuration block in provider.tf file.provider "aws" { alias = "new_alias" region = "us-west-2" profile = "new_consumer" }
-
To setup monitoring for new consumer account, use a new terraform provider configuration created in step#2 and create a new terraform module usage block in main.tf referring module
consumer_account_A.Example: To add a new consumer module with name
consumer_account_Bwith the provider aliasnew_alias, add below terraform configuration in main.tf file.module "consumer_account_B" { providers = { aws = aws.ami-consumer-account_B } source = "./modules/ami_consumer" configuration_inputs = module.ami_creator.configurations_details }
-
Update variable
account_email_mappingvalue present terraform.tfvars file to include account id and its corresponding email id. Terraform variableaccount_email_mappingcontains account id and email id mapping for AMI creation account as well as AMI consumer accounts.Example: To add new mapping of account id
"333333333333"and its respective email idsample3@example.comthen updated value foraccount_email_mappingwill be as following:account_email_mapping = [ { "account" : "111111111111", "email" : "sample1@example.com" }, { "account" : "222222222222", "email" : "sample2@example.com" }, { "account" : "333333333333", "email" : "sample3@example.com" } ]
Note: Owner email id will be receiving email notifications about AMI issues.
- How to setup multiple AWS CLI profiles?
- Refer how to access different AWS Account with the help of named profile.
- I have not received an email alert when AMI is still getting referred.
- There could be multiple reasons why email was not triggered, please follow below steps to debug:
- Validate if infrastructure has been configured properly in both the AWS Accounts.
- Validate lambda function CloudWatch logs. Refer how to view lambda function CloudWatch logs. Check if there is any permission issue due to Explicit Deny on permissions.
- Validate if you have confirmed email subscription from SES service.
- There could be multiple reasons why email was not triggered, please follow below steps to debug: