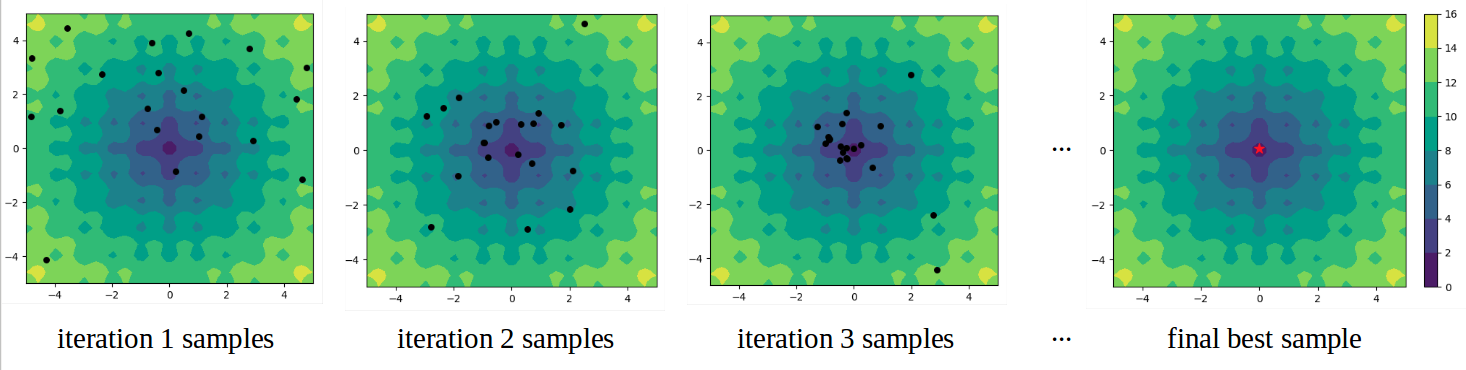
Official Github repo for the three black-box optimization methods described in “AdaNS: Adaptive Non-Uniform Sampling for Automated Design of Compact DNNs” published in the IEEE Journal of Special Topics in Signal Processing. The goal is to search for the global maxima or global minima of an expensive black-box function (e.g. optimal hyperparameters for simulation, neural network compression). Here is an example of searching for the minimizer of a 2-dimensional objective function:
The figures show the contours of the objective function and the black dots represent samples generated at each iteration. The final solution is shown with the red star.
We present three sampling strategies to perform the optimization. To use the library, the user selects the desired sampling strategy, provides an objective function, specifies the search domain (valid ranges of each hyperparameter), and sets the corresponding parameters for the optimization tool. The library then optimizes the provided objective function and returns the optimal set of hyperparameters.
We provide three examples for performing optimization with AdaNS in main_Gaussian.py, main_Genetic.py, and main_Zoom.py. Each of the files incorporates a different sampling strategy for optimization described in the paper. Below we summarize the common arguments needed for all files:
-
The objective function needs to be wrapped into this Python function.
def evaluator_fn(x): ... return f
where
xis a vector of design hyperparameters to be optimized, andfis the value of the objective function evaluated at x. You can also choose from a set of example objective functions provided inutils/example_functions.py. -
(Optional) desired constraints for sample needs to be wrapped into this Python function which will be checked during optimization.
def constraint_fn(x): ... return True
where
xis a vector of design hyperparameters to be optimized. -
The rest of the arguments used by the three optimization tools are as follows:
#------------- Sampler parameters parser.add_argument('--name', default='test_fn_0', help='experiment name, used to specify the folder to save sampling results (default: test_fn_0)') parser.add_argument('--minimize', action='store_true', help='if selected,the function will be minimized, otherwise maximized') parser.add_argument('--test_fn', type=str, help='(optional) choose from common optimization test functions [rastrigin, ]') parser.add_argument('--plot_contour', action='store_true', help='if selected, the sampler will save contours of the objective function along with per-iteration samples') parser.add_argument('--seed', default=0, type=int, help='random seed (default: 0)') parser.add_argument('--num_samples', default=50, type=int, help='per-iteration sample size (default: 50)') parser.add_argument('--dim', type=int,help='dimensionality of the search-space (default: None)') parser.add_argument('--path_to_boundaries', default='', type=str,help='path to csv file containing search-space boundaries (default: '')') parser.add_argument('--path_to_init_samples', default='', type=str, help='path to pickle file containing initial samples (default: '')') parser.add_argument('--n_iter', default=50, type=int, help='number of optimization iterations (default: 50)') parser.add_argument('--n_parallel', default=1, type=int, help='number of cores for parallel evaluations (default:1)') parser.add_argument('--alpha_max', default=1.0, type=float, help='alpha_max parameter (default:1.0)') parser.add_argument('--early_stopping', default=1000, type=int, help='number of iterations without improvement to activate early stopping (default: 1000)')
-
Arguments specifically used by
main_Gaussian.pyare as follows:#-------------- Gaussian Sampler parameters parser.add_argument('--u_random_portion', default=0.2, type=float,help='portion of samples to take unifromly random from the entire space (default:0.2)') parser.add_argument('--local_portion', default=0.4, type=float, help='portion of samples to take from gaussians using the Local method (default:0.4)') parser.add_argument('--cross_portion', default=0.4, type=float, help='portion of samples to take from gaussians using the Cross method (default:0.4)') parser.add_argument('--pair_selection', default='top_and_random', type=str, help='how to select sample pairs for crossing, choose from [random,top_scores,top_and_nearest,top_and_furthest,top_and_random] (default:top_and_random)')
-
Arguments specifically used by
main_Genetic.pyare as follows:#-------------- Genetic Sampler parameters parser.add_argument('--p_cross', default=0.8, type=float, help='probability of crossover (default: 0.8)') parser.add_argument('--p_swap', default=0.2, type=float,help='per-bit exchange probability (default: 0.2)') parser.add_argument('--p_mutate', default=0.8, type=float, help='probability of mutate (default: 0.8)') parser.add_argument('--p_tweak', default=0.05, type=float, help='per-bit tweaking probability (default: 0.05)') parser.add_argument('--mutate_scale', default=0.2, type=float, help='std of the noise added during mutation (default: 0.2)') parser.add_argument('--is_discrete', action='store_true', help='select this option if the search-space is discrete (default: False)')
If you use this project please cite our work:
@article{javaheripi2020adans,
title={AdaNS: Adaptive Non-Uniform Sampling for Automated Design of Compact DNNs},
author={Javaheripi, Mojan and Samragh, Mohammad and Javidi, Tara and Koushanfar, Farinaz},
journal={IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing},
volume={14},
number={4},
pages={750--764},
year={2020},
publisher={IEEE}
}